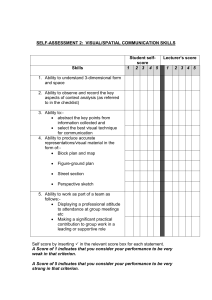
aaat4_exams_-_assessment_guidelines
advertisement

Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 General Education and Training Certificate Adult Basic Education and Training NQF Level 1 EXAMINATIONS AND ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY L4 CODE: AAAT4 Reviewed 2013 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 1|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3 2. The GETC-ABET Level 4 Qualification 4 3. Unit Standards for AAAT4 Learning Area 7 4. LTSM in PALCs 18 5. Weighting of the Specific Outcomes and Assessment Criteria 18 6. Core Knowledge Areas 18 7. Taxonomies used in scaffolding questions 24 8. Site-Based Assessment (Formative) 24 8.1 Structure of SBA Tasks 25 8.2 Exemplar SBA Tasks 26 9. External Assessment (Summative) 46 9.1 Structure of a question paper 46 9.2 Exemplar question paper 47 10. Promoting the Principles of quality assessment practices 61 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 2|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 1. INTRODUCTION This document aims to be an Examinations and Assessment Guidelines in its orientation. It should be seen against the background of the review of the General Education and Training Certificate (GETC): Adult Basic Education and Training (ABET) qualification and the re-registration of some of its constituent Unit Standards. Against this background, it must be seen to replace any other guideline document that has preceded it. What it does not do, however, is signal a radical shift from formal national assessment processes that have been managed by the Department of Higher Education and Training (DHET). It attempts to consolidate such assessment practices. It formalises them into a useful reference document for mainly examiners and moderators of ABET assessment. At the same time it is a useful guide to educators, in order to prepare their learners for assessment. The AAAT4 Examinations and Assessment Guidelines document is based on the GETC-ABET interim qualification with the SAQA ID number 71751. The guidelines should be viewed as developmental in nature aimed at enhancing the quality of the implementation of assessment for the interim qualification. The other users of this document shall be the Public Adult Learning Centres (PALCs) management teams, departmental officials, policy analysts, learning area coordinators or advisers and any interested stakeholder in adult education. Furthermore, the guidelines document is intended to assist the Learning Area Facilitator in preparing the learner for the examination as well as the site-based assessment. It should be treated as resource material that seeks to indicate the unit standards for the AAAT4 learning area and how to unpack them for assessment. It also indicates the possible content knowledge (as mentioned in the unit standards) to be assessed. It will provide clarity on how specific outcomes and assessment criteria are weighted. The possible teaching and learning support materials relevant to the learning area are also highlighted. While our aim is not to be prescriptive on curriculum, it is our hope that this document will offer educators more guidance in their own teaching and assessment practice. The document creates a uniform framework for examinations and formative assessments, in order to avoid a variety of different approaches to examinations. It must be pointed out that while the guidelines are based on the Unit Standards, it should not be read without the accompanying unit standards, or replace the unit standards as a guideline to teaching. The document also contains the GETC - ABET qualification which among others reflects on the rules of combination, core components and the academic learning areas. The structure of an examination question paper, the taxonomies used in scaffolding of questions, an exemplar question paper and marking memorandum together with exemplar site-based assessment tasks are outlined. This examination guidelines document provides guidance on how to use available resources to achieve the specified unit standards of the learning area. The national Policy on the Conduct, Administration and Management of the GETC - ABET Level 4 examinations and assessment has a bearing on this document. All users are encouraged to alert the Department of Higher Education and Training of any unrealistic suggestions that might hinder quality implementation of the assessment for the interim GETC – ABET Level 4 qualification. It must be noted that these guidelines are by no means exhaustive in its suggestions of possible assessment activities. Suggestions to improve the implementation of assessment in the AAAT4 learning area will be greatly appreciated. 2. THE GETC-ABET LEVEL 4 QUALIFICATION The General Education and Training Certificate (GETC) in Adult Basic Education and Training (ABET) with ID No. 71751 will provide adult learners with fundamental basics of general education learning. It replaces SAQA qualification ID No. 24153. The table below provides a synoptic view of the qualification. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 3|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SAQA QUAL ID QUALIFICATION TITLE 71751 General Education and Training Certificate: Adult Basic Education and Training ORIGINATOR REGISTERING PROVIDER Task Team - Adult Basic Education and Training QUALITY ASSURING ETQA QUALIFICATION TYPE FIELD SUBFIELD National Certificate Field 05 - Education, Training and Development Adult Learning ABET BAND MINIMUM CREDITS NQF LEVEL QUAL CLASS ABET Level 4 120 Level 1 Regular-Unit Standards Based REGISTRATION STATUS SAQA DECISION NUMBER REGISTRATION START DATE REGISTRATION END DATE Registered SAQA 1179/08 2008-11-26 2011-11-26 LAST DATE FOR ENROLMENT LAST DATE FOR ACHIEVEMENT 2012-11-26 2015-11-26 The purpose of the Qualification is to equip learners with foundational learning by acquiring knowledge, skills and values in specified Learning Areas. In addition, it also allows learners to choose Elective Unit Standards which relate to occupational type learning relevant to their area of interest or specialisation. In particular, the purpose of the qualification aims to: Give recognition to learners who achieve and meet the necessary requirements and competencies as specified in the Exit Level Outcomes and Associated Assessment Criteria. Provide a solid foundation of general education learning which will help prepare learners and enable them to access Further Education and Training learning and qualifications, particularly occupational workplace-based or vocational qualifications. Promote lifelong learning to enable learners to continue with further learning. Prepare learners to function better in society and the workplace. Rationale: Adult Basic Education is identified as a critical priority in South Africa and plays a vital role in equipping adult learners with the necessary knowledge, skills and values in order to be functional in society and as a person by contributing to the workforce, community and economy. This GETC: ABET qualification provides learners with foundational learning through the acquisition of knowledge and skills needed for social and economic development and the promotion of justice and equality. It also seeks to promote and instill learners with a culture of life-long learning needed for future learning. It also enables learners to acquire the necessary competencies in order to access further education and training, career development and employment opportunities. The achievement of the GETC: ABET qualification allow learners the following learning pathways: To choose a vocational route through completion of the National Certificate (Vocational) Qualifications at Levels 2, 3 and 4 which contain vocational specialisations. To access academic learning at NQF Level 2 and above. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 4|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 To access Occupational specific qualifications at NQF Level 2, which consist of knowledge, skills and workplace experience and learning. The qualification aims to equip learners to: Develop and apply relevant skills, knowledge and attitudes in the chosen Learning Areas. Function better in and contribute to the world of work. Be sensitive and reflective of issues relating to diversity, inclusivity, cultural values, human rights, gender, development and change. Develop an appreciation for lifelong learning. Function better as a citizen in South Africa and contribute to cultural, social, environmental and economic development. Make informed judgments about critical ethical issues. Develop study skills to be able to access further learning. It is assumed that learners have literacy and numeracy skills in order to cope with the complexity of learning in this qualification. Recognition of Prior Learning: The structure of this Qualification makes Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) possible through the assessment of individual Unit Standards. The learner and assessor should jointly decide on methods to determine prior learning and competence in the knowledge, skills, and values implicit in the Qualification and the associated Unit Standards. RPL will be done by means of an integrated assessment which includes formal, informal and non-formal learning and work experience. This Recognition of Prior Learning may allow for accelerated access to further learning at this or higher Levels on the NQF; gaining of credits for Unit Standards in this Qualification; and obtaining this Qualification in whole or in part. All RPL is subject to quality assurance by the relevant ETQA or an ETQA that has a Memorandum of Understanding with the relevant ETQA. It is recommended that learners have achieved the following in order to access this qualification: Communication at ABET Level 3 or equivalent and Mathematical Literacy at ABET Level 3 or equivalent. The GETC-ABET qualification comprises the Fundamental, Core and Elective components in its rules of combination. Learners are expected to offer a minimum of 5 Learning Areas. The 2 fundamental Learning Areas and the 1 Core Learning Area are compulsory offerings. Learners may choose 2 or more Learning Areas from the Elective component. Learners are expected to meet the following requirements to be awarded a GETC-ABET qualification: RULES OF COMBINATION FOR THE GETC-ABET QUALIFICATION: 120 CREDITS FUNDAMENTALS COMPONENT: COMPULSORY 1. 2. 3. One Official Language: 23 Credits Mathematical Literacy: 16 Credits OR Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences: 16 Credits NOT BOTH CORE COMPONENT: COMPULSORY 1. 39 CREDITS 32 CREDITS Life Orientation: 32 Credits GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 5|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 ELECTIVES COMPONENT: OPTIONAL 51 CREDITS Academic Learning Areas: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Human and Social Sciences: 23 Credits Natural Sciences: 15 Credits Economic and Management Sciences: 21 Credits Arts and Culture: 17 Credits Technology: 11 Credits One Additional Official Language (Excluding the language chosen as a Fundamental): 23 Credits Vocational Learning Areas: 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Applied Agriculture and Agricultural Technology: 20 Credits Ancillary Health Care: 45 Credits Small, Medium and Micro Enterprises: 17 Credits Travel and Tourism: 38 Credits Information Communication Technology: 23 Credits Early Childhood Development: 26 Credits Wholesale and Retail: 37 Credits OPTION 1 (5 Learning Areas) TWO Fundamentals ONE Core and TWO Electives OPTION 2 (6 Learning Areas) TWO Fundamentals ONE Core and THREE Electives OPTION 3 (7 or more Learning Areas) TWO Fundamentals ONE Core and FOUR Electives Critical Cross-field Outcomes (CCFO): UNIT STANDARD CCFO IDENTIFYING Identify and solve problems in which responses display that responsible decisions using critical and creative thinking have been made. UNIT STANDARD CCFO WORKING Work effectively with others as a member of a team, group, organisation and community. UNIT STANDARD CCFO ORGANISING Organise and manage oneself and one`s activities responsibly and effectively. UNIT STANDARD CCFO COLLECTING Collect, analyse, organise and critically evaluate information. UNIT STANDARD CCFO COMMUNICATING Communicate effectively using visual, mathematical and/or language skills in the modes of oral and/or written presentation. UNIT STANDARD CCFO SCIENCE Use science and technology effectively and critically, showing responsibility towards the environments and health of others. UNIT STANDARD CCFO DEMONSTRATING GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 6|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 Demonstrate an understanding of the world as a set of related systems by recognising that problem-solving contexts do not exist in isolation. 3. UNIT STANDARDS FOR AAAT4 LEARNING AREA The AAAT4 Learning Area comprises the following unit standards: SAQA ID 13354 13355 113356 13357 13358 SAQA ID 13354 US US TITLE Demonstrate an understanding of agriculture as a challenging and applied system Demonstrate an understanding of the physical and biological environment and its relationship to sustainable crop production Assess the influence of the environment on sustainable livestock production Demonstrate an understanding of agricultural production management practices in relation to the socio-economic environment Implement and maintain the principles, systems, practices and technology applicable to an agricultural venture Total US US TITLE Demonstrate an understanding of agriculture as a challenging and applied system CREDITS 2 4 4 3 7 20 CREDITS 2 PURPOSE OF THE UNIT STANDARD A learner credited with this competence will be capable of: discovering the nature of agriculture; differentiating between the various agricultural disciplines; and observing and analysing the geographical distribution and economic impact of agriculture. LEARNING ASSUMED TO BE IN PLACE AND RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING Open GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 7|Pa g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: SPECIFIC OUTCOME 1 Investigate the nature of agriculture as an applied science and relate it to other sciences ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The nature of agriculture as an applied science is described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Agriculture is clearly defined. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The relationship between agriculture and the natural sciences is established. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The significance of the relationship between agriculture and other sciences is discussed. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 2 Identify various agricultural disciplines and describe how they are linked SPECIFIC OUTCOME 3 Analyse the geographical distribution of agriculture and its socio-economic impact. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 4 Describe agricultural technology and its link to applied agriculture. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 5 Investigate the opportunities and challenges of agriculture in developing society. OUTCOME RANGE Examples of agricultural disciplines include crop science; soil science; agricultural economics; agricultural engineering; animal science; horticultural science; agricultural forestry and agricultural extension. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The links between agricultural and other economic activities are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Agricultural technology as a field in agriculture is described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The role of agriculture in food security is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The principles of appropriate agricultural technology are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The significance of commercial agriculture for social development is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Applications of agricultural technology are given. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The link between agricultural technology and applied agriculture is shown ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The significance of commercial agriculture for economic empowerment is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Various agricultural disciplines are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Agricultural disciplines are described and listed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Agricultural disciplines are compared and contrasted. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Relationships between the disciplines are discussed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Maps to show the type and distribution of agricultural production are labelled, interpreted, summarised and presented. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Information which summarises and demonstrates the significance of agriculture in society is collected and presented. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Information which demonstrates the significance of agriculture in the society is summarised and presented. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Study options in agriculture fare investigated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Employment opportunities in agriculture are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Link between society and agriculture is established and clarified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 6 Link between economy and agriculture is established and clarified. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 8|Page Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SAQA US ID 13355 US TITLE CREDITS Demonstrate an understanding of the physical and biological 4 environment and its relationship to sustainable crop production PURPOSE OF THE UNIT STANDARD A candidate credited with this unit standard will be capable of: identifying and describing the nature of soil; soil as a factor in agricultural production; climatic factors influencing crop production and their practical implications; the importance of water as a factor in agricultural production; the influence of topography on agricultural production; biological organisms as a factor influencing crop production and assessing the effects of crop production practices on the sustainability of the environment. LEARNING ASSUMED TO BE IN PLACE AND RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING Open GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 9|Pa g e SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: SPECIFIC OUTCOME 1 Identify and describe the nature of soil. OUTCOME RANGE Physical properties of soil ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The principle that soil is a product of its environment is described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Soil components are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Soil texture is identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Soil texture is described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Soil structure is identified SPECIFIC OUTCOME 2 Analyse soil as a factor in crop production ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Reasons why soil is a factor in crop production are provided. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Factors affecting the role of soil in crop production are described ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The concept of soil productivity is explained ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Factors that improve soil productivity and crop production are investigated ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Soil limitations in crop production are identified ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SPECIFIC OUTCOME 3 Identify and describe climatic factors influencing crop production and their practical implications ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Climatic factors influencing crop production are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Climatic factors influencing crop production are described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The influence of climatic factors on crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Crop production practices that can be adapted to climatic factors are investigated and reported SPECIFIC OUTCOME 4 Identify and describe the importance of water as a factor in crop production. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 5 Identify and describe the influence of topography on crop production. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 6 Identify, describe and explain the biological organisms as a factor influencing crop production. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 7 Assess the effects of crop production practices on the sustainability of the environment. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Sources of water are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Topography is defined and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The beneficial effects of micro-organisms on crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The concept of sustainability is explained and defined. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The role of water in crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The principle of water as a finite resource in crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The optimal use of water resources in crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Conclusions regarding the significance of water in crop production are ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Topography as a factor influencing crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Topography as a factor influencing crop production practices is evaluated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Practices for overcoming topographical limitations to crop production are investigated and reported GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The harmful effects of micro-organisms in crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Control options of harmful microorganisms in crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The beneficial effects of invertebrates in crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Existing crop production practices are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Crop production practices that enhance agricultural sustainability are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Crop production practices that have a negative impact on the sustainability of the environment are identified and explained. 10 | P a g e CRITERION 6 Ways to overcome soil limitations in crop production are explained and justified. Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 drawn. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 The harmful effects of invertebrates on crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 6 Control options for invertebrates in crop production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 7 Weeds as a limiting factor in crop production is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 8 Control options for weeds in crop production are discussed. 1. The concept of sustainability is explained and defined. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 11 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SAQA US US TITLE ID 113356 Assess the influence of the environment on sustainable livestock production CREDITS 4 PURPOSE OF THE UNIT STANDARD A candidate credited with this general competence will be able to: Describe and analyse the different components of a typical business plan and design a business plan relevant to a selected business idea. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 12 | P a g e SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: SPECIFIC OUTCOME 1 Identify and describe environmental factors influencing the veld. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Ecological factors that influence the veld are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The significance of ecological factors that influence the veld are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The three major vegetation types are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The three major vegetation types are explained. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 2 Assess and modify the influence of veld composition on livestock feeding preferences and habits. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The concept of veld composition is investigated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Veld composition as a factor in veld management is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Palatable and nonpalatable species of plants are distinguished. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Browsing and grazing habits are distinguished. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Livestock preferences and needs are distinguished. Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SPECIFIC OUTCOME 3 Analyse and describe environmental factors that influence livestock selection. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 4 Investigate supplementary feeding options for livestock production. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 5 Identify and describe beneficial and harmful organisms that influence livestock production. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The significance of environment as a factor influencing livestock selection is investigated and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The different ways of supplementary feeding are identified. OUTCOME RANGE Emphasis on locally important parasites and diseases ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Livestock breeds and their requirements (characteristics) are analysed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The regionalisation of the livestock industry as a factor influencing livestock selection, is investigated and analysed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The management of existing environmental factors ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Ways of supplementary feeding appropriate to the learners` context are distinguished. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The different types of cultivated pastures are investigated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Different grazing control practices on cultivated pastures are distinguished. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Licks as dietary supplements are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Beneficial organisms are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The effects of internal and external parasites in livestock production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Noxious plants that hinder livestock production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Control options for internal and external parasites are discussed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Major livestock diseases are identified and described. ASSESSMENT GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 SPECIFIC OUTCOME 6 Conduct an investigation into the effects of agricultural management practices on the sustainability ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Principles of veld management are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The concept of sustainability is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Existing livestock production practices are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Livestock production practices that enhance agricultural sustainability are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Livestock production practices that have a negative impact on the sustainability of the environment are identified and explained. 