Energy - Newton.k12.ma.us
advertisement

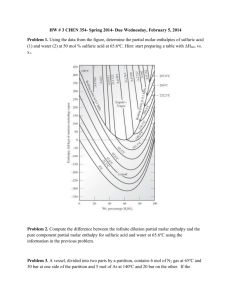
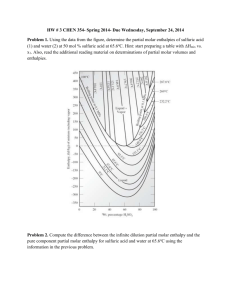
Navah, Mike, Sylvie, Natasha F-block Energy Final Exam Preparation Big Ideas: Delta H Bond energies Enthalpies of formation/reaction Bond energies Hess’s Law of heat summation Key Terms: -endothermic - exothermic - calorimetry - enthalpy - Specific heat QUESTIONS 1] What is the meaning if a positive sign for the enthalpy of a reaction? 2] Define heat capacity; 3] Define specific heat; 4] A reaction absorbs 15.0 Joules of heat. How many calories is this? 5] If the heat of a reaction is -20 Joules, is this reaction endo or exothermic? 6] Are the products of the above reaction less or more stable than the reactants? 7] What is the reaction between bond strengths between the atoms in a molecule of a compound and the thermodynamic stability of the compound? 8] Define a calorie in terms of the quantity of water in its temperature change: 9] What is delta H? 10] Write the formula of delta H 11] What is the first law of thermodynamics? 12] What is Hess’s Law? 13] How is delta Hrxn related to enthalpies of formation of the reactants and the products? 14] If a bond is broken and the potential energy is connected to kinetic energy, what can you say about the delta H of the reaction? 15] It took 478 J to heat 199.9 g of "Z" from 34.62 degrees Celsius to 46.64 degrees Celsius. What was the specific heat of "Z"? 16] 1 CH4 + 2 O2 1CO2 + 2 H2O + 890. KJ. a) How many KJ of energy will be released when 12.50 L of CH4 (gas at SATP) is burned? 17] 1 S + 1 O2 1SO2 ∆H = -297Kj/mol 1 SO2 + 1/2 O2 1SO3 ∆H = -144Kj/mol 1 SO3 + 1 H2O 1 H2SO4 ∆H = -84Kj/mol Calculate the ∆H for the reaction 1 S + 3/2 O2 + 1 H2O 1 H2SO4 17] Use the following enthalpies of formation to calculate the ∆H for the following reaction and indicate whether the reaction is exo or endothermic. *remember: all elements in their standard states have 0 for their enthalpy of formation SiC: -27, CO: -26, SiO2: -205 18] How many grams of C2 H4 must be burned in oxygen to release 1550 KJ? (Equation? ∆H?) C2 H4 + 3 CO2 2 CO2 + 2 H2O +52 + 0 -788 + -527 -1412 = ∆H 19] How many joules of heat is released when 2.0 L of water is cooled from 40 degrees Celsius to 15 degrees Celsius? 20] The specific heat capacity of copper is 0.38 J g –1 degrees C-1. What is the temperature increase of 2.0 kg of copper after absorbing 8.4 kJ of heat? Energy Final Exam Preparation; ANSWERS 1] This means energy was released during the reaction. 2] The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of on mole of a substance by 1 degree Celsius. 3] The heat capacity of 1 gram of a substance. 4] 3.59 calories 5]Exothermic 6] products= thermodynamically more dynamic 7] Energy is required to break bonds and the same amount of energy is released when that type of bond forms. If the bond strength is large, the molecule is more stable. 8] One calorie is the heat/energy required to raise 1g H2O 1 degree Celsius. 9] The sum of the internal energy change of a system and its pressure- volume is called delta H enthalpy change. 10] delta H= delta E + P delta V at constant pressure 11] Energy is neither created nor destroyed. 12] Enthalpy changes of different steps of a reaction can be added to obtain the delta H for the reaction. 13] delta Hrxn = sum of delta Hf ( products)- sum of delta Hf ( reactants) 14] Energy is being released but not absorbed ( an endothermic reaction). 15] C= Q/M∆T C= 478 J / (199.9 g x 12.02 g) = .199 J/g x degrees Celsius .199 J/g x degrees Celsius 16] 12.50 L CH4 x 1 mol CH4 x 16.0 g CH4 24.8 L CH4 1 mol CH4 = 6.74 g CH4 6.74 g CH4 17] 1 S + 1 O2 1SO2 ∆H = -297Kj/mol 1 SO2 + 1/2 O2 1SO3 ∆H = -144Kj/mol 1 SO3 + 1 H2O 1 H2SO4 ∆H = -84Kj/mol -297 + -144 + -84 = -525 ∆H = -525 kJ/mol S (*remember: use whatever product/reactant there is one whole mole of (i.e. 1S as opposed to 1/2 O2 when giving the unit of mol/x.) 17] Reaction: 3 C +1 SiO2 1 SiC + 2CO 0 + -205 -27 + -52 = +126 KJ/mol SiO2 +126 KJ/mol SiO2 ; Endothermic reaction 18] 1550 kJ x 1 mol C2 H4 x 28.4 C2 H4 1412 KJ 1 mol C2 H4 = 30.7 g C2H4 30.7 g C2H4 19] 2.1 x 105 joules 20] 11.1 degrees Celsius