Essentials
advertisement

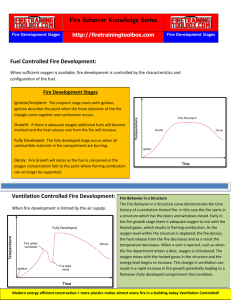
Firefighter I Fire Behavior Chapter 3 Test Name: Date: Directions: Write the correct letter on the blank before each question. Objective 1: Describe physical and chemical changes of matter related to fire. ________ 1. Which of the following occurs when a substance remains chemically the same but changes in size, shape, or appearance? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ 2. Which of the following occurs when a substance changes from one type of matter into another? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ 3. 4. Physical change Chemical reaction Exothermic change Non-molecular reaction Which of the following is a chemical reaction involving the combination of oxygen (or similar types of substances) with other materials? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ Physical change Chemical reaction Exothermic change Non-molecular reaction Sparking Pyrolysis Oxidation Vaporization Which of the following refers to reactions that give off energy as they occur? (87) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Kinetic reactions Positive reactions Exothermic reactions Endothermic reactions Chapter Test 3-1 Firefighter I ________ Fire Behavior 5. Which of the following refers to reactions that absorb energy as they occur? (87) A. B. C. D. Kinetic reactions Negative reactions Exothermic reactions Endothermic reactions Objective 2: Discuss modes of combustion, the fire triangle, and the fire tetrahedron. ________ 6. Modes of combustion are differentiated based on: (87) A. B. C. D. ________ 7. Which of the following modes of combustion requires liquid or solid fuels to be converted to the gas phase or vaporized? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ 8. 9. Standard combustion Flaming combustion Linear combustion Nonflaming or smoldering combustion Which of the following modes of combustion occurs when solid fuels undergo oxidation at the surface of the fuel? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ type of fuel. potential size of fire. where the reaction is occurring. whether the fuel can self-ignite. Standard combustion Flaming combustion Linear combustion Nonflaming or smoldering combustion Which of the following are the three components of the fire triangle? (87) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Oxygen, fuel, and heat Fuel, heat, and energy Oxygen, fuel, and a self-sustained chemical reaction Oxygen, heat, and a self-sustained chemical reaction Chapter Test 3-2 Firefighter I ________ 10. Fire Behavior Flaming combustion is accurately explained BEST by which of the following? (87) A. B. C. D. ________ 11. Fire triangle Fire tetrahedron Autoignition Piloted ignition Which of the following is NOT an element of the fire tetrahedron? (87) A. B. C. D. Oxygen Fire inhibitor Fuel Self-sustained chemical reaction Objective 3: Explain the difference between heat and temperature. ________ 12. Which of the following is energy possessed by a moving object? (89) A. B. C. D. ________ 13. Temperature is a measurement of: (89) A. B. C. D. ________ 14. forward energy. kinetic energy. thermal energy. potential energy. In the customary system, the unit of measure for heat is: (89) A. B. C. D. ________ 15. Forward energy Kinetic energy Thermal energy Potential energy joules. degrees squared. British thermal units. Standard thermal units. Applying large amounts of heat to solid fuels such as wood causes: (90) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University pyrolysis. vaporization. deflagration. autoignition. Chapter Test 3-3 Firefighter I ________ 16. Fire Behavior Which of the following is the temperature to which the surface of a substance must be heated for ignition and self-sustained combustion to occur? (90-91) A. B. C. D. Piloted ignition Autoignition Pre-combustion ignition Self-starting ignition Objective 4: Describe sources of heat energy. ________ 17. Which of the following is the most common source of heat in combustion reactions? (91) A. B. C. D. ________ 18. Which of the following occurs when any combustible is in contact with oxygen? (91) A. B. C. D. ________ 19. Oxidation Pyrolysis Spontaneous ignition Pre-combustion ignition Which of the following modes of electrical heat energy occurs when electric current flows through a conductor at a normal design limit? (92) A. B. C. D. ________ 20. Light heat energy Electrical heat energy Chemical heat energy Mechanical heat energy Arcing Sparking Resistance heating