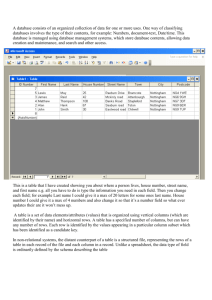
SQL Interview Questions for Software Testers
advertisement

SQL Interview Questions For Software Testers
Software testing - Questions and Answers - SQL Interview
Questions
SQL recognizes 4 general type of Data
Character Strings
These are sentences, symbols or both
VARCHAR2 and CHAR
Math functions can not be done at the
character string data.
NUMERIC Data
DATE, Timestamp, Numbers, and Integer
BOOLEANS
Boolean values are either True or False.
NULLS
A NULL Value indicates that nothing exists
in that field
Allowing NULL values can be decided at the
time of creating the table.
What is an Operator?
Operators are a means by which SQL can manipulate
numbers and strings or test for equality
Four
types of Operator
Arithmetic
Range
Equality and
Logical
RDBMS provides a lot of built in Functions to perform
an operation. And it is an excellent tool inside a
query.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM table one;
An Expression is a special statement that returns a
value
4 types of Expressions
Boolean
The Boolean Expression returns the
True/False Result
Numeric
It generally returns a Number
AVG()
SUM()
Character
Character expressions are used to test for
values of a string
Date Expressions
Date and Timestamps
Q. What is a primary key?
A. Primary key : Each row of the data in a table uniquely
identified by a Primary Key The column (columns) that has
completely unique data throughout the table is known as the
primary key field.
primary key, also called a primary keyword, is a key in a
relational database that is unique for each record. It is a
unique identifier, such as a driver license number,
telephone number (including area code), or vehicle
identification number (VIN). A relational database must
always have one and only one primary key. Primary keys
typically appear as columns in relational database tables.
Primary Key
A primary key is a property given to a table column
that distinguishes that record apart from each
There are 3 Types of Primary Key
Simple Primary Key
Composite Primary Key
Surrogate Primary Key
Simple Primary Key
It uses only one field to identify a record.
Composite Primary Key
Multiple fields joined together to identify a
record in a table.
Surrogate Key
Unique running sequence number is generated to
identify a record.
Q. What is the main role of a primary key in a table?
A. The main role of a primary key in a data table is to
maintain the internal integrity of a data table.
Q. What are foreign keys?
A.Foreign key, also called a foreign keyword, in a database
table is a key from another table that refers to (or
targets) a specific key, usually the primary key , in the
table being used. A primary key can be targeted by multiple
foreign keys from other tables. But a primary key does not
necessarily have to be the target of any foreign keys.
A. Foreign Key : You can logically relate data from
multiple tables using Foreign Keys
Q. Can a table have more than one foreign key defined?
A. A table can have any number of foreign keys defined. It
can have only one primary key defined.
Q. What is difference between UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY
constraints?
A table can have only one PRIMARY KEY whereas there can be
any number of
UNIQUE keys.
The columns that compose PK are automatically define NOT
NULL, whereas a column that compose a UNIQUE KEY can have
null values.
Q. Can a primary key contain more than one columns?
Yes. Primary key created on more than one column is called
composite primary key.
Constraints
The Oracle Server uses constraints to prevent invalid data
entry into tables.
You can use constraints to do the following:
• Enforce rules on the data in a table whenever a row is
inserted, updated, or deleted from that
table. The constraint must be satisfied for the operation
to succeed.
