File
advertisement

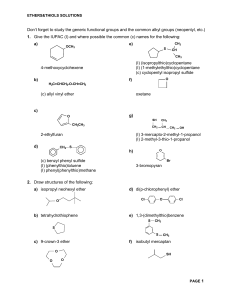
Alkyl Halide:It is the class or family of organic compounds which contain halide group-x is called alkyl halides. Its general formula CnH2 n + IX or R-X. Where “R” is called alkyl group-x is halide (Cl,Br,I). A- Nomenclature:1:-Common system: - In this system these compounds are named as .first writing the name of alkyl group to which x is attached, the then writing the name of halide ion. Example: - (i) CH3 –CL (ii) CH3-CH2 –Cl (iii) CH 3 –CH2 – CH2 – Cl Methyl chloride Ethyl chloride Propyl chloride 2:-IUPAC SYSTEM:- (compounds are named as Haloalkane). 1.Select the longest chain to which the halogen is attached and give it the name of corresponding alkane. 2.Prefix the name of the alkane by chloro, bromo, iodo or fluoro. 3.Number the chain beginning at the end which is nearest to the halogen atom or side chain. 4.The position of halogen atom and other susbtituents is indicated by number, name and placed as prefixes in alphabetical order. 5.Two or more identical halogens substituents are named by prefixes di, tri, tetra etc. Structure formula Common name IUPAC system 1,CH3-Cl Methyl chloride Chloro methane 2,CH3-CH2-Br Ethyl bromide Bromo ethane 3,CH-Cl3 Chloroform Tri-chloro methane 4,CH2-I2 Methyl di iodide Di iodo methane 5,CCl4 Carbon tetra chloride Tetra chloro methane 6,CH3- CH –CH3 Iso-propyl chloride 2-Chloro propare Cl 7,CH3-CH-CH2-CH3 Cl 8,CH3-CH-CH2-I Iso-butyl chloride 2- Chloro butane 2-methyl-1-iodo propane. Iso-butyl iodide CH3 CH3 9,CH3-C-Br Ter:butyl bromide 2-blomo-2-methyl propane. CH3CH3 10,CH3-C-CH2-Cl Neo-pentyl chloride CH3 11,CH2=CH-Cl 12,CH2=CH-CH2-Cl 1-chloro -2,2-di methyl propane. 1-chloro ethane Vinyl chloride Allyl chloride 3-chloro-1-propene 1 ALCOHOLS:Alcohols are compounds in which a hydroxyl group (-OH) is bonded to an alkyl group. The general formula of alcohol is CnH2 n+1OH or R-OH. The functional group is -OH group or hydroxyl group. Common System:In this system ethyl alcohols are named as alkyl alcohol, the name of alkyl group is written first followed by the word alcohol. Alcohol containing up to five carbon atoms are known by their common names. IUPAC System:1. Select the longest chain of carbon atoms as the parent hydrocararbon, the carbon containing hydroxyl group. 2. Name the longest chain by dropping “e” of the cottesponding alkane and adding the ending –Ol. Alkane –e +Ol alkanol 3. Numbering starting from that end where the –OH group in nearest. 4. The position of –OH group and alkyl group indicated by number of carbon atoms to which they are attached. 5. If more than one –OH group are present in the longest chain of carbonators the use the suffixes, adiol, triol, etc. without replacing the final “e” from the parent alkane. Sr.NoStructure . formula 1. CH3-OH 2. 3. 4. CH3-CH2-OH CH3-CH2 –CH2-OH CH3-CH-OH 5. CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-OH Common name Methyl alcohol Ethyl alcohol n-propyl alcohol Sec: propyl alcohol Or iso propyl alcohol I.U.P.A.C Name Methanol Ethanol 1-propanol 2-proupanol Iso- butyl alcohol methyl 1-propanol CH3 CH3 -CH-CH2-CH3 6. Sec :butyl alcohol 2-butanol n-pentyl alcohol 1-pentanol neo- pentyl alcohol 2,2-di methyl 1-propanol tert : butyl alcohol 2-methyl -2- propanol iso- pentyl alcohol 2-methyl -1- butanel OH CH 7. 