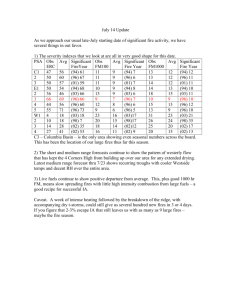
Essentials of Fire Fighting (4th Edition-FF1)
advertisement

Essentials of Firefighting (4th Edition) Chapter 14-Fire Control FF1 Test Review What does the SUCCESS of a fire fighting team depend on? skill & knowledge of personnel involved in initial-attack operations What permits firefighters to apply FIRE STREAMS from positions close to the fire? Full PPE, SCBA, and PASS devices What are some HAZARDOUS CONDITIONS to watch for in fire control? imminent building collapse fire behind, below, or above attack team kinks or obstructions in hoselines holes, weak stairs, or other fall hazards suspended loads on fire-weakened supports hazardous or highly flammable commodities likely to spill backdraft or flashover conditions electrical shock hazards overexertion, confusion, or panic by team members victims What is important between crews performing DIFFERENT FUNCTIONS? coordination What happens when attack is COORDINATED with attack crews? improved visibility, entry can be made to facilitate rescue, assessment of fire conditions can be made, and suppression What tools should TEAMS advancing hoselines carry? equipment that may be needed to force entry/exit or perform other tasks equipment should include: a portable light, an axe, and a prying tool of some type What should an ATTACK TEAM do prior to entry? bleed air from line & check operation of nozzle settings or set to proper pattern for the fire based on conditions found What should firefighters do until FIRE OFFICER gives the order to advance? wait at structures entrance & stay low and out of doorway What should be EXTINGUISHED before entry? burning fascia & soffit, boxed cornices, and other doorway overhangs From which side should a fire be ATTACKED and Why? from the unburned side to prevent spreading it through the structure Why should MATTRESSES not be removed from structure for extinguishment? it may erupt in flames or get stuck in doorway, blocking exit What should be worn during MOP-UP & OVERHAUL? full PPE and SCBA What should be done with VALUABLES found? taken immediately to supervisor What factors determine the METHOD of fire attack? size of fire, type of nozzle used, ventilation conditions, & other factors What type of FOG PATTERN may be used if ventilation is adequate? a narrow fog pattern proper ventilation gives smoke, heat, & steam a place to go also, helps maintain thermal layering What TYPE of STREAM should be used if ventilation is inadequate? a straight stream to avoid upsetting thermal layering Where must personnel be POSITIONED if a door to a fire area must be opened? to one side of the entrance and STAY LOW What type of stream should be used BEFORE fire is encountered? a protective stream ONLY IF NECESSARY discharging water at smoke decreases visibility and increases water damage Where should stream be DIRECTED if fire is localized? direct at the base of the fire If area is WELL INVOLVED, how should water be applied? by sweeping the ceiling in a side-to-side motion which will break the stream into smaller droplets that rain down on the base of the fire, increasing extinguishment How should a hose crew BACK OUT of a fire area? with the stream operating until all personnel are in a safe area How should personnel exit during IMMINENT BUUILDING COLLAPSE conditions? personnel should exit IMMEDIATELY What makes WATER APPLICATION successful? if amount of water applied is sufficient to cool burning fuels What types of fires are BOOSTER LINES good for? small, exterior fires, small brush fires, and dumpster fires 1 1/2-inch hoselines are NOT to make an interior attack What fire conditions & factors determine HOSELINE SELECTION? fire load & material involved volume of water needed for extinguishment reach needed # of persons available to handle hoselines mobility requirements tactical requirements speed of deployment potential fire spread What is a DIRECT ATTACK? applying a solid or straight stream in short bursts directly at the base of the fire until the fire "darkens down" What is and INDIRECT ATTACK? made from outside through a window or door when entry to structure or fire area is not possible due to intense fire conditions not desirable when victims may be trapped or spread of fire to uninvolved areas cannot be contained solid, straight, or narrow fog stream directed back and forth at ceiling level to cool superheated gases should be shut down before thermal layering is disturbed What is a COMBINATION ATTACK? uses steam-generating technique of ceiling level attack combined with direct attack of burning materials near floor level nozzle may be moved in a T, Z, or O pattern starting with a solid, straight, or penetrating fog stream directed at the ceiling level and then lowered to attack combustibles near floor level What is the MOST FAMILIAR method of combination attack? the O pattern to perform the O pattern, direct stream at the ceiling, wall, floor, then opposite wall How