AH Statistics – Education Scotland – March 2015
advertisement

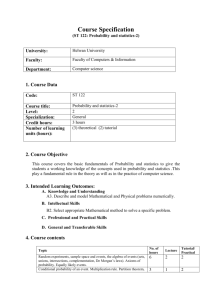
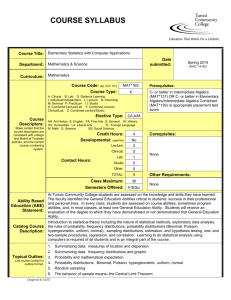
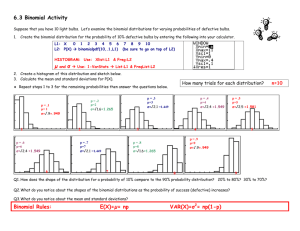
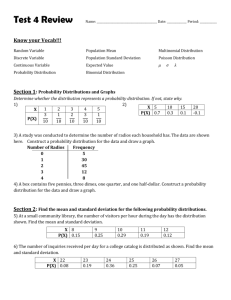
Course: Statistics Level: Advanced Higher March 2015 This advice and guidance has been produced for teachers and other staff who provide learning, teaching and support as learners work towards qualifications. These materials have been designed to assist teachers and others with the delivery of programmes of learning within the new qualifications framework. These support materials, which are neither prescriptive nor exhaustive, provide suggestions on approaches to teaching and learning which will promote development of the necessary knowledge, understanding and skills. Staff are encouraged to draw on these materials, and existing materials, to develop their own programmes of learning which are appropriate to the needs of learners within their own context. Staff should also refer to the course and unit specifications and support notes which have been issued by the Scottish Qualifications Authority. http://www.sqa.org.uk Acknowledgement © Crown copyright 2015. You may re-use this information (excluding logos) free of charge in any format or medium, under the terms of the Open Government Licence. To view this licence, visit http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-governmentlicence/ or e-mail: psi@nationalarchives.gsi.gov.uk. Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned. Any enquiries regarding this document/publication should be sent to us at enquiries@educationscotland.gov.uk. This document is also available from our website at www.educationscotland.gov.uk. 2 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 Contents Introduction 4 Resources 8 Additional resources 24 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 3 © Education Scotland 2015 INTRODUCTION Introduction Understanding statistics is an important skill for everyday life, allowing us to make sense of the information around us. It is an essential feature of the modern workplace and is crucial to competitiveness in the global market. The majority of academic subjects rely on knowledge and understanding of data and statistics. The course content includes applying skills in data analysis and modelling, statistical inference and hypothesis testing, and the interpretation of situations involving data collections, probability and sampling. This advice and guidance provides online links to a range of resources, including simulators, games, e-books, case studies, experiments and data sets, to support the learning and teaching of: data analysis and modelling statistical inference hypothesis testing within the context of Advanced Higher Statistics. The resources incorporate opportunities for collaborative and independent learning using a range of real-life situations. Learners will be expected to use statistical reasoning skills to make and explain their decisions within a given relevant context. Assumed prior knowledge, skills and understanding from the National 5 mathematics course are: Comparing data sets using statistics Applications Forming a linear model from a given set of data Applications These are needed to provide a firm foundation for further learning within SCQF level 7. 4 ADVANCED HIGHER MATHEMATICS © Education Scotland 2015 INTRODUCTION Increased emphasis on skills development Advanced Higher Statistics has an increased emphasis on skills development and higher-order thinking skills, which are developed through the selection and application of operational skills in: data presentation and interpretation probability theory discrete random variables probability distributions sampling and central limit theorem intervals and estimation bivariate analysis and tests parametric and non-parametric tests to a variety of statistical and real-life situations. Learning and teaching approaches should provide opportunities to build progressively through these higher-order thinking skills: Image courtesy of Me and My Laptop blog ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 5 © Education Scotland 2015 INTRODUCTION Active learning Learners will be expected to take an active role in the learning process, extending their reasoning and analytical skills through a range of statistical tasks and activities. Learning activities, linked to their own interests or aspirations, will develop their ability to analyse, evaluate, solve problems and apply learning in other aspects of their lives. Through engaging learning, learners should experience tasks and activities that require them to analyse and justify decisions, explain their thinking and synthesise aspects of their existing skills. When learners are increasingly active in their learning, they think deeply about statistical ideas and concepts, and construct their own understanding about them. They use existing skills and knowledge in different contexts, test out their ideas and solve problems. Independence, responsibility and collaboration Learners undertaking Advanced Higher Statistics will continue to develop as independent learners either working on their own or in groups. They can develop confidence and self-motivation through activities that offer a choice of approaches and resources, and which encourage them to be self-reliant. This could nurture their leadership skills and promote responsibility and team working – essential skills for learning, life and work. Learners should be expected to take responsibility for, and plan, their own learning based on an understanding of how best they themselves learn. Opportunities for personalisation and choice will enable learners to show what they can do. This will promote motivation and ensure individuals are challenged appropriately. Collaborative learning challenges learners to think independently and engage in discussion, debate and activity to achieve specific outcomes. For example, collaborative approaches will support learners to develop confidence in the application of hypothesis tests and the use of statistical language to explore statistical ideas. In planning activities, staff should provide opportunities for learners to collaborate more widely with others. This is a key change that recognises that learning takes place both within and beyond the classroom. Working with business partners provides the relevant and real-life contexts and situations that promote investigative and problem-solving approaches. 