• Prevent the deletion of a table if there are dependencies
from other tables
• Provide rules for Oracle tools, such as Oracle Developer
CONSTRAINTS
PRIMARY CONSTRAINTS
SECONDARY CONSTRAINTS
: PRIMARY,UNIQUE,CHECK,REFERENCES)
: NOT NULL,DEFAULT)
CONSTRAINTS BASED ON
LEVEL
2 LEVELS COLUMN LEVEL and
TABLE
Eg. For SECONDARY CONSTRAINTS
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1. NOT NULL CONSTRAINT
CREATE TABLE EMP9( ENO NUMBER(3)
ENAME VARCHAR2(10));
NOT NULL,
2. DEFAULT CONSTRAINT
CREATE TABLE EMP9(ENO NUMBER(3) NOT NULL,
ENAME VARCHAR2(10),DOJ DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE);
3. PRIMARY CONSTRAINT(COLUMN LEVEL)
UNIQUE
CREATE TABLE EMP9( ENO NUMBER(3)
NOT NULL CONSTRAINT
UNIEMP
UNIQUE,ENAME VARCHAR2(10));
PRIMARY KEY
CREATE TABLE EMP9( ENO NUMBER(3)
PRIMARY
VARCHAR2(10));
CONSTRAINT PKEMP9
KEY,ENAME
4. CHECK CONSTRAINT
CREATE TABLE BANK( ACNO NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT PKBANK
PRIMARY
KEY,ACTYPE VARCHAR2(2) CONSTRAINT CKBANK CHECK
(ACTYPE IN
('SB','CA','RD')),ACNAME VARCHAR2(10),AMOUNT
NUMBER(4));
5. REFERENCES
CREATE TABLE EMP9( ENO NUMBER(3) CONSTRAINT PKE9
PRIMARY
KEY,JOB VARCHAR2(10),ENAME
VARCHAR2(10),MGR NUMBER(4) REFERENCES EMP9(ENO));
6. REFERENCES(REFERING TO DIFFERENT TABLE)
CREATE TABLE DEPT9(DEPTNO NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT PKDNO
PRIMARY KEY, DNAME VARCHAR2(10), LOC VARCHAR2(10));
CREATE TABLE EMP9( EMPNO NUMBER(4),ENAME
VARCHAR2(10),
SAL NUMBER(7,2),DEPTNO NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT FKDNO
REFERENCES DEPT9(DEPTNO));
7. TABLE LEVEL CONSTRAINTS
UNIQUE
TABLE LEVEL
CREATE TABLE BANK( ACNO NUMBER(3),ACTYPE VARCHAR2(10),
BAL NUMBER(7,2),PLACE VARCHAR2(10),CONSTRAINT
UNIBANK
UNIQUE(ACNO,ACTYPE));
PRIMARY KEY(TABLE LEVEL)
CREATE TABLE BANK( ACNO NUMBER(2), ACTYPE VARCHAR2(2)
CONSTRAINT
CKBANK CHECK (ACTYPE IN
('SB','CA','RD')),AMOUNT NUMBER)
DATA Integrity Constraints
Constraint Description
Describe
the
different
type
of
Integrity Constraints
supported by ORACLE ?
NOT NULL Constraint
- Disallows NULLs in a table's
column.
UNIQUE
Constraint
- Disallows duplicate values in a
column or set of columns.
PRIMARY
KEY
Constraint - Disallows duplicate values and
NULLs in a column or set of columns.
FOREIGN KEY
Constrain - Require each value in a column
or set of columns match a value in a related table's UNIQUE
or PRIMARY KEY.
CHECK
Constraint
- Disallows values that do not
satisfy the logical expression of the constraint.
What is difference between UNIQUE constraint and PRIMARY
KEY constraint?
A column defined as
UNIQUE can contain NULLs while a
column defined as PRIMARY KEY can't contain Nulls.
What are the Limitations of a CHECK Constraint ?
The
condition
must
be a Boolean expression evaluated
using the values in the row being inserted or updated and
can't contain subqueries, sequence, the SYSDATE,UID,USER
or USERENV SQL functions, or the pseudo columns LEVEL or
ROWNUM.
What is the maximum number of CHECK constraints that can
be defined on a column ?
No Limit.
Q What is an Index ?
An Index is an optional structure associated with a table
to have direct access to rows, which can be created to
increase the performance of data retrieval. Index can be
created on one or more columns of a table.
Indexes are automatically maintained and used by ORACLE.
Changes to table data are automatically incorporated into
all relevant indexes.
Indexes
Index will improve the throughput of the SQL Query.
The Index should be created based on the frequently
used columns in the WHERE clause.
CREATE INDEX emp_idx ON emp(emp_name);
SELECT ename,dept_id,sal,mgr
FROM
EMP
WHERE ename like ‘Sun%’;
Q What is the Subquery ?
A Subquery is a query whose return values are used in
filtering conditions of the main query.
Q. What is correlated sub-query ?
A Correlated sub_query is a sub_query which has reference
to the main query.
Q. What is an Integrity Constraint ?
A
Integrity constraint is a rule
values to a column in a table.
that
restricts
Q. What is Referential Integrity ?
A
Maintaining data integrity through a set of rules that
restrict the values of one or more columns of the tables
based on the values of primary key or unique key of the
referenced table.
Q. what is Case Function
Case facilitates conditional inquires by doing the work of
an if-then-else statement
CASE TATEMENT
In SQL case works with either the select or update clauses.
