6th Grade Science - Lafayette Parish School System
advertisement

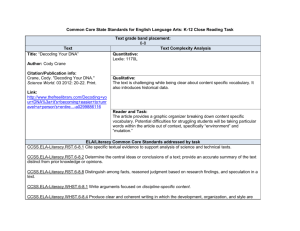
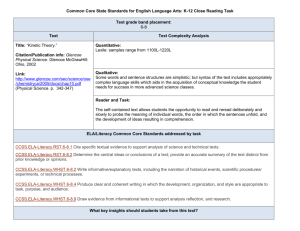
6th Grade Science Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 LPSS Science Teacher Leader Cadre Allison Bloomer – Youngsville Sarah Boudreaux – Milton Pam Deshotel – LJ Alleman Debra Milligan – Acadian Terry Turner – Paul Breaux Bridget Trahan – LPSS Science Lead Teacher Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 6th Science: Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Time Frame: December 2 – January 24 (6 Weeks) Unit Description and Student Understandings: This unit is designed to introduce students to the concepts of force and motion with an emphasis on Newton’s Laws of Motion. This unit provides a good opportunity to introduce controlled experimentation, as well as the concept of measurement errors and how to address them in data interpretation. Newton’s Laws of Motion explain movement, direction, speed, and forces that can and do influence objects in nature and in the laboratory. Using models and investigations, the laws of motion can be demonstrated. Students can then explain and predict actions and reactions. This unit introduces the concepts of force, work, power, and efficiency and how they are interrelated. The review of simple machines is an integral part of this unit. The relationships among work, machines, and the real world will be considered. Students will be able to identify forces. They will describe the relationship between kinetic and potential energy. Further, the idea of work and its relationship to power and efficiency will be introduced with regard to simple machines. Guiding Questions: 1. Can students state and explain Newton’s three fundamental Laws of Motion? 2. Can students identify the forces that act upon objects and the effect those forces have on the object? 3. Can students relate their understanding of Newton’s Laws to real life situations? 4. Can students identify forces such as push, pull, lift, twist, and press? 5. Can students describe the relationship between work input and work output in a simple machine? 6. Can students explain the relationship between work, power, and efficiency? Key Concepts: Analyze motion graphs and predict future movement Describe friction Describe how resistance of materials affects electrical flow Identify forces acting on objects Give examples of forces Describe gravity Compare and contrast forces and explain the causes and effects of gravity Differentiate velocity from speed Identify that velocity is speed and direction Identify acceleration, deceleration, and constant speed graphs Describe the relationship among force, mass, and acceleration Draw a distance-time line graph indicating motions such as constant speed, acceleration, deceleration (negative acceleration) Explain that an object will remain at rest or in a constant motion unless an unbalanced force acts upon it Explain net force Determine or illustrate with arrows the motion of an object subjected to balanced or unbalanced forces; indicate direction and magnitude or distance 6th Grade Science 2013-2014 Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 6th Science: Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Time Frame: December 2 – January 24 (6 Weeks) Recognize balanced and unbalanced forces Understand simple machines (relationship of work input to work output) Vocabulary List: Movement, Reference point Velocity Inertia, Isaac Newton, Newton’s First Law of Motion Newton’s Second Law of Motion, Friction, Sliding Friction, Rolling Friction, Fluid Friction Catapult, Unbalanced Forces, Balanced Forces, Newton’s Third Law of Motion, Momentum Force, Work, Friction Inclined plane, Vertical, Horizontal Simple Machine, Compound Machine, Input force, Output force, Mechanical Advantage GLEs CCSS Literacy Standards NGSS Practices Instructional Strategies Probe: Rolling Marbles Video: LPB- United Streaming: Exploring Laws of Motion/Video Questions PS-14 (E) Construct and analyze graphs that represent onedimensional motion (i.e., motion in a straight line) and predict the future positions and speed of a moving object (PS-MB1) NGSS Practices: 1-8 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 6 pgs. 224-231, Lessons 1 & 2 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6 WHST.6-8.1,2,9,10 Act 1: How Do You Know it is Moving? (2 days) *optional: Domino Dash, Speed Challenge, Bubble Gum physics http://www.science-class.net/index.htm PS-17 (E) Describe and demonstrate that friction is a force that 6th Grade Science 2013-2014 Addressed in LCC Activity 2, 4 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 pgs. 256-260, Lesson 2 Differentiation (Enrichment/Remediation Strategies) Forces, Motion, and Laws activities and powerpoints: http://www.scienceclass.net/Physics/force_motion.htm BrainPop Videos: http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/brain pop_movies.html Interactive Activities: http://www.sciencespot.net/Pages/kdzphysics.ht ml Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 14-27 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/unit4/ chapter10/section_1_self-check_quiz-eng_.html http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/unit4/ chapter10/section_2_self-check_quiz-eng_.html Powerpoints: http://science.pppst.com/motion.html Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 55-63 http://mypages.iit.edu/~smile/ph9311.html Forces 2 telecast: “Friction Opposes Motion” Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 6th Science: Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Time Frame: December 2 – January 24 (6 Weeks) acts whenever two surfaces or objects move past one another (PS-MB2) PS-19 (E) Identify forces acting on all objects (PS-M-B3) (26 minutes)—Integrated Science 7 Addressed in LCC Activity 1, 2, 4 NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6,7 WHST.6-8.1,2,9,10 PS-15 (E) Explain why velocity is expressed in both speed and direction (PS-M-B1) PS-16 (E) Compare line graphs of acceleration, constant speed, and deceleration (PS-M-B1) PS-22 (E) Demonstrate that an object will remain at rest or move at a constant speed and in a straight line if it is not subjected to an unbalanced force (PS-M-B5) (PS-M-B3) PS-23 (E) Predict the direction of a force applied to an object Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 pgs. 252-255, Lesson 1 Chapter 7 pgs. 261-263, Lesson 2 http://science.pppst.com/motion.html Act 9: It’s the Law Addressed in LCC Activity 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 6 pgs. 232-233, Lesson 2 Addressed in LCC Activity 2, 6 NGSS Practices: 1-8 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 6 pgs. 236-241, Lesson 3 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.7 WHST.6-8.4,6,9,10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,8 WHST.6-8.2,3,9,10 Act 2: Motion Graphs Practice calculating speed and velocity Motion Graphs NGSS Practices: 1,2,3,4,6,7,8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6,7 WHST.6-8.1-10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 Act 5: Seat-Belt-R-Us 6th Grade Science 2013-2014 Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 pgs. 264-265, Lesson 3 Act 4: Inertia—Newton’s First Law of Motion Introduction to Newton’s 1st Law (lecture/discussion) Forces 1Telecast: Forced into Motion (19 minutes) Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 24-25 Motion Graphs Practice: http://www.mysciencesite.com/motion_graphs.p df Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 44-51 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/unit4/ chapter11/section_1_self-check_quiz-eng_.html Addressed in LCC Activity 7 Interactive Science Textbook: Review Chapter 7 pgs. 254-255, Lesson 1 Chapter 7 pgs. 266-267, Lesson 3 Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 52-54 http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/unit4/ Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 6th Science: Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Time Frame: December 2 – January 24 (6 Weeks) and how it will change the speed and direction of the object (PS-M-B5) CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6,7 WHST.6-8.1,2,3,9,10 PS-20 (E) Draw and label a diagram to represent forces acting on an object (PS-M-B4) PS-21 (I) Determine the magnitude and direction of unbalanced (i.e. net) forces acting on an object (PS-M-B4) PS17 (E) Describe and demonstrate that friction is a force that acts whenever two surfaces or objects move past one another (PS-MB2) PS-22 (E) Demonstrate that an object will remain at rest or move at a constant speed and in a straight line if it is not subjected to an unbalanced force (PS-M-B5) (PS-M-B3) PS27 (I) Explain the relationship between work input and work output by using simple machines (PS-MC2) NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6,7 WHST.6-8.1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,7 WHST.6-8.1,2,3,7,9,10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 Act 6: Newton’s Second Law of Motion chapter11/section_2_self-check_quiz-eng_.html Interactive Science Textbook: Covered with GLE 19 and 23 Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 44-46 Addressed in LCC Activity 6, 7, 8 http://zonalandeducation.com/mstm/physics/me chanics/forces/netForce/netForce.htm Interactive Science Textbook: Chapter 7 pgs. 254-255, Lesson 1 Chapter 7 pgs. 268-271, Lesson 3 Motion, Forces, Energy: Book M pp. 64-69 Act 7: Catapults (2 days) *optional: Hovercraft, Rocket Racer http://glencoe.mcgrawhill.com/sites/007877846x/student_view0/unit4/ chapter11/section_3_self-check_quiz-eng_.html Addressed in LCC Activity 6, 7 Telecast: “May the Force Be With You” Machines 5 Activity 1: The Force May Be With You Video: Work, Energy, and the Simple Machine (17 minutes) LPB-United Streaming Introduction to Simple Machines Simple Machines Scavenger Hunt—edheads.com Simple Machines: Can You Match Them? Activity 2: Rolling Right Along! http://www.engineeringinteract.org/resources/pa rkworldplot/flash/concepts/friction.htm http://zonalandeducation.com/mstm/physics/me chanics/forces/netForce/netForce.htm CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,7 WHST.6-8.2,3,9,10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6 WHST.6-8.3,4,5,7,9,10 6th Grade Science 2013-2014 Science Interactive Textbook: Chapter 12 pgs. 448-453, Lesson 2 Chapter 12 pgs. 456-463, Lesson 3 Chapter 12 pgs. 464-469, Lesson 4 Activity 3: Simply Machines Simple Machines Presentations: http://science.pppst.com/simplemachines.html Simple Machines http://www.mos.org/sln/Leonardo/InventorsToo lbox.html http://sln.fi.edu/qa97/spotlight3/spotlight3.html Lafayette Parish School System 2013-2014 Curriculum Map Grade: 6th Science: Unit 3: Motion, Work, Power, and Efficiency Time Frame: December 2 – January 24 (6 Weeks) NGSS Practices: 1,2,3,4,6,7,8 Activity 5: Classy Levers Proving a screw is an inclined plane: http://sln.fi.edu/qa97/spotlight3/screwdemo.html Science Interactive Textbook: Chapter 12 pgs. 442-445, Lesson 1 Chapter 12 pgs. 454-455, Lesson 2 Honda Commercial: http://autorepair.about.com/library/multimedia/h honda-ad-300k.swf CCSS: ELA-Literacy WHST.6-8.1,2,7,9,10 PS29 (I) Compare and/or investigate the relationship among work, power, and efficiency (PS-M-C2) NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy WHST.6-8.1,2,7,9,10 NGSS Practices: 1-8 CCSS: ELA-Literacy RST.6-8.1,2,3,4,6 WHST.6-8.1,2,4,5,6,7,9,10 Activity 4: Work and the Inclined Plane Activity 6: Power Book M pp. 118-128, 132-134, Guided Study Workbook pp. 50-52 Simply Machines Project---Rube Goldberg UNIT 3 BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT 6th Grade Science 2013-2014 JANUARY 24, 2014