3- 8. CH2-CH2-CH2-CH-OH CH3 CH3-C-CH2-OH CH3 CH3 CH3-C-OH 9. CH3 CH3-CH2-CH-CH2-OH 10. CH3 ethane-1,2-diol 2 11. ethylene glycol (1,2-ethane diol) glycerol 1,2,3-propantriol CH2=CH-OH lohoV AVliniV Ethene – 1-ol CH2=CH-CH2-OH AVVoV AVliniV 2- propene-1-ol CH2-CH2 OH 12. OH CH2-CH2-CH2 OH 13. OH OH 14. ETHERS:Ethers are compounds in which oxygen is bonded to two alkyl group are called ethers. Its general formula is R-O-R or CnH2n+2O. Nomenclature:Common system:Ethers are organic compounds usually named on the basis of the two alkyl groups attached to the oxygen atom are named in alphabetical order and the word ether is added. If the groups are same, the prefix –di-used before the name of alkyl group. I.U.P.A.C Name:In the IUPAC system other are named as alkoxy alkanes (the others are alkanes in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by an alkoxy (-OR) group). (It is the smaller alkyl group with oxygen atom is called alkoxy substituents). The larger radical in selected as parent hydro carbon. 3 2 1 E.g.:- CH3 CH2-CH2-O-CH3 1-methoxy propane CH3 OCH2-CH3 CH3-CH- CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 2- Ethoxy-5-methoxy hexane. Sr Structure Fourmula No Common Name IUPAC Name 1 2 CH3-O-CH3 CH3-CH2-O-CH3 Common system Di methyl ether Ethyl methyl ether IUPAC Name Methoxy methane Ethoxy ethane 3 C2H5-O-C2H5 Di – ethyl ether Ethoxy ethane 4 CH3-CH-O-CH3 I so- propyl methyl ether 2-methoxy propane CH3 3 5 CH3 │ CH3-CH2-O-C-CH3 │ CH3 Ethyl tert: butyl ether 2-methyl – 2-methoxy propane 6 CH3-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 Methyl- propyl ether 1-methoxy propane ALDEHYDE:Aldehydes are compounds in which the carbonyl group (C=O) is bonded to an alkyl group and hydrogen are called aldehydes. Its general formula CnH2nO or R-CHO functional group -CHO or -C-H O Nomenclature:A: - COMMON SYSTEM:The common name of aldehyde is derived from the common name of acid to which the aldehyde is oxidized- The ending –IC acid is replaced by the word aldehyde. e.g. H--CHO formaldehyde CH3 – CHO acetaldehyde Thus root name of carboxylic acid is written first then name of family or class i.e. aldehyde is added as a suffix. B:- IUPAC NAME (system):01:- Select the longest chain of carbon atom containing the aldehyde group (-CHO) as a parent structure. 02:- The name is obtained by dropping the final –e from the name of corresponding alkane and adding ending –al. Alkane – e + al alkanal. 03:- Number the carbon chain by assigning number –I to the aldehydic carbon. 04:- The positions of substituents are indicated by the number of the carbon to which they are attached. 05:- when two or three aldehydes group in a molecule it is named as alkandial. S.No Structural formula Common name IUPAC Name 1. H-C-H Formaldehyde Methanal O 2. CH3- C-H Acetaldehyde Ethanal 3. 4. 5. O CH3-CH2-CH2 CHO CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CHO CH3-CH2-CHO Butyrelaldelyde Valeraldehyde Propionaldehyde Butanal Pentanal Propanal 4 6. 7. 8. 9. CH3-CH-CHO CH 3 γ β α CH3-C-CH2-CHO │ CH3 Iso-butyraldelyde or α-methyl Propionaldehyde 2-methyl-1- propanal β methyl butyre aldehydie 3-methyl -1- Butanal CHO-CHO Glaxol CH2-CH-CHO Glyceraldehyde 1,2-ethandial 2,3-dihydroxy-1-proponal OH OH 9. CH3 CH3-CH-CH-CH2-CHO 10. β-ethyl γ methyl Valeraldehyde 3-ethyl-4-methyl Pentanal α-methylα-bromopropionaldehyde 2-bromo-2-methyl -1-propanal C2H5 CH3 11. CH3-CH-CHO Br KETONE:Ketenes are compounds in which the carbonyl group (=C=O) is bonded to two alkyl radicals. O 01. 