BOH4M1_EX
advertisement
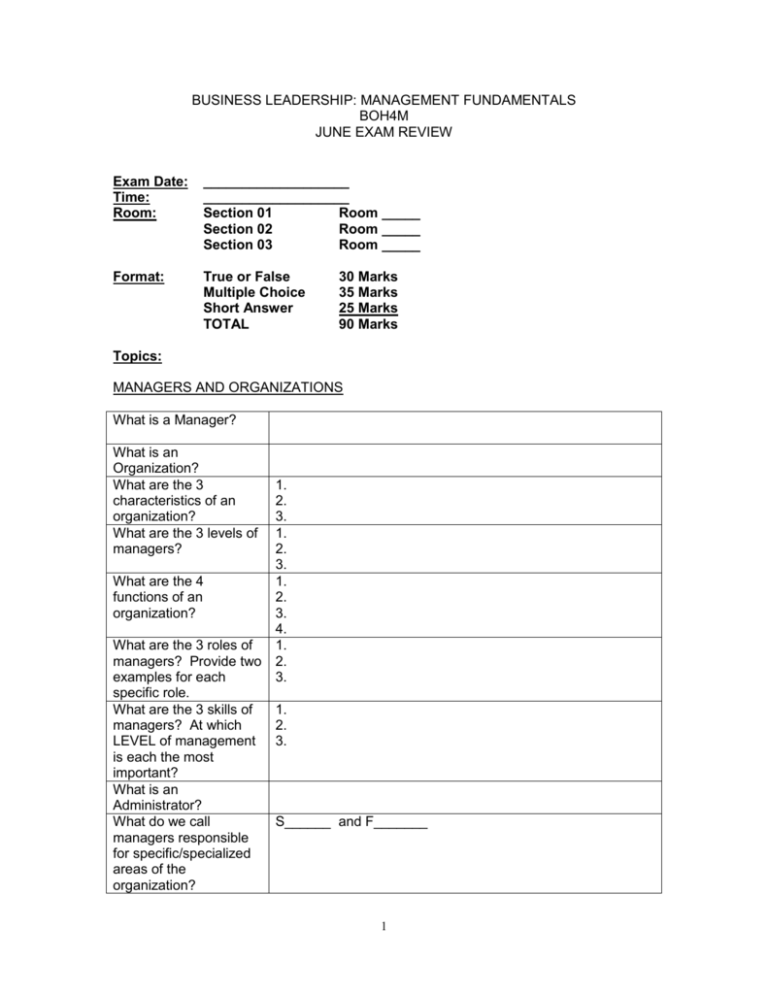
BUSINESS LEADERSHIP: MANAGEMENT FUNDAMENTALS BOH4M JUNE EXAM REVIEW Exam Date: Time: Room: ___________________ ___________________ Section 01 Room _____ Section 02 Room _____ Section 03 Room _____ Format: True or False Multiple Choice Short Answer TOTAL 30 Marks 35 Marks 25 Marks 90 Marks Topics: MANAGERS AND ORGANIZATIONS What is a Manager? What is an Organization? What are the 3 characteristics of an organization? What are the 3 levels of managers? 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. What are the 4 1. functions of an 2. organization? 3. 4. What are the 3 roles of 1. managers? Provide two 2. examples for each 3. specific role. What are the 3 skills of 1. managers? At which 2. LEVEL of management 3. is each the most important? What is an Administrator? What do we call S______ and F_______ managers responsible for specific/specialized areas of the organization? 1 What do we call managers responsible for contributing to the bottom line ($) and broad areas of the organization? What are the 6 major challenges faced by managers and organizations in 2014? **Be able to define each with examples. L______ and G________ 1. Diversity 2. Intellectual Capital 3. Globalization 4. Ethics 5. Careers 6. Technology Define “prejudice”. Define “glass ceiling”. Define “discrimination”. Who is Charles Handy and what are the 3 types of workers according to his shamrock theory? (look at your DIGECT internet search package) Define “fees-forservices”. Define “free agents”. What is decisionmaking? What is problemsolving? What are the 2 types of decisions managers are faced with? What are the 3 decision conditions/environments that managers are faced with? How do the types of decisions match up with the 3 types of decision environments? What are the 2 main types of thinking that managers use to solve problems? 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 2 What are the 5 steps of the decision-making process? List one advantage and one disadvantage of group decision-making over individual decisionmaking. What is a heuristic? What are the 3 types of heuristics studied in class? What are Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y assumptions? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Advantage: Disadvantage: 1. 2. 3. PLANNING Mission Statement Core Values Short-term Goals Strategic vs. Operational Goals BCG Matrix SWOT Analysis Observable Organizational Culture Core Organizational Culture ORGANIZING AND ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN Departmentalization Functional Organizational Chart 3 Divisional Organizational Chart (4 types) Matrix Organizational Chart Informal/Shadow Organizations 6 Trends in Organizing 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Bureaucratic (Adaptive) Organizational Design Mechanistic (Organic) Organizational Design Contingencies of Design (PESTS) P– ESTS- HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT (see review package for unit test) Attracting a Quality Workforce Recruitment: Interviews: Psychological Testing: Reference Checks: Developing a Quality Workforce Employee Orientation: On-the-job vs. Off-the-job Training: Performance Appraisals (360 degree feedback, BARS, etc.) 4 Maintaining a Quality Workforce Work-life Balance: Compensation Methods: Flexible/Cafeteria Benefits: Retention vs. Turnover: Exit Interviews: Health and Safety laws OHSA WSIB Demographics and Retirement OSA CPP Ontario and Canada Labour Laws Canadian Human Rights Code – Canada Labour Code – Employment Equity Act – Pay Equity Act – LEADERSHIP Position Power 1. 2. 3. Personal Power 1. 2. Trait Approach Behavioural Approach Contingency Approaches 1. Fiedler 2. Hersey-Blanchard 3. House 4. Vroom-Jago 5 Transformational Leadership (4 I’s) 1. 2. 3. 4. MOTIVATION AND REWARDS/COMPENSATION What is Motivation? Intrinsic Rewards Extrinsic Rewards Content Theories 1. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 2. Alderfer’s ERG 3. Herzberg’s 2 Factors 4. McClelland’s Needs Process Theories 1. Equity 2. Expectancy (M = E x I x V) 3. Goal-setting Reinforcement Theories 1. Positive Reinforcement 2. Punishment 3. Extinction 4. Negative Reinforcement 4 Types of Rewards 1. Seniority 2. Job-status 3. Competency-based 4. Performance-based COMMUNICATION, PERCEPTION, CONFLICT and NEGOTIATION What is Communication? Efficient vs. Effective Communication 6 Barriers to Communication Channel Richness What is perception? Attribution Error Self-serving Bias Perceptual Biases/Distortions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5 Conflict Management Styles Negotiation Process Pitfalls of Negotiating Bargaining Zone Mediator vs. Arbitrator ETHICS AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY What are ethics? 