6 ADVANCED HIGHER MATHEMATICS © Education Scotland 2015 INTRODUCTION Areas of change and points of stability Advanced Higher Statistics is now a course in its own right, rather than part of Advanced Higher Mathematics. Two-sample t-tests have been introduced as new content to this course. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 7 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Resources SQA Statistical Formulae and Tables booklet, for use in NQ examinations http://www.sqa.org.uk/files_ccc/2004_Applied_Maths_Stats_and_Tables.pdf Unit Resources Data Analysis and Modelling Applying skills to data presentation and interpretation Undertaking the exploratory data analysis of univariate data 8 http://www.statgraphics.com/eda.htm Data presentation – examples include stem and leaf diagrams, boxplots and scattergraphs. http://www.abs.gov.au/websitedbs/a3121120.nsf/home/statistical+language+-+census+and+sample Animation explains the concept of census and sample. Information on when to use a census and sample and on selecting samples. http://surfstat.anu.edu.au/surfstat-home/cont1.html Summarising and presenting data by topic. Information and explanation, progress check and links to glossary for each topic: types of data, discrete data, continuous data (Java needed for applet), characteristics of a distribution, measure of central tendency (Java needed for applet), measure of variability, normal distribution, two continuous measurements, exploring data in tables. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Data Analysis and Modelling Applying skills to probability theory Working with theoretical and experimental probabilities Calculating conditional probabilities http://www.censusatschool.org.uk/resources/probability/173-too-many-boys Probability of gender at birth. Real data contrasted with theoretical probabilities of family make-up. Can extend to using Bayes’ theorem. http://interactivemaths.net/index.php?q=category/1/75 A selection of probability activities and experiments: Are you a psychic? Cereal box problem, The birthday problem, Stick or switch. Some of these need Java to run applets. Also included are random generators for numbers, coins, dice and playing cards. http://cims.nyu.edu/~kiryl/Elementary%20Statistics/Chapter_6.pdf Some rules of probability – a useful reference for learners. http://www.statlect.com/bayes_rule.htm Bayes’ rule – proof, worked example in a practical context, terminology, examples with solutions. https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/27 Probability and distribution functions information. Useful for revision and support. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch1.pdf Probability – theoretical and empirical – ideas for activities and experiments. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 9 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Data Analysis and Modelling Applying skills to discrete random variables Modelling a discrete random variable Using the laws of expectation and variance http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/plinko-probability ‘Run Now’ and see balls drop randomly through a triangular grid of pegs. Watch the histogram build up and approach the binomial distribution. Balls can be released one at a time or continuously. Encourage discussion on expected distribution as the histogram builds. http://www.mathsrevision.net/advanced-level-maths-revision/statistics/expectation-and-variance Worked example and explanations for expectation and variation. Could be used as an introduction or for independent revision. http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/maths/probability-distributions/revise-it/expectation-and-variance Worked examples and prompts on expectation and variance. Good for revision. http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fairprojects/project_data_analysis_variance_std_deviation.shtml Detailed worked example and explanation of variance and standard deviation. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch1.pdf Continuous probability distributions – worked examples and questions on expectation, mean and variance, and distributions. 