It provides when-then-else functionality (WHEN this_happens
THEN do_this) also known as nested IF-THEN-ELSE - IF
conditional statements
SELECT ename,
CASE WHEN sal > 0 AND SAL <= 100000 THEN 1
WHEN sal > 100000 AND SAL < 250000 THEN 2
WHEN sal > 250000 AND SAL < 5000000 THEN 3
ELSE 99
END AS emp_category
FROM EMP
Q. Decode function
Decode : facilitates conditional inquires by doing the work
of a case or if then else statement
SELECT supplier_name,
decode(supplier_id, 10000, 'IBM',
10001, 'Microsoft',
10002, 'Hewlett Packard',
'Gateway') result
FROM suppliers;
Q. How you will avoid duplicating records in a query?
A By using DISTINCT
Q. What is difference between Rename and Alias?
Rename is a permanent name given to a table or column
whereas Alias is a temporary name given to a table or
column which do not exist once the SQL statement is
executed.
Q. What is a view ?
A view is a virtual table based on one or more tables.
Why Use views ?
To restrict data access
• To make complex queries easy
• To provide data independence
• To present different views of the same data
Q. What are the advantages of Views ?
• Views restrict access to the data because the view can
display selective columns from the table.
• Views can be used to make simple queries to retrieve the
results of complicated queries. For example, views can be
used to query information from multiple tables without the
user knowing how to write a join statement.
• Views provide data independence for ad hoc users and
application programs. One view can be used to retrieve data
from several tables.
• Views provide groups of users access to data according to
their particular criteria.
Provide an additional level of table security, by
restricting access to a predetermined set of rows and
columns of a table.
Hide data complexity.
Simplify commands for the user.
Present the data in a different perpecetive from that of
the base table.
Store complex queries.
Q. What are various privileges that a user can grant to
another user?
SELECT
CONNECT
RESOURCES
Q. What is schema?
A schema is collection of database objects of a User.
Q. what is Table ?
A table is the basic unit of data storage in an ORACLE
database. The tables of a database hold all of the user
accessible data. Table data is stored in rows and columns.
Q. Do View contain Data?
Views do not contain or store data.
Q. Can a View based on another View ?
Yes.
Q. What is a Sequence ?
A sequence generates a serial list of unique numbers for
numerical columns of a database's tables.
Q. What is a Synonym ?
A synonym is an alias for a table, view, sequence or
program unit.
There are two types of Synonyms Private and Public.
A Private Synonyms can be accessed only by the owner.
A Public synonyms can be accessed by any user on the
database.
Synonyms are used to : Mask the real name and owner of an
object.
Provide public access to an object
Provide location transparency for tables,views or program
units of a remote database.
Simplify the SQL statements for database users.
Q. What is difference between TRUNCATE & DELETE ?
TRUNCATE commits after deleting entire table i.e., can not
be rolled back. Database triggers do not fire on TRUNCATE
DELETE allows the filtered deletion. Deleted records can
be rolled back or committed.
Database triggers fire on DELETE.
Advantages of COMMIT and ROLLBACK Statements
With COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements, you can:
• Ensure data consistency
• Preview data changes before making changes permanent
• Group logically related operations
Q. Difference between SUBSTR and INSTR ?
INSTR (String1,String2(n,(m)),
INSTR returns the position of the mth occurrence of
the string 2 in
string1. The search begins from nth position of string1.
SUBSTR (String1 n,m)
SUBSTR returns a character string of size m in string1,
starting from nth postion of string1.
Q. Explain UNION, MINUS, UNION ALL, INTERSECT ?
INTERSECT returns all distinct rows selected by both
queries.
MINUS - returns all distinct rows selected by the first
query but not by the second.
UNION - returns all distinct rows selected by either query
UNION ALL - returns all rows selected by either
query, including all duplicates.
Union
The union clause places two separate queries together
forming one table. A union works best when using two
tables with similar columns because each column must
have the same data type
SELECT dno FROM emp
UNION
SELECT dno FROM dept;
UNION ALL selects all rows from each table and
combines them into a single table
The Difference between UNION and UNION
The difference between Union and Union
Union all will not eliminate duplicate
it just pulls all rows from all tables
query specifics and combines them into
Q. What is ROWID ?
ALL,
all is that
rows, instead
fitting your
a table
ROWID is a pseudo column attached to each row of a
table. It is 18 character long, blockno, rownumber are the
components of ROWID.