4 Viewpoints 1. individualism 2. justice 3. utilitarian 4. human-rights Whistleblower 7 Extra Review: There are True/False and Multiple Choice questions from each of the following major categories in the textbooks at the back of the classroom. In preparation for your exam, as “reminders/warm-ups”, you should try the following T/F and M/C questions from your textbook. The answers can be found at the back of your textbook. ORGANIZING Page 277-278 M/C #1-6, 8-10 T/F # 11-20 ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN Page 298-299 M/C # 2-4, 6, 7 T/F # 11-14 HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT Page 330-332 M/C #1, 3, 6, 9, 10 T/F #14, 19 LEADERSHIP Page 357-358 M/C #3, 6, 7, 9 T/F #11-13, 15-20 MOTIVATION AND REWARDS Page 383-384 M/C #1-6, 9, 10 T/F #11, 12, 14, 16-18, 20 COMMUNICATION AND INTERPERSONAL SKILLS, PERCEPTION, CONFLICT and NEGOTIATION Page 468-470 M/C #1, 2, 8, 9 T/F #11, 16, 17, 19, 20 ETHICS AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY Page 166-168 M/C #1, 2, 5, 6, 10 T/F #11, 12, 15, 17 Questions to answer: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The Corporate Culture is also known as the _______________________. It refers to the way things are done in an organization, each organization being slightly different. An Observable Culture is visible – it can be seen and heard. Elements include: ________, ________, ___________, and __________. Problem solving is… What do we ultimately want to be able to do at the end of the problem-solving process? (also known as making a choice among alternative courses of action) When do we make a Programmed Decision? When do we make a Nonprogrammed Decision? Who usually makes these decisions? 8 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. A non-programmed decision is made when there is a _________ situation. A decision must be made quickly and properly to avoid disaster. Decisions are made under which conditions (also known as environments)? Identify and describe each condition in detail! Planning sets the direction, otherwise known as a plan that states actions to be taken in order to accomplish company ___________________. Fill in the blanks for the Types of Plans used by Managers: -___________________ and Long-Range -Strategic and ___________________ -Policies and ____________________ A policy is… A procedure is… Policies are (a) standing plans, used over and over OR (b) single-use plans, used only once. Budgets are (a) standing plans, used over and over OR (b) single-use plans, used only once. What is the difference between a competitive advantage and a sustainable competitive advantage? The mission of the organization is it’s… Which 3 questions do company’s ask themselves when developing their Mission? Core values support an organization’s _________________. What do Core Values accomplish for an organization? What do the letters SWOT stand for? Which of the components of SWOT are used to look at problems and opportunities that are external to a company? Come up with one of each S, W, O and T for the company Google Inc. What do the letters BCG stand for? What are the major quadrants of a BCG Matrix analysis? A company is considering investing money in a new product that is already being offered by other companies (e.g: a special sports shoe). Which two “things” will the company want to analyze on the BCG Matrix? Make an assumption and state where the company sits in relation to these two “things”. What should their strategy be going forward? ________________________ is the process of arranging people and other resources to work together to accomplish a goal. This is visually represented by drawing an __________________________. You have been asked to change the following organizational chart for Danier leather to a functional organizational chart. (a) What type of departmentalization is being used in the org. chart above? _____________________ (b) Draw the functional chart below. 9 26. 