Document
advertisement

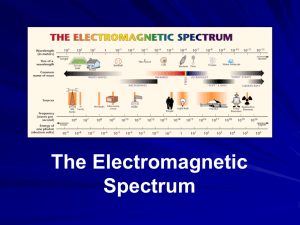
Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1. What kind of light can a bee see that you cannot see? A bee can see ultraviolet light. 2. In what way is visible light similar to ultraviolet light? Both visible light and ultraviolet light are kinds of electromagnetic waves CHARACTERISTICS OF EM WAVES 3. How is the speed of a wave determined? The speed of a wave is determined by multiplying its wavelength by its frequency. 4. The entire range of EM waves is called the electromagnetic spectrum 5. Name and arrange the seven kinds of EM waves in order from long wavelength to short wavelength. From the longest to the shortest wavelength, the EM waves are radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet, X rays, and gamma rays. RADIO WAVES 6. Waves used for broadcasting radio signals are called radio waves 7. Describe how radio signals are broadcast? A radio station converts sound into an electric current. The current produces radio waves that are sent out in all directions by the antenna. A radio receives radio waves and then converts them into an electric current, which then is converted into sound. 8. Changing the amplitude or frequency of waves is called modulation. 9. Which type of radio waves—AM waves or FM waves—can travel a longer distance and why? AM waves can travel farther because they can bounce off the atmosphere. 10. Why does music broadcast from FM stations sound better than music broadcast from AM stations? FM waves are less affected by electrical noise, so the sound quality is better 11. Which kind of radio waves are used by television stations to carry sound? Television stations use frequency-modulated (FM) waves to carry sound Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 4 The Nature of Light Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ 12. Which kind of radio waves are used by television stations to carry pictures? Television stations use amplitude-modulated (AM) waves to carry pictures. 13. How are cable television signals sent to televisions in homes? Cable television signals are transmitted to artificial satellites orbiting Earth. The waves are amplified and relayed back to ground antennae. They then travel through cables to home televisions. MICROWAVES 14. In what way are the wavelengths and frequencies of microwaves different from radio waves? Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than radio waves 15. Name three ways microwaves are used. Microwaves are used to cook food, to send information over long distances, 16. In a microwave oven, the microwaves are created by a device called a(n) magnetron, which accelerates charged particles. 17. What do the letters in radar stand for? The letters stand for radio detection and ranging. 18. In addition to checking the speed of a car, what are two other ways radar is used? Radar is used to watch the movement of airplanes and to help ships navigate at night. INFRARED WAVES 19. In what way are the wavelengths and frequencies of infrared waves different from the wavelengths and frequencies of microwaves? Infrared waves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than microwaves. 20. How are infrared waves able to make you feel warm? Skin absorbs infrared waves that strike the body. The energy of the waves causes the particles in the skin to vibrate. 21. Name three sources of infrared waves. Three sources of infrared waves are buildings, tires, and people. 22. On What does the amount of infrared waves that an object gives off depend? It depends on an object’s temperature VISIBLE LIGHT 23. The very narrow range of wavelengths and frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see is visible light 24. In what ways are the wavelengths of visible light different from infrared waves? Visible light waves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than infrared waves 25. The visible light of all wavelengths combined is white light Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 5 The Nature of Light Name ______________________________ Class ___________________ Date __________________ 26. What color are the longest wavelengths of visible light? Red Light 27. What color are the shortest wavelengths of visible light? Violet 28. The range of colors of visible light is called the visible portion of the EM spectrum 29. What does each letter in the imaginary name ROY G. Bi V stand for? They stand for red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet 30. What can cause all the colors of visible light to be seen in a rainbow? Water droplets separate white light into visible light of different lengths. ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT 31. In what way are the wavelengths and frequencies of ultraviolet light different from the wavelengths and frequencies of visible light? Ultraviolet light waves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies than visible light. 32. Describe four bad effects of ultraviolet light. Too much ultraviolet light can cause sunburn, skin cancer, wrinkles, and damage to the eyes. 33. What are two ways you can protect yourself against ultraviolet light? You can use sunscreen with a high SPF and wear sunglasses. 34. Describe two good effects of ultraviolet light. Ultraviolet waves are used to kill bacteria on food and surgical cells, and skin cells that have been exposed to ultraviolet light produce vitamin D. X RAYS AND GAMMA RAYS 35. Which EM waves have some of the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies? X rays and gamma rays have the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. 36. What is one use of X rays in the medical field? X rays are used to take pictures of bones. 37. What can happen from too much exposure to X rays? Too much exposure to X rays can damage or kill living cells 38. How are patients protected from exposure to X rays? Special aprons lined with lead protect patients from too much exposure to X rays. 39. How are gamma rays used to treat cancer? Gamma rays are focused on tumors inside the body to kill cancer cells. 40. What do gamma rays kill in food? harmful bacteria Original content Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt Science and Technology 6 The Nature of Light