02. 03. 04. Its general formula CnH2nO or R-C-R functional group of ketone is R-CO-R. Where “R” stands for alkyl group may be different or same. A: Common system:- In common system, the name of alkyl group is written first then name of family ketone is added. When two alkyl groups are same, the prefix “di” is added before the name of alkyl group. The name of lower alkhyl group is written first if two different alkyl radicals are different. When two alkyl groups are same then it is said to be simple or symmetrical ketone. When two alkyl groups are different then it is said to be un-symmetrical ketone. For example: CH3-CO-CH3 C2H5-CO-CH3 Diethyl ketone. Ethyl methyl ketone IUPAC SYSTEM:Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms containing the carbonyl group as a parent structure. Name the longest chain by dropping “e” from the name of corresponding Alkane and adding the “one”. Alkane –e+one alkanone Number the carbon chain from the end nearest to the carbonyl group. The position of substituents is indicated by the number of carbon atom to which they are attached. 5 05. Locate the position of carbonyl group by writing its number followed by a hyphene at the name of ketone. S.No 01. Structural formula CH3-CO-CH3 Common name Di methyl ketone or Acetone IUPAC Name 2-Propanone 02. CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3 Di ethyl ketone 3-Pentanone 03. CH3-CO-CH2-CH3 Methyl ethyl ketone 2- Butanone 04. CH3-CO-CH2-CH2-CH3 Methyl n-propyl ketone 2- Pentanone 05. CH3-CO-CH-CH3 Methyl Iso propyl ketone 3-methyl -2-butanone 06. CH3 CH3-CH-CO-CH2-CH2-CH3 Sec: butyl Iso propyl ketone 2,4-dimethyl -3-hexanone Methyl vinyl ketone 1-butene-3-one CH3 CH3 07. CH3-CO-CH2=CH2 08. CH3-CO-CH2-CH2-CO-CH3 2,5-hexane dione 09. CH-CO-CH=CH-CO-CH3 3-hexene -2,5-dione CARBOXYLIC ACID: Organic compounds which contain carboxyl group –COOH in their molecule are called carboxyl acid. It’s general formula CnH2 n +1COOH Or R-COOH A: COMMON SYSTEM: Common name of carboxylic acid are derived from their origions (occurrences) 6 SR No 01. Structure HCOOH Common name Formic acid Occurrences Ants (L-Formica) 02. CH3 COOH Acetic acid Vinegar (L-acetum) 03. CH3 CH2 COOH Prop ionic acid Milk (Gr: protos=first, pion=fat) Found in butter (L-butyrum) 04. CH3 (CH2)2 COOH Butyric acid 05. CH3(CH2 )3 COOH Valeric acid 06. CH3(CH2)4 COOH Caproic acid 07. CH3(CH2)14 COOH Palmitic acid Valerian roof (L-valere=to be strong ) Goat (L-caper) (goat milk ) palms fats 08. CH3-(CH2)16 COOH Stearic acid NOTE: - L=Latin Gr=Greek IUPAC RULES FOR NAMING CARBOXYLIC ACID 01. Select the longest chain of carbon atoms containing the carboxylic group as parent structure. 