File
advertisement

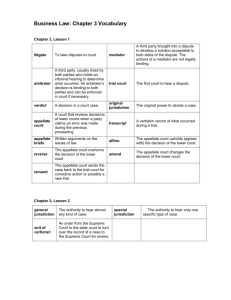
Name: ____________________________ CHAPTER 3 COURT SYSTEMS 3-1 FORMS OF DISPUTE RESOLUTION DISPUTE RESOLUTION How can disputes be resolved without going to court? _________________- Independent third party who tries to develop a non-binding solution acceptable to both sides in a dispute. _________________________ ________________ - Independent third party who develops a binding and enforceable resolution to a dispute. How do courts settle disputes? Award Damages or _________________________________ ______________________– take your disputes to court HOW DO COURTS SETTLE DISPUTES? Court: ____________________________________________________________ Two levels of courts are involved in deciding a dispute _____________ – court in which a dispute is first heard ______________ – reviews decisions of lower courts when a party claims an error was made during the lower courts proceeding Trial Court: __________, lawyers, clerks, sheriffs or marshals, bailiffs, and __________ Steps in Trial Court Judge __________________________ __________________________ Has _______________________ or the original power to decide the case because they had initial contact with case Name: ____________________________ Appellate Court: Examine the ______________, which is a verbatim record of what went on at the trial They also read the ___________________, which are _________________________________ The appellate court then decides one of four things (p. 50). 1. _____________-affirmed-trial court decision OK. No error 2. Reversed_____________ 3. Amended – ______________ 4. Remanded – sent back to the trial court for correction or a new trial Concerned solely with _________________ 3-2 FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM Article III, Section 1 of the U.S. Constitution The judicial Power of the United States shall be vested in one Supreme Court, and in such inferior Courts as the Congress may from time to time ordain and establish. JURISDICTION OF THE FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM Judiciary Acts established: _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ _____________________ Types of Jurisdiction ___________________, a court with general jurisdiction can hear almost any kind of case Special Jurisdiction, __________________________________________________________________ FEDERAL COURTS WITH GENERAL JURISDICTION Name: ____________________________ _____________________________ Federal Courts of Appeals _____________________________ FEDERAL DISTRICT COURTS The Federal District Court is ______________________with ________________________ It is the ______________________ of the federal system. It has the power to determine the facts and to make initial determinations of the law to use in deciding the case. FEDERAL COURTS OF APPEALS The federal courts of appeals have appellate jurisdiction over the _______________, ______________________, and many federal administrative agencies. There are ________ federal courts of appeal. __________ of these are circuit courts, each of which is responsible for an assigned ___________________. The thirteenth court is dedicated to the ____________________. UNITED STATES SUPREME COURT The United States Supreme Court (USSC) has both ____________ and ____________ jurisdiction. It has original jurisdiction over cases affecting _______________, other ______________ and consuls and those in which ________________________. __________________________ is exercised over cases on appeal from the U.S. Courts of Appeals or from the highest courts of the various states. FEDERAL COURT SYSTEM- REVIEW How many levels of federal courts are there? ________________________________________ What is the function of the federal district court? ________________________________________________________________________________ Name: ____________________________ What is the highest federal appellate court? Does the Supreme Court have original or appellate jurisdiction? __________________________________________ ____________ What is the most important function of the U.S. Supreme Court? ________________________________ 3-3 A TYPICAL STATE COURT SYSTEM ___________________ ___________________ ___________________ Primary difference between the federal court system and a state court system? The type of specialized courts found therein. _________________ - Bankruptcy, court of international trade, tax court __________________- Probate, juvenile, family, small claims Both courts often deal with the same issues, so few issues can be considered exclusively state or federal STATE TRIAL COURTS State courts have general original jurisdiction over both _____________and __________ matters. States refer to trial courts as _____________, _______________, ________________, or courts of common pleas. Trial courts are the courts of record in the state system. State trial courts also ____________________________________________________________ A ____________________keeps an exact account of what goes on at trial. STATE COURTS OF APPEALS An appeal from a court of record is typically reviewed by __________________ in a state court of appeals. Name: ____________________________ _____________________________ - it checks to be sure the correct law was used and properly applied to resolve the case STATE SUPREME COURT In states with the intermediate level of courts of appeal, only cases that involve the most complex legal issues are taken to the justices of the state supreme court. _______________-is the title given to judges who sit on State Supreme Courts and the Federal Supreme Court State supreme courts issue the _________________________ on matters of law appealed to them. If a U.S. Constitutional or other federal question of law is involved, a further appeal can go to the U.S. Supreme Court. STATE COURTS WITH SPECIALIZED JURISDICTIONS __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ STATE COURTS WITH SPECIALIZED JURISDICTIONS __________________________ Court that hears minor criminal cases, state traffic offenses, and lawsuits involving amount of ____________________________________________ _____________________________________ __________________________________ _____________________________ City court, usually divided into ____________________________________ State courts that handle disputes in which ______________________________________________ Juvenile courts Name: ____________________________ Courts specifically created and given authority to try and pass judgments for crimes committed by persons _________________________________________. In most modern legal systems, crimes committed by children and minors are treated differently and differentially (unless severe, like murder or gang-related offenses) regarding the same crimes committed by adults. _______________________________________________________________ ________________________ ____________________________________