THE URINARY SYSTEM
advertisement
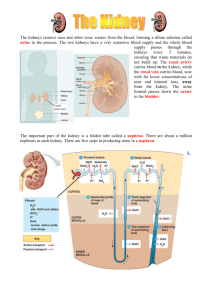
THE URINARY SYSTEM FORM AND FUNCTION COMPONENTS 2 Kidneys 2 ureters 1 urinary bladder 1 urethra FUNCTIONS: Excretion and filtration Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of blood solutes Regulation of pH Regulation of Red Blood Cell synthesis Vitamin D synthesis Regulation of blood cell synthesis Production of Erythropoietin (a glycoprotein hormone) by the kidneys controls manufacture of new RBC’s EPO is banned from use by professional athletes The kidneys and Vitamin D The skin synthesizes inactive Vitamin D and the kidneys convert it to the active form. KIDNEY STRUCTURE Kidneys are fist sized organs They are located on the posterior abdominal wall on either side of the vertebral column THE NEPHRON Each kidney is composed of millions of microscopic filtering units known as nephrons The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, doing all of the actual work INTERNAL STRUCTURE NEPHRON STRUCTURE FILTRATION 21% of blood pumped by the heart each minute flows through the kidneys 19% of the blood plasma that flows through the capillary bed of the glomerulus passes through the filtration membrane into Bowman’s Capsule, the first part of the nephron. The liquid is called the filtrate. What is in the filtrate? The filtrate should contain water, salts, glucose, amino acids, wastes such as urea, vitamins, minerals, drug metabolites, and ions (H+, Na+, and K+) Bowman’s Capsule FILTRATION Glomerulus The filtrate should not contain blood cells, proteins, or glucose (after initial rebsorbtion). REABSORPTION 180 liters of filtrate are produced daily! Plasma volume is only 3 liters so how many times daily is the entire plasma volume filtered? 60 times! Only 1-2 L of urine are produced daily Almost all of the water and useful solutes are reabsorbed THE PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE Absorbs 65% of water and NaCl that passes through The Na+/K+ pump transports ions from the filtrate into the tubule cells (simple cuboidal epithelium) Important substances such as amino acids, glucose, vitamins, and minerals are reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries MORE REABSORPTION The descending Loop of Henle concentrates the filtrate by removing water through osmosis This reduces the filtrate volume by another 15% Urea is removed by facilitated diffusion In the acsending loop, the Na+/K+ pump moves Na+ to the interstitial fluid surrounding the loop. Cl- and K+ are moved by symport This part of the loop is impermeable to water, so it cannot follow the ions passively LOOP OF HENLE THE DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE About 80% of water and 90% of solutes have been removed from the filtrate so far Helps regulate pH by controlling H+ elimination and retention. Works with PTH to reabsorb Ca2+ ions Further water reabsorption is under hormonal control ADH- Anti-diuretic Hormone causes water to leave the filtrate and enter the tubule cells When do you need ADH? Not a vampire Vampire Sleeping Dehydration Sudden blood loss (aka, hypovolemic shock NITROGENOUS WASTE The metabolism of proteins produces nitrogen-based waste products such as ammonia and urea These two substances can be toxic if they remain in the body. The kidneys remove them in the distal convoluted tubule THE COLLECTING DUCT SYSTEM It is controlled by hormones like ADH and Aldosterone The cells are impermeable to water, so any water in the filtrate remains and is excreted with other wastes as urine The Collecting Duct What if your kidneys are not working? DIALYSIS TREATMENT The Kidneys at Work http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aQZaNXNroV Y&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glu0dzK4dbU