AP Chemistry
advertisement

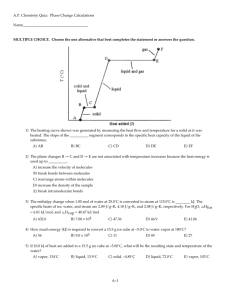
AP Chemistry Name : Worksheet : Ch 10-2 Date : CALCULATORS MAY NOT BE USED ON THE MULTIPLE CHOICE A. Review : _____ 1. An ideal solution of toluene and benzene is made at 20. ºC. What is the mole fraction of toluene if the vapor pressure of toluene is 30. mmHg and the vapor pressure of benzene is 20. mm Hg? a. 0.20 b. 0.30 c. 0.40 d. 0.50 e. 0.60 _____ 2. The mass of an element in 1.00 mole of four different compounds is found to be 24.0 grams, 36.0 grams, 72.1 grams and 96.1 grams. Which of the following is a possible atomic weight of this element? a. 14.0 g/mol b. 36.0 g/mol c. 9.0 g/mol d. 12.0 g/mol e. 18.0 g/mol _____ 3. The simplest formula of an oxide of sulfur that is 33% oxygen is a. SO2 b. S2O c. SO d. S2O3 e. SO3 _____ 4. As the temperature of a gas is raised from 5 ºC to 30 ºC, the kinetic energy of the gas increases by a factor of a. 6 b. 303/278 c. (303/278)0.5 d. 1/6 e. 3 _____ 5. A 12.0 gram sample of hydrogen gas is in a rigid container at 227 ºC and has a pressure of 2.0 atm. What would its pressure be at 27 ºC? a. 0.25 atm b. 0.50 atm c. 1.0 atm d. 1.2 atm e. 1.5 atm _____ 6. Samples of oxygen gas and chlorine gas are mixed in a container of fixed volume. The initial partial pressures of oxygen and chlorine are each 1.00 atm. After the reaction between the two gases the partial pressure of oxygen is 0.50 atm, chlorine is 0.00 atm and the gas formed is 1.00 atm. What is the formula of the gas formed? a. O2Cl b. OCl c. OCl2 d. OCl3 e. O2Cl3 _____ 7. At 25ºC ammonia (NH3, molar mass = 17 grams) effuses at a rate of 0.50 mol/minute. Under the same conditions, which of the following gases has a rate of effusion which is approximately twice that of ammonia? a. H2 b. He c. CH4 d. Ne e. F2 _____ 8. Which of the following deviates the most from ideal behavior at the same conditions of temperature and pressure? a. CH4 b. H2 c. Ne d. NH3 e. CO2 _____ 9. The molecular weight of a gas that has a density of 6.70 g/L at STP is ____ g/mol. a. 496 b. 150. c. 73.0 d. 3.35 e. 0.298 _____ 10. Ammonium nitrite decomposes according to the equation : NH4NO2(s) N2 (g) + 2 H2O(g). What volume of gas is produced in liters at STP from 16 grams of ammonium nitrite? a. 4.0 L b. 17 L c. 22 L d. 33 L e. 55 L _____ 11. A 250. mL flask has a mass of 112.00 g. It is filed with an unknown gas at STP, and the mass is found to be 112.13 g. What is the approximate molar mass of the gas? a. 4.0 g/mol b. 8.2 g/mol c. 12 g/mol d. 16 g/mol e. 44 g/mol _____ 12. A sample of oxygen gas is found to effuse at a rate of 3 times that of an unknown gas. What is the molar mass of the unknown gas? a. 290 g/mol b. 96 g/mol c. 55 g/mol d. 4.0 g/mol e. 11 g/mol 13. How much energy does it take to convert 0.500 kg ice at -20.°C to steam at 250.°C? Specific heat capacities: ice, 2.1 J/g • °C; liquid, 4.2 J/g • °C; steam, 2.0 J/g • °C, ΔHvap = 40.7 kJ/mol, ΔHfus = 6.02 kJ/mol. 14. What is the final temperature when 0.850 kJ of energy is added to 10.0 g ice at 0°C? (See 13 above.) 