American Government EOC Study Guide
advertisement
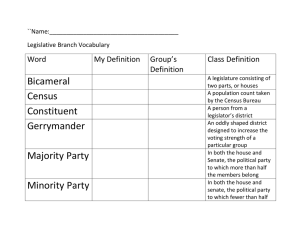
1 American Government 12A EOC Study Guide American Government: Origin & Structure (who, what, where, when, how, why) The definition, role and purpose of government Origins of democracy and republic. Difference between a democracy and a republic. England’s Influence on American Government Essential ideals and objectives of: the Magna Carta, the Declaration of Independence, the Articles of Confederation, the Bill of Rights, the Constitution The difference between presidential and parliamentary systems of government and between unitary or federal geographic distribution of power How John Locke’s natural rights philosophy influenced the formation of government; belief that government should serve the people The six purposes of government as stated in the Preamble to the Constitution. Why the Articles of Confederation failed The Virginia and New Jersey plans, leading to the Great Compromise/ Connecticut Compromise The basic outline of the Constitution and the amendment process Dictatorships and Democracies differ in the number of people allowed to participate in government Constitutional principles of separation of powers, checks and balances, limited government, federalism and popular sovereignty Common philosophy on government of John Locke (natural rights ), Thomas Hobbes, and Jean Jacques Rousseau Clauses in Constitution: Supremacy Clause, Necessary and Proper Clause Election Politics: who, what, where, when, how, why The factors that influence public opinion and voting (media, bias, propaganda, lobbyists, special interest groups, demographics, incumbent v. challenger) The various individual and organizations that contribute to campaigns and the impact of those contributions (PACs, FEC, political parties) The impact of redistricting and reapportionment on elections The role of political parties in elections; purpose of national convention The major political parties and an overview of their platforms The purpose of minor parties How to use a political spectrum in identifying political issues and individual beliefs Define suffrage and know the critical suffrage amendments and voting rights acts (Specific Amendments: 15,19,24,26, and the 1965 Voting Rights Act) Voter qualifications and state’s impact on them Primaries & Caucuses (main purpose of them) Requirements for elections (date of federal election & precinct & polling places) Constitutional requirements of candidates (age, residency, citizenship) Electoral College Revised October 2013 2 The Legislative Branch: who, what, where, when, how, why The legislative branch makes law. Congress is a bicameral legislature that is made up of a Senate and House of Representatives. The U.S. Constitution authorizes and limits congressional power A senator serves a six year term and a representative serves a two year term The Senate is made up of two members of each state The number of representatives in the House of Representatives Idaho’s Congressional districts and effect of the census The leadership of the Senate consists of president, president pro tempore, majority leaders, minority leaders, and committee chairs The House leadership consists of the Speaker of the House, the majority leader, the minority leaders and committee chairs The Speaker of the House is chosen by the majority party. The Speaker is the most powerful position in Congress. Reapportionment is the process of redrawing congressional districts to voters account for population changes among states. Redistricting??? The process by which a bill becomes a law: o Introduced by a member o Assigned/Debated/Amended in committee o Debated/Amended on floor o Process repeated in Senate/House o Conference Committee (if needed) o President can sign, veto, pocket veto, no action o If vetoed, Congress can override with 2/3 vote The three types of powers are: expressed, implied and inherent Congress divides into committees to manage the workload of lawmaking (standing, joint, select, special, conference) The role of lobbyists Know the following terms: seniority rule, quorum, patronage, partisanship, constituency, filibuster, cloture, precinct, politico, trustee, delegate and personal interests. Revised October 2013