Mammalian Heart ANSWERS
advertisement

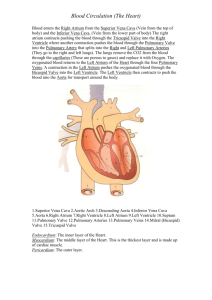
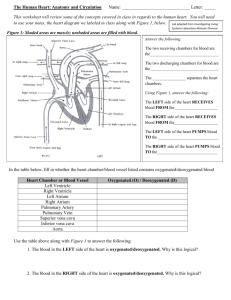
Unit 5 SBI3U 9.3 The Mammalian Heart - ANSWERS AMAZING Human Heart Facts: Pumps about 70x per minute, 90 000x per day through 160 000 km of blood vessels! Pumps in 2 directions at once without ever mixing the blood! Has a life expectancy of around 80 years Is about the size of your fist The Flow of Blood Watch the narrated animation and fill in the answers to discover how blood moves through the heart. http://www.medtropolis.com/VBody.asp Blood first enters the RIGHT ATRIUM through two large veins called the SUPERIOR vena cava and the INFERIOR vena cava. The blood entering the right atrium is low in OXYGEN since it is returning to the heart after nourishing various body parts with oxygen. The blood then moves from the right atrium into the RIGHT VENTRICLE through a valve called the TRICUSPID valve. The valve prevents blood from flowing from the right ventricle back to the right atrium, ensuring a one way flow. When the blood is in the right ventricle, the heart muscle pumps it the short distance to the lungs. Blood goes through the PULMONARY ARTERIES to the lungs, getting rid of its carbon dioxide and acquiring new oxygen, and then returns to the heart. The blood returns to the heart through the PULMONARY VEINS leading to the left atrium. When the left atrial wall contracts, the blood is pushed through the BICUSPID valve into the left ventricle. The left ventricle contracts and forces the oxygen-rich blood on its life giving journey throughout the body. The blood goes through the AORTA a large artery with branches that distribute blood to all parts of the body. Heart Diagram http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/in-out.htm LABELS http://www.smm.org/heart/lessons/lesson6.htm FUNCTIONS Part 1. Aorta 2 Superior Vena Cava 3. right pulmonary arteries 4. right pulmonary veins 5. right atrium 6. tricuspid valve 7. right ventricle 8. inferior vena cava 9. left pulmonary arteries 10. left pulmonary veins 11. left atrium 12. bicuspid valve 13. aortic valve 14. left ventricle 15. descending aorta Function Delivers oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body and delivers to right atrium Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium Receives deoxygenated blood from vena cava Prevents backflow of blood between the right atrium and ventricle Receives deoxygenated blood from right atrium Receives deoxygenated blood from the lower part of the body and delivers to right atrium Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins Prevents backflow of blood between the left atrium and ventricle Prevents backflow of blood between the left ventricle and aorta Receives oxygenated blood from left atrium Delivers oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle Trace the passage of OXYGENATED blood with a red arrow. Trace the passage of DEOXYGENATED blood with a blue arrow.