Q. What is the fastest way of accessing a row in a table ?
Using ROWID.
Q. What is difference between CHAR and VARCHAR2 ? ,
What is the maximum SIZE allowed for each type ?
CHAR pads blank spaces to the maximum length. VARCHAR2
does not pad blank spaces. For CHAR it is 255 and 2000 for
VARCHAR2.
Q.
How many LONG columns are allowed in a table ? Is it
possible to use LONG columns in WHERE clause or ORDER BY ?
A
Only one LONG columns is allowed. It is not possible
to use LONG column in WHERE or ORDER BY clause.
Q. What is
Database Link ?
A database link is a named object that describes a "path"
from one database to another.
Private Database Link, Public Database Link & Network
Database Link.
Private database link is created on behalf of a specific
user. A private database link can be used only when
the owner of the link specifies a global object name in a
SQL statement or in the definition of the owner's views or
procedures.
Public database link is created for the special user group
PUBLIC. A public database link can be used when any
user in the associated database specifies a global object
name in a SQL statement or object definition.
Network database link is created and managed by a network
domain service. A network database link can be used
when any user of any database in the network specifies a
global object name in a SQL statement or object
definition.
Q. Which is more faster - IN or EXISTS?
EXISTS is more faster than IN because EXISTS returns a
Boolean value whereas IN returns a value.
Q. What is a join?
A. Join is a process of retrieve pieces of data from
different sets (tables) and returns them to the user or
program as one “joined― collection of data.
Join & Union
JOIN
The join clause combines columns of one table to
that of another to create a single table
A join query does not alter either table, but
temporarily combines data from each table to be
viewed as a single table
3 different types of Join
Inner
Left
Right
Inner join
An inner join returns all rows that result in a match
such as the example above.
SELECT a.ename,b.dname,e.sal,e.mgr
FROM
emp a,
dept b
WHERE a.dno = b.dno
Types of Joins
• Equijoins
• Non-equijoins
• Outer joins
• Self joins
• Cross joins
• Natural joins
• Full or outer joins
Equijoins
To determine an employee’s department name, you compare the
value in the DEPARTMENT_ID
column in the EMPLOYEES table with the DEPARTMENT_ID values
in the DEPARTMENTS table. The relationship between the
EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables is an equijoin—that is,
values in the DEPARTMENT_ID column on both tables must be
equal. Frequently, this type of join involves primary and
foreign key complements.
Note: Equijoins are also called simple joins or inner
joins.
Non-Equijoins
A non-equijoin is a join condition containing something
other than an equality operator.
The relationship between the EMPLOYEES table and the
JOB_GRADES table has an
example of a non-equijoin. A relationship between the two
tables is that the SALARY
column in the EMPLOYEES table must be between the values in
the LOWEST_SALARY
and HIGHEST_SALARY columns of the JOB_GRADES table. The
relationship is
obtained using an operator other than equals (=).
SELECT e.last_name, e.salary, j.grade_level
FROM employees e, job_grades j
WHERE e.salary
BETWEEN j.lowest_sal AND j.highest_sal;
Outer join : to also see rows that do not meet the join
condition
Returning Records with No Direct Match with Outer Joins
If a row does not satisfy a join condition, the row will
not appear in the query result. For example, in the
equijoin condition of EMPLOYEES and DEPARTMENTS tables,
employee Grant does not appear because there is no
department ID recorded for her in the EMPLOYEES table.
Instead of seeing 20 employees in the result set, you see
19 records.
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id = d.department_id;
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE e.department_id(+) = d.department_id ;
Self Join :
Joining a Table to Itself
Sometimes you need to join a table to itself. To find the
name of each employee’s manager, you need to join the
EMPLOYEES table to itself, or perform a self join. For
example, to find the name of Whalen’s manager, you need to:
• Find Whalen in the EMPLOYEES table by looking at the
LAST_NAME column.
• Find the manager number for Whalen by looking at the
MANAGER_ID column. Whalen’s manager number is 101.
• Find the name of the manager with EMPLOYEE_ID 101 by
looking at the LAST_NAME column. Kochhar’s employee number
is 101, so Kochhar is Whalen’s manager.In this process, you
look in the table twice. The first time you look in the
table to find Whalen in the LAST_NAME column and MANAGER_ID
value of 101. The second time you look in the EMPLOYEE_ID
column to find 101 and the LAST_NAME column to find
Kochhar.