should TEAM MEMBERS assist nozzle person? by advancing hose as needed crowding behind nozzle makes manipulation of nozzle difficult When are MASTER STREAM DEVICES generally used? as a last resort of containing & controlling a large fire used when fire is beyond control of handlines or location is no longer safe for personnel What are the 3 MAIN USES of master stream devices? direct fire attack to back up handlines attacking the fire from the exterior exposure protection How must a MASTER STREAM device be moved? must be shut down to be moved Where should a MASTER STREAM be placed to attack a fire? close enough to a window or door that it can hit the base of the fire particularly important when using a fog nozzle because of lack of penetration should be place so that it enters structure at an upward angle where it can deflect off the ceiling to the base of the fire placement should also be where maximum coverage on face of building is obtained What can happen if a MASTER STREAM is operated at TOO LOW of an angle? loss of control of master stream and hoseline may occur What is the minimum expected FLOW of a master stream device? 350 gpm it is not practical to supply with any less than two 2 1/2-inch hoselines larger flows will require a third 2 1/2-inch line or LDH some devices are equipped to handle one 4-inch or larger supply line it is desirable to use a maximum of 100-feet of supply hose to reduce FL supply hose generally comes from the main supply in the bed of the engine How many FF's are needed to DEPLOY a master stream device and supply lines? minimum of 2, once in place, can be operated by one FF one FF should be stationed at master stream device at all times while water is flowing in case change of direction or prevention of device "crawling away" (moving) is needed An exception is when the device is in hazardous positions such as in collapse zone or near LPG tanks, or other hazardous objects How should an UNMANNED MASTER STREAM be operated? securely anchored, desired stream put in place, and personnel should back away if device starts to move, pressure should be decreased at the supply source What is a B.L.E.V.E.? Boiling Liquid Expanding Vapor Explosion found in vessels containing flammable liquids results in explosive release of pressure, pieces of tank, and big fireball with radiant heat most commonly occurs when flame contacts tank shell ABOVE the liquid line or when insufficient water is applied to keep the tank shell cool water should be applied with unmanned master streams to the upper portions of the tank Where is NATURAL GAS & LPG found and its use? found in houses, mobile homes, businesses used for cooking, heating, or industrial processes What are some CHARACTERISTICS of natural gas? made mostly of methane with small quantities of ethane, propane, butane, & pentane lighter than air, non-toxic, classified as an asphyxiant mercaptan gas is added to provide a distinctive odor How is NATURAL GAS distributed? from gas wells through pipes at pressure ranges of 1/4 to 1,000 psi (usually below 50 psi) to its point of usage What are some DANGERS of natural gas? explosive concentrations between 5% to 15% may be subject to B.L.E.V.E. when compressed or stored and shipped in cylinders CNG = Compressed Natural Gas What tools do EMERGENCY RESPONSE CREWS have for gas utilities? special non-sparking tools maps of distribution system training & experience to stop gas flow What is LPG? Liquified Petroleum Gas - fuel gas stored in a liquid state Used primarily as fuel gas in campers, mobile homes, agricultural applications, & rural homes Composed mainly of propane with small quantities of butane, ethane, ethylene, propylene, isobutane, or butylene added Non-toxic, classified as an asphyxiant What are some dangers of LPG? about 1 1/2 times heavier than air so it hugs the ground explosive in concentrations of 1.5% to 10% shipped from point to point in cylinders all cylinders are subject to B.L.E.V.E. How can LPG leaks be stopped? by dissipating with a fog stream of at least 100 gpm What measures should be taken at a LPG or CNG leak? approach & stage on the upwind side be prepared for a B.L.E.V.E or fires evacuate area around break and downwind of break eliminate ignition sources surrounding buildings checked for gas build-up What is the MOST COMMON situation FF's face in gas utility structure fire incidents? locating the service meter & turning off gas usually located outside building & normally visible from street (some are located inside structure) How should FF's turn off gas at a meter? with or without fire, advance a fog stream for protection while approaching valve What indicates the a GAS VALVE is closed? valve petcock at a right angle to pipe What is a CLASS C fire? fire involving energized electrical equipment Where can UNUSUAL electrical hazards be found? railroad locomotives, relay switching stations, & electrical substations What is the PRIMARY DANGER of electrical