Notes
advertisement
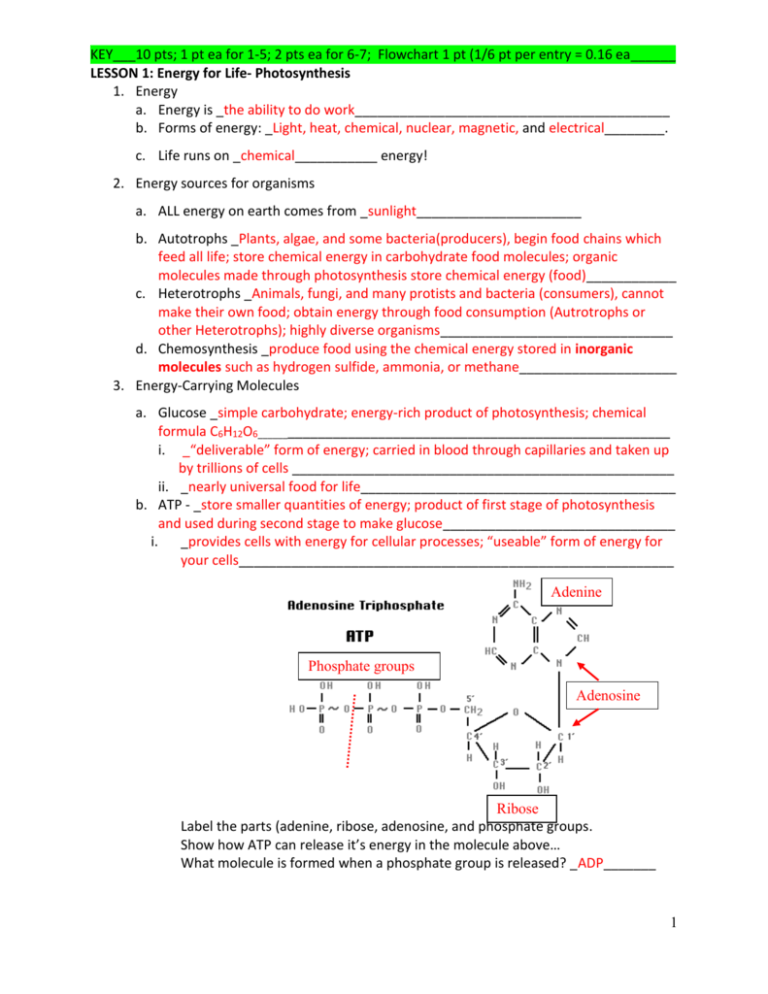
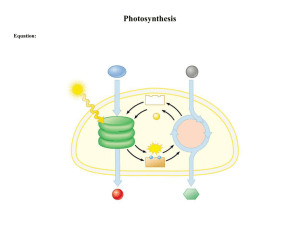
KEY___10 pts; 1 pt ea for 1-5; 2 pts ea for 6-7; Flowchart 1 pt (1/6 pt per entry = 0.16 ea______ LESSON 1: Energy for Life- Photosynthesis 1. Energy a. Energy is _the ability to do work__________________________________________ b. Forms of energy: _Light, heat, chemical, nuclear, magnetic, and electrical________. c. Life runs on _chemical___________ energy! 2. Energy sources for organisms a. ALL energy on earth comes from _sunlight______________________ b. Autotrophs _Plants, algae, and some bacteria(producers), begin food chains which feed all life; store chemical energy in carbohydrate food molecules; organic molecules made through photosynthesis store chemical energy (food)____________ c. Heterotrophs _Animals, fungi, and many protists and bacteria (consumers), cannot make their own food; obtain energy through food consumption (Autrotrophs or other Heterotrophs); highly diverse organisms_______________________________ d. Chemosynthesis _produce food using the chemical energy stored in inorganic molecules such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, or methane_____________________ 3. Energy-Carrying Molecules a. Glucose _simple carbohydrate; energy-rich product of photosynthesis; chemical formula C6H12O6_________________________________________________________ i. _“deliverable” form of energy; carried in blood through capillaries and taken up by trillions of cells ___________________________________________________ ii. _nearly universal food for life__________________________________________ b. ATP - _store smaller quantities of energy; product of first stage of photosynthesis and used during second stage to make glucose_______________________________ i. _provides cells with energy for cellular processes; “useable” form of energy for your cells__________________________________________________________ Adenine Phosphate groups Adenosine Ribose Label the parts (adenine, ribose, adenosine, and phosphate groups. Show how ATP can release it’s energy in the molecule above… What molecule is formed when a phosphate group is released? _ADP_______ 1 4. Photosynthesis – an Overview a. Write the chemical equation that shows the photosynthetic reaction: REACTANTS PRODUCTS b. Label the reactants & the products in the equation that you have written above. c. What are the roles of each of the following in the photosynthetic reaction? i. Enzymes – proteins to speed up chemical reactions ii. Chlorophyll – pigment which absorbs light iii. Chloroplasts – contain chlorophyll, accessory pigments, and enzymes in patterns which maximize photosynthesis d. What are the two stages of photosynthesis? (1) _Light Reactions____________________________ a. _uses water; changes light energy into chemical energy; releases oxygen as a waste product___________________________________________________ (2) _Calvin cycle____________________________ a. _uses chemical energy in ATP and NADPH to make glucose_______________ 5. Chloroplasts & Chlorophyll a. Label the drawing of the chloroplast below: 1. _Outer membrane___________ 2. _Inner membrane___________ 3. _Thylakoid membrane_______ 4. _Stroma__________________ 5. _Grana___________________ b. Why does chlorophyll appear green? _green is the color they reflect_____________ c. What colors are absorbed by chlorophyll? _absorbs blue-violet and red wavelengths of light, and reflects green_______________________________________________ 2 6. Light Dependent Reactions (Light Reactions) a. In your own words, briefly describe what occurs in this phase of photosynthesis _1st Pigments in photosystem II absorb light; makes high-energy electrons; electrons passed to the ETC; Thylakoid membrane provides new electrons to chlorophyll; the new electrons come from water molecules; enzymes on inner surface of thylakoid membrane break down each H20 into 2 electrons, 2 H+ ions, and 1 oxygen atom through photolysis (“splitting by light”); 2 electrons replace high-energy electrons chlorophyll lost to electron transport chain; oxygen released into