SELECT worker.last_name || ’ works for ’
|| manager.last_name
FROM employees worker, employees manager
WHERE worker.manager_id = manager.employee_id ;
Left Outer Join :
This query retrieves all rows in the EMPLOYEES table, which
is the left table even if there is no match in the
DEPARTMENTS table.This query was completed in earlier
releases as follows:
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE d.department_id (+) = e.department_id;
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e
LEFT OUTER JOIN departments d
ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) ;
Left Outer Join Syntax
A Left join returns all rows of the left of the conditional
even if there is no right column to match
SELECT
a.eno, a.ename,d.dname
FROM emp a LEFT OUTER JOIN dept b
ON
a.dno = b.dno;
Right Outer Join :
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e
RIGHT OUTER JOIN departments d
ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) ;
Example of RIGHT OUTER JOIN
This query retrieves all rows in the DEPARTMENTS table,
which is the right table even if there is no match in the
EMPLOYEES table.
This query was completed in earlier releases as follows:
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e, departments d
WHERE d.department_id = e.department_id (+);
Right
Outer Join
A Right join returns all rows of the Right of the
conditional even if there is no right column to match
SELECT
a.eno, a.ename,b.dno,b.dname
FROM emp a RIGHT OUTER JOIN dept b
ON
a.dno = b.dno;
Full outer join
SELECT e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
FROM employees e
FULL OUTER JOIN departments d
ON (e.department_id = d.department_id) ;
Example of FULL OUTER JOIN
This query retrieves all rows in the EMPLOYEES table, even
if there is no match in the
DEPARTMENTS table. It also retrieves all rows in the
DEPARTMENTS table, even if there is no match in the
EMPLOYEES table.
Cartesian Products
A Cartesian product results in all combinations of rows
displayed. This is done by either omitting the WHERE clause
or specifying the CROSS JOIN clause.
Table Aliases
• Table aliases speed up database access.
• Table aliases can help to keep SQL code smaller, by
conserving memory.
Q. What kinds of joins do you know? Give examples.
A. We have self join, outer joint (LEFT, RIGHT), , crossjoin ( Cartesian product n*m rows returned)
Exp:
outer joint
SELECT Employee.Name, Department. DeptName
FROM Employee, Department
WHERE Employee.Employee_ID = Department.Employee_ID;
cross-join
SELECT * FROM table1, table2;
self join
SELECT e1.name | |’
‘ | | e2.ename FROM emp e1, emp
e2 WHERE e1. emp_no = e2.emp_no;
Q. How do you add record to a table?
A. INSERT into table_name VALUES (‘ALEX’ , 33 ,
‘M’);
Q. How do you add a column to a table?
A. ALTER TABLE Department ADD (AGE, NUMBER);
Q. How do you change value of the field?
A. UPDATE EMP_table
‘CD’;
set
number = 200 where item_munber =
update name_table set status = 'enable'
'4161112222';
where phone =
update SERVICE_table set REQUEST_DATE = to_date ('2006-0304 09:29', 'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:MI') where phone =
'4161112222';
What does COMMIT do ?
COMMIT makes permanent the changes resulting from all SQL
statements in the transaction. The changes made by the SQL
statements of a transaction become visible
to
other
user
sessions
transactions
that
start
only
after
transaction is committed.
What does ROLLBACK do ?
ROLLBACK
retracts
any of the changes resulting from the
SQL statements in the transaction
Q. What is the highest value that can be stored in a BYTE
data field?
A. The highest value that can be stored in a BYTE field is
255. or from -128 to 127. Byte is a set of Bits that
represent a single character. Usually there are 8 Bits in a
Byte, sometimes more, depending on how the measurement is
being made. Each Char requires one byte of memory and can
have a value from 0 to 255 (or 0 to 11111111 in binary).
What is a Procedure ?
A Procedure consist of a set of SQL and PL/SQL statements
that are grouped together
as a unit to solve a specific
problem or perform a set of related tasks.
Q. What is a stored procedure?
A. A procedure is a group of PL/SQL statements that can be
called by a name. Procedures do not return values they
perform tasks.
Q. Describe how NULLs work in SQL?
A. The NULL is how SQL handles missing values.
Arifthmetic operation with NULL in SQL will return a
NULL.
What is a SNAPSHOT ?
Snapshots are read-only copies of a master table located
on a remote node which
is
periodically
refreshed
to
reflect changes made to the master table.