fires? failure of emergency personnel to recognize the safety hazard How should POWER FLOW to commercial or high-rise buildings with fire be controlled? de-energize area around fire How should fires in DELICATE electronic or computer equipment be extinguished? with carbon dioxide or halon use of water is an inherent shock hazard What are some other fires that use CLASS C suppression techniques? transmission lines & equipment, underground lines, & commercial high-voltage installations What is the area that should be CLEARED when fires occur as a result of TRANSMISSION LINES breaking? area equal to the span between poles on either side of break What components are VITAL in fires involving transmission lines & equipment? reduce risk to life & property consult with power company personnel live wires should NOT be cut EXCEPT by experienced power company personnel What is a DANGEROUS chemical found in transformers? PCB's (polychlorinated biphenyls) flammable because of their oil base also, carcinogenic (cancer-causing) should be extinguished with a dry chemical extinguisher What do UNDERGROUND transmission systems consist of? cableways & vaults beneath surface What are the MOST FREQUENT hazards associated with underground lines? explosions that may blow utility covers a considerable distance sparks from fuses or short-circuit arcing can ignite accumulation of gases area should be clear & no apparatus should be parked over utility covers When should FF's enter a UTILITY VAULT? NEVER, unless rescue must be made How should fire in UNDERGROUND systems be extinguished? by discharging carbon dioxide or dry chemical into vault & replacing cover a wet blanket or salvage cover should be placed over the utility cover to exclude oxygen water is not suggested for extinguishment runoff of water could become a conductor of electricity Where might VOLTAGE in excess of 600 volts be found? in industry, large buildings, & apartments What types of COOLANTS are used in some transformers? flammable oils What should NOT be used to extinguish high-voltage equipment? water should NOT be used What are additional HAZARDS in high-voltage equipment? toxic chemicals used in plastic insulation, coolants, & smoke What methods should be used in ENTRY of areas with high-voltage equipment? wear SCBA & use a safety line monitored by someone on the outside of structure search with a clenched fist or the back of hand to avoid reflex action of grabbing live equipment Why should POWER remain on for as long as possible? to provide lighting, run ventilation equipment, or run pumps also, once turned off, it cannot be restored How should POWER be turned off? by a power company employee it is NOT RECCOMMENDED for FF's to pull electrical meters to turn off power FF's should control power at panel box by opening main switch or removing fuses What does CONTROLLING electrical flow accomplish? reduces danger of igniting combustibles or accidentally turning on equipment What are CONSEQUENCES of electrical shock? cardiac arrest ventricular fibrillation respiratory arrest involuntary muscle contractions paralysis surface or internal burns damage to joints ultraviolet arc burns to eyes What FACTORS affect the seriousness of electrical shock? path of electricity through the body degree of skin resistance: wet (low resistance), dry (high resistance) length of exposure available current: amperage flow available voltage: electromotive force frequency: alternating current (AC), or direct current (DC) What are some GUIDELINES for electrical emergencies? establish danger zone of one span in either direction for safety guard against electrical shock, burns, & eye injuries from arcing treat all wires as energized, high-voltage lines do not cut any power lines. Wait for utility workers use electrical lockout/tagout devices to ensure power will not be inadvertently turned back on (also, padlock tagout device) wear full PPE use only regularly tested & approved insulated tools use care when raising or lowering ladders, hoselines, or equipment near overhead lines do not touch any vehicle or apparatus that is in contact with electrical wires if necessary to leave apparatus, FF should jump clear of apparatus. DO NOT touch the apparatus and the ground at the same time consider all downed power lines equally dangerous DO NOT use solid or straight streams around energized equipment Use fog streams with at least 100psi Give special consideration for fences. Once electrical line comes in contact with fence, all of fence is energized Heed any tingling sensation in feet when working around downed lines Avoid ground gradient hazard by maintaining extra large safety distance from downed lines What situations should LOCKOUT devices be used? elevator rescues, compactor malfunctions, industrial process equipment mishaps, & related incidents What is a GROUND GRADIENT? tendency of an energized electrical conductor to pass current along path of least resistance (from highest