Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

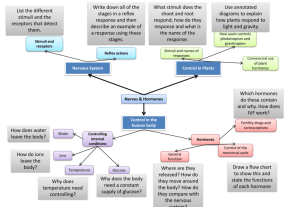
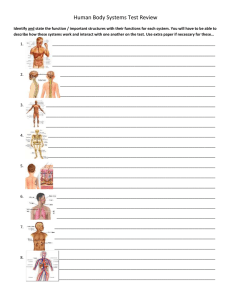
Anatomy and Physiology: Final Exam Study Guide Chapter 1 1. homeostasis 2. levels of structural organization 3. lateral 4. dorsal 5. medial 6. proximal 7. inferior 8. superior 9. ventral 10. deep 11. distal Chapter 4: Integumentary System 12. functions of the skin 13. how does skin regulate body temp 14. keratin 15. melanin 16. name the 5 layers of the epidermis in order 17. dangers of burns 18. how to recognize a melanoma Chapter 5: Skeletal System 19. what does long bone come from 20. compound fracture 21. axial skeleton vs appendicular skeleton 22. male vs female pelvis 23. ossification 24. functions of the skeletal system Chapter 6: Muscular System 25. fascicle and the membrane that wraps it 26. functions of the muscular system 27. sarcomere 28. acetylcholine Chapter 7: Nervous System 29. parts of the central nervous system 30. peripheral nervous system 31. parts of a neuron, specifically incoming stimuli 32. sequence of a reflex arc 33. lobe of the brain that contains the primary motor are and voluntary muscle movements 34. part of the brain controls temp, metabolism, thirst 35. controls the visceral activities (heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, vomiting) 36. afferent nerves/efferent nerves and motor/sensory 37. blood/brain barrier blocks... 38. sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system are subdivision of... 39. sympathetic nervous system controls... Chapter 8: Special Senses 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. path that light travels through the eye rods vs cones; color receptors are sensitive to which lights? name of hearing receptors location of equilibrium receptors location of chemoreceptors number of taste sensations Chapter 8: Endocrine System (EXTRA CREDIT) 46. define hormones 47. enlargement of the thyroid : goiter 48. major metabolic hormone 49. hormones that regulates calcium 50. what does insulin do? 51. name the pituitary hormones 52. hormones that target the gonads Chapter 10: Blood 53. most abundant formed element 54. WBC: chemotaxis, diapedesis, ameboid motion, amount in blood 55. formation of platelets 56. steps of hemostasis 57. hematopoesis Chapter 11: CV System 58. right/left AV valves also known as... 59. location of sinoatrial node 60. EC: path for transmission of an impulse in the intrinsic conduction system of the heart 61. when are valves open/closed 62. path of blood through systemic vascular system 63. what do veins transport? arteries? 64. vessels with the highest blood pressure 65. peripheral resistance 66. arteries vs veins 67. where gas exchange occurs 68. diastolic vs systolic blood pressure reading 69. vasoconstriction 70. systemic vs pulmonary circuits 71. path of blood through heart 72. heart sounds 73. interstitial fluid Chapter 12 Lymphatic System 74. lymph nodes 75. function of spleen 76. nonspecific body defenses 77. immunocompetent T and B cells 78. naturally and artificially acquired passive immunity 79. naturally and artificially acquired active immunity 80. T cells: what type of immunity 81. types of autoimmune diseases 82. humoral immunity Chapter 13: Respiratory System 83. role of mucus in nose 84. epiglottis 85. exchange of O2 and Co2 by... 86. what has to happen to inspire (inhale) 87. apnea 88. normal, adult respiratory rate 89. thyroid cartilage 90. location of trachea 91. why air moves out of the lungs 92. CO2 as chemical regulator of respiration- why? Chapter 14: Digestive System 93. order that food passes through alimentary canal 94. pyloric sphincter 95. where protein digestion begins 96. function of small intestine 97. function of large intestine 98. amylase 99. bile production and storage 100. mechanical digestion vs chemical digestion 101. peristalsis 102. what part of the nervous system controls digestion Chapter 15: Urinary System 103. organs of the urinary system 104. Bowman’s capsule 105. location of nephrons 106. order of the renal tubule regions 107. substances normally and not normally found in urine Diagrams: bones heart digestive system respiratory system kidneys urinary system