02. The terminal “e” of the Alkane is replaced by adding –oic acid Alkane-e+oic acid Alkanoic acid 03. Number the chain starting with carboxyl carbon as number I. 04. Other substituents are numbered, named and placed as prefixes in alphabetical order. e.g.: ` CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-COOH 3-Methyl butanoic acid 05. When there are two carboxyl groups in a molecule, it is named as Alkane dioic acid. e.g. HOO-C-C-OOH 1, 2-Ethandioc acid or oxalic acid CH3 γ β α CH3-CH2-CH-COOH α-Methyl butyric acid or 2-methyl butanoic acid. δ γ β α CH3-CH2-CH3-CH2-COOH CH3 CH3 - α,β– dimethyl valeric acid or 2, 3- di methyl pentanoic acid β α CH3-CH2-COOH OH 7 α-Hydroxy propionic acid or 2-hydroxy propanoic acid HOOC-CH2-CH2-COOH OH OH Tartaric acid or 2, 3-dihydroxy butandioc acid HOOC-CH2 CH2-COOH Succinic acid or 1, 4- butandioc acid HOOC-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH Gultenic acid or 1, 5- pentandioic acid HOOC-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH Adipic acid OR 1, 6- hexandioic acid CH2 - COOH OH-C-COOH CH2-COOH Citric acid or 2- hydroxy-1, 2, 3-propan – trioic acid CH3 CH3-C-COOH CH3 Piralic acid or 2, 2-di methyl propanoic acid HOOC-CH== CH-COOH Maleic acid or 2-butendioic acid α,β,γ and δ system in common names : Greek letters α , β, γ and δ are used to indicate the position of substiluents in common names α carbon is that to which is functional group (-COOH) is attached – next to α is β carbon and next to β is γ carbon. i.e. C - C - C - C - COOH δ γ β α Thus (i) α -methyl propionic acid CH3 – CH - COOH CH3 (ii) β - methyl butyric acid CH3-CH-CH2-COOH γ β α CH3 δ (iii) γ β α α , β di methyl valeric acid CH3-CH2-CH-CH-COOH 8 CH3 CH3 δ γ β α δ- Hydroxy caproic acid CH3-CH-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH (vi) OH α - chloro Succinic acid (vii) α COOH-CH2-CH- COOH Cl NOMENCLATURE OF ESTER Esters are formed from carboxylic acid R-COO-H by the replacement of H by an alkyl radical. It’s general formula CnH2nO2 or R-COO-R. Its F.G is – COOR (Alkoxy carbonyl group). The name of ester consists of two words. First we write the name of alkyl radical attached to oxygen atom, and then we write the second word the name of parent acid whose suffix –ic acid is changed by –ate. EXAMPLE: - HCOOCH3 Methyl formate Sr.No COMMON NAME STRUCTURE FORMULA H-C-O-CH3 01. Methyl formate Methyl methanoate O CH3-C-O-CH2-CH3 02. Ethyl acetate I.U.P.A.C NAME Ethyl ethanoate O 03. Ethyl propionate C2H5-C-O-CH2-CH3 Ethyl propanoate 04. Methyl propionate O C2H5-COO-CH3 Methyl propanoate 05. Iso – propyl acetate or sec:propyl acetate CH3COO-CH-CH3 Iso-propyl propanoate CH3 CH3 06. C CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-COO-C-CH3 Tert:butyl ethanoate CH3 Cl-COO-CH2-CH3 Ethyl chloro carbonate or methanoate. 9 NOMENCLATURE OF AMINE: Alkyl or aryl derivative of NH3 are called AMINES. They are of three types. 1. Primary amine. They have only one radical R- NH2 2. Secondary amine They have two radicals E.g. R-NH-R 3. Tertiary amine. they have three radicals e.g. R – N - R R A COMMON NAME OR TRIVIAL: The name of alkyl group is written first then name of family is added as a suffix. The suffix amine is used. 01. CH3 – NH2 02. C2H5 – NH2 Methyl amine Ethyl amine CH3 03. CH3-CH-NH2 Iso –propyl amine Or sec: propyl amine 04. CH3-CH2 – CH – NH2 CH3 SEC: butyl amine 05. CH3 – CH – CH2 – NH2 CH3 Iso-butyl amine 06. CH3 – NH CH3 Di methyl amine sec: CH3 07. CH3 – NH – C - CH3 CH3 Methyl tert : butyl amine 10 NH 08. Di phenyl amine 09. N Tri-phenyl Amine 10. CH3-N-C6H5 C2H5 Ethyl methyl phenyl amine NOMENCLATURES OF PHENOL. Phenols are aromatic hydroxy compounds in which –OH group is attached directly to benzene ring or to the ring of derivative. CLASSIFICATION: They are classified as the number of –OH groups they contain. 