Overcurrent or overload Which of the following types of heat energy is generated by friction or compression? (93) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Light heat energy Electrical heat energy Chemical heat energy Mechanical heat energy Chapter Test 3-4 Firefighter I Fire Behavior Objective 5: Discuss the transmission of heat. ________ 21. The rate at which heat is transferred is related to the temperature differential of the bodies and the: (93) A. B. C. D. ________ 22. Which of the following refers to the transfer of heat within a body or to another body by direct contact? (94) A. B. C. D. ________ 23. Convection Conduction Radiation Absorption Which of the following refers to transmission of energy as an electromagnetic wave without an intervening medium? (95) A. B. C. D. ________ 25. Convection Conduction Radiation Absorption Which of the following refers to the transfer of heat energy from a fluid (liquid or gas) to a solid surface? (95) A. B. C. D. ________ 24. size of the objects involved. manner in which combustion started. part of the fire triangle that is the weakest. thermal conductivity of the material involved. Convection Conduction Radiation Absorption Which of the following statements about radiant heat is MOST accurate? (95) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Materials that reflect radiated heat energy increase the transmission of heat. Radiant heat is not a factor in fire development and spread in compartments. Matter having a temperature above absolute zero may or may not transmit radiant heat. Radiant heat becomes the dominant mode of heat transfer when the fire grows in size. Chapter Test 3-5 Firefighter I ________ 26. Fire Behavior Which of the following refers to materials that absorb heat but do not participate actively in the combustion reaction? (96) A. B. C. D. Reactive agents Passive agents Secondary agents Tertiary agents Objective 6: Explain how the physical states of fuel affect the combustion process. ________ 27. Fuel in a combustion reaction is known as the: (96) A. B. C. D. ________ 28. For flaming combustion to occur, fuels must be in the: (97) A. B. C. D. ________ 29. liquid state. solid state. gaseous state. chemical state. In order to burn, liquids must be: (97) A. B. C. D. ________ 30. primary agent. increasing agent. reducing agent. combustion agent. pyrolysized. vaporized. flowing. contained. Which of the following refers to the temperature at which a liquid gives off sufficient vapors to ignite, but not sustain, combustion? (98) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Fire point Flash point Autoignition point Volatility rating Chapter Test 3-6 Firefighter I ________ 31. Fire Behavior Which of the following is the primary consideration in whether solids are easy or difficult to ignite? (101) A. B. C. D. ________ 32. Surface-to-mass ratio Source of ignition Proximity to the source of heat Orientation to the source of heat Which of the following is NOT a factor that heat release rate is dependent upon? (103) A. B. C. D. Type of fuel Quantity of fuel Orientation of fuel Ignition source Objective 7: Explain how oxygen concentration affects the combustion process. ________ 33. Which of the following is the primary oxidizing agent in most fires? (103) A. B. C. D. ________ 34. Which of the following statements is MOST accurate about materials that do not burn at normal oxygen levels? (104) A. B. C. D. ________ 35. Oxygen Methane Carbon monoxide Carbon dioxide These materials will also not burn in oxygen-enriched atmospheres. These materials may burn readily in oxygen-enriched atmospheres. There materials will generally autoignite in oxygen-enriched atmospheres. These materials must reach the neutral flammable limit to sustain burning. Which of the following refers to the minimum concentration of fuel vapor and air that supports combustion? (105) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Upper flammable limit Lower flammable limit Neutral flammable limit Minimum flammable limit Chapter Test 3-7 Firefighter I Fire Behavior Objective 8: Discuss the self-sustained chemical reaction involved in the combustion process. ________ 36. Which of the following statements about self-sustained chemical reactions is MOST accurate? (105-106) A. B. C. D. ________ 37. Which of the following statements about surface combustion is MOST accurate? (106-107) A. B. C. D. ________ 38. This process is a simple process that involves the release of energy as heat. This process creates heat and light but does