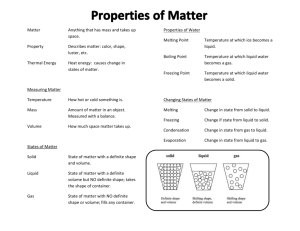
Matter can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space
advertisement

Matter can be defined as anything that has mass and takes up space (volume). Mass is the amount of MATTER in an object. Volume is the amount of space that the MATTER in an object takes up. Matter can exist in 4 forms (also called states): 1. solid - has definite shape and volume. Example: ice, salt, wood. 2. liquid - has definite volume but no definite shape. Example: water, milk, mercury. 3. gas - has no definite volume or shape. Example: air, water vapor, CO2. 4. plasma - the state of matter that exists at high temperatures, it consists of electrically charged particles. Example: sun, nuclear fusion. Physical property are the qualities and characteristics of matter used to describe it but do not produce a new substance. Examples of Physical Properties include: Color – every object has a color Odor – intensity of smell Texture - the feel it has Density – The amount of mass in a given volume. Calculated mass divided by volume. Luster – how shiny or dull it is when reflecting light Ductility – ability to be drawn into thin wires Malleability – ability to be beaten into thin sheets Elasticity – ability to return to original shape Viscosity - the resistance of a liquid to flow Hardness – ability to be scratched or resist being scratched Conductivity – allows energy to flow through it, electricity or heat Insulator – resists flow of energy, electricity or heat Change Points – Melting Point, Boiling Point, Condensation Point, and Freezing Point Chemical properties involve changes (or attempted changes) of matter to produce a new substance that can not easily be changed back. It can be typically described by the following: Color – change in color indicates a chemical change Temperature – change in temperature indicates a chemical change.