27. A matrix chart is … Bell Canada technicians get together every Friday to play softball. There is some business/ “shop” talk that takes place in between innings. This is referred to as the ________________ structure of a company. An organizational chart on the other hand is referred to as the ____________ structure. 28. Identify which of the 6 trends of organizational structures is being adhered to/followed/referred to: (a) Individual banks in geographically dispersed locations (e.g: bank branches) are closely monitored by upper management in head office for performance results. (b) Dilbert’s boss tells him that he is responsible for coming up with a name for their newest product. He has one week and a small team to accomplish this task. Dilbert must handle the entire naming process from beginning to end. (c) There are only 3 layers of management at “Flat-Pancake Inc.” – the Supervisors who report to the Directors who report to the Chief Officers (CEO, CIO, COO, etc.). (d) The “Flat-Pancake Inc.” company Directors only have 2 Supervisors reporting to them. Last year they had 10 Supervisors each. (e) The “Flat-Pancake Inc.” company only has 2 assistants and 1 computer network administrator to support the entire organization. (f) Each person at the “Flat-Pancake Inc.” reports to only one boss. Organizational design is different in concept from an organizational chart. Describe the difference. A bureaucratic organization follows a(n) __________ design while an adaptive organization follows a(n) ___________ design. Identify each of the following as Bureaucratic (B) OR Adaptive (A). (a) based on order, logic and authority ___ (b) encourage worker empowerment and participation ___ (c) informal and personal ___ (d) many rules and procedures ___ (e) shared tasks ___ (f) narrow spans of control ___ (g) few teams ` ___ Identify each of the following as either (A) Mass production; (B) Continuous process; or (C) Small-batch production. (i) GM assembly plant ___ (v) Weston Bakery ___ (ii) Sign of the Skiier ___ (vi) Trophies-R-Us ___ (iii) Tasty Maple Syrup Co. ___ (vii) Abitibi Toothpick Mill ___ (iv) Petro-Canada Refinery ___ What is ethics? What is considered ethical behaviour vs. legal behaviour vs. values? What are: individualism view, justice view, utilitarian view, human-rights view? What is a whistleblower? 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 10 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. How does a company maintain high ethical standards? -code of ethics, whistleblower protection, role models, training, etc. What is the “ethics double-check”? What is controlling? What are the 4 major controls that company’s put into place? What does it take to attract a quality workforce? What is a behavioural interview? What is an example of a psychological test? What is the difference between a reference check and a background check? What does it take to develop a quality workforce? What is employee orientation and what is it’s purpose? What is on-the-job training vs. off-the-job training? What is a coach and what are the 2 types of coaching? What does it take to maintain a quality workforce? What is retention and what is turnover? What is leadership? What are the 3 approaches to leadership What are the concepts of the 4 contingency approaches of leadership - Fiedler’s Least-Preferred Co-worker, House’s Path-Goal, Hersey-Blanchard’s Situational Leadership, and Vroom-Jago’s Leadership Participation Theory? What are the 4 “I”’s of transformational leaders? What are the 5 types of power and which are position vs. personal? What is the difference between extrinsic rewards and intrinsic rewards? What are the details behind the content theories of motivation (Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, ERG Theory, Two-Factor Theory, Acquired Needs) and how do they relate to intrinsic and extrinsic rewards? What are the details behind the process theories of motivation (Equity Theory, Expectancy Theory, Goal-Setting Theory)? What are the 4 reinforcement theory approaches? What are the 4 main compensation methods? Provide examples of each. What is involved in the communication process? What makes communication effective vs. efficient? What is a barrier to communication? What is channel richness? What is perception? What is the difference between attribution error and self-serving bias? What are the 4 perceptual distortions? What are the 2 types of negotiation? What are the pitfalls of negotiation? What is the bargaining zone? What is mediation vs. arbitration? 11