to lowest potential) to ground What are the 2 problems that occur with combustible metal (CLASS D) fires? burn at extremely high temperatures reactive to water When is WATER effective on CLASS D fires? only in large amounts to cool metal below its ignition temperature What is the USUAL method of control in CLASS D fires? to protect exposures and permit metal to burn out What types of metals are MORE REACTIVE to water? small metal chips or metal dust ingots & finished products (LESS REACTIVE TO WATER) How can combustible metal fires be RECOGNIZED? by a characteristic brilliant white light given off until ash layer covers substance HOW HOT can combustible metal fires get? greater than 2,000oF even when extinguished What is a RIC? Rapid Intervention Crew - rescue personnel to assist FF's in trouble As per NFPA 1500 Consist of at least 2 members wearing full PPE & SCBA with rescue tools needed to rescue other personnel May be assigned other duties until needed but must be ready to deploy immediately if needed What is the job of the CHIEF OFFICER or IC? to coordinate the overall activities at the scene to constantly evaluate the effectiveness at the scene and need for additional resources When can ELEVATORS be used in high-rise fires? if elevators are in banks and do not extend all the way to the fire floor Where is an ATTACK in a high-rise building typically initiated? the floor below the fire floor How should hose be CONNECTED to fight high-rise fires? at a standpipe one floor below the fire floor and then flaked to the floor above the fire floor Where is staging of extra equipment in high-rises usually located? 2 floors below the fire floor What do stairs to BELOW-GROUND fires become? chimneys for superheated air and fire gases to escape Where should ventilation of BELOW-GROUND fires be located? as far from the opening to gain access as possible ground level floor should be vented to remove as much smoke as possible How should FF's descend into a BELOW-GROUND fire? by using a protective fog stream ONLY if ventilation has occurred At what temperature do steel supports ELONGATE? 1,000oF How can fires in BELOW-GROUND areas be attacked INDIRECTLY? with cellar nozzles (for inaccessible areas), piercing nozzles, distributors, or by using high-expansion foam What is important about the use of HIGH-EXPANSION FOAM? must be carefully coordinated with ventilation to avoid major fire extension or flashover What other areas of a structure should be watched in BELOW-GROUND fires? the attic area where fire gases may rise and accumulate What types of FIXED fire suppression systems are available? sprinkler systems carbon dioxide systems standpipe systems halogenated systems dry chemical systems foam systems What are some of the DANGERS associated with fixed fire protection systems? oxygen depletion during carbon dioxide activation poor visibility energized electrical equipment toxic environmental exposures What do PRE-INCIDENT plans at fixed fire protection occupancies include? construction features contents, protection systems, and surrounding property What are the MOST COMMON type of vehicle fire FF's encounter? single-passenger vehicles What type of ATTACK should be made on vehicle fires? at least 1 1/2 inch attack line fight fire from uphill and upwind DO NOT use booster lines A backup line should be deployed ASAP Portable extinguishers may be used on small engine compartment fires, such as carburetors First, extinguish any ground fire around or under vehicle then attack remaining fire Hoseline should be placed between vehicle and any exposures What if a vehicle fire involves COMBUSTIBLE METALS? large amounts of water or Class D extinguishing agents will be needed How can fire be EXTINGUISHED under a hood? by using a piercing nozzle or using a tool to make a hole to extinguish through How should ATTACK be made in a vehicle's passenger compartment? by approaching from the front or rear corner with a wide fog attempt to open door, if not, break window once open, attack with a medium fog in a circular motion How can UNDERCARRIAGE fires be extinguished? by deflecting water off pavement What should OVERHAUL in vehicle fires include? checking for extension or hidden fires as well as securing air bags and cooling fuel tanks What is the temperature of CATALYTIC CONVERTERS & why is it important? 