13 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 CRITERION 6 Control and treatment interventions and programmes for livestock disease are discussed. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 14 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SAQA US ID 13357 US TITLE Demonstrate an understanding of agricultural production management practices in relation to the socio-economic environment CREDITS 3 PURPOSE OF THE UNIT STANDARD A candidate credited with this competence will be capable of: explaining and applying ethical business principles to an agricultural enterprise; explaining the influence of supply and demand on agricultural production; distinguishing between different land ownership and tenure systems; discussing the relationship between entrepreneurship and agricultural ventures; and explaining the role and importance of human resources in agricultural production. LEARNING ASSUMED TO BE IN PLACE AND RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING Open GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 15 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: SPECIFIC OUTCOME 1 Apply ethical business principles to an agricultural enterprise. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 2 Modify agricultural production practices to a changing business environment. OUTCOME RANGE Case studies and/or in the learner`s context; the concept of gross margin, including basic (elementary) bookkeeping OUTCOME RANGE Local and national ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The business principles related to an agricultural enterprise are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The concept of gross margin is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Simple enterprise budgets are interpreted. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The significance of ethical business principles in an agricultural enterprise is explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Ethical business principles are applied. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The concept of supply and demand is defined and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION RANGE By way of appropriate, real life, agricultural examples. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The impact of supply and demand in relation to agricultural production is analysed and explained. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 3 Distinguish between different land ownership & tenure systems in relation to agricultural production ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The concepts of land tenure systems and ownership are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Applicable land tenure systems are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Applicable land tenure systems are analysed, compared and contrasted. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Possible agricultural land management options for the different land tenure systems are suggested. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 4 Investigate the relationship between entrepreneurship and agricultural ventures. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 5 Explain the role and importance of human resources in agricultural production. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The concept of entrepreneurship is explained. OUTCOME RANGE Introduction of the principles of basic labour relations ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The link between entrepreneurship and an agricultural venture is investigated and discussed. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 . Categories/types of human resources relevant to agricultural production are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Entrepreneurial principles are applied. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The characteristics of the different categories of human resources in relation to agricultural production are identified and described. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The importance of the different categories of human resources in relation to agricultural production is evaluated and reported. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The roles of various human resources in agricultural production are defined. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 6 The application of business principles is evaluated. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 16 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SAQA US ID 13358 US TITLE Implement and maintain the principles, systems, practices and technology applicable to an agricultural venture CREDITS 7 PURPOSE OF THE UNIT STANDARD A candidate credited with this competence will be capable of: selecting an appropriate agricultural venture; identifying and selecting agricultural systems appropriate to the selected venture; identifying, selecting, and implementing agricultural practices appropriate to the selected venture; identifying and select technology appropriate to the selected agricultural venture in the learners context.; implementing, operating and maintaining agricultural technology relevant to the selected; and evaluating the selected agricultural venture according to applicable criteria. LEARNING ASSUMED TO BE IN PLACE AND RECOGNITION OF PRIOR LEARNING Agri/002; and/or Agri/003; Agri/004 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 17 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA: SPECIFIC OUTCOME 1 Select an appropriate agricultural venture. SPECIFICOUTCOME 2 Implement agricultural systems appropriate to the selected venture. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Prevailing physical conditions are identified and explained. OUTCOME RANGE "Systems" relates to, for example, the degree of intensity and/or combination of agricultural ventures. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Prevailing biological conditions are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Prevailing socio-economic factors are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 An agricultural venture appropriate to prevailing conditions is selected. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 The choice of agricultural venture is justified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 The appropriate agricultural system(s) are identified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 The appropriate agricultural systems are explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The most appropriate/suitable agricultural system is selected. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 The choice of agricultural system is justified and reported. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 3 Identify, select, and implement agricultural practices appropriate to the selected venture. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 4 Apply technology appropriate to the selected agricultural venture in the learner’s context. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 5 Operate and maintain agricultural technology relevant to the selected agricultural venture. SPECIFIC OUTCOME 6 Evaluate the selected agricultural venture according to applicable criteria. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Appropriate agricultural practices are identified and explained. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Examples of appropriate technology relevant to the agricultural venture are identified and investigated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Conditions for successful operation of the selected technology are identified. OUTCOME RANGE Including gross margin analysis ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Appropriate agricultural practices are compared. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Appropriate agricultural practices are selected. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Choices of agricultural practices are justified and reported. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Appropriate agricultural technology relevant to the agricultural venture in the learners` context is selected. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 The choice of appropriate technology is justified. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Appropriate agricultural practices are implemented. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Factors for successful operation of agricultural technology are identified for the selected venture. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Appropriate agricultural technology is implemented in the selected venture. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Appropriate agricultural technology is operated in the selected venture. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Appropriate agricultural technology is maintained in the selected venture. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 6 Operation of agricultural appropriate technology is sustained GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 ASSESSMENT CRITERION 1 Appropriateness of the agricultural venture is evaluated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 2 Appropriateness of the agricultural systems is evaluated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 3 Appropriateness of the agricultural practices is evaluated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 4 Appropriateness of the agricultural technology is evaluated. ASSESSMENT CRITERION 5 Suggestions for improvement of the agricultural venture are proposed. 18 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 4. LTSM IN PALCs The possible Learning and Teaching Support Materials to be used in the learning area are to be found in the catalogue provided by the AET Curriculum Directorate of the Department. However, the catalogue listed LTSM do not represent an exhaustive list, any other resources that respond positively to the prescribed learning area unit standards could be used. 5. WEIGHTING OF THE SPECIFIC OUTCOMES AND ASSESSMENT CRITERIA UNIT STANDARD 13354 13355 13356 13357 13358 TOTAL CREDITS Demonstrate an understanding of agriculture as a challenging and applied system Demonstrate an understanding of the physical and biological environment and its relationship to sustainable crop production Asses the influence of the environment on sustainable livestock production Demonstrate an understanding of agricultural production management practices in relation to the socio-economic environment Implement and maintain the principles , systems, practices and technology applicable to an agricultural venture 2 WEIGHTING %/ MARKS 10 4 20 4 20 3 15 7 35 20 100 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 19 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 6. CORE KNOWLEDGE AREAS Unit standard 1: US ID 13354: Demonstrate an understanding of agriculture as a challenging and applied system Specific Outcome 1: Investigate the nature of agriculture as an applied science and relate it to other sciences Knowledge Skills AC1 & 2: Nature of agriculture Describing agriculture as an applied science Defining agriculture AC3 & 4: Relationship between agriculture and Establish & discuss the relationship between agriculture natural science & natural sciences Specific Outcome 2: Identify various agricultural disciplines and describe how they are linked Knowledge Skills AC1-4:Various agricultural disciplines Identify, list, label, describe, compare and discuss agricultural disciplines Values Showing insight of how various agricultural disciplines are linked Specific Outcome 3: Analyse the geographical distribution of agriculture and its socio-economic impact Knowledge Skills AC1 & 2:The geographical distribution of Explain links between agriculture and other economic agriculture and its socio-economic impact activities. Label, interpret, summarise and present the type and distribution of agricultural production AC 3 - 6: The significance of agriculture in society Collect, summarise and present information on the significance of agriculture. Establish how agriculture link with society & economy Specific Outcome 4: Describe agricultural technology and its link to applied agriculture Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Agricultural technology and its link to Describe agricultural technology applied agriculture Explain principles of appropriate technology Give applications of agricultural technology by way of examples (tools, technology, methods) Specific Outcome 5: Investigate the opportunities and challenges of agriculture in developing society Knowledge Skills GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 Values Demonstrating an understanding of agriculture and its relationship to other sciences Values Demonstrate the impact of geographical distribution on socio-economic conditions Values Care of implements (technology, tools) by way of cleaning and servicing them after use Values 20 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 AC1-5:Opportunities and challenges of agriculture in developing society Explain the role of agriculture in food security. Explain the significance of commercial agriculture for economic and social empowerment. Investigate study options (career opportunities) in agriculture. Explain employment opportunities Application of knowledge acquired in assisting subsistence farmers, commercial farmers and the society Unit standard 