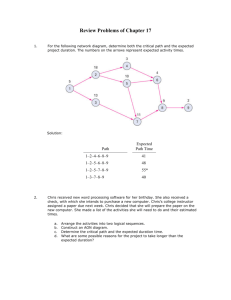
LAB-1 Understanding the Control Scheme in a LabVIEW VI
advertisement

Homework-10 IET 320 Industrial Project Management Student Name: DUE DATE: Nov. 13, 2010 Please read Chapter Ten of your textbook, complete following review questions. Fill in the black (0.5pt each): 1. The process of accelerating a project is referred to as _Crashing_________. 2. In analyzing crash options for project activities, each activity has a slope that is calculated as the _Crash cost – normal cost_________ divided by the _normal time – crash time_________. 3. If a project is extraordinarily complex, rather than showing every possible path through the network and every activity sequence, a(n) _Meta-network_________ that shows only the key subroutines or network paths can be created. 4. An activity of duration zero whose sole purpose is to maintain network logic is a(n) ___Dummy Activities_______. Multiple Choices (1pt each): 1. Activities A and B have a finish to finish relationship and early start and finish times as shown. What is the result of incorporating a 4 day lag between activities C and B? 20 A 27 7 22 C 26 4 24 B 27 3 a. The early finish for A increases to 31. b. The early start for A increases to c. The early finish time for B increases to 31. d. The early start time for D falls to 23. 27 D 39 12 24. This is the correct answer 2. What is the early start time for activity C if it has the start to start relationship shown? 20 A 27 7 -125 B 29 4 ?? C 30 ?? 30 D 42 12 a. Day 20 b. Day 25 c. Day 27 d. Day 29 This is the correct answer 3. Which statement about this Gantt chart is best? a b c d e f 10 20 30 40 50 a. Activity A has a duration that could be as short as 1 day and as long as 10. b. Activity B probably has activity A as a predecessor. This is the answer c. No progress has been made on activity C. d. Activity D is the longest activity. 4. Use the Gantt chart and the activity list to determine when resource 2 is free. Time Activity 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 A B C D E F G H J K Activity Resources Activity Resources A 1 F 1 B 5 G 2 C 4 H 5 D 3 J 3 E 2 K 2 -2- a. Between 0 and 15 b. Between 15 and 30 c. Between 30 and 45 d. Between 45 and 60 This is the answer 5. A basic Gantt chart: a. clearly displays early and late start and finish times for all activities. b. cannot be used to track the project’s progress. c. permits scheduling resources well before they are needed . This is my answer d. shows dummy activities to preserve network logic. 6. One reason for crashing a project is: a. the project has slipped behind schedule. This is my b. that the initial schedule may be too pessimistic. c. market needs change and the project is not in demand any more. d. there are no repercussions for delivering the project late. answer 7. A project has the activity duration and cost information indicated in the table where all times are in weeks. What is the lowest total cost for completing this project in 40 days? Activity Predecessor Normal Normal Crash Crash Time Cost Time Cost A -8 $12,000 5 $21,000 B A 12 $20,000 9 $30,000 C A 15 $24,000 10 $60,000 D B 3 $10,000 2 $15,000 E C 9 $17,000 6 $34,000 F E 7 $5,000 6 $6,000 G D 8 $14,000 6 $20,000 H A 12 $22,000 10 $30,000 I H 6 $50,000 5 $55,000 J F,G,I 11 $33,000 9 $50,000 a. $242,667 b. $255,600 This is my answer c. $263,333 d. $272,500 8. The AOA network described by this table needs: Activity Predecessor A -B -C A, B D B E C, D -3- a. zero dummy activities b. one dummy activity. c. two dummy activities. d. three dummy activities. This is my answer Discussion Questions (1pt each): 1. In crashing a project, we routinely focus on those activities that lie on the critical path, not activities with slack time. Explain why this is the case. There is very little that we can do to enhance slack time. Slack time is waiting on a component to be fabricated and/or delivered or something that is totally out of our control. That is why it is called slack time. On the critical path, we are in control of what is going on. We have the resources in hand, and the people get those resources in place on the critical path, so that is where we want to focus our attention to. To try and focus attention on slack time instead of critical path is not productive and will not enhance crashing a project. 