First Aid Quiz Review
advertisement

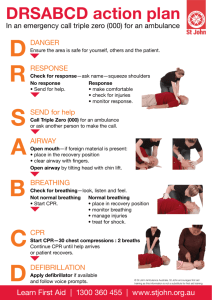
FIRST AID UNIT: REVIEW First Aid: The immediate, temporary care given to an ill or injured person until professional medical care can be provided. Universal precautions: Actions taken to prevent the spread of disease by treating all blood and body fluids as if they are contaminated. Basic precautions include: 1) Wear protective gloves when handling bodily fluids 2) Use a mouthpiece to provide CPR/Rescue breathing 3) Wash hands before and after providing care Good Samaritan Law: This law may protect you from legal liability as long as you act in good faith while providing emergency care. Check-Call-Care – These are the first steps taken in an emergency situation: Check: Check the scene and the victim Call: Call for help 911 Care: Provide care for the victim ** If dealing with a child or infant with a breathing emergency you must change the order of response to 1) Check 2) Care – at least 1 minute of CPR 3) Call BREATHING EMERGENCIES ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK Anaphylaxis: A severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. Treatment: Give adrenaline injection (Epi-Pen) in the thigh of the victim and monitor victim closely. Get medical attention immediately. CHOKING Choking: An object lodged in the airway, preventing the essential flow of oxygen. Treatment: If the victim is forcefully coughing, encourage continued coughing. If the victim cannot speak, cough, or breathe - have someone else call 911. Perform the Heimlich maneuver – Give “J” thrusts to force out object ABC’s Airway: Open the airway by doing a head tilt/chin lift. Breathing: Look, listen and feel for breathing Compressions: Compress the chest 2 inches on an adult (8+ “hard & fast” * CAB: The order to follow in a breathing emergency ): Cardiopulmonary Rescuscitation (CPR The letters in CPR stand for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, combination of rescue breathing (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) and chest compressions. If a child isn't breathing or circulating blood adequately, CPR can restore circulation of oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Without oxygen, permanent brain damage or death can occur in less than 8 minutes. AED (Automated External Defibrillator): A device that delivers an electric shock to the heart to restore its normal rhthym. If a victim is unresponsive & NOT breathing: Perform CPR Give 30 chest compressions and 2 breaths: You should complete 5 cycles of CPR in 2 minutes. Steps for a Breathing Emergency. 1. Check the scene for safety. 2. Call 911 – Send someone to get an AED 3. Begin Chest Compressions (30 chest compressions/2 breaths) 4. Hook up the AED as soon as it arrives on the scene.