2: US ID 13355: Demonstrate an understanding of the physical and biological environment and its relationship to sustainable crop production Specific Outcome 1: Identify and describe the nature of the soil Knowledge Skills AC1-5: Physical and biological environment Describe soil as a product of the environment Identify components of the soil. Identify and describe soil texture(sand, loam, clay) and structure (single grain and crumb) Specific Outcome 2: Analyse soil as a factor in crop production Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Soil as a production factor Give reasons why soil is a factor in crop production. Describe factors affecting soil as a production factor Explain soil productivity and limitations (shortcomings) Values Care of soil (preventing soil erosion, leaching of nutrients, water runoff) Appreciation of soil as a natural resource Values Appreciation of soil as a production factor Specific Outcome 3: identify and describe climatic factors influencing crop production and their practical implications Knowledge Skills Values AC1-4: Climatic factors influencing crop Displaying understanding of the role of climatic Identifying, explaining and describing climatic factors production factors (rainfall, temperature, wind) influencing crop production Specific Outcome 4: Identify and describe the importance of water as a factor in crop production Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Importance of water in crop production Identify sources, quality and quantity of water Explain role of water in crop production Explain the principles, optimal use and significance of water as a finite resource GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 Values Responsible use of water (conservation) Maintenance of water sources Water recycling 21 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 Specific Outcome 5: Identify and describe the influence of topography on crop production Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Topography as a factor influencing Define and explain topography as a crop production factor crop production Evaluate topography as a factor influencing crop production practices Investigate and report practices for overcoming topographical limitations (shortcomings) Specific Outcomes 6: Identify, describe and explain the biological organisms as a factor in crop production Knowledge Skills AC1-7:The micro-organisms as a factor Identify, describe and explain both the beneficial and harmful influencing crop production effects of micro-organisms Indicate the control measures of both harmful microorganisms and invertebrates Explain the harmful effects of weeds and their control thereof Specific Outcome 7: Assess the effects of crop production practices on the sustainability of the environment Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Crop production practices on the Define the concept sustainability sustainability of the environment Identify and explain both positive and negative impact of existing crop production practices on the sustainability of the environment Values Demonstrate understanding of topography as a factor influencing crop production (contour planting) Values Have an insight into soil micro-biology as a factor influencing crop production Values Evidence of an understanding of the crop production practices is displayed Unit standard 3: US ID 13356: Assess the influence of the environment on sustainable livestock production Specific Outcome 1: Identify and describe environmental factors influencing the veld Knowledge Skills AC 1-4: Environmental factors influencing the Identify and explain the ecological factors and their veld influence on the veld List and explain the different types of veld) sweetveld,sourveld, mixed veld) Values Show an insight into the environmental factors influencing the veld Specific Outcomes 2: Assess and modify the influence of veld composition on livestock feeding practices and habits Knowledge Skills Values AC1-5: Veld composition as a factor Display an understanding of the influence Explain and describe the composition of the veld GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 22 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 influencing livestock feeding preferences and habits List and explain different types of feeding habits of animals (browsers., grazers) Explain the concept selective grazing as one of the feeding preferences and needs by animals Specific outcome 3: Analyse and describe environmental factors that influence livestock selection Knowledge Skills AC1-4: Environmental factors influencing Investigate and explain the importance of environment as a livestock selection factor influencing livestock selection Analyse and investigate livestock breeds and their needs (requirements) Analyse livestock breeding areas (regions-national, provincial, local) Discuss the management of the environmental factors Specific Outcome 4: Investigate supplementary feeding options for livestock production Knowledge Skills AC1-5: Supplementary feeding options for Identify different ways (methods) of supplementary feeding livestock production (green fodder, silage, roughage, concentrate) Distinguish different types of cultivated pastures Distinguish different grazing control practices on cultivated pastures Identify licks as dietary supplements (rumovite block) Specific Outcome 5: Identify and describe beneficial and harmful organisms that influence livestock production Knowledge Skills AC1-5: Beneficial and harmful organisms Identify and describe beneficial (useful) and harmful influencing livestock production organisms (parasites) Identify and describe effects of both internal and external parasites Identify and describe noxious (poisonous) plants which affect livestock products ( skin/ hides, meat, milk ) Discuss the control of internal (e.g. dosing) and external (e.g. dipping, injection by tramisol) parasites Identify and describe major livestock diseases GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 of veld composition on livestock feeding preferences and habits Values Demonstrate understanding of the influence of environment on livestock selection Values Use of appropriate supplementary feeding methods for livestock production Values Ability to indicate effects of both beneficial and harmful organisms (internal & external parasites) 23 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 Specific Outcome 6: Conduct an investigation into the effects of agricultural management practices on the sustainability of environment Knowledge Skills Values AC1-5: Effects of agricultural management Demonstrate understanding of principles Explain principles of veld management practices on sustainability of livestock of veld management and how they Explain the concept ‘sustainability’ production impact on agricultural sustainability and Identify livestock production practices and indicate how they environment enhance agricultural sustainability Identify and explain negative impact of livestock production practices on sustainability of the environment Unit standard 4: US ID 13357: Demonstrate an understanding of agricultural production management practices in relation to the socio-economic environment Specific outcome 1: Apply ethical business principles to an agricultural enterprise Knowledge Skills AC 1-6: Ethical business principles to an Use case studies to identify, explain and apply business agricultural enterprise (venture) principles related to an agricultural enterprise Explain and interpret concepts such as gross margin and simple enterprise budget Evaluate application of business principles Specific Outcome 2: Modify agricultural production practices to a changing business environment Knowledge Skills AC 1-2: Agricultural production practices in a Define and explain the concepts supply and demand changing business environment Explain and analyse the impact of supply and demand in agricultural production Values Uphold ethical business principles in agricultural Values Illustration using real life agricultural examples Specific Outcome 3: Distinguish between different land ownership and tenure systems in relation to agricultural production Knowledge Skills values AC 1-4 : Different land ownership and tenure Identify and explain the concepts land tenure systems and Display an insight into different land systems in relation to agricultural production ownership and tenure systems for effective ownership agricultural production Identify, describe, analyse and compare applicable land tenure Suggest possible agricultural management options for different land tenure systems GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 24 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 Specific Outcome 4: Investigate the relationship between entrepreneurship and agricultural ventures Knowledge Skills AC 1-3:The relationship between Explain the concept ‘ entrepreneurship’ entrepreneurship and agricultural ventures Discuss the link between entrepreneurship and agricultural venture Use case studies to apply entrepreneurial principles Specific Outcome 5: Explain the role and importance of human resource in agricultural production Knowledge Skills AC 1-4: The role and importance of human Identify types (categories) of human resources (labourer) resource in agricultural production relevant to agricultural production Identify and describe characteristics of different types (categories) of human resources Define roles of different human resources in agricultural production Identify principles of basic labour relations prescripts Values Demonstrate an understanding of entrepreneurial principles applicable to agricultural ventures Values Display sound knowledge of the role and importance of human resources in agricultural production Unit standard 5: US ID 13358: Implement and maintain the principles, systems, practices and technology applicable to an agricultural venture Specific Outcome 1: select an appropriate agricultural venture Knowledge Skills AC1-5: Appropriate agricultural venture Identify & explain prevailing physical and biological conditions Identify & explain prevailing socio-economic factors Motivate the choice of an appropriate agricultural venture Specific Outcome 2: Implement agricultural systems appropriate to the selected venture Knowledge Skills AC 1-4: Agricultural systems appropriate to Select and explain appropriate agricultural systems the selected venture Select and motivate the most appropriate/suitable agricultural system GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 values Showing an understanding of relevant and appropriate agricultural venture Values Ability to select and motivate the most appropriate agricultural systems 25 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 Specific Outcome 3: Identify, select and implement agricultural practices appropriate to the selected venture Knowledge Skills AC 1-5: Agricultural practices appropriate to Identify, select ,explain and compare appropriate the selected venture agricultural practices Motivate the choice of agricultural practices Use scenarios showing implementation of appropriate agricultural practices Specific Outcome 4: Apply technology appropriate to the selected agricultural venture in the learners context Knowledge Skills AC 1-3: Technology appropriate to the Give examples of appropriate technology relevant to the selected agricultural venture in the learners agricultural venture context Select appropriate technology relevant to the agricultural venture in the learners context Motivate the choice of appropriate technology Specific Outcome 5: Operate and maintain agricultural technology relevant to the selected venture Knowledge Skills AC 1-6: Agricultural technology relevant to the Identify conditions for successful operation of the selected selected venture venture Identify factors for successful operation of agricultural technology for the selected venture Show how to implement appropriate agricultural technology in a selected venture Show how to sustain operation of agricultural appropriate technology Specific outcome 6: Evaluate the selected agricultural venture according to applicable criteria Knowledge Skills AC 1-5: Evaluating the selected agricultural Use of scenarios to evaluate the appropriateness of venture according to applicable criteria agricultural venture, systems, practices and technology Suggesting for improvement of the agricultural venture GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 Values Display an understanding of appropriate and relevant agricultural practices Values Show an understanding of appropriate technology selected for agricultural venture Values Indicating the maintenance and operation of agricultural technology relevant to agricultural ventures Values Understanding of relevant criteria and suggestions for appropriateness of venture, systems, practices and technology 26 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 7. TAXONOMIES USED IN SCAFFOLDING QUESTIONS There are numerous taxonomies used in scaffolding questions. However, the AAAT4 learning area assessment will be mainly focused on Bloom’s taxonomy and will include the following: Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation 8. SITE-BASED ASSESSMENT (FORMATIVE) The ABET level 4 site-based assessment tasks are part of a developmental process aimed at increasing capacity in the ABET sector and enhancing the level of teaching and learning in the PALCs. The tasks are also aimed at quality assurance and standardisation of site-based assessment in all PALCs across the country. In delivering the ABET level 4 curriculum, it is suggested that the assessment tasks should be integrated into planning for teaching and learning and implemented in conjunction with the assessment guidelines for ABET. Teaching, learning and assessment are intertwined and planning for assessment is an integral part of planning for teaching and learning. It is therefore strongly recommended that the assessment tasks should be conducted as part of the teaching and learning process. This means that the assessment tasks should be incorporated into an educator’s work schedule for the year. It is further recommended that educators use different teaching strategies and informal assessment to ensure that learners are adequately prepared for the formal assessment tasks. The tasks were carefully designed to ensure that a variety of skills are assessed in each learning area and that the unit standards and assessment criteria are adequately covered. The performance-based tasks are to be completed or administered over a period of time whilst the pen-and–paper tasks should be administered under controlled conditions. It is recommended that the tasks be used as part of the formal site based assessment programme at PALCs. All formal assessment must be recorded and ongoing feedback must be given to learners. Evidence of the formally recorded assessment tasks should be included in the educator’s portfolio while the learners’ evidence of learning must contain the recorded pieces of evidence for each assessment. Continuous moderation at site level, cluster level, district level and provincial level is strongly recommended. The results of assessment should be used to support the learners’ development and make improvements to the learning and teaching process. It is important that learners who might experience barriers to learning and development are identified early, assessed, and provided with learning support. In such cases the assessment tasks should be adapted to accommodate these learning needs. We expect you to critically engage with the assessment tasks as we are aware that they do not reflect a “zero-defect” or a “one-answer-solution”. