NOTES Ch 4 sect 5 Life in the Colonies
advertisement

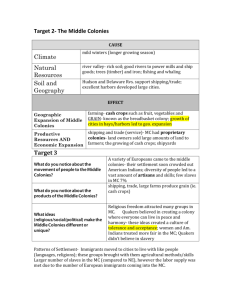
US I C NOTES: Life in the Colonies (ch #5, section #5) During the 1700s, England’s 13 colonies became societies with their own ideas and traditions. Colonial Society: Colonists enjoyed more rights and freedoms than people in England but social classes still existed. GENTRY ↓ MIDDLE CLASS ↓ HIRED HANDS, INDENTURED SERVANTS, SLAVES Gentry- wealthy planters, merchants, ministers, lawyers, and royal officials. Middle Class- farmers who owned their own land, skilled crafts workers, some tradespeople. o *** ¾ of all white colonists were in the middle class*** Indentured Servants- people who signed contracts to work without wages for a period of four to seven years in exchange for passage across the Atlantic Ocean. o Servants could receive “freedom dues”- a set of clothes, tools, and 50 acres of land. o Women could often shorten their terms by marrying colonists. o Many indentured servants were able to move up into the middle class. Women in the Colonies: The role of women included taking care of their household, their husbands, and their families. o Women cooked all the meals, raised the children, made all the family’s clothing, and helped with the chores around the farm. Women in the country often worked next to their husbands during harvest time doing the same tasks as men. City women, mostly single women, often worked outside the home (maids, cooks, nurses, midwives, and seamstresses) Women often learned a trade from male family members and often took over for the family business when their husbands died. African American Influences: In the South, Africans were able to keep many parts of their cultures alive o Languages (example-Gullah); music; names; art; ceremonies. Many Africans worked on the docks or on ships or as skilled craftsmen. Some Africans were able to purchase their freedom and have their own businesses. The Great Awakening (1730s-1740s) A religious movement in the colonies that used emotion and drama to get people to be more religious. Jonathon Edwards- “sinners in the hands of an angry God” George Whitefield- emotional preacher who held huge religious retreats Many new churches were formed in the colonies. Helped spread tolerance and the idea of independence and democracy against the British Education in the Colonies: New England- Massachusetts established the first PUBLIC SCHOOLS (allowed children of the lower classes an opportunity to become educated) Middle Colonies- only wealthy families could afford to sent their students to private schools. Southern Colonies- wealthy planters hired private tutors or sent their sons to schools in England. Apprenticeships- a boy around the age of 12 or 13 would be hired to work for a master in order to learn a trade. Dame Schools- private schools run by women in their homes. o ***for the most part, Africans were denied any type of education*** Enlightenment and Change for the Colonies: Members of the gentry often read about the ideas of the Enlightenment and many of those ideas started to change colonial society. Benjamin Franklin- became a successful businessman in the printing industry, inventor, community leader, and government official. City life- entertainment and trade were important aspects of city life and many cities published weekly newspapers. Freedom of the Press- The libel trial of John Peter Zenger established the freedom of the press in the United States.