10 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Data Analysis and Modelling Applying skills to particular probability distributions http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Distributions.html Interactive distribution applets (Java) which allow the user to vary parameters and visualise the change in shape of the distribution. A snapshot can also be taken and saved as a JPG image. The range of distributions include: binomial – select number of trials and success probability chi-squared – select number of degrees of freedom normal – select mean and standard deviation Poisson – select shift and lambda Student’s t-distribution – select degrees of freedom. http://www.socr.ucla.edu/htmls/SOCR_Experiments.html A selection of interactive simulations and experiments (Java) using a range of distributions, including: binomial coin, binomial timeline, chi-square dice, Poisson, two-dimensional Poisson, uniform estimate, bivariate normal and bivariate uniform. The user can update the frequency and select whether the number of trials is discrete or continuous. The changes can be visualised in graphs and tables. A snapshot can also be taken and saved as a JPG image. http://www.onlinemathlearning.com/statistics.html Section F – More Advanced Statistics – contains a series of statistics lessons which comprise theory and videos. Bayes’ theorem – Laws of probability: addition law, multiplication law and Bayes’ theorem. Two videos introduce Bayes’ theorem (10.02 minutes and 7.24 minutes). ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 11 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Binomial distribution – Video 1 (12.16 minutes) and video 2 (11.05 minutes) introduce the binomial distribution in the context of a flipped coin experiment. Video 3 (13.27 minutes) and video 4 (10.45 minutes) use basketball shots and visualise the distribution using Excel. Video 5 discusses what a binomial experiment is and the formula for finding the probability associated with the experiment, and gives an example to illustrate the concepts. Poisson distribution – Video 1 (11.01 minutes) and video 2 (12.42 minutes) show how to derive the Poisson formula from the binomial formula. Video 3 (5.58 minutes) discusses simulation that can be modelled by a Poisson distribution to give the formula and do a simple example illustrating Poisson distribution, based on customers entering a fast-food restaurant. Using discrete probability distributions http://www.distributome.org/V3/exp/BinomialExperiment.html Binomial distribution interactive experiment. http://www.distributome.org/V3/exp/PoissonExperiment.html Poisson interactive experiment. http://distributome.org/blog/?cat=4 Colourblindness activity (binomial and normal distributions). Homicide trends activity (Poisson distribution). http://www.distributome.org/V3/exp/DiscreteUniformExperiment.html Uniform distribution interactive experiment – discrete. http://www.censusatschool.org.uk/resources/probability/387-secrets-of-the-talent-show Introduction to the binomial distribution, based on a popular talent show. 12 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES http://www.censusatschool.org.uk/resources/probability/176-fillings-what-are-the-chances Use of the Poisson distribution with real-life data on dental health and number of fillings for school children. http://www.distributome.org/V3/exp/ContinuousUniformExperiment.html Continuous uniform distribution interactive experiment. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch6.pdf Poisson distributions – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://www.umass.edu/wsp/resources/poisson/ Poisson distribution – computing probabilities, contextual examples, approximation to binomial, problems with solutions (including the king’s coiner, Ozzie’s risk, the prisoner’s dilemma), tables of numbers (including Pascal’s triangle, factorials, Poisson table). Historical information is also given about statisticians such as Simeon-Denis Poisson, Jacob Bernouilli and Carl Friedrich Gauss. https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/19 Binomial distribution information. Useful for revision and support. http://www.distributome.org/V3/exp/NormalExperiment.html Normal distribution interactive experiment. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch5.pdf (will need to paste url into address bar) Binomial distribution – ideas for activities and examples to try. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 13 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES http://opl.apa.org/contributions/Rice/rvls_sim/main.htm Applets (Java) to simulate experiments and show their distributions. These include: robustness of t-test and ANOVA – simulates t-test/ANOVA with normality and homogeneity of variance assumptions violated normal approximation to the binomial distribution – view binomial distribution and the normal approximation to it as a function of the probability of success on a given trial and the number of trials chi-square test of deviations from expected frequencies – sample from either a uniform or normal distribution; applet does the sampling and tests the significance of deviations repeated measures – investigate differences between correlated and independent t-tests. Using continuous probability distributions https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/20 Normal distribution information. Useful for revision and support. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch7.pdf Continuous probability distributions – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch8.pdf Normal distribution – ideas for activities and examples to try. Using the normal approximation to discrete probability distribution http://simulation-math.com/_ElementaryStatistics/BinomialVSNormal4.cshtml Binomial distribution versus normal distribution – series of comparisons between binomial distribution calculations and normal distribution calculations examples. Link to simulation (top of page) – program designed to run with Firefox or Google Chrome. 