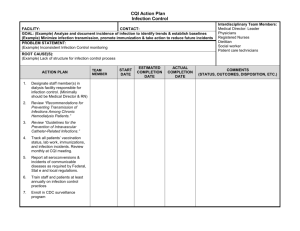
Ch 11 Human Microbe Interactions Study Guide
advertisement
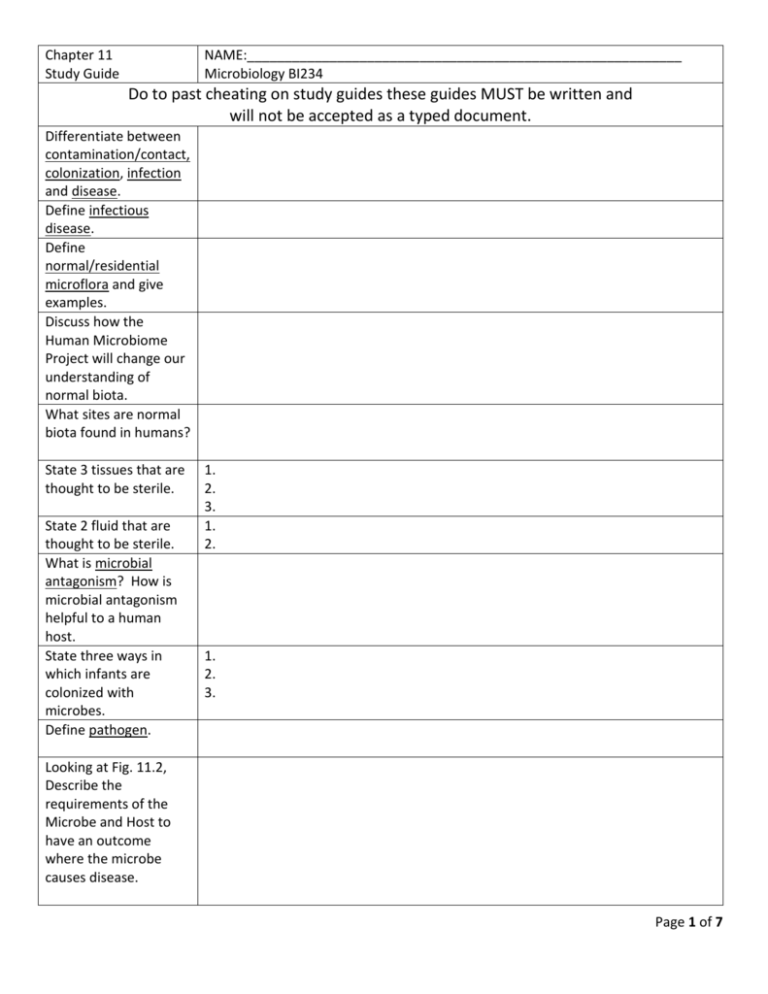
Chapter 11 Study Guide NAME:__________________________________________________________ Microbiology BI234 Do to past cheating on study guides these guides MUST be written and will not be accepted as a typed document. Differentiate between contamination/contact, colonization, infection and disease. Define infectious disease. Define normal/residential microflora and give examples. Discuss how the Human Microbiome Project will change our understanding of normal biota. What sites are normal biota found in humans? State 3 tissues that are thought to be sterile. State 2 fluid that are thought to be sterile. What is microbial antagonism? How is microbial antagonism helpful to a human host. State three ways in which infants are colonized with microbes. Define pathogen. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. Looking at Fig. 11.2, Describe the requirements of the Microbe and Host to have an outcome where the microbe causes disease. Page 1 of 7 Differentiate between pathogenicity and virulence. Explain the difference between true pathogens and opportunistic pathogens and give an example of each. What are some factors that would allow an opportunistic pathogen to cause infection? Describe two factors that influence a microbe's virulence. 1. What are the five steps on the progression of an infection? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2. Step One: _________________________ What is a portal of entry? What are some characteristics of a portal of entry? What is the difference between an exogenous and endogenous infection? Can all parasites use all of the various portals of entry? Defend your answer with an example. Define infectious dose. Give an example of a disease that has a low ID and one that has a high ID. Page 2 of 7 Step Two: _________________________ Why is attachment/adhesion an important step in the progress of an infection? Pathogens cannot all bind to the same types of cells, for example rhinoviruses bind only to respiratory cells. How do they identify the cell’s type? What are some structures that aid in the attachment/ adhesion of pathogens? Step Three: _________________________ Is it easy for pathogens to survive host defenses? Describe at least 2 mechanisms used by host cells to battle pathogens. What are antiphagocytic factors? Give an example. Step Four: _________________________ Describe the three ways microbes cause tissue damage. Explain the effects of the exoenzymes hyaluronidase, coagulase, and streptokinase. Define a toxin. What is an endotoxin? What type of bacteria produce these? What is an exotoxins? What type of bacteria produce these? Define hemolysin and Page 3 of 7 describe the types of microbes that use it. Provide a definition of virulence factors. Differentiate between the following types of infections localized infection systemic infection focal infection mixed infection primary infection secondary infection acute infection chronic infection What is the difference between a sign and a symptom? Give examples of each. State 2 terms that are used when infections are not apparent. Step Five: _________________________ Define portal of exit and give examples. What are some characteristics of a portal of entry? Define latency and give at least two examples of this type of infection. Page 4 of 7 Draw a diagram of the stages of disease in a human with time on the X-axis and symptoms on the Yaxis. Make sure to label the: incubation period, prodromal stage, period of invasion, acme, decline phase, and convalescent period. What is a reservoir and transmitter/source and give an example of each. What is the difference between a carrier and an asymptomatic carrier? Describe the three main types of living reservoirs as shown in Table 11.6 and give examples of each. 1. 2. 3. What are some examples of non-living reservoirs. What is zoonosis? What are some examples? Differentiate communicable, contagious and noncommunicable diseases and give an example of each. Communicable= Contagious= Noncommunicable= What is the difference between vertical and horizontal transmission? Page 5 of 7 Describe direct contact transmission and give examples. Describe indirect contact transmission and give examples. What is a fomite? Give examples. What is a vehicle? Give examples. Define nosocomial infection. List the three most common types of nosocomial infections. What are the main pathogens found in nosocomial infections? Explain some ways to prevent nosocomial infections. Define etiologic agent. 1. 2. 3. List Koch's postulates, and when they might not be appropriate in establishing causation. Define epidemiology. Identify the need for some diseases being denoted "notifiable" and give examples of at least 3 reportable diseases. Define incidence and prevalence. Differentiate between mortality and morbidity. Discuss point-source, common-source, and propagated epidemics, and predict the shape of the epidemic curves associated with each. Page 6 of 7 Differentiate between disease occurrences that are endemic, epidemic, sporadic and pandemic and give at least one example of each. What type of data is being collected during the following epidemiological studies? Descriptive: Analytical: Experimental: ***Understanding of ALL of the underlined terms in this document is needed to succeed in this class. To further study these terms do one of the following: Make flash cards of all terms Make a concept map of all terms (if you don’t know what this is look it up on Wikipedia) Write out definitions of all terms Or come up with your own way of studying these terms. Just make sure to ok it with me to make sure you’ll get your extra credit. This must be turned in attached to this study guide at the time the study guide is due!!!! What’s working well and what’s a suggestion to help things work better? Page 7 of 7