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 27 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 9.1 STRUCTURE OF SBA TASKS The SBA is made out of an educator’s guide and a learner’s tasks. The learner’s tasks for each learning area contain five assessment tasks focusing on the unit standards that should be covered in formative assessment. The educator’s guide contains the assessment instrument(s) (memorandum, rubric and/or checklist) for each of the assessment tasks. The tasks include a variety of appropriate assessment strategies and different forms of assessment of which one is a project as prescribed by Umalusi. Additional is a learning area assessment plan which is aimed at assisting the educator with the spreading of the formal assessment tasks throughout the year. Each SBA task is worth 50 marks and the five SBA tasks total 250 marks. All formal and informal assessment leading to formal moderation must be recorded accordingly. These marks should be converted to 50% which is the weighting of the site-based assessment. Moderation of these SBA tasks must be done according to the provincial management plan on the conduct, administration and management of the GETC-ABET Level 4 examinations and assessment. Exemplar Learning Area Assessment Plan LEARNING AREA: APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY LEARNING AREA CODE: AAAT Assessmen 1 2 t Tasks Form(s) of TEST ASSIGNMENT assessmen t US IDs and US ID 13354 US ID 13356 SOs and SO 1: AC1-3 SO 1: AC 1-3 ACs SO 2: AC 2,3 SO 2: AC SO 3: AC 1,2 1,2,4,5 SO 3: AC 1-4 US ID 13355 SO 5: AC 1-6 SO 1-7 SO 6: AC 1,2,3 US ID 13356 SO 1-6 US ID 13357 SO 1: AC 1,4,5 US ID 13357 S0 1, 2,3,5 USID13358 Marks 50 Tools of MEMORAND Assessmen UM t Dates to be AUGUST completed 50 MEMORANDU M GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 APRIL Year: 2008 3 4 5 PROJECT PRACTICAL DEMONSTRA TION US ID 13355 SO 1: AC 1,3,4,5 SO 2 AC 1-6 SO 3 AC 1,2,3 SO 4 AC 1,2,3,4,5 SO 7 AC 1,2,3,4 INVESTIGATIO N 50 MARKING GUIDELINE CHECKLIST MARCH 50 MARKING GUIDELINE US ID 13355 SO 1: AC 3,4 SO 2: AC 2,3,4 SO 4: AC 2,4 SO 6: AC 3,4 SO 7: AC 2,3 US ID 13358 SO 3: AC 1,3 SO 4: AC 2,3,5 SO 5: AC3,4 50 RUBRIC MAY US ID 13354 SO 4 AC 2,3 SO 5 AC 1,2 US ID SO 3 SO 6 SO 7 13355 AC 1,2,3 AC 3,7 AC 2,3,4 MAY 28 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 9.2 EXEMPLAR SBA TASKS GENERAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING CERTIFICATE NQF LEVEL 1 ABET LEVEL 4 SITE-BASED ASSESSMENT LEARNING AREA : APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY CODE : AAAT4 TASK : TEST TIME : 1 HOUR MARKS : 50 This assessment task consists of 5 pages. INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This test consists of TWO sections: 2. Section A: 20 marks Section B: 30 marks. 3. This task should be completed within an hour. 4. Answer ALL questions. SECTION A QUESTION 1 Various possible options are provided as answers to the following questions. Choose the correct answer and write only the correct letter (A – D) next to the corresponding question number (1.1 – 1.10) in the ANSWER BOOK. 1.1 An example of an agricultural venture is ….. A B piggery. budgeting. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 29 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 C D 1.2 (1) Tick Tapeworm Blowfly Louse (1) A tertiary agricultural industry renders the following service: A B C D 1.5 economics. geomorphology. meteorology. botany. A ... is a parasite found inside the body of an animal. A B C D 1.4 (1) The science that helps us to understand weather and climate better is known as …. A B C D 1.3 motivation. grazing. Producing crops. Harvesting crops. Irrigating the soil. Packaging produce. (1) The type of soil that can be rolled into a sausage and bent into a ring is … A B C D silt. loam. sand. clay. (1) [5] QUESTION 2 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Choose the correct answer and write only ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the corresponding question number (2.1 – 2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. 2.1 Soil texture plays an important role in crop production. (1) 2.2 It is important to practice rotational grazing on a farm. (1) 2.3 Farm workers are not affected by labour legislation. (1) 2.4 Agriculture is about cultivating land and rearing stock, piggery, poultry). (1) 2.5 Technology is not important in milk production as a venture. domestic animals (livestock, small (1) [5] QUESTION 3 Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing word(s).Write only the word(s) next to the question number (3.1 – 3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. 3.1 3.2 Water … with automatic valves is used to ensure a supply of cold and clean water all the time. (1) … property is when the land has been passed from generation to generation. (1) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 30 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 3.3 The loss of water from the soil in the form of vapour is known as … (1) 3.4 The method of ploughing along the slope is known as … ploughing. (1) 3.5 … is the physical feature of the landscape. (1) [5] QUESTION 4 Choose a/an item/word/description from COLUMN B that matches a/an item/word/description in COLUMN A. Write only the correct letter (A – G) next to the corresponding question number (4.1 –4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. COLUMN A COLUMN B 4.1 A place where fruit trees are grown A Human resources When animals are allowed to walk around freely and choose plants they eat B Skilled workers 4.2 C Freehold D Selective grazing E Concentrates F Orchard G Market Feed made up as a balanced ration 4.3 People who help the farmer in production 4.4 4.5 A system whereby a person owns land ‘ (5) SECTION B QUESTION 5 Read the case study below and answer the questions that follow. Sibusiso is a small scale farmer who in the past five years was using things like hand hoes and ox- driven ploughs for his crop production venture. He wanted to use modern technology but did not have much information. He therefore went to seek advice from the local extension officer. He was advised by the local extension officer that there is a wide variety of farming technologies. The extension officer also informed him that the technology to be used should be affordable. Sibusiso was also informed that technology will help to make better use of water, save time, make work easier and save energy. Sibusiso took the advice of the extension officer and bought affordable technology for his crop production. This led to improved production. ( Adapted from Applied Agriculture Book 3) 5.1 State FIVE ways in which the use of modern technology will help Sibusiso. (5) 5.2 List TWO traditional technologies used by Sibusiso. (2) 5.3 Name THREE modern technologies that Sibusiso may use for crop production. (3) 5.4 Mention FIVE ways in which to handle and keep technology correctly. (5) [15] GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 31 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 QUESTION 6 Study the table below on crop rotation and answer the questions that follow: Plot First year Second year Third year A Maize Sunflower Beans B Fallow Beans Maize C Beans Maize Fallow D Sunflower Fallow Sunflower 6.1 Explain the term ‘crop rotation.’ (2) 6.2 Mention FOUR advantages of a crop rotation system. (4) 6.3 State the reason why sunflower cannot be planted on the same plot year after year. (2) 6.4 List TWO crops from the table that can be easily damaged by frost. (2) 6.5 What is the role of a fallow in a crop rotation system? (2) 6.6 Identify TWO ventures from the table.. (2) 6.7 List ONE produce made from the crop in plot D. (1) [15] GRAND TOTAL: 50 TASK 2: ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This task consists of TWO activities. 2. This task must be completed within an hour. In order for you to complete the task, you must have read about broiler and layer farming. You should also have information on market survey and feasibility study. ACTIVITY 1: BROILERS AND LAYERS Read the passage and answer the questions that follow. Transporting broilers or old hens live, you need something to carry them. You could use a plastic crate or just a big cardboard box with holes cut on the sides so that the birds can breathe. It is important that you do not put too many chickens into a container. If you treat chickens badly, you may be fined by the Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (SPCA) inspectors. Eggs are usually sold according to grade (different weight categories). If you do not have a proper egg grader, you could sell mixed sizes. It is helpful to have proper egg trays or egg boxes. This will mean less egg breakages. Some producers sell boiled eggs when there is a demand. (Source: The South African Chicken Book ) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 32 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 1.1 Explain the terms ‘broiler chicken’ and ‘layer chicken’. (4) 1.2 State TWO ways from the passage through which you could transport broilers. (4) 1.3 At what age are broilers ready to be sold? (1) 1.4 Mention THREE different weight categories (grades) of eggs. (3) 1.5 According to the passage, what can be used to carry eggs? (1) 1.6 Name the organisation which will fine people who handle chickens badly. (1) 1.7 Mention TWO professionals/institutions that can give you advice on poultry farming. (2) 1.8 List TWO most common diseases in chicken. (2) 1.9 List SEVEN equipment/technologies you will need for your chicken farming business. (7) 1.10 State FOUR ways that could be used to improve village chicken farming. (4) [29] ACTIVITY 2: FEASIBILITY STUDY AND MARKET SURVEY 2.1 It is important to do a feasibility study before you start a business. Mention SIX items that can be part of a feasibility study for poultry /chicken venture. (6) Mention FIVE questions that you should ask yourself when you do market survey for poultry/chicken venture. (5) 2.3 Name FIVE places where you can sell boiled eggs. (5) 2.4 Name FIVE points that you should consider when you evaluate your poultry/chicken venture. 2.2 GRAND TOTAL: (5) [21] 50 TASK 3: PROJECT INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This project consists of THREE activities. 2. The project is a group task and should be done in groups of not more than four learners. 3. Each activity should be submitted on the due date. 4. The project should be completed within three weeks from the date it was issued. The project is about the importance of drainage in plant growth. You are therefore expected to plant two bean seeds in two separate tins in order to observe how drainage affects plant growth. The planted seeds should be watered daily. Pour the same amount of water in each tin. You are further expected to write your findings as guided by the given questions. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 33 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 ACTIVITY 1: COLLECT MATERIAL For you to start with the project, you must collect the following materials: Two tins of the same size (you can use jam tins). Nail and hammer. Good planting soil. Two bean seeds. 250 ml container for watering. (10) ACTIVITY 2: PREPARATION AND PLANTING THE SEEDS Follow the steps below to prepare the material. Take the two tins and label them clearly as S and T. Use the nail and hammer to make holes at the bottom of tin S. Do not make holes in tin T. Put equal amounts of good planting soil in both tins. Plant a bean seed in each tin. Water the tins with the same amount of water every day for three weeks. (15) ACTIVITY 3: OBSERVE AND WRITE DOWN YOUR FINDINGS After three weeks, the seeds should have germinated. Observe the two plants Write your findings as guided by the following questions: 3.1 Describe the differences in the plants by looking at the following: appearance above soil. height of plant. colour. root growth. water drainage. (10) 3.2 Indicate the tin with the better growth. (1) 3.3 Indicate the tin with poor growth. (1) 3.4 Mention THREE possible reasons why plants in one tin have better growth. (3) 3.5 State TWO possible reasons why plants in the other tin have slower growth. (2) 3.6 List your conclusion based on the growth of the two plants in both tins. (4) 3.7 List steps that are to be taken to improve the growth of plants that shows slow growth. GRAND TOTAL: (5) [25] 50 TASK 4: INVESTIGATION INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This task consists of THREE activities. 