Economies In the Colonies
advertisement

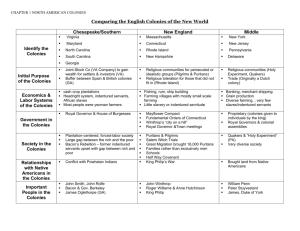
Economies In the Colonies • Southern Colonies – Based on commercial agriculture (Tobacco – 1st cash crop) • Rice, Indigo – Plantations – Tobacco • High demand in Europe (1620-60) • Intensive labor effort • Virginia had perfect geography for growing tobacco – Few roads, everything moved by water – Indentured servants – Rice and Indigo • South Carolina • Used slaves • Rice and indigo could be grown in different seasons in different types of ground • New England – Diverse economy (Farming, Fishing, Shipbuilding, Sawmills, Etc.) – Farming • No large demand for their crops, No large plantations (Subsistence Farming) • Main crop was corn – Also barley, oats, rye, beans, peas, pumpkins, squash, apples, berries – Raised livestock • Fishing – Grand Banks (Great spot for fishing) – Brought most prosperity to New England – Whaling (Cape Cod, Nantucket) • Shipbuilding / Mills – – – – Lots of forests providing lumber Fall Line (Waterfalls created powered mills) Wood was important to every town Ships easily built because forests and mills were close to the coast • Middle Colonies – Agricultural Base (Most fertile land on the continent, “Bread Basket “ colonies) • Farmers produced a surplus • Used rivers that ran deeper into the country to farm further inland • Wheat Boom (Population explosion in Europe in early 1700’s) – New wave of immigrants, high demand for food – Made some farmers in the middle colonies rich » Entrepreneurs » Capitalists – Limits in technology kept many from becoming rich » Only those that could hire extra workers or could rent out land got rich Colonial Society • Southern Colonies – Plantation system created a distinct class system • Wealthy elite controlled the area (politics, economics) – Planter Elite (Enormous economic and political influence) – Plantations were their own communities (Schools, chapels, blacksmiths, etc.) – Size of plantations grew with the change from indentured servants to slave labor in the early 1700’s • • • Building of mansions Copying English upper class Hired oversees to work the fields – More leisure – Backcountry Farmers (Yeomen) • • • • Owned most of the land in the South Former indentured servants Mostly subsistence farming Bacon’s Rebellion – – – – Sir William Berkeley Dispute over Native controlled land in the back country Nataniel Bacon Accelerated the use of slavery in Virginia » Never would be free, so they couldn’t own land » Fewer white settlers were willing to become indentured servants • Slavery – 10-12 million transported from Africa between 1450 and 1870, 2 million of which died at sea • • • • – – – – 3.5 million – Brazil 1.5 million – Spanish colonies 4 million – Carribean 500, 000 – North America Horrific conditions on the voyage over Developed slowly in Middle Colonies Some could gain freedom by converting to Christianity As numbers increased status changed, soon all Africans were considered of a lower status. Hereditary system based on race – Slave Code (Virginia 1705) – Becomes a vital part of the plantation economy • New England – Social life centered on the towns – Desire to worship together encouraged the growth of communities – Town Meetings • Anyone could attend, only men could vote • Selectmen – Handled the towns affairs • Could directly participate in government, unlike in England – Puritan Society • Lived near Church (Meetinghouse) • Very strict – Did, however, drink rum, wear bright colors, listen to music – God made the world and the things in it are to be enjoyed • Salem Witch Trials • Middle Colonies – Distinct class system • Wealthy entrepreneurs at the top • Next those that owned a few acres, and generated a small surplus • Landless workers (Rented land or worked for wages) Trade and the Rise of Cities • Triangular Trade – To get English goods, New England’s merchants had to trade their goods somewhere else, then trade with England • Bills of Exchange • Triangular Trade with Caribbean and England; England and West Africa Growth of Urban Areas • Growth of trade causes some ports to grow rapidly – Philadelphia, Charles Town • Distinct Class System – Wealthy Merchants (Similar to Plantar Elite) at top • Were in the minority – Artisans and their families (Half the Population) • Carpenters, masons, coopers, irons, silversmiths – – – – Innkeepers and Retailers (Equal to Artisans) Unskilled laborers (30% of society) Indentured servants and Slaves (10-20% of population) Problems • Overcrowding, crime, pollution, epidemics