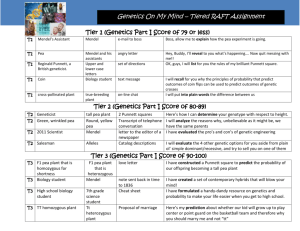
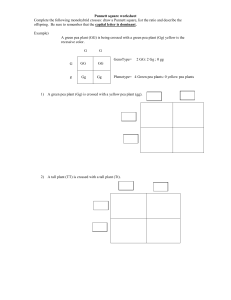
ANSWERS-Mendel'sPeas
advertisement
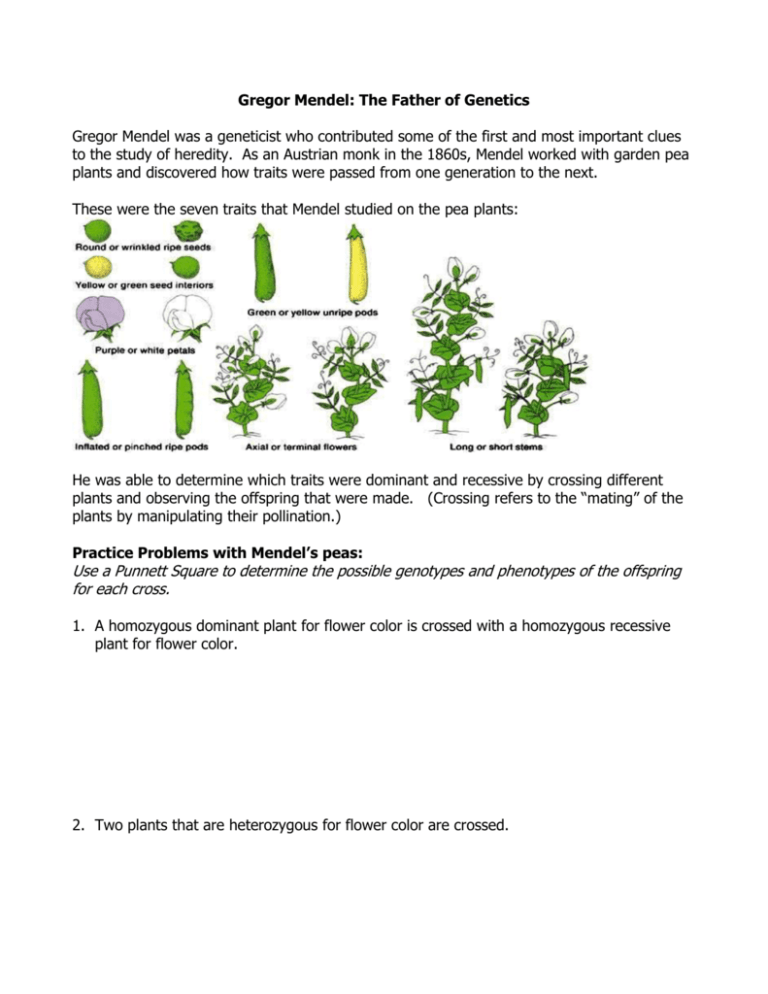
Gregor Mendel: The Father of Genetics Gregor Mendel was a geneticist who contributed some of the first and most important clues to the study of heredity. As an Austrian monk in the 1860s, Mendel worked with garden pea plants and discovered how traits were passed from one generation to the next. These were the seven traits that Mendel studied on the pea plants: He was able to determine which traits were dominant and recessive by crossing different plants and observing the offspring that were made. (Crossing refers to the “mating” of the plants by manipulating their pollination.) Practice Problems with Mendel’s peas: Use a Punnett Square to determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring for each cross. 1. A homozygous dominant plant for flower color is crossed with a homozygous recessive plant for flower color. 2. Two plants that are heterozygous for flower color are crossed. 3. Tall (T) is dominant to short (t). If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive pea plant, what is the chance that they will produce short plants? 4. In the P (parental) generation, Mendel crossed two plants that were purebred for pea color. (A purebred is an organism that received the same genetic traits from both of its parents. So, YY x yy.) What color peas will there be in the F1 generation? (F1 is the generation that is produced from a cross in the P generation.) 5. If two plants from the F1 generation from question #4 are crossed, what are the possible pea colors for the F2 generation? 6. Round pea shape is dominant to wrinkled pea shape. Cross a plant that is heterozygous for pea shape with one that is homozygous recessive for pea shape. 7. In the F1 generation, 6 purple-flowered plants and one white-flowered plant grew. What must have been the genotypes of the P generation? 8. The flowers on a pea plant can either be axial (in the middle of the stem) or terminal (at the end of the stem). What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring when a plant that is heterozygous for flower position is crossed with a plant that is homozygous dominant for flower position?