135. What is a SNAPSHOT LOG ?
A snapshot log is a table in the master database that is
associated with the master table. ORACLE uses a snapshot
log to track the rows that have been
updated
in
the
master table. Snapshot logs are used in updating the
snapshots based on the master table.
Q. What is Normalization?
A. The process of table design is called normalization.
Q. What is referential integrity constraints?
A. Referential integrity constraints are rules
that are partnof the table in a database schema.
What is Database Trigger ?
A Database Trigger is procedure (set of SQL
and PL/SQL
statements) that is automatically executed as a result
of an insert in,update to, or delete from a table.
Q. What are the uses of Database Trigger ?
Database
triggers
can
be
used
to automatic data
generation, audit data modifications, enforce complex
Integrity constraints, and customize complex security
authorizations.
Q. What are the differences between Database Trigger
and Integrity constraints ?
A
declarative
integrity constraint is a statement about
the database that is always true. A constraint applies to
existing data in the table and any statement that
manipulates the table.
A trigger does not apply to data loaded before the
definition of the trigger,
therefore,
it does not
guarantee all data in a table conforms to the rules
established by an associated trigger.
A
trigger
can
constraints where
cannot be used.
be
used
to
enforce
transitional
as a declarative integrity constraint
Q. Which of the following WHERE clauses will return only
rows
that have a NULL in the PerDiemExpenses column?
A.
WHERE PerDiemExpenses <>
B.
WHERE PerDiemExpenses IS NULL
C.
WHERE PerDiemExpenses = NULL
D.
WHERE PerDiemExpenses NOT IN (*)
A. B is correct � When searching for a NULL value
in a column, you must
use the keyword IS. No quotes are required around the
keyword NULL.
Q. You issue the following query:
SELECT FirstName FROM StaffList
WHERE FirstName LIKE'_A%'
Which names would be returned by this query? Choose all
that apply.
A.
Allen
B.
CLARK
C.
JACKSON
D.
David
A. C is correct � Two wildcards are used with the
LIKE operator.
The underscore (_) stands for any one character of any
case, and the percent sign (%) stands for any number of
characters of any case including none. Because this string
starts with an underscore rather than a percent sign, it
won't
return Allen or Clark because they represent zero and two
characters before the "A". If the LIKE string had been
"%A%",
both of these values would have been returned.
David was not returned because all non-wild card characters
are case sensitive. Therefore, only strings
with an uppercase "A" as their second letter are returned
Q. Write a SQL SELECT query that only returns each city
only once from Students table?
Do you need to order this list with an ORDER BY clause?
A. SELECT DISTINCT City FROM Students;
The Distinct keyword automatically sorts all data
in ascending order. However, if you want the data
sorted in descending order, you have to use an ORDER BY
clause
Q. Write a SQL SELECT sample of the concatenation operator.
A.
SELECT LastName ||',' || FirstName, City FROM Students;
Q. How to rename column in the SQL SELECT query?
A.
SELECT LastName ||',' || FirstName
AS "Student Name", City AS "Home City"
"FROM StudentsORDER BY "Student Name"
Q. Write SQL SELECT example how you limiting the rows
returned with a WHERE clause.
A. SELECT InstructorID, Salary FROM Instructors
WHERE Salary > 5400 AND Salary < 6600;
Q. Write SQL SELECT query that returns the first and
last name of each instructor, the Salary,
and gives each of them a number.
A. SELECT FirstName, LastName, Salary, ROWNUM FROM
Instructors;
Q. Which of the following functions can be used only with
numeric values?
(Choose all that apply.)
A.
AVG
B.
MIN
C.
LENGTH
D.
SUM
E.
ROUND
A. A and D � Only A and D are correct. The MIN
function
works with any character, numeric, or date datatype.
The LENGTH function is a character function that returns
the number of letters in a character value. The ROUND
function works with both numeric and date values.
Q. Which function do you use to remove all padded
characters
to the right of a character value in a column with a char
datatype?
A.
RTRIM
B.
RPAD
C.
TRIM
A. C � The TRIM function is used to remove padded
spaces.
LTRIM and RTRIM functions were included in earlier versions
of Oracle, but Oracle 8i has replaced them with a single
TRIM function
Q. Which statement do you use to eliminate padded spaces
between the month and day values in a function
TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'Month, DD, YYYY') ?
A. To remove padded spaces, you use the "fm"
prefix before the date element that contains the spaces.
TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,'fmMonth DD, YYYY')
Q. Is the WHERE clause must appear always before the GROUP
BY clause in SQL SELECT ?