2. What are some of the advantages in the use of AOA notation as opposed to AON? Under what circumstances does it seem better to apply AON methodology in network development? AOA is widely accepted, in the construction field for example, because it is easy to apply to complex problems because of the ease in which one can employ the path process used in AOA. The activity and node systems is used for projects that have many significant milestones, such as supplier deliveries, AOA event nodes are very easy to identify and flag. AON is used in popular computer formats, such as MS Project, and use a more user friendly nodes. It places the activity within a node and uses arrows merely as connection devices, thereby simplifying the network labeling. The dummy activities are hard to follow with the AOA, and the AON is becoming more popular with new software, but for long projects AOA is the best and shorter projects that required ease is a necessity to follow, use the AON. -4- 3. Please identify and discuss some of the problems or dangers in using project networks. Under what circumstances can they be beneficial and when can they be dangerous? Networks are an abstract representation of events in which time is reduced to a numerical value. Sometimes these values can be misleading because they may or may not be drawn to a scale that has a relationship to the ongoing pattern of events. Sometimes they become too large and complex to be meaningful; they can be oversimplified and create incorrect representations due to faulty reasoning. Sometimes networks are used for tasks they are not well suited, it is hard to get subcontractors on board with following the guide to get the work done on time or at all, and there is a strong potential for bias in PERT estimations used in network construction. However, if used properly and the data is not bias, they can be a very useful tool in coordinating efforts to get a project started and finished on time. Problems (7pts total): 1. (2pts) Consider a project with the following information. Construct the project activity network using AOA methodology and label each node and arrow appropriately. Identify all dummy activities required to complete the network. Activity Duration Predecessors A 3 -B 5 A C 7 A D 3 B, C E 5 B F 4 D G 2 C H 5 E, F, G Activity A B C D E F G H Duration 3 5 7 3 5 4 2 5 ES 0 3 3 10 8 13 10 17 EF 3 8 10 13 13 17 12 22 LS 0 5 3 10 12 13 15 17 LF 3 10 10 13 17 17 17 22 Slack -2 --4 -5 -- -5- 2. (3pts) When deciding on whether or not to crash project activities, a project manager was faced with the following information. Activities of the critical path are highlighted with an asterisk: Normal Activity Crashed Cost Duration Extra Cost Duration A 5,000 4 weeks 4,000 3 weeks B* 10,000 5 weeks 3,000 4 weeks -6- C 3,500 2 weeks 3,500 1 week D* 4,500 6 weeks 4,000 4 weeks E* 1,500 3 weeks 2,500 2 weeks F 7,500 8 weeks 5,000 7 weeks G* 3,000 7 weeks 2,500 6 weeks H 2,500 6 weeks 3,000 5 weeks 1) Identify the sequencing of the activities to be crashed in the first four steps. Which of the critical activities should be crashed first? Why? Start with D, B, C then A. The cost of D is the least, it has the biggest benefit in time saving, and it is on the critical path. 2) What is the project’s critical path? After four iterations involving crashing project activities, what has the critical path shrunk to? The critical path of the project is B, D, E, and G. It is shrunk to 16. 3) Suppose project overhead costs accrued at a fixed rate of $500 per week. Chart the decline in direct costs over the project life relative to the increase in overhead expenses. 30000 25000 20000 15000 Overhead Cost 10000 5000 0 4) Assume that a project penalty clause kicks in after 19 weeks. The penalty charged is $5,000 per week after 19 weeks. When the penalty charges are added, what does the total project cost curve look like? Develop a table listing the costs accruing on a per week basis. Refer to chart -7- 5) If there were no penalty payments accruing to the project, would it make sense to crash any project activities? Show your work. If there is no penalty for being late with a project, why the big rush? If you spend a lot more money at the start of the project than you needed to crash the project, you are heading for budget overruns for no apparent reason. If you have another project to start before this one gets finished, then you may want to consider. But that would be the only reason I could think of to crash a project with no time table. 3. (2pts) You are considering the decision of whether or not to crash your project. After asking your operations manager to conduct an analysis, you have determined the “pre-crash” and “post-crash” activity durations and costs, shown in the table below: Normal Activity A B C D E F G Duration 4 days 5 days 3 days 7 days 2 days 5 days 9 days Cost $1,000 $2,500 $750 $3,500 $500 $2,000 $4,500 Crashed Duration 3 days 3 days 2 days 5 days 1 day 4 days 7 days Cost $2,000 $5,000 $1,200 $5,000 $2,000 $3,000 $6,300 1) Calculate the per day costs for crashing each activity. Using the equation for cost calculating of crash from page 300 of the text and a computer program, I did one for each day and this is the result. Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Day 8 Day 9 Day 10 Day 11 Day 12 Day 13 Day 14 Day 15 333.33 333.33 333.33 416.67 416.67 416.67 225 225 150 150 150 150 150 1500 250 -8- Day 16 Day 17 Day 18 Day 19 Day 20 Day 21 Day 22 Day 23 Day 24 Day 25 250 250 250 421.43 421.43 421.43 421.43 421.43 421.43 421.43 2) Which are the most attractive candidates for crashing? Why? Days 9 through 13 because they cost very little to do for the money it would cost to do them and save the most time for the money. -9-