not create flammable or toxic products. This process inhibits the formation of free radicals and slows the oxidation reaction. This process involves many types of intermediate combustion products, many of which are flammable and toxic. It can be extinguished by chemical flame inhibition. It cannot be extinguished by chemical flame inhibition. It involves initiation or continuation of the chemical chain reaction found in combustion. It cannot be extinguished by eliminating one side of the fire triangle. In flaming combustion, the fire will continue to burn until the fuel or oxygen is exhausted or: (106) A. B. C. D. surface combustion takes over. more than 72 hours have passed. the chemical chain reaction causes molecules of methane and oxygen to break apart. an extinguishing agent is applied in sufficient quantity to interfere with the ongoing reaction. Objective 9: Describe common products of combustion. ________ 39. Which of the following causes the most fire deaths? (108) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Heat Toxic smoke Exhaustion Structural collapse Chapter Test 3-8 Firefighter I ________ 40. Fire Behavior Which of the following products of combustion is frequently identified as the cause of death for civilian fire fatalities and acts as a chemical asphyxiant by binding with hemoglobin in the blood? (108) A. B. C. D. ________ 41. Which of the following products of combustion is produced in the combustion of materials containing nitrogen and is a significant byproduct of the combustion of polyurethane foam? (108) A. B. C. D. ________ 42. Methane Carbon monoxide Hydrogen cyanide Carbon dioxide Methane Carbon monoxide Hydrogen cyanide Carbon dioxide Which of the following products of combustion is a product of complete combustion of organic materials and also acts as a respiratory stimulant? (108) A. B. C. D. Methane Carbon monoxide Hydrogen cyanide Carbon dioxide Objective 10: Distinguish among classifications of fires. ________ 43. Which of the following classifications of fires involve ordinary combustible materials such as wood, cloth, paper, rubber, grass, and many plastics? (110) A. B. C. D. ________ 44. Class Class Class Class A fires B fires C fires D fires Which of the following classifications of fires involve energized electrical equipment? (110-111) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Class Class Class Class A fires B fires C fires D fires Chapter Test 3-9 Firefighter I ________ 45. Fire Behavior Which of the following classifications of fires involve flammable and combustible liquids and gases such as gasoline, oil, lacquer, paint, mineral spirits, and alcohol? (110) A. B. C. D. ________ 46. A fires B fires C fires K fires Which of the following classifications of fires involve combustible metals such as aluminum, magnesium, potassium, sodium, titanium, and zirconium? (111) A. B. C. D. ________ 47. Class Class Class Class Class Class Class Class A fires B fires C fires D fires Which of the following classifications of fires involve oils and greases normally found in commercial kitchens and food preparation facilities using deep fryers? (112) A. B. C. D. Class Class Class Class A fires B fires C fires K fires Objective 11: Describe the stages of fire development within a compartment. ________ 48. When fire development is limited by the air supply, it is said to be: (113) A. B. C. D. ________ 49. fuel controlled. ventilation controlled. combustion controlled. environmentally controlled. During which stage of fire development is the fire small, confined to the material first ignited, and may self-extinguish? (114) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Incipient stage Growth stage Fully developed stage Decay stage Chapter Test 3-10 Firefighter I ________ 50. Fire Behavior During which stage of fire development has the fire not yet influenced the environment to a significant extent? (114) A. B. C. D. ________ 51. During which stage of fire development does the fire begin to influence the environment within the compartment? (116) A. B. C. D. ________ 52. the top layer. the lower layers. the neutral plane. both the top and lower layers. Rollover Flashover Backdraft Isolated flames Which of the following refers to a condition where the unburned fire gases accumulated at the top of a compartment ignite and flames propagate through the hot gas layer or across the ceiling? (118) A. B. C. D. ________ 55. in in in in Which of the following refers to pockets of flames that may be observed moving through the hot gas