A. Yes.
The proper order for SQL SELECT
clauses is: SELECT, FROM, WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING, ORDER
BY.
Only the SELECT and FROM clause are mandatory.
Q. How Oracle executes a statement with nested subqueries?
A. When Oracle executes a statement with nested subqueries,
it always executes the innermost query first. This query
passes its results to the next query and so on until it
reaches the outermost query. It is the outermost query that
returns a result set.
Q. Which operator do you use to return all of the rows
from one query except rows are returned in a second query?
A. You use the MINUS operator to return all rows from one
query except where duplicate rows are found in a second
query. The UNION operator returns all rows from both
queries minus duplicates. The UNION ALL operator returns
all rows from both queries including duplicates. The
INTERSECT operator returns only those rows that exist in
both queries.
Q. Which of the following statements are Data Manipulation
Language commands?
A.
INSERT
B.
UPDATE
C.
GRANT
D.
TRUNCATE
E.
CREATE
A. A and B � The INSERT and UPDATE statements are
Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands.
GRANT is a Data Control Language (DCL) command.
TRUNCATE and CREATE are Data Definition Language (DDL)
commands
Q. What is Oracle locking?
A. Oracle uses locking mechanisms to protect data from
being destroyed by concurrent transactions.
Q. What Oracle lock modes do you know?
A. Oracle has two lock modes: shared or exclusive.
Shared locks are set on database resources so that many
transactions can access the resource. Exclusive locks are
set on resources that ensure one transaction has exclusive
access to the database resource
Q. What is query optimization?
A. Query optimization is the part of the query process in
which the database system compares different query
strategies and chooses the one with the least expected cost
Q. What is transaction?
A. A transaction is a collection of applications
code and database manipulation code bound into an
indivisible unit of execution.it consists from:
BEGIN-TRANSACTION Name Code END TRANSACTION Name
Q. What databases do you know?
Informix
DB2
SQL
Oracle
Q. Explain SQL SELECT example:
select j.FILE_NUM from DB_name.job j, DB_name.address a
where j.JOB_TYPE ='C'
AND j.COMPANY_NAME = 'TEST6'
AND j.OFFICE_ID = '101'
AND j.ACTIVE_IND = 'Y'
AND a.ADDRESS_STATUS_ID = 'H'
AND a.OFFICE_ID = '101'
AND a.FILE_NUM = j.FILE_NUM
order by j.FILE_NUM;
Answer: j and a aliases for table names. this is outer
joint select statament from two tables.
Q. Describe some Conversion Functions that you know
A. TO_CHAR converts a number / date to a string.
TO_DATE converts a string (representing a date) to
a date.
TO_NUMBER converts a character string containing
digits to a numeric data type, it accepts one parameter
which is a column value or a string literal
Q. In what sequence SQL statement are processed?
A. The clauses of the subselect are processed in the
following sequence (DB2):
1. FROM clause
2. WHERE clause
3. GROUP BY clause
4. HAVING clause
5. SELECT clause
6. ORDER BY clause
7. FETCH FIRST clause
Q. What is a pseudo column. Give some examples?
It is a column that is not an actual column in the table.
Eaxmple USER, UID, SYSDATE, ROWNUM, ROWID, NULL, AND LEVEL.
Q. Suppose a customer table is having different columns
like customer no, payments.
What will be the query to select top three max payments?
SELECT customer_no, payments from customer C1
WHERE 3<=(SELECT COUNT(*) from customer C2 WHERE C1.payment
<= C2.payment)
Q. Find out nth highest salary from emp table
SELECT DISTINCT (a.sal) FROM EMP A
WHERE &N = (SELECT COUNT (DISTINCT (b.sal)) FROM EMP B
WHERE a.sal<=b.sal);
Q. What are the difference between DDL, DML and DCL
commands?
DDL is Data Definition Language statements. Some examples:
CREATE - to create objects in the database
ALTER - alters the structure of the database
DROP - delete objects from the database
TRUNCATE - remove all records from a table, including all
spaces allocated for
the records are removed
COMMENT - add comments to the data dictionary
GRANT - gives user's access privileges to database
REVOKE - withdraw access privileges given with the GRANT
command
DML is Data Manipulation Language statements. Some
examples:
SELECT - retrieve data from the a database
INSERT - insert data into a table
UPDATE - updates existing data within a table
DELETE - deletes all records from a table, the space for
the records remain
CALL - call a PL/SQL or Java subprogram
EXPLAIN PLAN - explain access path to data
LOCK TABLE - control concurrency
DCL is Data Control Language statements. Some examples:
COMMIT - save work done
SAVEPOINT - identify a point in a transaction to which
you can later roll back
ROLLBACK - restore database to original since the last
COMMIT
SET TRANSACTION - Change transaction options like what
rollback segment to use
Can we drop a column from a table?
yes. ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;
Q.
