The Senses
advertisement
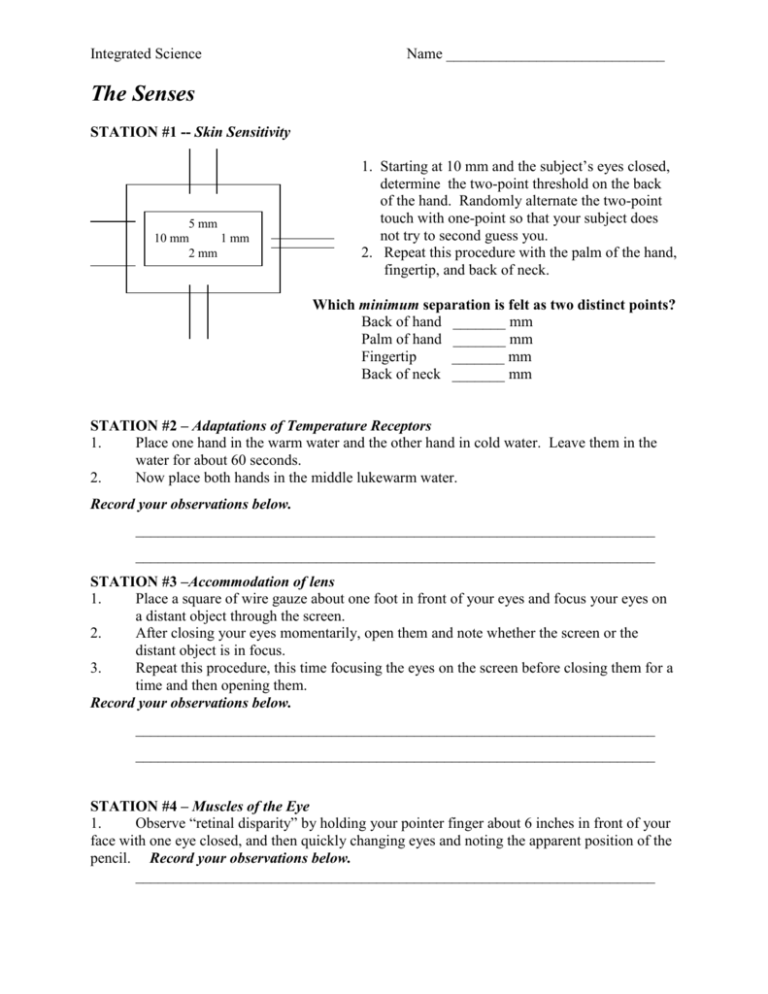
Integrated Science Name _____________________________ The Senses STATION #1 -- Skin Sensitivity 5 mm 10 mm 1 mm 2 mm 1. Starting at 10 mm and the subject’s eyes closed, determine the two-point threshold on the back of the hand. Randomly alternate the two-point touch with one-point so that your subject does not try to second guess you. 2. Repeat this procedure with the palm of the hand, fingertip, and back of neck. Which minimum separation is felt as two distinct points? Back of hand _______ mm Palm of hand _______ mm Fingertip _______ mm Back of neck _______ mm STATION #2 – Adaptations of Temperature Receptors 1. Place one hand in the warm water and the other hand in cold water. Leave them in the water for about 60 seconds. 2. Now place both hands in the middle lukewarm water. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ STATION #3 –Accommodation of lens 1. Place a square of wire gauze about one foot in front of your eyes and focus your eyes on a distant object through the screen. 2. After closing your eyes momentarily, open them and note whether the screen or the distant object is in focus. 3. Repeat this procedure, this time focusing the eyes on the screen before closing them for a time and then opening them. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ STATION #4 – Muscles of the Eye 1. Observe “retinal disparity” by holding your pointer finger about 6 inches in front of your face with one eye closed, and then quickly changing eyes and noting the apparent position of the pencil. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Hold your pointer finger out at arm’s length and focus one eye on the tip as it is slowly brought in to the bridge of the nose. Notice the change in the diameter of the subject’s pupil. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ STATION #5 – Blind Spot 1. Hold the index card with the cross and circle about 20 inches from your face with the left eye closed or covered. Focus on the circle; this is most easily done if the circle is positioned in line with the right eye. 2. Keeping the right eye focused on the circle, slowly bring the card towards your face until the cross disappears. Have your partner measure this distance: ___________ cm 3. Repeat the above procedure using the left eye focused on the cross (right eye covered or closed). Have your partner measure this distance: ___________ cm Do both your eyes seem to have a “blind spot” at about the same distance? _________ Do you and your partner have the similar distances? __________ What causes the “blind spot?” ________________________________________________ STATION #6 – Conduction of Sound Waves 1. Strike a tuning fork on the bottom of your shoe to produce vibrations. Do not strike bench tops. 2. Place the handle of the vibrating tuning fork against the bony prominence behind the ear. When the sound has almost died away, move the tuning fork near the outer ear. If there is no damage to the middle ear (by infection or wax), the sound should reappear. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ STATION #7 – Localization of Sound 1. Working with a partner whose eyes are closed, strike the tuning fork and ask your partner to locate the source of the sound. Place the vibrating fork at various positions (front, back, up, down, left or right side) about a foot from their head. 2. Repeat the above procedure, but this time have your partner also place a finger in one ear to plug the ear. Record your observations below. _____________________________________________________________________ STATION #8 – Reflexes 1. The knee-jerk, or patellar reflex. The subject should sit on the edge of a table or a high chair so that his/her leg hangs freely. The observer should locate the patella (knee cap) and the tendon below it. The tendon should then be stuck sharply with the edge of the observer’s hand. If properly done, this will produce the so-called knee-jerk – an involuntary upward motion of the foot and an elevation of the leg. Describe what happened or problems you had: 2. Motor reinforcement of the knee-jerk. Repeat the above procedure, but have the subject interlock his fingers and attempt to pull them apart as vigorously as possible just as the blow is stuck. a. What effect does this muscular tension have on the reflex action? b. Explain how clenching your fist during a fight or athletic contest may affect your reflex responses. 3. Draw a diagram showing the path followed by the nerve impulse in bringing about a knee-jerk. Use page 682 in your book to help but remember the knee-jerk does not involve the brain. (Use the back of this page if you need more room) 4. Cilio-spinal reflex. Gently pinch the skin at the nape of the subject’s neck. Note the reaction of the pupils of his/her eyes. Describe what happened or problems you had: 5. Sneezing reflex. Stimulate the lining of the nose with some pepper. Be very careful that it is not inhaled. Try to inhibit this reflex by having the subject press on the upper lip just below the nose. Describe the results you obtain. Describe what happened or problems you had: 6. Pupillary reflex. An excellent example of the integration of the nervous system is found in the reflex activities of the pupils of the eyes. Have the subject close eyes for ninety seconds and then have him/her open them. Describe the results in your own words. Describe what happened or problems you had: QUESTIONS Text Pages 678-684 1. What is a reflex? (p. 682) 2. Where are reflex responses controlled? 3. Name the THREE types of neurons are reflex impulse travels through. (p. 682) 4. Describe the TWO divisions of the nervous system. (p. 680) 5. Where are the interneurons located?