1,300oF-2,500oF, may start grass fires under vehicle Why are SEALED COMPONENTS important in vehicle fires? under fire, components pressurize and fail, releasing projectiles such as absorber-type bumpers, hollow driveshafts, and hatchback supports tires may also blow out What other materials should not be OVERLOOKED in vehicle fires? saddle fuels tanks, LPG or CNG tanks, alternative fuel tanks, explosives, hazardous materials military vehicles may carry munitions What contents can make DUMPSTER fires hazardous? hazardous materials, or plastics that give off toxic gases aerosol cans and batteries that may explode What type of ATTACK lines should be used on DUMPSTER FIRES? small fires with a booster line large fires with at least a 1 1/2 inch attack line What are some types of CONFINED SPACES? caves, sewers, storage tanks, and trenches What ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS can be expected in confined spaces? oxygen deficiencies flammable gases and vapors toxic gases elevated temperatures explosive dusts What PHYSICAL HAZARDS can be encountered in confined spaces? limited means of entrance cave-ins or unstable support members deep standing water or other liquids utility hazards - electric, gas, sewer What are PRE-INCIDENT plans used for in confined space? to reduce the guesswork of existing enclosed spaces How should POWER EQUIPMENT used in non-fire rescues be rated? for use in explosive atmospheres includes: flashlights, portable fans, and radios When should FF's enter ENCLOSURES? NOT until IC has decided upon a course of action and issued specific orders What is the FUNCTION of a safety officer? to track personnel and equipment entering or leaving the enclosure What should be TIED to each rescuer before entry? a life line, which is constantly monitored and a standyby crew of at least the same # of rescuers should be standing by What is the O-A-T-H method? communication for lifeline O (OK), A (Advance), T (Take Up), H (Help) Another method of communication is a sound-powered phone that do not require power Why is OXYGEN checked first in confined spaces? because air monitoring devices can give false readings in oxygen-deficient atmospheres What is the PURPOSE of the accountability system? to ensure only authorized and properly equipped personnel enter a hazardous area and that their location and status is known at all times How can fires in CONFINED SPACES be attacked indirectly? with piercing nozzles, cellar nozzles, distributors, or high-expansion foam How far can FF's enter a CONFINED SPACE? NOT farther than their air supplies will allow a SAFE MARGIN of retreat What do WILDLAND fires include? fires in weeds, grass, field crops, brush, forests, and similar vegetation What 3 FACTORS affect a wildland fire? topography, fuel type, and weather What are WILDLAND FUELS? Subsurface Fuels - roots, peat, duff, & partially decomposed organic matter that lie underground Surface Fuels - needles, twigs, grass, field crops, brush up to 6 feet, logging slash, small trees Aerial Fuels - suspended and upright fuels over 6 feet What are FACTORS that affect the burning characteristics of fuels? Fuel Size - small or light fuels burn fast Compactness - tightly compacted (burn slow), loosely compacted (burn fast) Continuity - fuels close together (spreads faster), patchy (burns slower) Volume - amount of fuel present Fuel Moisture Content - moist (burns slow), dry (burns fast) What are some WEATHER factors that affect fires? Wind - can fan flame to greater intensity; some fires create their own wind Temperature - has effects on wind; closely related to humidity Relative Humidity - impact on dead fuels with no moisture content Precipitation - determines moisture content of fuels What are TOPOGRAPHICAL factors that affect wildland fires? Aspect - compass direction and slope faces (southern exposures receive more sunlight and burn faster) Local Terrain Features - obstructions such as ridges, trees, and large rock outcroppings may alter airflow and cause turbulence resulting in erratic fire behavior Drainages - terrain features that create turbulent updrafts (chimney effect): Chutes (steep V-shaped drainage), Saddles (depression between 2 adjacent hilltops) What are the PARTS of a wildland fire? Origin - where fire starts and point from which it spreads Head - part that travels most rapidly Finger - long narrow strips extending from main fire Perimeter - outer boundary of fire Heel - rear of fire (opposite the head) Flanks - side of the fire Islands - unburned areas inside the perimeter Spot fire - separate fires caused by sparks or embers landing outside main fire Green - unburned fuels next to involved area Black - area which fire has consumed (relatively safe area) What is the OBJECTIVE of attacking a wildland fire? to establish a control line around the perimeter What is a DIRECT attack on a wildland fire? action taken directly against the flames at the edge or parallel to it What is an INDIRECT attack on a wildland fire? used at varying distances to halt progress of the fire by constructing a line to stop the spread What are the TEN FIRE ORDERS? Fight fire aggressively with safety Initiate all action based on current & expected fire behavior Recognize current weather conditions Ensure instructions are given and understood Obtain current info on fire status Remain in communication with crew, supervisor, and adjoining forces Determine safety zones & escape routes Establish lookouts in hazardous situations Retain control at all times Stay alert, keep calm, think clearly, act decisively