How_Neurons_Communicate_Handout_reg
advertisement

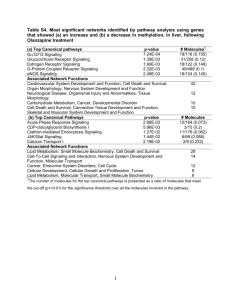
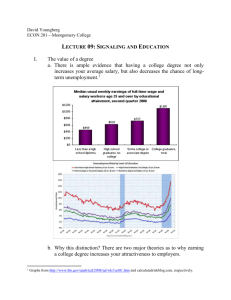
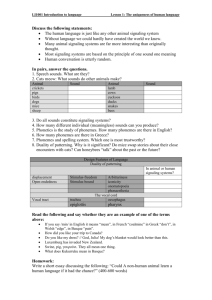
Name: . Date: . How Neurons Communicate: Exploring the different types of cell signaling in the Central Nervous System Goals: • Identify the parts of the neuron and describe their function(s) in cell signaling • Understand various types of synaptic transmission • Design and build a model to explain how several different types of cell signaling occur in the central nervous system Previous Knowledge Needed: Cells communicate with one another through chemical and/or mechanical signaling The process by which signals are received, processed and responded to, is called the signal transduction pathway The nervous system controls communication between different parts of the body and the body’s interactions with the environment Introduction: In the brain, cells communicate with each other at spaces called synapses. A synapse is the space between one neurons’ end and another neurons’ start. Synaptic transmission is the process by which a pre-synaptic (before the synapse) neuron communicates a chemical signal to a post-synaptic (after the synapse) neuron. However, there are many ways in which neurons can send and receive signals. We will explore, construct and present the following ways neuron communication can occur: chemical signaling, electrical signaling, mechanical signaling, gaseous signaling, immune cell signaling and hormone signaling. Procedure: Each group will be assigned a type of neuron communication, and will be responsible for creating a poster describing the process and the molecules involved of their assigned cell communication. You may use your textbooks to gather information and details about the neuronal communication you are assigned. In the last 30 minutes of class, each group will have 5 minutes present their posters to the entire class. The class will be responsible for completing the activity worksheet sections pertaining to each type of communication. Materials: Poster board, one per group Markers Tape Glue sticks Cut-out molecules involved in neuron communication Biology books Post-Activity Questions 1. If neurons communicate chemically, what is the name of the area between neurons where chemical signals can be released? 2. Name the three process of the “signal transduction pathway”. a. b. c. 3. Give a short description of each type of cell signaling presented: a. Chemical signaling b. Electrical signaling c. Gaseous signaling d. Mechanical signaling e. Immune cell signaling f. Hormone signaling 4. True or False: neurons cannot send signals long-distance. 5. Hormone signaling involves activation of receptors found in which part of the cell? a. Membrane b. Nucleus c. Axon d. Golgi apparatus 6. Fill in the blank: Electric signals travels down a neurons’ called “saltatory conduction”. This occurs because of close one after the other within very short time periods. by a process channels open and Post-Activity Discussion You should now have a better understanding of the many ways neurons communicate in the brain to govern body functions. Though they can be very different, each type is similar in that important signals are sent and received and that the receipt of these signals causes changes in the receiving neuron to activate a response. All types of cell signaling covered in this activity occur in healthy states. But what happens when the brain is not healthy? Can you think of situations where the brain might not be healthy? Discuss this with your neighbor, then write them down here. How might cell signaling be affected in conditions when the brain is not healthy? We’ll discuss this as a class.