2. Follow the guidelines as given in each activity. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 34 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 3. This investigation is a group task and must be completed in two weeks from the date it was issued. 4 You will be assessed on the effort of your visit, submission on time and the provision of relevant information. In order for you to complete the task, you must visit either a local livestock owner, a local farmer, an agricultural school/college or a local feedlot. ACTIVITY 1: Investigate feeding/grazing habits of farm animals. 1.1 In a group of not more than four learners, you must investigate the feeding/grazing habits of each of the farm animals listed below. Observe the animals as they feed/graze. Use the table below as a guide/example. Redraw the table below and record two observations for each animal. FARM ANIMAL Goats Sheep Cattle Poultry Pigs OBSERVATIONS (10) ACTIVITY 2: Investigating farm animal diseases 2.1 Ask the owner/farmer/livestock breeder to indicate which farm animals are mainly affected by the diseases in the table below. Get information about the agents that cause these diseases and two symptoms of each disease. Redraw the table given below as an example and record as the owner/farmer/breeder is providing you with information. Name of disease Farm animal affected What causes the disease Symptoms (Two for each disease) Redwater Tuberculosis Mastitis Anthrax Foot and mouth Newcastle Fowlpox Blue tongue (32) ACTIVITY 3: Investigating the economic disadvantages of the diseases. 3.1 3.2 Ask the farmer/owner/breeder to indicate FOUR reasons why diseases in farm animals are economically important. (4) You will be assessed on the effort of your visit, submission on time and the relevant information you supply. TOTAL: GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 50 35 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 TASK 5: WORKSHEET INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This worksheet consists of TWO activities. 2. This is an individual task and must be completed within an hour. 3. Answer the task on the provided worksheet. A farm manager like any other entrepreneur has to draw up a budget as a plan of the future income and expenditure of the venture. ACTIVITY 1: Drawing up a budget. Make use of the worksheet provided to draw up a budget for a tomato venture. One table is for expected expenses and the other is for expected income. Use the following steps for expected expenses. 1.1 List SEVEN expenditure items in a tomato venture. List the amount (how much/how many) you will need for each expense item. List the price that you shall have to pay for each item at a time. Write down the total price that you are expected to pay for each expense item. Use the following steps for expected income. 1.2 Write down the products you will sell for income. Write down the profit that you expect to receive for one item that you are going to sell. Write down the number of boxes that you expect to sell. Indicate the total income that you hope to receive from selling all boxes. Calculate and indicate the profit. [40] WORKSHEET NAME OF LEARNER:__________________________________ LEARNING AREA :____________________________________ DATE OF SUBMISSION:________________________________ GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 36 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 EXPECTED EXPENSES AMOUNT(How PRICE PER UNIT TOTAL PRICE much/how many) ITEMS TOTAL EXPENSES EXPECTED INCOME ITEMS AMOUNT(How many much) PRICE PER UNIT TOTAL PRICE TOTAL INCOME EXPECTED PROFIT [40] ACTIVITY 2: Answer the following questions on budget. 2.1 Explain the term budget. ______________________________________________________________ 2.2 Name TWO institutions that may assist you with a loan. ______________________________________________________________ 2.3 (2) Name TWO technologies that may assist you in drawing a budget. ______________________________________________________________ 2.5 (2) Which TWO documents will be able to assist you to draw a budget? _____________________________________________________________ 2.4 (2) (2) Mention TWO types of farming systems in agriculture. (2) [10] GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 37 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 GRAND TOTAL: 50 GENERAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING CERTIFICATE NQF LEVEL 1 ABET LEVEL 4 SITE-BASED ASSESSMENT LEARNING AREA : APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY CODE : AAAT4 TOOL : TEST TIME : 1 HOUR MARKS : 50 This assessment tool consists of 4 pages. INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This assessment task consists of the following unit standards: US 13354 SO1 AC2 SO3 AC 1 SO2 AC 4 SO5 AC1 US 13355 SO1 AC 1,4, SO2 AC4,6 SO3 AC 1,3 SO4 AC 3 SO5 AC1 US 13356 SO2 AC4,6 SO3 AC 3 SO4 AC6 SO5 AC 1,4 SO6 AC 1 US 13357 SO1 AC4 SO3 AC 1,6 SO5 AC 1,4 US 13358 SO2 AC4 SO3 AC1,2 SO4 AC2,3 SO5 AC1,3 2. Learners have to complete the test within an hour. 3. Learners must answer All questions. QUESTION 1 1.1 A (1) 1.2 C (1) 1.3 B (1) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 38 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 1.4 D (1) 1.5 D (1) [5] QUESTION 2 2.1 True/T (1) 2.2 True/T (1) 2.3 False/F (1) 2.4 True/T (1) 2.5 False/F (1) [5] QUESTION 3 3.1 Troughs (1) 3.2 Inherited (1) 3.3 Evaporation (1) 3.4 Contour (1) 3.5 Topography (1) [5] QUESTION 4 4.1 F (1) 4.2 D (1) 4.3 E (1) 4.4 A (1) 4. 5 C (1) [5] QUESTION 5 5.1 5.2 5.3 FIVE ways in which the use of modern technology will help Sibusiso. - better use of water - save water - make work easier - save energy - improved production. (5) TWO traditional technologies used by Sibusiso - hand hoes - ox-driven ploughs (2) THREE modern technologies that Sibusiso may use for crop production - tractors GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 39 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 5.4 harrowers planters water pumps/irrigators maize shelling machine harvesters Any three FIVE ways on how to handle and keep technology correctly. - equipment must be kept neat - equipment must be stored away when not used - used for the purpose that it was meant for - the condition of the equipment must be good - service regularly those that need service - must be cost effective - must be washed and kept clean - store under the roof shed/garage away from rain and sun burn (3) Any five (5) [15] QUESTION 6 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 Crop rotation is a practice whereby different crops are planted on the same land every year. (2) FOUR advantages of a crop rotation system. - helps the soil to stay rich and healthy - helps to control pests - helps to control diseases - gives resting time - prevent one sided use of plant food (4) Any four Sunflower cannot be planted on the same plot year after year - it will lead to a build up of diseases and pests. (2) TWO crops from the table that can be easily damaged by frost. - Beans - Maize (2) The role of a fallow in a crop rotation system - Allows the land to rest/allows the soil to regain the texture (2) TWO ventures from the table. - Maize production - Sunflower production - Bean production Any two (2) List ONE produce made from the crop in plot D. - oil - seeds Any one (1) [15] GRAND TOTAL: 50 TOOL 2: ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This assignment consists of the following unit standards: US 13358 SO2 AC SO3 AC3,5 SO4 AC1 US 13357 SO1 AC1,6 US 13356 SO5 AC5 SO6 AC5 US 13354 SO5 AC4 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 40 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 2. For this assignment, the learners must have read about farming on broilers and layers. They should also know market survey and feasibility study. 3. This assignment should be completed within an hour. ACTIVITY 1:BROILERS AND LAYERS 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 Broiler chicken – chicken kept mainly for meat layer chicken – chicken kept mainly for eggs (4) TWO ways from the passage in which you could transport broilers - may use a plastic crate - may use a big cardboard box with holes (4) Age at which broilers are ready to be sold - six(6) weeks (1) THREE different weight categories (grades) of eggs. - jumbo - extra large - large - medium - small (3) Any three Material used to carry eggs - egg trays/egg boxes (1) An organisation that will fine people who handle chickens badly - SPCA (1) TWO professionals/institutions that can give you advice on poultry farming - extension officer/office - veterinarian - Department of Agriculture Any two (2) TWO most common diseases in chicken - Newcastle disease - fowl pox (2) SEVEN equipment/technologies you will need for your chicken farming business - gas brooders - gas cylinders - paraffin - chick feed pans - chick founts - tubular plastic feeders - automatic drinkers electricity infrared tube drinkers laying nests water tanks plastic crates buckets wheelbarrows hard brooms shovels chicken wire fencing egg trays/egg boxes GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 Any seven (7) 41 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 1.10 FOUR ways to improve village chicken keeping - good housing to keep them safe - better diet/feed - clean water - vaccination against common diseases/pests - extra protection for broody hens and chicks Any four (4) [29] ACTIVITY 2 FEASIBILITY STUDY AND MARKET SURVEY 2.1 2.2 2.3 Six items that can be part of a feasibility study - chicken/broiler/layer cost - feed cost - equipment cost - medicine cost - salaries/wages - electricity - transport - water - market/ buyers (6) FIVE questions that you should ask yourself when you do market survey - Where will I sell broilers/layers/meat/eggs/my produce? - Who will I sell to? - Will I sell chicken live or dressed? - Who else are selling/competitors? - How much are they charging? - How old are their chicks? - Why will people buy from me? - What will be my price of live/dressed chick? - How can I sell per week? - Will I sell boiled or raw eggs? Any five (5) FIVE places where boiled eggs could be sold - buses - trains - schools - taxi ranks - mini markets - stations - 2.4 Any six bus stops sports grounds industrial areas Any five (5) FIVE points that you should consider when you evaluate your business after selling your produce - How many chickens/eggs did I sell? - Can I be able to sell more? - Were there extra costs I did not think of - How much did I spend on the business? How much did I receive from selling? - Did I make profit? (Was it reasonable?) - Did I make loss this year? - Is there any competitors in my area? - Is the demand high for my business venture? Any five GRAND TOTAL: GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 (5) [21] 50 42 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 TOOL 3: PROJECT INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This project covers the following unit standards: US 13355 SO1 AC2 SO2 AC 2,4 SO3 AC 1-2 2. The project consists of THREE activities. to be spread over three weeks 3. This project should be done in groups of not more than four learners. 4. Provide submission dates for each activity. 5. Assess each activity according to memorandum and rubric provided. Give each group a copy of rubric for activity 1 and activity 2. Learners are expected to plant two bean seeds in two separate tins. The planted seeds should be watered daily with equal amount of water in each tin. Learners are further expected to observe the seeds as they germinate and write a report .This is to check the role of drainage in plant growth. ACTIVITY1: COLLECT MATERIALS Assess learners on the collection of material by using the rubric below. Group members:________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Submission date:________________________________ Criteria Marks 0 Tins One tin Nail and hammer Good planting soil No nail and no hammer No soil Bean seeds No bean seeds Container for watering No container GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 1 Two tins but not equal sizes Only nail or hammer Good soil but not equal amounts Two seeds but not bean seeds Wrong size container 2 Two tins of equal size Both nail and hammer Good soil with equal amounts Two bean seeds Correct size container (10) 43 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 ACTIVITY 2: PREPARATION AND PLANTING THE SEEDS Assess learners on the preparation of the material by using the rubric below. Group members:___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Submission date:___________________________________ Criteria Marks Labelling 1 Tins not labelled 2 Only one tin labelled/Both tins incorrectly labelled Holes in both tins Making holes No holes Putting soil Poor soil in tins Planting seeds No bean seeds planted Good soil but not in equal amounts Two seeds planted in one tin Watering Watered once Not watered daily 3 Both tins correctly labelled Holes on one tin/correctly done Good soil with equal amounts A bean seed planted in each tin Watered daily with equal amounts (15) ACTIVITY3: OBSERVATION AND FINDINGS Use the memorandum below to assess learners on their observations and findings. 