What are CLASS B fires? fires involving flammable and combustible liquids and gases What are considered FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS? Those materials that have flash points LESS than 100 oF Examples are gasoline and acetone What are considered COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS? those materials that have flash points GREATER than 100oF examples are kerosene and vegetable oil What are HYDROCARBONS and POLAR SOLVENTS? Hydrocarbons - those that do NOT mix with water Polar Solvents - those that DO mix with water What is the FIRST PRECAUTION a FF must take in Class B fires? DO NOT STAND in pools of fuel or water runoff containing fuel Protective clothing can absorb fuel which can lead to burns of the skin or flaming clothes if an ignition source is present What should be done if fires around RELIEF VALVES or PIPING cannot be turned off? fire should NOT be extinguished try to contain the pooling liquid until flow can be stopped What usually happens to UNBURNED VAPORS? form pools or pockets of gas in low spots where they may ignite What are some IGNITION SOURCES that FF's must control? vehicles, smoking materials, electrical fixtures, & sparks from steel tools What can indicate the IMMINENT RUPTURE of a vessel? increase in the intensity of sound or fire coming from a relief valve What is the PREFERABLE METHOD to control flammable liquid fires? use of foam What forms can WATER be used in to control Class B fires? as a cooling agent, mechanical tool, substitute medium, and protective cover What types of incidents usually require Class B firefighting TECHNIQUES? Accidents involving vehicles transporting flammable fuels and gas utilities What affects how Class B fires are EXTINGUISHED? whether the material is a hydrocarbon (does NOT mix with water) or polar solvents (mix with water) How is water used as a COOLING AGENT? by applying water in droplet form to fires in heavier oils (raw crude) water is not effective on lighter petroleum distillates (gasoline, kerosene) or alcohols water is most useful for protecting exposures water should form a protective water film on exposed surfaces How is water used as a MECHANICAL TOOL? to move fuels to areas where they can safely burn or where ignition sources are more easily controlled fuels must never be flushed into storm drains or sewers stream should be gently played from side to side to sweep the fire and fuel away leading edge of fog stream must be kept in contact with fuel surface to avoid fire running under stream toward nozzle fog streams may also be used to dissipate flammable vapors What can be done to control SMALL LEAKS in containers? a solid stream may be directed into the opening to keep liquid back the pressure of the stream must be greater than the escaping liquid care must be taken to NOT overflow the container How is water used as a SUBSTITUTE MEDIUM? to displace fuel from pipes or tanks that are leaking displacement of fuel floats the product on top of water as long as water pressure exceeds leak pressure water is filled to a level above the leak water is seldom used to dilute flammable liquids because of the water-to-product ratio How is water used as PROTECTIVE COVER? streams used to protect teams advancing to shut off liquid or gaseous fuel valves 2 lines with a backup line is preferred How should tanks or containers be REPAIRED or SHUT OFF? on tanks or containers exposed to flame, solid streams should be "lobbed" from their maximum effective reach to the top of the tank so that water runs down both sides. Tank supports should also be cooled. Hose teams should advance under widened protective fog patterns to make temporary repairs or shut off valves Approach should never be made from the ends of the tank A back-up line should be supplied from a separate pump and water source Why should pre-incident plans for TRANSPORTATION emergencies be followed? to reduce life loss, property damage, & environmental pollution What are the difficulties posed by TRANSPORTATION emergencies? amount of fuel available to burn, vessel failure, and danger to exposures What are the DIFFERENCES in transportation emergencies and flammable fuel storage facility fires? increased life safety risk from traffic increased life safety risk to passing motorists reduced water supply difficulty in determining products involved difficulty in containing spills and runoff weakened or damaged tanks & piping from collision forces instability of vehicles location of incident (near residential, schools, etc.) How many LANES should be closed during a transportation accident? one lane and the incident lane use of open-flame flares should be avoided keep tools out of traffic lanes when PD is unavailable, one FF should be assigned traffic-control officer How should fire apparatus be POSITIONED? to take advantage of topography (land surface configuration) consider weather conditions (uphill & upwind) to protect FF's from traffic