01 MONOHYDRIC PHENOL OH Ex. Phenyl alcohol or phenol (carbolic acid) 02 DI HYDRIC PHENOL. OH OH OH OH OH OH CATECHOL RESORCINOL HYPROQUINONE 03 TRIHYDRIC PHENOL OH Ex. OH OH OH 11 OH OH HYDROXY HYDRO QUINONE PYROGALLOL NAPHATHOLS: Compounds in which – OH group is attached to Naphathalein ring are called Naphthols. Example: - α -Naphthol Or 2-naphthol. β-naphthol Or 1-naphthol DERIVATIVE OF PHENOLS: Substituted phenols are named as derivative of phenol when –CH3 is attached to phenol it is called CRESOL. Ex. OH OH OH CH3 CH3 O-cresol or 2-methyl phenol M-cresol 3- methyl phenol CH3 P-cresol or 4 -methyl Phenol OH NO2 NO2 NO2 Picric acid or 2, 4, 6-trinitro phenol. I.U.PAC NAMES: Basic compound is called phenol. The position of other groups is denoted by number. Numbering should give the substituents smallest possible number. Ex. OH Cl OH OH 12 2-Chloro phenol OH 1, 3, 5-tri hydroxy Benzene OH . OH CH (CH3)2 NO2 4-nitro phenol or p-nitro phenol m-iso propyl phenol Or 3-iso propyl . OH OH COOH 4 SO3H p- phenol or 4- phenol Sulphonic acid Or p-Hydroxy Benzene Sulphonic acid O-Hydroxy benzoic acid or 2-hydroxy benzoic acid Or SALICYLIC ACID BENZENE NOMENCLATURE: 1. OH 2. CH2 CO O CH2 CO Succinic anhydride Cyclo hezanol 3. 4. CH3 CO CH2 Lead acetate CO Pb Cydohexene 5. 6. CH3 COO Ca Cyclopentene CH3 COO Calcium acetate CH3 13 CH 7. 8. CH3 CH3 CO Iso – propyl benzene or cumene O CH3 CO Acetic anhydride 9. CH2 CH2 10. CH==CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 Cyclo – pentane Styrene 11. . CH2 CH2 12. OCH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 anisole or methoxy benzene Cyclohexane 13. NH2 14. Cl Cl Cl Aniline or amino benzene 15. 17. 16. Benzene OH Carbolic acid or phenol 1, 2, 3-tri-chloro benzene CH3 toluene 18. N 14 Pyridine 19. COONa 20. CH3 CH3 CH3 Sodium benzoate 21. CH3 Durene or 1, 2, 4, 5- tetra methyl benzene SO3H 22. NO2 nitro – benzene Benzene Sulphonic acid 23. COOH 24. CO-CH3 Benzoic acid 25. acetophenone COOH 26. NO2 COOH NO2 Pthalic acid meta-dinitro benzene CH3 27. NO2 NO2 NO2 28. NO2 2, 4, 6-trinitro toluene Or 2, 4, 6-trinitro methyl Benzene 29. COCl NO2 Meta Dinitro Benzene 30. 15 Benzoyl chloride Naphthalene 31. 32. CHO Benzaldehyde Bi - phenyl 33. 34. H-CO-O CONH2 Ca H-CO-O Calcium formate Benz amide 35. OH 36 .CH2 – CN OH Cyno – hydrin Cyclo – hexanol 37. NH2 – CH2 – COOH Glycine 38. O ‖ CH - C ‖ CH – C ‖ O O Maleic anhydride 16 39. CH2 – CH – CHO OH OH Glyceraldehydes 41. OHC – CHO GLOXAL 40. H – C – H N – OH OXIME 42. H – C – Cl O Formyl chloride 43. CH2 – CH2 – Cl S CH2 – CH2 – Cl Musturad gas 44. H – COO▔ formate 45. CH 2 = CH – CN Vinyl cyanide Or Acrylonitrile 46. Anthracene 47. CH3 – CH – COOH NH Alanine 17 Sr No Structure Fourmula Common Name IUPAC Name 1 2 CH3-O-CH3 CH3-CH2-O-CH3 Common system Di methyl ether Ethyl methyl ether IUPAC Name Methoxy methane Ethoxy ethane 3 C2H5-O-C2H5 Di – ethyl ether Ethoxy ethane I so- propyl methyl ether 2-methoxy propane Ethyl tert: butyl ether 2-methyl – 2-methoxy propane Methyl- propyl ether 1-methoxy propane 4 CH3-CH-O-CH3 CH3 5 6 CH3 │ CH3-CH2-O-C-CH3 │ CH3 CH3-O-CH2-CH2-CH3 CH3 18