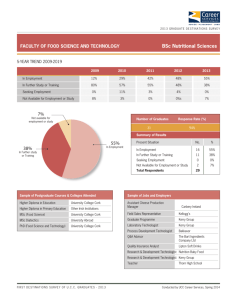
Working in Health Care
advertisement

Working in Health Care -Licensure, certification, registration and accreditation -Licensure- a mandatory credentialing process established by law, usually at the state level, that grants the right to practice certain skills and endeavors -Certification- a voluntary credentialing process whereby applicants who meet specific requirements may receive a certification -Registration- an entry in an official registry or record, listing the names of persons in a certain occupation who have satisfied specific requirements -Accreditation- official authorization or approval for conforming to a specified standard -Refer to p. 26-27, about joint Commission on accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) -Reciprocity- the process by which a professional license obtained in one state may be accepted as valid in other states by prior agreement without reexamination -Medical practice acts and medical boards -Medical practice acts- state laws written for the express purpose of governing the practice of medicine -Medical boards- bodies established by the authority of each state’s medical practice acts for the purpose of protecting the health, safety, and welfare of health care consumers through proper licensing and regulation of physicians and other health care practitioners -Health care professions -Share responsibility for delivery of health services -Have generally received a certificate, associate’s drgree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, doctoral degree, or post baccalaureate training in a science related to health care and have met all state requirements concerning licensure, certificate, and registration -Anesthesiologist -Athletic trainer -Audiologist -Cardiovascular technologist -Clinical exercise specialist -Cytotechnologist -Dental hygienist -Diagnostic medical sonographer -Dietician and nutritionist -ECG technician -EEG technician and technologist -Electroneurodiagnostic technologist -Emergency medical technician-paramedic -Health and fitness specialist -Health information administrator -Health information technician -Kinesiotherapist -LPN/LVN -Medical assistant -Medical illustrator -Medical laboratory technician and medical technologist -Medical massage therapist -Medical transcriptionist -Nurse practitioner -Nursing assistant -Occupational therapist -Occupational therapy assistant -Ophthalmic medical technician/technologist -Optician -Optometrist -Orthotist and prosthetist -Perfusionist -Phlebotomist -Physical therapist -Physical therapist assistant -Physician assistant -Polysomnographic technologist -Radiologic or medical imaging technologist -Registered nurse -Respiratory therapist -Specialist in blood bank technology -Surgical technologist -Respondeat superior- literally, “Let the master answer.” A doctrine under which an employer is legally liable for the acts of his or her employees, if such acts were performed within the scope of the employees’ duties -Medical practice management system -4 basic types of medical practice -Sole proprietorship- a form of medical practice management in which a physician practices alone, assuming all benefits and liabilities for the business -Partnership- a form of medical management system whereby two or more parties practice together under a written agreement specifying the rights, obligations, and responsibilities of each partner -Professional corporation- a body formed and authorized by law to act as a single person -Group practice- a medical management system in which three or more licensed physicians share the collective income, expenses, facilities, equipment, records, and personnel for the business -Types of managed care- a system in which financing, administration, and delivery of health care are combined to provide medical services to subscribers for a prepaid fee -Health maintenance organizations (HMO)- a health plan that combines coverage of health care costs and delivery of health care for a prepaid premium -Preferred provider organizations (PPO)- a network of independent physicians, hospitals, and other health care providers who contract with an insurance carrier to provide medical care at a discount rate to patients who are part of the insurer’s plan -Physician-hospital organizations (PHO)- a health care plan in which physicians join with hospitals to provide a medical care delivery system and then contract for insurance with a commercial carrier or an HMO -Other variations in managed care plans -Gatekeeper or primary care plan- primary care physician directs all of a patient’s medical care and generates any referrals to specialists or other health care practitioners -Point-of-service (POS)- a health care plan that allows members to seek health care from nonnetwork physicians but pays the highest benefits for care when it is given by the PCP or via a referral from the PCP -Open access- a managed care feature whereby subscribers may see any innetwork health care provider without a referral -Legislation affecting health care plans -Health care quality improvement act of 1986-a federal statute passed to improve the quality of medical care nationwide. One provision established the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB) -NPDB- a repository of information about health care practitioners -Health insurance portability and accountability act- helps workers keep continuous health insurance coverage for themselves and their dependents when they change jobs, protects confidential medical information from unauthorized disclosure or use, and helps curb the rising cost of fraud and abuse -Controlling health care fraud and abuse- laws have been passed to control 3 types of illegal conduct -False claims in billing -Kickbacks -Self-referrals -Risk management- steps taken to minimize danger, hazard, and liability -Quality improvement- measures taken by health care providers and practitioners to uphold the quality of patient care -Telemedicine- remote consultation by patients with physicians or other health professionals via telephone, closed-circuit television, or the internet -Cybermedicine- a form of telemedicine that involves direct contact between patients and physicians over the internet, usually for a fee -E-health- the term for the use of the internet as a source of consumer information about health and medicine - Refer to court case -Physician disciplined by board of medical examiners, p. 30 -Board upheld in permanently revoking physician’s license, p. 30 -Medical group liable under respondeat superior, p. 39 -Nurse sues under false claims act, p. 46 -Illegal telemedicine drug sale, p. 49