The cell cycle
advertisement

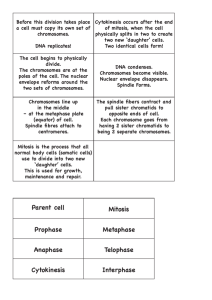
Chromosomes, the Cell Cycle, and Cell Division A. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Stages in the life of an actively dividing eukaryotic cell: G1 S G2 M Stationary phase (G0): Nondividing cells The cell cycle is controlled predominately at two key regulatory points: between G1 and S, and between G2 and M. B. Interphase and Mitosis: An Overview During G1: Chromosomes are uncondensed and unreplicated During S: Chromosomal (DNA) replication takes places but the two copies do not separate. By the end of S, the chromosomes are in an uncondensed, replicated state. Each chromosome consists of a pair of sister chromatids connected at a centromere During G2: Chromosomes are uncondensed, replicated. The cell makes the proteins it needs for mitosis. During Mitosis: The chromosomes condense and become visible; the sister chromatids separate and become daughter chromosomes, the daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell; the daughter chromosomes decondense. Usually after mitosis, the cell divides. By the end of mitosis, the chromosomes have returned to an uncondensed, unreplicated state (G1). C. Stages of Mitosis 1. Prophase Chromosomes condense and become visible Nuclear membrane disperses Spindle apparatus begins to form 2. Metaphase Chromosomes align on equator of the spindle apparatus 3. Anaphase Chromatids separate and become daughter chromosomes Daughter chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell 4. Telophase At each pole of the spindle, the chromosomes decondense and form new nuclei New nuclear membranes form Usually, cytokinesis occurs at this time. D. Meiosis: An Overview Function of meiosis: To produce gametes In sexually reproducing organisms Meiosis takes place only in germ-line cells, found in the gonads. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes is halved, so that a gamete has half the number of chromosomes as the original germ-line cell. Diploid number: The number of chromosomes in the original germ line cell (for example, 46 chromosomes in humans) Haploid number: The number of chromosomes in the gamete (for example, 23 chromosomes in humans) During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate Homologous chromosomes are similar chromosomes, each from a different parent, in sexually reproducing species E. Prokaryotic Chromosomes and Division Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce by simple fission: the chromosome is replicated and then the cell divides.