14 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Statistical Inference Applying skills to sampling and the central limit theorem http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/res_methd/samp ling/sampling_01.html Research methods workshop resource – sampling strategies and test your knowledge workshop quiz. Identifying and using appropriate random sampling methods http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch2.pdf Data collection – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch9.pdf Estimation – ideas for activities and examples to try. Working with the distribution of sample means http://interactivemaths.net/index.php?q=category/1/76/107 Sampling distributions (Java), applet estimates and plots sampling distributions of various statistics. Sampling pennies (Java) applet shows the difference between the distribution of the members of a dataset and the distribution of sample means. Sampling distribution of the mean simulation shows the consistency of sample means from variously shaped populations. http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/sta nd_error/stand_error_01.html Standard error workshop resource – sampling distribution and standard error of the mean, calculate standard error and test your knowledge workshop quiz. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 15 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/cnt _lim_therm/cnt_lim_therm_01.html Central limit theorem workshop resource – sampling, populations, distributions and test your knowledge workshop quiz. http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/sa mpling_dist/sampling_dist_01.html Sampling distribution workshop resource – samples and hypotheses, hypothesis testing, variance, distributions and test your knowledge workshop quiz. Statistical Inference Applying skills to intervals and estimation Obtaining confidence intervals http://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/MPHModules/BS/BS704_Confidence_Intervals/BS704_Confidence_Intervals_print.html Comprehensive information on confidence intervals taking account of number of groups, outcome variable and parameter. http://www.math.usu.edu/~schneit/CTIS/CI/ Confidence intervals (Java) applet. Estimate the proportion of orange balls in a jar, with questions to consider. https://www.usablestats.com/lessons/SamplesVary Interactive tutorial to introduce confidence intervals. https://explorable.com/statistics-confidence-interval Information on what confidence intervals mean. Useful for an introduction. 16 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES http://www.ditutor.com/inference/confidence_interval.html Information and examples on confidence intervals and critical values. http://www.measuringu.com/blog/ci-10things.php Ten things to know about confidence intervals, including the location and precision of a measure and the width of the confidence interval. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch2.pdf Estimation/confidence intervals – ideas for activities and examples to try. Using control charts http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch8.pdf Statistical process control – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://www.qimacros.com/control-chart/shewhart-control-chart-excel/ Shewhart control charts – creating the seven Shewhart control charts in Excel. Information given on purpose and when to use each of these control charts. http://www.micquality.com/six_sigma_glossary/western_electric.htm Western Electric rules limits displayed graphically. http://www.micquality.com/six_sigma_glossary/control_charts.htm Purpose of control charts with links to the glossary for each of the different types of control charts. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 17 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Statistical Inference Applying skills to bivariate analysis Fitting a linear model to bivariate data Measuring the strength of the linear association between two variables http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/sc atter/scatter_01.html Bivariate scatter plots workshop resource – scatter plots and bivariate plots, correlation coefficient and regression, and test your knowledge workshop quiz. http://geographyfieldwork.com/SpearmansRank.htm Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient – real-life example which looks at the strength of the price of a convenience item (bottle of water) and distance from a museum. Considers the hypothesis, calculating the coefficient and what this value means http://changingminds.org/explanations/research/analysis/pearson.htm Description of Pearson correlation with worked example and what the result indicates. Estimating with bivariate data http://www.uvm.edu/~naguiar/courses/lessons_111/Lecture_10_1.html Correlation and simple linear regression – explanations and examples on scatterplots, Pearson correlation coefficient, regression models and analysis. https://www.ma.utexas.edu/users/mks/statmistakes/CIvsPI.html http://www.physics.csbsju.edu/stats/least_squares.html Least-squares fitting worked example on comparing the diameter of an oak tree with its age. 18 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Hypothesis Testing http://www.zoology.ubc.ca/~whitlock/bio300/lecturenotes/HypothesisTesting/HypothesisTesting.html Introduction to hypothesis testing – explanation of null and alternative hypotheses and using test statistics. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch10.pdf Hypothesis testing – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://www.nuffieldfoundation.org/fsmqs/level-3-hypothesis-testing Hypothesis testing activities: Successful HE applicants – carry out significance tests on proportions to test hypotheses about applicants to higher education. Gender differences – carry out significance tests on means in order to test hypotheses about the body measurements of boys and girls at different ages. Appling skills to parametric tests http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/hy pth_test/hypth_test_01.html Hypothesis testing workshop resource – null and alternative hypotheses, power and statistical errors, and test your knowledge workshop quiz. http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/tes t_means/test_means_01.html Test of means workshop resource – one-sample z-test, one-sample t-test, t-test for dependent and independent means, selecting the appropriate test, and test your knowledge workshop quiz. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 19 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Identifying and applying an appropriate onesample test for the population mean and proportion http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/zs cores/zscores_01.html z-scores workshop resource – data types, examples and big ideas, and test your knowledge workshop quiz. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch3.pdf Hypothesis testing: one-sample t-test, normal, binomial and Poisson populations, population medians – ideas for activities and examples to try. http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/tte st_one/ttest_one_01.html Single sample t-test workshop resource – use the t-test to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis, and test your knowledge workshop quiz. Identifying and applying an appropriate twosample test (independent or paired) for population means or proportions http://www.amstat.org/education/stew/pdfs/AnAmazingComparison.pdf This demonstrates an investigation using the two-sample t-test and can easily be modified for this course. The two-sample t-test is new content. http://www.gla.ac.uk/sums/users/jdbmcdonald/PrePost_TTest/chooset1.html Statistics tutorial on choosing a t-test. Explanation given on when to choose a paired or independent ttest. Test your knowledge of choice of t-test type, tail number and experimental design. http://www.gla.ac.uk/sums/users/jdbmcdonald/PrePost_TTest/pairedt1.html Statistics tutorial on paired t-tests. Explanation given on what a paired t-test does, what it measures and how to use it. Test your knowledge of whether a paired t-test should be used for given scenarios, the most useful average for comparing pairs of values and experiment conclusions. 20 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch4.pdf Hypothesis testing – two-sample tests, normal populations, sign test for paired samples, results of paired samples design – ideas for activities and examples to try. Hypothesis Testing Applying skills to nonparametric tests Identifying and carrying out an appropriate test for population median/s http://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/MPH-Modules/BS/BS704_Nonparametric/BS704_Nonparametric5.html Non-parametric tests to compare two groups for matched or paired samples. Real-life example of a clinical investigation which looks at the effectiveness of a new drug for children with autism. One-sided versus two-sided tests and the special circumstance of the sign test giving zero difference scores are considered. http://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/MPH-Modules/BS/BS704_Nonparametric/BS704_Nonparametric6.html Wilcoxon signed rank test. Re-analyses the clinical investigation example above (previous page of this website). Comprehensive worked examples. Useful for instructional phase in class, revision and support. https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/32 One-sample test: the sign test information. Useful for revision and support. http://geographyfieldwork.com/Mann%20Whitney.htm Mann–Whitney U test of significance – real-life example which compares and contrasts the differences ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 21 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES of two urban areas. There are eight pairs of data, one of which is the quality of the architecture. https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/37 Mann–Whitney test and confidence information. Useful for revision and support. https://onlinecourses.science.psu.edu/stat464/node/36 Wilcoxon rank sum test information. Useful for revision and support. Identifying and carrying out an appropriate chisquared test http://wadsworth.cengage.com/psychology_d/templates/student_resources/workshops/stat_workshp/chi _sqr/chi_sqr_01.html Chi-squared workshop resource – example on workplace discrimination, test of independence, visual chi-square and test your knowledge workshop quiz. http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/fstats_ch5.pdf Goodness-of-fit tests – calculating expected frequencies, using the chi-squared distribution to test if a set of observations fits an appropriate probability model, discrete and continuous probability models – ideas for activities and examples to try. 22 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Hypothesis Testing Applying skills to bivariate tests Identifying and carrying out an appropriate hypothesis test on bivariate data http://www.cimt.plymouth.ac.uk/projects/mepres/alevel/stats_ch12.pdf Correlation and regression – investigate strength and direction of a relationship between two variables, evaluate and interpret Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient and the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, find equations of regression lines, bivariate distributions – ideas for activities and examples to try. ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 23 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Additional resources http://www.mathportal.org/calculators/statistics-calculator/ Free online statistics calculators, with optional step-by-step explanations: descriptive statistics: find the arithmetic mean, mode, median, minimum and maximum of a data set standard deviation: find the standard deviation, variance and range of a data set discrete probability distributions: find the mean, standard deviation and variance of a discrete probability distribution z-score: find the area under a standard normal curve normal distribution: find the area under a normal distribution curve t-test: one-sample and two-sample t-test calculator correlation and regression: find the linear correlation coefficient and regression line. Calculator generates a graph of a regression line as well as a detailed explanation. http://wiki.stat.ucla.edu/socr/index.php/EBook Statistics eBook which is a useful reference for definitions, methods and examples in probability and statistics. This could be used for home study or in the classroom. http://web.grinnell.edu/individuals/kuipers/stat2labs/Labs.html Activities and games based on labs that allow learners to develop their own research questions, use their own unique data to make decisions and then tie their conclusions to actual research (hypothesis testing). Tangrams: one-sample and two-sample t-tests. Memorathon game: z-test or one-sample t-test. Statistically grounded game: understanding p-values and introducing multivariate issues in a simplified game environment. http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/DASL/allmethods.html Data files for stories that illustrate the use of statistical methods. The data could be used in investigations in the Hypothesis Testing and Statistical Inference units. Data for use with chi-squared test, Mann–Whitney U test, paired t-test, ANOVA, t-test and two-sample t-test methods are included. http://www.censusatschool.org.uk/resources/relevant-a-engaging-stats Free downloadable booklet, by chapter, which provides practical advice and suggestions: statistical facts, formulae and information 24 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES data visualisation examples of curriculum resources teaching through statistical investigations using random samples of real data using spreadsheets using the whole problem-solving approach using your learners’ own data. http://www.censusatschool.org.uk/resources/simulationsA selection of statistical simulations in Excel. Numerous examples can be randomly generated: S1 binomial hypothesis test – one-tail and two-tail tests S1 dot plots – same size samples from two populations with the same mean and standard deviation. Which is normal and which is uniform? S2 CLT simulation – graphs of distributions of sample means. Central limit theorem in action S2 normal approximation to binomial – how do values for n and p affect the graphs? S2 normal approximation to Poisson – how does value of lambda (λ) affect the graph? S2 Poisson approximation to binomial – how do binomial parameters for n and p affect the graphs? S3 die chi-squared – chi-squared statistic for rolling a fair die S3 t and normal distributions – comparing these distributions stats random dots – dots scattered across grid. Amount in any square has Poisson distribution. Look at extreme values. http://www.amstat.org/education/stew/ A website of lesson plans for staff use. Lessons are organised around four elements: formulate a statistical question, design and implement a plan to collect data, analyse the data by measures and graphs, and interpret the data in the context of the original question. Some of the Grades 9–12 section would correspond with this course, including: 10000 steps – paired t-test Double stuffed – two-sample t-test An A-MAZE-ING comparison – two-sample t-test I always feel like somebody’s watching me – hypothesis test on proportion, chi-squared test, binomial distribution, binomial test The case of the careless zookeeper – chi-squared test When 95% accurate isn’t – Bayes’ theorem ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS 25 © Education Scotland 2015 RESOURCES Maths is Fun – Statistics These pages provide learners with the opportunity to review and consolidate their learning. Clearly explained key information and worked examples, followed by ten questions to check knowledge and understanding. http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/binomial-distribution.html Binomial distribution and a link to a game which demonstrates this. http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/standard-normal-distribution.html Normal distribution. http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/standard-normal-distribution-table.html Standard normal distribution table. Excel simulations The change to the shape of the distributions can be seen by altering the variables in these spreadsheets. http://wps.prenhall.com/bp_groebner_busstats_8/145/37312/9551949.cw/cont ent/index.html Binomial distribution, chi-square distribution, confidence interval distribution, fdistribution, hypothesis distribution, normal curve distribution, t- distribution. http://www.quantitativeskills.com/sisa/ A collection of procedures to do simple interactive statistical calculations online. Useful as a tool for checking. http://www.socscistatistics.com/tests/ Online statistical test calculators. Useful as a tool for checking. http://www.socscistatistics.com/pvalues/ Online p-value calculators. Useful as a tool for checking. http://davidmlane.com/hyperstat/glossary.html Glossary of statistical terms. http://www.stats.gla.ac.uk/glossary/ Useful glossary of statistical terms, many of which are more advanced than required for this course. Clear concise explanations, many with exemplification. 26 ADVANCED HIGHER STATISTICS © Education Scotland 2015