3.1 Describe the differences in the plants by looking at the following Tin S Appearance above soil 3.2 3.3 3.4 Tin T Height of plant The seedling/plant appeared first Good and clearly visible Colour Green The seedling/plant took time to appear The seedling/plant is short Yellowish Root growth Long and strong roots Short and weak roots Water drainage Good/well drained Poorly drained (10) The tin with better growth Tin S (1) The tin with poor growth Tin T (1) Mention THREE possible reasons why a tin have better growth. The plant could breath/air is circulating/soil is aerated. The tin is well drained/water has drained through the holes. There is enough water. (3) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 44 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 3.5 3.6 3.7 State TWO possible reasons why a tin have slow growth The plant could not breath properly/air is not circulating/soil not well aerated The tin had too much water/water is not drained/no holes (2) Your conclusion based on the growth of the two plants Plants need enough air to grow well Too much water destroys the plants The well drained soil will lead to normal plant growth The poorly drained soil will lead to poor plant growth (4) Four steps to improve the growth of the plant with slow growth. The soil must be drained Allow air to circulate in the soil/make holes Loosen the soil Add manure/compost to the soil/add nutrients to the soil (4) [25] GRAND TOTAL: 50 TOOL 4: INVESTIGATION INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. The investigation covers the following unit standards: US 13356 SO1 AC4 SO5 AC 5 SO6 AC5 2. For this investigation, learners must visit a local livestock owner, a local farmer, an agricultural school/college or a local feedlot. 3. The investigation is a group task and should be completed within 2 weeks from the date it was issued. 4 Use the checklist to assess the groups on the effort of their visits, submission on time and the relevant information. 5. Groups will have to redraw the tables below in their answer books. ACTIVITY 1: Investigating feeding/grazing habits of farm animals 1.1 TWO observations on the investigated feeding/grazing habits of the farm animals FARM ANIMAL Goats Sheep Cattle Poultry Pigs OBSERVATION - prefer trees and tall grass - like to graze early in the morning - prefer low lying grass - like to graze early in the morning - needs access to 30 litres of water per day - use tethers and herd division - like to graze early in the morning Any two - prefer feeding troughs - prefer to feed for the whole day - prefer to be fed indoors Any two - eat all sorts of household waste - eat both plants and meat GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 [10] 45 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 ACTIVITY 2: Investigating farm animal diseases NAME OF DISEASE Redwater FARM ANIMAL AGENT SYMPTOMS cattle protozoa Tuberculosis cattle bacteria Mastitis dairy cattle bacteria Anthrax sheep goats (Any one) Bacteria - Foot and mouth virus - blisters on mouth and feet - lameness Newcastle cattle goats sheep (Any one) poultry virus Fowlpox poultry virus Blue tongue sheep cattle (Any one) virus - reddish urine from pale to dark coffee colour urine loose cough discharge from eyes and nose swollen udder/teats of milk cows blood in milk blood stained faeces death within 24 hours coughing and sneezing birds twist their heads around difficult breathing yellow diarrhoea (Any two) sores on the comb ulcers in the mouth difficult breathing wattles on the skin or the wings (Any two) fever loss of appetite rapid breathing bluish red mucus membrane of tongue (Any two) [32] ACTIVITY 3: Investigating economic disadvantages of diseases . Loss of production . Poor quality of carcass/meat . Decrease in revenue income . Loss of stock/death of animals . Cannot market ill stock/animals . Cost for caring for animals increase/maintenance costs increase Any four [4] CHECKLIST Assess groups on the following criteria CRITERIA Has the group visited any of the mentioned places/people? Is there proof/evidence of the visit? Has the group used the correct template to record information? Has the group submitted on time? YES [4] GRAND TOTAL: GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 NO 50 46 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 TOOL 5: WORKSHEET INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. This project covers the following unit standards: US 13357 SO1 AC 3-4 SO4 AC3 US 13358 SO1 AC4 SO3 AC1 US 13354 SO3 AC4 2. For this project your learners will use the provided answer sheet. 3. Learners must submit on the due date from the date it was issued. Learners are expected to use the provided answer sheet to indicate a budget as a plan of the future income and expenditure of a tomato venture. Note that items, figures and prices shown are examples. They will differ from one learner to the other, however calculations should be correct. ACTIVITY 1:Drawing a budget EXPECTED EXPENSES ITEMS AMOUNT (How much/ how many) PRICE PER UNIT TOTAL PRICE 1.Seed 2.Fertiliser 3.Transport for fertilizer 4.Wages 5.Spraying (fungicides, insecticides) 6.Tomato boxes 7.Transport to market TOTAL EXPENSES 3kg 50kg 15 bags 5 people 500g R300-00 per kg R 70-00 per 50kg R 8-00 per bag R270-00 per worker R165-00 per 500g R 900-00 R1050-00 R 120-00 R1350-00 R 165-00 2000 6 trips R 2-00 per box R300-00 per trip R4000-00 R1800-00 R9385-00 Other relevant expenditure items may be included like: weeding, trellising costs and harvesting. Mark allocation is 30 and extra information should not affect this mark allocation. EXPECTED INCOME PRICE PER UNIT ITEMS AMOUNT Tomatoes 2000 boxes R15-00 per box (2) TOTAL PRICE R30 000-00 TOTAL INCOME R30 000-00 EXPECTED PROFIT=INCOME-EXPENSES R20 615-00 [40] ACTIVITY 2: Answers on budget 2.1 2.2 2.3 A budget is a plan of the future income and expenses(expenditure) of a business(venture) (2) TWO institutions that may assist you with a loan. - Land bank - Commercial bank/bank (name of a bank) - Insurance policies - Agricultural co-operatives (2) Any two TWO documents that will assist you to draw a budget. - Receipts - Quotations GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 47 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 2.4 Price lists Labour cost in the market/farm Previous Budget Any two TWO technologies that may assist in drawing a budget. - Computer/laptop - Calculator 2.5 (2) TWO types of farming systems in agriculture. - subsistence farming - commercial farming (2) [10] TOTAL: 9. (2) 50 EXTERNAL ASSESSMENT (SUMMATIVE) The summative assessment component of the AAAT4 learning comprises 50% of the total assessment. The policy on the conduct, administration and management of the GETC-ABET Level 4 examinations gives details on how this component of assessment should be managed. It prescribes the examination processes like registration of PALCs as examination centres, registration of candidates, conduct of examinations, marking, capturing of marks, standardization, resulting, to mention but a few. 9.1 Structure of a Question Paper The examination question paper in AAAT4 is written out of 100 marks. The duration of the paper is 3 hours. The paper consists of three sections namely Section A, Section B and Section C. SECTION A is compulsory and consists of FOUR questions (20 marks) Question 1 Multiple Choice (5 marks) Question 2 True /False (5 marks) Question 3 Fill in the missing word(s) (5 marks) Question 4 Match Type (5 marks) SECTION B consists of THREE choice questions (20 marks each question) Answer only TWO questions for 40 marks. Questions in this section shall include among others data handling (graphs, tables, illustrations, scenarios and case studies). SECTION C consists of THREE questions (20 marks each question) Answer only TWO questions for 40 marks. Questions in this section shall include among others data handling (graphs, tables, illustrations, scenarios and case studies) In all sections, questions will require recall, comprehension and application Recall (low order questions) - 40% Comprehension (middle order questions) – 30% Application (high order questions) - 30% GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 48 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 9.2 Exemplar Question Paper GENERAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING CERTIFICATE NQF LEVEL 1 ABET LEVEL 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT LEARNING AREA : APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY CODE : AAAT4 DATE : NOVEMBER 2011 TIME : 3 HOURS MARKS : 100 This question paper consists of 7 pages. INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. ALL questions must be answered in the ANSWER BOOK. Make sure that you write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER on the ANSWERBOOK. 2. Make sure that you write your CENTRE NUMBER and EXAMINATION NUMBER. 3. The question paper consists of THREE COMPULSORY sections: SECTION A: QUESTION 1, 2, 3 & 4 = 20 marks. SECTION B: QUESTION 5 & 6 = 40 marks. SECTION C: QUESTION 7 & 8 = 40 marks. 4. Read the instructions for each section carefully before answering the questions. _____________________________________________________________________________ SECTION A Answer ALL questions. QUESTION 1 Various possible options are provided as answers to the following questions. Choose the answer and write only the letter (A – D) next to the question number (1.1 – 1.5), in the ANSWER BOOK GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 49 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 1.1 Livestock farming involves … A B C D 1.2 (1) Jersey. Hereford. Sussex. Drakensberger. (1) … is a summer vegetable and is not damaged by frost. A B C D 1.5 plough. roller. harrow. planter. An example of a milk breed is a … A B C D 1.4 (1) The appropriate technology used to destroy weeds just after they have germinated is a … A B C D 1.3 growing crops. soil preparation. animal production. irrigating the land Tomato Onion Peach Pumpkin (1) The farmer as an entrepreneur uses a … to plan for farming activities. A B C D credit card bank loan budget (1) [5] QUESTION 2 Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only the word ‘true’ or ‘false’ next to the question number (2.1 – 2.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. 2.1 Economics is the science that helps to understand business and management principles better. (1) 2.2 The vegetation remains palatable during all seasons. (1) 2.3 Migrant workers live permanently on the farm. (1) 2.4 Technology helps to improve agricultural production. (1) 2.5 Dipping of livestock is used to control roundworms. (1) [5] QUESTION 3 Read the sentences below and fill in the missing word(s) to complete the statement. Write only the missing word(s) next to the question number (3.1 – 3.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 50 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 3.1 … rock is the solid bedrock that lies below the subsoil layer. (1) 3.2 A … is a building used for young growing plants that need protection from bad weather conditions. (1) 3.3 Weeds that live for a number of years are called … weeds. (1) 3.4 Land ownership where a person owns land is known as … . (1) 3.5 Merino sheep are known for the production of … . (1) [5] QUESTION 4 Match the statement(s) in COLUMN B with the word(s) in COLUMN A. Write only the letter (A – G) next to the question number (4.1 – 4.5) in the ANSWER BOOK. 4.1 COLUMN A Wheat production COLUMN B A land owned by one person 4.2 Frost B land received from a line of ancestors 4.3 Lung-worm C environmental factor damaging crops 4.4 Labour Relations Act D protects interests of labourers 4.5 Inherited land E appoints labourers F sucks blood and cause anaemia [5] G agricultural venture TOTAL SECTION A: 20 SECTION B This section consists of QUESTIONS 5 and 6, answer BOTH. QUESTION 5 The picture below is an illustration of agricultural food production. Study it and answer the questions that follow. PICTURE 1 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 51 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 SUN MEAT PORRIDGE BREAD SUGAR FAMILY EGGS MIELIES WHEAT SUGAR CANE GRASS COW CHEESE CHICKEN (Source: Animal Traction Level 4 Module 2) 5.1 Name the TWO farming animals from the above illustration. (2) 5.2 List THREE field crops shown in the above illustration. (3) 5.3 Indicate one by-product for each plant, namely maize, wheat and sugar cane as indicated in the illustration only that are needed by the family. (3) 5.4 Name the TWO milk products shown in the illustration. (2) 5.5 State FOUR environmental factors that may affect livestock in a bad way. (4) 5.6 Indicate THREE livestock ventures from the illustration. (3) 5.7 What is the type of farming called where food is only produced for the family? (1) 5.8 Explain what the family can do with their surplus produce. (2) [20] QUESTION 6 The picture below shows a crop rotation system on a farm. Study it and answer the questions that follow. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 52 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 PICTURE 2 First Season Fruit vegetables Tomatoes and pumpkins: do not need a lot of plant food Fifth Season Leave the soil bare: allow for a growth period Second Season Leguminous vegetables Peas and beans: improve the soil’s fertility Fourth Season Root vegetables Carrots and onions: do not need fertilizer like farm manure Third Season Leafy vegetables Cabbage and celery: need a lot of plant food (Source: Your farming venture book 3) 6.1 Explain crop rotation. (2) 6.2 Name TWO crops that are planted in the fourth season. (2) 6.3 Indicate TWO fruit vegetables in the above crop rotation system. (2) 6.4 State a reason why leguminous vegetables are planted before leafy vegetables. (2) 6.5 Explain why the soil is left bare in the fifth season. (2) 6.6 State FOUR importance of crop rotation. (4) 6.7 Indicate THREE appropriate manual and mechanical technologies that may be used to control weeds. (3) 6.8 Name THREE types of workers that may be used on the farm. (3) [20] TOTAL SECTION B: 40 SECTION C This section consists of QUESTIONS 7 and 8, answer BOTH. QUESTION 7 The table below shows the amount of water given to citrus trees over different ages. TABLE 1 Tree age 1 to 2 years 3 to 4 years 5 to 6 years 7 to 8 years 9 to 10 years GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 July to March (water every 2 weeks) 55 litres 110 litres 165 litres 220 litres 285 litres April to June (water every 4 weeks) 55 litres 110 litres 165 litres 220 litres 285 litres 53 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 11 to 12 years 13 to 14 years 15 to 20 years 20 years onwards 345 litres 400 litres 480 litres 560 litres 345 litres 400 litres 480 litres 560 litres (Source: The People’s Guide to FARMING) 7.1 How often are citrus trees watered from July to March? (1) 7.2 How much water is used for the trees with age of 9 to 10 years? (2) 7.3 At what age of the citrus trees do we use 400 litres of water? (1) 7.4 Name THREE examples of citrus fruit. (3) 7.5 In what type of soil do most citrus trees grow well? (1) 7.6 Calculate the litres of water used during the period April to June for the age 1 to 10 years. (3) 7.7 In which season of the year is there a high demand for oranges? (1) 7.8 Explain what will happen when the supply of oranges is higher than the demand of oranges. (2) 7.9 Explain THREE ways to control pests in citrus trees. (3) 7.10 Give the ripening time for: 7.10.1 Naartjie (1) 7.10.2 Grapefruit (1) 7.10.3 Lemon (1) [20] QUESTION 8 Vuyo has a small pig business. She keeps pigs and sells them to a local abattoir. Some of the pigs are sold to the community members in the village. The pig manure is used for her garden. Things started to go wrong one morning, the piglets developed sores inside the mouth, on the tongue and between the hooves. They had a spit running out of the mouth. They were eating and walking little. They did not die but were weak. Vuyo went to a local veterinarian who came and diagnosed the piglets problem. The veterinarian indicated that the piglets suffer from foot and mouth disease. 8.1 Name Vuyo’s agricultural venture. (1) 8.2 Name THREE things that Vuyo may have done before starting the business. (3) 8.3 What is the function of an abattoir? (2) 8.4 Name TWO places in the case study where Vuyo sold her pigs. (2) 8.5 State THREE importance of pig farming. (3) 8.6 What disease were Vuyo's piglets suffering from? (1) 8.7 State FOUR signs or symptoms of the disease in QUESTION 8.6 as in the case study. (4) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 54 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 8.8 Explain what is a veterinarian. (2) 8.9 Name TWO other places where Vuyo would have gone to look for assistance. (2) [20] TOTAL SECTION C: GRAND TOTAL: 40 100 GENERAL EDUCATION AND TRAINING CERTIFICATE NQF LEVEL 1 ABET LEVEL 4 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT LEARNING AREA : CODE : APPLIED AGRICULTURE AND AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY AAAT4 DATE : NOVEMBER 2011 TIME : 3 HOURS MARKS : 100 This memorandum consists of 6 pages. SECTION A QUESTION 1 1.1 C (1) 1.2 C (1) 1.3 A (1) 1.4 B (1) 1.5 D (1) [5] GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 55 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 QUESTION 2 2.1 True. (1) 2.2 False. (1) 2.3 False. (1) 2.4 True. (1) 2.5 False (1) [5] QUESTION 3 3.1 Parent. (1) 3.2 Greenhouse. (1) 3.3 Perennial. (1) 3.4 Freehold. (1) 3.5 Wool. (1) [5] QUESTION 4 4.1 G. (1) 4.2 C. (1) 43 F. (1) 4.4 D. (1) 4.5 B. (1) [5] TOTAL SECTION A: 20 SECTION B QUESTION 5 5.1 5.2 5.3 TWO farming animals in the illustration Cow/cattle/bull/ox/beast chicken (2) THREE field crops shown in the illustration. Mielies Wheat Sugar cane (3) THREE products of plants that are needed by the family. Porridge Bread sugar (3) GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 56 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 5.4 5.5 5.6 TWO milk products shown in the illustration. Maas cheese FOUR environmental factors that may affect livestock in a bad way. Heavy rainfall/rainfall/floods Storm Hail Drought Snow Frost Veld fires THREE livestock ventures from the illustration. Cattle farming/production Dairy/milk production Beef production Poultry/chicken farming/ production Broiler farming/production Layer farming/ production/ egg production 5.7 Subsistence farming 5.8 They can give/sell to neighbours Give to orphanage/old age homes Give to home based centres. (2) (4) Any four (3) Any three (1) Any one (2) [20] QUESTION 6 6.1 Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops on the same land year after year./cultivating a different kind of vegetable in the same place every year (2) 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 TWO crops planted in the fourth season. Carrots Onions (2) TWO fruit vegetables in the above crop rotation system. Pumpkins Tomatoes (2) A reason why leguminous vegetables are planted before leafy vegetables. Improves the soil’s fertility Provides nitrogen to the soil Any one (2) To allow for a growth period To allow for a resting period Any one (2) FOUR importance of crop rotation. Avoid one sided use of the nutrients To control weeds To control pests and diseases To allow for a growth period Prevents competition for nutrients Any four (4) THREE appropriate manual and mechanical technologies that may be used to GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 57 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 control weeds. Hand hoe Harrow Subsoiler Rake Fork 6.8 (3) Any three THREE types of workers that may be used in the crop rotation system. Permanent workers Temporary/ Seasonal/part time workers Casual workers Migrant workers Any three (3) [20] TOTAL SECTION B: 40 SECTION C QUESTION 7 7.1 Every two(2) weeks (1) 7.2 285 + 285 = 570 (2) 7.3 13 to 14 years (1) 7.4 THREE examples of citrus fruit. Oranges Grapefruit Naartjies Lemons Lime (3) Any three 7.5 Deep and well drained soil/loam soil (1) 7.6 55 + 110 + 165 +220 + 285 = 835 (3) 7.7 Winter/May to July/cold season (1) 7.8 - The price of oranges will be less/cheaper/price drops/price goes down - oranges may be spoiled/rot/decay/decompose/loose value if not bought Any one (2) THREE ways to control pests in citrus trees. Spraying/boom spray Dig and burn infected trees Buy grafted trees Use mineral oil Use of a predator(biological control) (3) 7.9 Any three 7.10.1 May to July (1) 7.10.2 May to July (1) 7.10.3 All year/ any time during the year (1) [20] QUESTION 8 GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 58 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 8.1 Piggery/pig farming (1) 8.2 THREE things that Vuyo may have done before starting the business Check the availability of land Establish funds needed Determine the needs of the community Budgeting Do correct selection of an animal Check the resources available Needs assessment/ viability study/ market analysis study Any three (3) 8.3 Is to slaughter animals/livestock for meat/sell meat/make meat available (2) 8.4 TWO places in the case study where Vuyo sold her pigs. Abattoir Community/village (2) 8.5 THREE importance of pig farming Meat production(pork, bacon, sausages) Manure Fat Job creation/provides job opportunities/reduce poverty/economy Profit making Any three (3) 8.6 Foot and mouth disease (1) 8.7 FOUR signs or symptoms of the disease in 8.6 as in the case study. Sores inside the mouth/tongue Sores in between the hooves A spit running out of the mouth Walking little Eating little piglets become weak Any four (4) 8.8 Veterinarian is an animal doctor/one who specialises in animal diseases/ animal pathologist 8.9 TWO other places where Vuyo would have gone to look for assistance. Local extension office/officer Department of agriculture. Agricultural college/office/research council Any two TOTAL SECTION C: GRAND TOTAL: (2) (2) [20] 40 100 Hints of marking of the answer scripts: Once candidates have completed the examination they entrust their confidence in a marking process for which they have no control. It is up to markers to ensure that the integrity of the process of marking is beyond question and the quality is excellent. Marking of the answer scripts is part of an assessment process. It is therefore important to ensure that marking is done according to marking guidelines like the above cited. The marking guidelines GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 59 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 should have well structured model answers to questions. Marking of the learning area should therefore be done by people well conversant with the learning area unit standards. It is also imperative that before starting to mark, there must be a training session of all marking personnel. The marking procedure should accommodate the following hints: Effective use of marking guidelines Adherence to the marking guidelines All answers (responses) to be marked One tick, one mark Use appropriate ink for marking( red for markers and green for moderators) Ensure uniform standard throughout the marking session (marking guideline to be adapted to accommodate all possible answers) Ensure correct transfer of marks on both the scripts and the mark sheets 10. PROMOTING THE PRINCIPLES OF QUALITY ASSESSMENT PRACTICES The Department of Higher Education and Training views assessment as a process of making decisions about a learner’s performance. It involves gathering and organising evidence of learning, in order to review what learners have achieved. It informs decision making in education, and helps educators to establish whether learners are performing according to their full potential and are making process towards the required unit standards credits as outlined in the qualification cited above. Principles of assessment that are always considered when assessment tasks and tools are developed include among others the following: Validity Assess what is supposed to be assessed. Examination question papers and SBAs take the US, and their related assessment criteria into account in setting appropriate types of questions. Reliability Assessment should produce reliable results instructions that are clear, consistent and unambiguous. Assessment criteria are strictly adhered to. Marking guidelines/memoranda are clear and markers apply the same standard. Transparency Accomplished through guidelines, uniform SBAs and national examinations which are moderated internally and externally. Question Papers and SBAs are moderated externally by Umalusi. Stakeholders know what to expect and candidates have the right to appeal. Fairness Assessment does not disadvantage anybody (based on age, race, gender, ethnicity, geographic location, etc) Assessment is accessible to all candidates Covers different cognitive levels Nature of the learning environment of learners is considered. Currency Assessment keeps up with current events and life-world of ABET learners. This is reflected in the content and nature of the texts selected, and the topics offered for interaction. Authenticity Assessment is original and encourages originality, creativity and avoids repetition. It consciously tries to avoid predictability. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 60 | P a g e Examinations and Assessment Guidelines: AAAT4 The different types, descriptions and uses of assessments are given below to serve as a reminder to everybody with an interest in adult education that only quality assessment practices is suitable for this sector of our education system. Baseline Assessment: Usually used at the beginning of a learning experience to establish what learners already know, can do or value. It assists educators with the planning of learning programmes and learning activities. Formative Assessment: It is developmental and used to inform both the teacher and the learner about how the learner has progressed (or not). It enhances teaching and learning. Teachers use it to adapt learning activities to the learner needs. It is also known as assessment for learning Summative Assessment: It gives an overall and final picture of the achievements of a learner at a given time. The examination is an example of summative assessment for ABET Level 4. This could be viewed as a “snapshot” whilst formative assessment is viewed as a “video” of a learner’s progress. Diagnostic Assessment: It is a form of formative assessment that leads to intervention, remedial action or revision programme. It identifies both the strengths and weaknesses of either the learner or the teaching methodology Systemic Assessment: It is an external way of monitoring the education system by comparing learners’ performance to national indicators of learner achievenement. It involves monitoring learner attainment at regular intervals using national or provincially defined measuring instruments. Note of the following Assessment Strategies should also be taken. Methods (WHO) Forms (WHAT) Instruments/Tools (HOW) Purposes (WHY) Educator assessment, Selfassessment, Peerassessment and Groupassessment. Tests, Drawings, Paintings, Graphs, Physical activities, Projects, Demonstrations, Poems, Dramas, Role-plays, Stories, Songs/music, Oral presentations, Written presentations, Worksheets, Questionnaires, Cassettes, Posters, Assessment grids, Rubrics, Memoranda and Observation sheets. Baseline, Diagnostic, Formative, Summative and Systemic. In conclusion please note that assessment must always be fair to learners and all possible barriers preventing learners from expressing their knowledge, skills and values in an assessment task, must be considered when developing, marking and moderating the assessment task. GETC-ABET Level 4 ~ @ NQF Level 1 61 | P a g e