Punnett Square Worksheet: Genetics Practice
advertisement

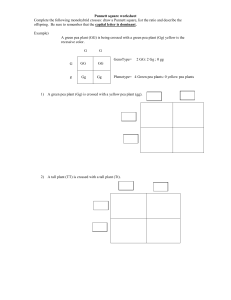
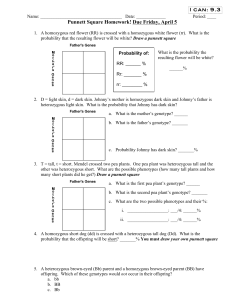
Name Punnett square worksheet Complete the following Punnett squares. Put in the alleles (letters) outside the box for the corresponding rows and columns. Then cross the alleles from the parent generation (P) to come up with the different possible genotypes for the first generation (F1). After crossing P, come up with the probabilities for both genotype (alleles) and phenotype (appearance) for F1. See example below: Example: A green pea plant (GG) is being crossed with a green pea plant (Gg). (A yellow pea plant would have the genotype of gg). G G GG G GG g Gg Gg Genotype= 2 GG, 2 Gg,0 gg Probability of GG= 50% Probability of Gg=50% Probability of gg=0% Phenotype= 4 Green pea plants: 0 yellow plants Probability of Green pea plant=100% Probability of Yellow pea plant=0% 1) A green pea plant (Gg) is crossed with a yellow pea plant (gg). Probability (%) of GG = Gg= Probability (%) of green pea plant= gg= Yellow pea plant= 2) A tall plant (TT) is crossed with a tall plant (Tt). Probability of TT= Tt= Probability of tall plant= tt= short plant= 3) A tall plant (Tt) is crossed with a short plant (tt). Probability of TT= Tt= Probability of tall plant= tt= short plant= 4) A red flower (Rr) is crossed with a white flower (rr). Note: A heterozygous genotype leads to a pink flower. This is an example of incomplete dominance. Probability of RR= Rr= Probability of red flower= rr= pink flower= white flower= 5) A white flower (rr) is crossed with a white flower (rr). Probability of RR= Rr= Probability of red flower= white flower= rr= pink flower= 6) A black chicken (FBFB) is crossed with a white chicken (FWFW). (This is an example of codominance.) Probability of FBFB= FBFW= Probability of black chicken= FWFW= black and white chicken= white chicken= Punnett square problems continued Complete the following problems. List the P genotypes, draw and fill in a Punnett square, and then list the probabilities for F1 genotypes and phenotypes. 1. A homozygous dominant brown mouse is crossed with a heterozygous brown mouse (tan is the recessive color). 2. Two heterozygous white (brown fur is recessive) rabbits are crossed. 3. Two heterozygous pink flowers (red flowers are dominant and white flowers are recessive) are crossed. 4. A horse has codominant traits for hair color. Red hairs and white hairs are the homozygous traits, a heterozygous horse would be roan in color, which means it looks pinkish-brown. A red haired horse is crossed with a roan horse.