layer above the neutral plane? (118) A. B. C. D. ________ 54. Incipient stage Growth stage Fully developed stage Decay stage In thermal layering, the hottest gases tend to be: (117) A. B. C. D. ________ 53. Incipient stage Growth stage Fully developed stage Decay stage Rollover Flashover Backdraft Isolated flames Which of the following refers to the transition when conditions in the compartment change very rapidly from partial to full involvement of the compartment? (118) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Rollover Flashover Backdraft Isolated flames Chapter Test 3-11 Firefighter I ________ 56. Fire Behavior Which of the following does NOT occur just before flashover? (120) A. B. C. D. ________ 57. During which stage of fire development are all combustible materials in the compartment burning? (121) A. B. C. D. ________ 58. Incipient stage Growth stage Fully developed stage Decay stage During which stage of fire development does the fuel become consumed or the oxygen concentration fall to the point where flaming combustion can no longer be supported? (121) A. B. C. D. ________ 59. Temperatures rapidly increase Temperatures decline suddenly Additional fuel becomes involved Fuel in the compartment gives off combustible gases Incipient stage Growth stage Fully developed stage Decay stage An increase in ventilation in a fire that is in the decay stage can result in a deflagration called a: (122) A. B. C. D. rollover. flashover. backdraft. flameover. Objective 12: Summarize factors that affect fire development within a compartment. ________ 60. Which of the following are the most fundamental fuel characteristics influencing fire development in a compartment fire? (125) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Mass and surface area Age and flammability Fuel moisture and mass Surface area and density Chapter Test 3-12 Firefighter I ________ 61. Fire Behavior Which of the following is NOT a factor that influences the availability and location of additional fuels? (125) A. B. C. D. ________ 62. All other things being equal, a fire in a large compartment will: (127) A. B. C. D. ________ 63. Structural openings Construction type Occupant load Building ventilation systems Which of the following is NOT a thermal property of the enclosure? (128) A. B. C. D. ________ 65. develop faster than one in a small compartment. develop more slowly than one in a small compartment. develop at the same rate as one in a small compartment. develop at a rate either faster or slower than a small compartment. Which of the following is NOT a determination of pre-existing ventilation? (128) A. B. C. D. ________ 64. Contents (nonstructural fire load) Construction (structural fire load) Configuration of the building Distance to the nearest fire sprinkler Insulation Retention Conductivity Occupant load Which of the following ambient conditions can be an extremely significant factor in structural fire development? (129) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Humidity Temperature Barometric pressure Strong winds Chapter Test 3-13 Firefighter I Fire Behavior Objective 13: Describe methods used to control and extinguish fire. ________ 66. Which of the following methods of controlling and extinguishing a fire depends on reducing the temperature of a fuel to a point where it does not produce sufficient vapor to burn? (130) A. B. C. D. ________ 67. Which of the following methods of controlling and extinguishing a fire effectively extinguishes any fire? (131) A. B. C. D. ________ 68. Fuel removal Temperature reduction Oxygen exclusion Chemical flame inhibition Which of the following methods of controlling and extinguishing a fire interrupts the combustion reaction and stops flame production? (132) A. B. C. D. ________ 70. Fuel removal Temperature reduction Oxygen exclusion Chemical flame inhibition Which of the following methods of controlling and extinguishing a fire reduces a fire’s growth and may totally extinguish it over time, but is not generally used for extinguishment in structure fires? (131) A. B. C. D. ________ 69. Fuel removal Temperature reduction Oxygen exclusion Chemical flame inhibition Fuel removal Temperature reduction Oxygen exclusion Chemical flame inhibition Which of the following methods of controlling and extinguishing a fire uses water for the extinguishment of smoldering fires? (130) A. B. C. D. Fire Protection Publications Oklahoma State University Fuel removal Temperature reduction Oxygen exclusion Chemical flame inhibition Chapter Test 3-14