Describe some Group Functions that you know
A. 1) The COUNT function tells you how many rows were in
the result set.
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM TESTING.QA
2) The AVG function tells you the average value of a
numeric column.
SELECT MAX(SALARY) FROM TESTING.QA
3) The MAX and MIN functions tell you the maximum and
minimum value of a numeric column.
SELECT MIN(SALARY) FROM TESTING.QA
4) The SUM function tells you the sum value of a
numeric column.
SELECT SUM(SALARY) FROM TESTING.QA
Group functions: Group functions operate on sets of rows to
give one result per group
Count function : COUNT(*) returns the number of rows in a
table.
SELECT COUNT(*)FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 50;
Having clause
If you restrict rows based on the result of a group
function, you must have a GROUP BY clause as well as the
HAVING clause.
SELECT department_id, MAX(salary)
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id
HAVING MAX(salary)>10000 ;
Query Syntax
Write a query to display the name, who is getting the max
salary from EMP table
SELECT ename FROM EMP
WHERE sal=(SELECT MAX(sal) FROM EMP)
Select ename, max( sal) from emp ( Wrong)
Write a query to display the employee name and respective
manager name in the Emp table
SELECT a.ename, b.ename FROM EMP a , EMP b
WHERE a.MGR= b.EMPNO
Write a query to display the employee name and respective
manager name in the Emp table including the manager is null
SELECT a.ename ||' is working under '||b.ename
FROM EMP a,EMP b
WHERE a.mgr=b.empno
UNION
SELECT 'There is no manager to '||ename FROM EMP
WHERE mgr IS NULL
Write a query to sum all the positive and negative values
in the column
Table name tab1
COL1
1
2
-1
-2
1)To get 2,3,N maximum salaries with complete row
select * from emp where sal=(select min(sal) from(
select * from (select * from emp order by sal desc) where
rownum<=2))
(Replace 2 with the desired Number)
2) To get 2 Max Salary with complete row
select * from emp where sal=
(select max(sal) mx from emp where
from emp))
(Sal) <(select max(sal)
4)To Get Top N rows
select * from (select * from emp order by sal desc) where
rownum<=5))
(replace 5 with the desired Number)
5)To Get Nth Row
select * from emp where 7=(Select count(Rowid) from emp x
where
emp.rowid>=x.rowid)
(Replace 7 with the Desired Number)
6)To Get Employees whose salary is greater the the avg
salary of dept
select empno,emp.deptno,sal,a.av from emp,
(select Deptno,avg(sal) av from emp group by deptno) a
where a.deptno=emp.deptno and emp.sal>a.av
Other way
SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SAL>(sELECT AVG(SAL) FROM EMP X
WHERE
X.DEPTNO=EMP.DEPTNO) ORDER BY EMPNO
7)Deletion of Duplicate Records
Delete from emp where rowid in(select min(rowid) from emp x
where
x.rowid=emp.rowid)
--Select Case Example
select ename,sal, case when sal between 500 and 1000 then
'D'
when sal between 1001 and 1500 then 'C'
when sal between 1501 and 2500 then 'B'
else 'A' end Rank from emp ,salgrade where
emp.sal between losal and hisal
--Rows from emp and Salgrade tables
select ename,sal,grade from emp,salgrade where
emp.sal between losal and hisal
--Use of Rank to Retervie top rows
select e.*,rank() over(order by sal desc)rank from
emp e where rownum<=5
Q. Describe TO_DATE function.
A. The TO_DATE function returns a timestamp from a
character string that has been interpreted using a
character template.TO_DATE is a synonym for
TIMESTAMP_FORMAT.
Write a syntax for To_Date function
To_date('2003/07/09', 'yyyy/mm/dd') would return a date
value of July 9, 2003.
To_date('070903', 'MMDDYY') would return a date value of
July 9, 2003.
To_date('20020315', 'yyyymmdd') would return a date value
of Mar 15, 2002.
SELECT TO_DATE('January 15','MONTH DD') "Sample" FROM DUAL