15. An ice cube tray contains enough water at 22.0°C to make 18 ice cubes that each have a mass of 30.0 g. The tray is placed in a freezer that uses CF2Cl2 as a refrigerant. The heat of vaporization of CF2C12 is 158 J/g. What mass of CF2C12 must be vaporized in the refrigeration cycle to convert all the water at 22.0°C to ice at -5.0°C? The heat capacities for H2O(s) and H2O(/) are 2.08 J/g • °C and 4.18 J/g • °C, respectively, and the enthalpy of fusion for ice is 6.02 kJ/mol. 16. Some ice cubes at 0°C with a total mass of 475 g are placed in a microwave oven and subjected to 750. W (750. J/s) of energy for 5.00 min. Does the water boil? If not, what is the final temperature of the water? (Assume all of the energy of the microwaves is absorbed by the water and that no heat is lost from the water. See 15 above.) 17. Consider the phase diagram given below. What phases are present at points A through H? Identify the triple point, normal boiling point, normal freezing point, and critical point. Which phase is denser, solid or liquid? 18. Use the accompanying phase diagram for sulfur to answer the following questions. a. How many triple points are in the phase diagram? b. What phases are in equilibrium at each of the triple points? c. What phase is stable at room temperature and 1.0 atm pressure? d. Can monoclinic sulfur exist in equilibrium with sulfur vapor? e. Is the normal boiling point of sulfur above or below 119°C? Explain. 19. Use the accompanying phase diagram for carbon to answer the following questions. a. How many triple points are in the phase diagram? b. What phases can coexist at each triple point? c. What happens if graphite is subjected to very high pressures at room temperature? d. If we assume that the density increases with an increase in pressure, which is more dense, graphite or diamond? P2 H vap 1 1 H Vapor pressure use Clausius-Clapeyron eqn : ln P1 vap 1 1 or ln P T T P R R 1 T1 T2 1 2 2 20. The temperature inside a pressure cooker is 115°C. Use Equation (10.5) to calculate the vapor pressure of water inside the pressure cooker. What would be the temperature inside the pressure cooker if the vapor pressure of water was 3.50 atm? 21. What pressure would have to be applied to steam at 350.°C to condense the steam to liquid water? 22. The enthalpy of vaporization of acetone is 32.0 kJ/mol. The normal boiling point of acetone is 56.5°C. What is the vapor pressure of acetone at 25.0°C? 23. The enthalpy of vaporization of mercury is 59.1 kJ/mol. The normal boiling point of mercury is 357°C. What is the vapor pressure of mercury at 25°C? Answers : 13. 1680 kJ 14. 0 ºC, not all the ice will melt. 15. 1490 g 16. 33 ºC, the water will not boil. 17. A: solid; B: liquid; C: vapor; D: solid + vapor; E: solid + liquid + vapor (triple point); F: liquid + vapor; G: liquid + vapor (critical point); H: vapor; the first dashed line (at the lower temperature) is the normal melting point, and the second dashed line is the normal boiling point. The solid phase is denser. 18a. 2 18b. triple point at 96 ºC : rhombic, monoclinic, vapor ; triple point at 119 ºC : monoclinic, liquid, vapor 18c. Rhombic 18d. Yes (share boundary line) 18e. Higher, vapor pressure must equal 760 mmHg, at 119 ºC, the vapor pressure is only 0.027 mm Hg 19a. 2 19b. higher triple point : graphite, diamond and liquid ; Lower triple point : graphite, liquid and vapor 19c. It is converted to diamond – more dense, solid form) 19d. Diamond – more dense. 20. P2 = 1.7 atm : 413K 21. 194 atm 22. 221 torr 23. 2.56 x 10-3 torr