Std-5st-Maths - Divine Buds School
advertisement

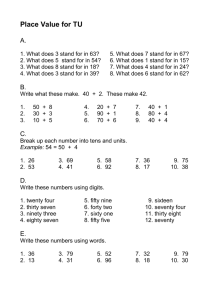
Divine Buds English School Worksheet For FA2 (2014-2015) Std : 5 Sub: Maths ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Course : L : 1 Numbers L : 11 Roman Numerals L : 2 Operations of Large Numbers L : 21 Basic Geometrical Concepts Paper Style : Section A Total Marks : 40 [ 20 Marks] Section B Q : 2 Sol.the following (2 marks each) Q : 3 Sol.the following (3 marks each) [20 Marks] (2X4=8) (3X4=12)\ Q : 1 MCQ’s Ch : 1 Numbers Numbers Beyond 9,99,999 Largest 6 digit number is 9,99,999. When we add 1 to 9,99,999 , we get 10,00,000 the smallest 7 digit number. We read it as ten lakh. Largest 7 digit number is 99,99,999. We read it as ninety-nine lakh, ninety – nine thousand, nine hundred ninety – nine. When 1 is added to 99,99,999 we get 1,00,00,000 the smallest 8 digit number. We read it as one crore. The largest 8 digit number is 9,99,99,999. We read it as nine crore, ninety-nine lakh, ninety-nine thousand, nine hundred ninety-nine. When 1 is added to this number, we get 10,00,00,000 the smallest 9 digit number. We read it as Ten Crore. Indian Place Value Chart To make it easy to read and write the large numbers, the Indian Place Value Chart has been divided into periods. The First Period is the ONES PERIOD with three places- Once (0), Tens (T) and Hundreds (H) Second period is the THOUSANDS PERIOD with two places –Thousand (Th) and Ten Thousands (TTh) Third period is the LAKHS PERIOD with two places – Lakhs (L) and Ten Lakhs (TC) Fourth Period is the CRORES PERIOD with two places –crores (C) and Ten Crores (TC) Indian Place Value Chart Periods Crores Lakhs Thousands Ones Places Ten Crores Ten Lakhs Ten Thousand Hundred Tens Ones Crores Lakhs Thousand TC C TL L T-Th Th H T O 3 9 8 4 5 3 2 1 8 Thirty nine Eighty Four Fifty three Thousand Two hundred eighteen Crore Lakh While reading a number all the digit in the same period are read together and the name of the period(expect the ones is read along with them). While writing a number ,we usually put a comma after every period to separate the periods. The plural of periods is not written. For example instead of writing five crores, three lakhs , ninety –four thousands, six hundreds eighty –one, we write five crore, three lakh, ninety – four thousand, six hundred eighty – one. EXERCISE – 1A A. Write the following numbers in a place value chart : 1. 3,52,46,789 2. 7,16,02,030 3. 16,25,43,434 4. 15,42,89,356 5. 42,53,62,517 6. 28,75,30,005 7. 3,83,528 8. 78,31,806 9. 79,10,29,668 10 85,43,96,345 B. Write the following numbers in words : 1. 72,38,618 2. 67,81,285 3. 38,52,906 4. 2,06,00,612 5. 2,74,38,016 6. 43,11,64,006 7. 2,26,18,396 8. 16,17,90,034 9. 74,25,637 10. 43,68,258 11. 3,69,47,891 12. 2,18,45,679 13. 35,84,217 14. 6,25,30,149 15. 8,24,62,157 16. 32,14,62,190 C . Write each of the following numbers in figures : 1. Seventy two lakh , thirty seven thousand, four hundred seventy nine. 2. Thirty seven lakh, twenty eight thousand two hundred seventy two. 3. Ninety two lakh seventy eight thousand three hundred eighteen. 4. Five crore thirty nine lakh twenty seven thousand two hundred seventeen. 5. Forty three crore seventy two lakh thirty eight thousand five hundred twenty seven. 6. Seven crore fifty five lakh thirty thousand nine hundred thirty three. 7. Sixty seven crore ninety. 8. Fifty crore ninety thousand seventy five. 9. Seventy crore, five lakh. 10. Nine crore, nineteen lakh, eighty thousand. 