the air as O2; 2 H+ ions released inside thylakoid membrane creating electrochemical gradient 2nd High-energy electrons move through ETC from photosystem II to photosystem I; energy from electrons used by molecules moving through the ETC to transport H+ ions from the stroma into the inner thylakoid rd 3 Pigments in photosystem I use energy from light to reenergize the electrons; NADP+ picks up high-energy electrons from outer surface of thylakoid plus an H+ ion and becomes NADPH 4th H+ ions released during the splitting of water molecules and electron transport, inside the thylakoid membrane positively charged and outside is negatively charged (electrochemical gradient). Difference in charge provides the energy to make ATP. th 5 H+ ions cannot cross the membrane directly. Membrane has a protein called ATP synthase that allows H+ ions to pass through it. ATP synthase rotates like a turbine when the H+ ions pass through it and binds ADP and a phosphate group together to form ATP. th 6 ATP and NADPH go to the light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle)__________ 3 7. Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent Reactions) a. Why are these reactions sometimes called the “Light- Independent Reactions”? _do not require light energy to occur_______________________________________ b. Why is CO2 “fixed”? _Life on Earth is carbon-based; needed in building blocks of biological molecules; ultimate source of carbon is carbon dioxide; Animals and most other heterotrophs cannot take in CO2 directly; Only autotrophs can build low energy inorganic CO2 into high-energy organic molecules like glucose_____________ c. Explain how your breath can be food to a plant: _You exhale CO2________________ d. In your own words briefly explain what happens during each phase of the Calvin cycle (Carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration) below: _Step 1: Carbon Fixation. Carbon dioxide from the atmosphere combines with a simple, five-carbon compound called RuBP. This reaction occurs with the help of an enzyme named RuBisCo and produces molecules known as 3PG (a three-carbon compound, 3Phosphoglyceric acid). Step 2: Reduction. Molecules of 3PG (from Step 1) gain energy from ATP and NADPH (from the light reactions) and re-arrange themselves to form G3P (glycerate 3phosphate). This molecule also has three carbon atoms, but it has more energy than 3PG. One of the G3P molecules goes on to form glucose, while the rest of the G3P molecules go on to Step 3. Step 3: Regeneration. The remaining G3P molecules use energy from ATP to form RuBP, the five-carbon molecule that started the Calvin cycle. This allows the cycle to repeat. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4 8. List the three pathways of carbon fixation and give examples of the types of plants that use each type of pathway below. (1) _C-3 pathway; most photosynthetic plants that don’t live in harsh environments (2) _C-4 pathway; plants like corn_________________________________________ (3) _CAM; plants in hot, dry areas; cacti & succulents__________________________ 9. What are the three main factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis? _Shortage of water, temperature, and intensity of light____________________________________ 10. Let’s Review: Where does photosynthesis occur? _chloroplast________________ What are the saclike photosynthetic membranes in the chloroplast called? _thylakoids________________ The thylakoids are arranged in stacks called _grana_________. What is found inside the grana? _Clusters of chlorophyll and other pigments_______ What are photosystems? _proteins found in grana___________________________ What do photosystems do? _capture energy or sunlight_______________________ How many stages does photosynthesis have? _2_____ What are they? _Light Reactions and Calvin cycle__________________________ Where do the light-dependent reactions take place? _thylakoid membranes______ Where do the light-independent reactions take place? _stroma_________________ 11. Complete the flowchart on the back of this page… 5 H2O NADPH ATP ADP + P NADP+ CO2 6