11. Seven crore, seventy one lakh, eleven thousand one hundred one. 12. Two crore, five thousand, one hundred seventeen. 13. Fifty crore, fiftylakh, fifty thousand fifty. 14. Eighty one lakh ,sixty thousand, three hundred seven. 15. Six crore, six lakh, sixty thousand , sixty six. 16. Thirteen crore, twelve lakh, eleven thousand, one hundred one. FACE VALUE AND PLACE VALUE Face Value : The face value of a digit is always the digit it self. For example, face value of 5 in 74,58,962 is 5 only. Face value of 2 in 42,58,973 is 2 only. Place Value : Place value of a digit depends on the place it occupies in the place value chart. Place value = Face Value X Value of the place Place values of the digits of 92,14,67,352 are: 921467352 2x1=2 5 x 10 = 50 3 x 100 = 300 7 x 1000 = 7000 6 x 10000 = 60000 4 x 100000 = 100000 1 x 1000000 = 1000000 2 x 10000000 = 20000000 9 x 100000000 = 900000000 Place value of 0 is always 0 whatever place it may occupy. Successor of a number : The number that comes just after a given number is called its successor. Eg : Successor of 78,69,599 = 78,69,599 + 1 = 78,69,600 Predecessor of a number : The number that comes just before a given number is called its predecessor. Eg: Predecessor of 5,68,74,956 = 5,68,74,956 – 1 = 5,68,74,955 FORMATION OF THE GREATEST AND THE SMALLEST NUMBERS : To form the greatest number, arrange the given digits in the descending order. To form the smallest number, arrange the given digits in ascending order. Zero should never be the 1st digit in the extreme left. To get the smallest number, zero should always be the 2nd digit from the left. Fro Eg : Form the greatest and the smallest numbers from the digits 2,0,1,7,3 and 4 . The greatest number = 743210 The smallest number = 102347 EXERCISE – 1 B 1. Find the place value of : 1. 4 in 3,41,06,315 2. 2 in 87,34,21,301 3. 8 in 4,53,80,051 4. 9 in 20,04,13,988 5. 4 in 94,32,96,031 6. 3 in 6,25,72,623 2. Find the place value of 6 in the following numbers : 1. 60,35,41,325 2. 3,20,06,151 3. 55,36,00,140 4. 3,17,52,601 5. 6,20,31,053 6. 70,26,52,123 3. Find the difference between two 8 in 81,16,865. 4. Write the following numbers in the expanded form. 1. 3,82,865 2. 78,365 3. 1,78,328 4. 6,78,356 5. 3,56,218 6. 2,83,867 7. 28,31,628 8. 1,61,24,978 9. 4,29,00,781 10. 12,05,73,471 11. 30,94,10,367 12. 74,52,91,146 5. Write the numerals in the short form. 1. 70,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 800 + 10 + 6 2. 40,00,000 + 7,00,000 + 30,000 + 4000 + 800 + 20 + 5 3. 20,00,000 + 8,00,000 + 70,000 + 20 + 7 4. 80,00,000 + 700 + 80 + 9 5. 30,00,000 + 7,00,000 + 90,000 + 8000 + 70 + 1 6. 8,00,00,000 + 70,00,000 + 9,00,000 + 80,000 + 6000 + 800 + 90 + 7 7. 2,00,00,000 + 70,00,000 + 5,000 + 800 + 70 + 6 6. Compare the following numbers using < or > in the blanks. 1. 2,73,75,896 ___________ 3,41,95,123 2. 1,56,37,536 ___________ 15,19,758 3. 67,234 ____________ 67,534 4. 4,10,999 _____________ 4,10,898 5. 21,24,371 ____________ 2,56,721 6. 4,79,059 ____________ 4,79,056 7. 21,24,371 ____________ 42,56,721 8. 34,35,36,789 ___________ 34,35,36,879 7. Find the greatest number in each group. 1. 31,20,567 ; 31,20,167 ; 3,12,667 ; 3,21,667 2. 10,49,178 ; 17,38,758 ; 10,38,278 ; 15,39,128 3. 45,69,108 ; 45,69,206 ; 45,39,206 ; 45,69,308 4. 11,29,08,164 ; 11,29,80,164 ; 11,28,90,164 ; 11,28,90,614 5. 25,17,01,294 ; 25,71,01,294 ; 15,27,01,294 ; 25,17,40,294 8. Find the smallest number of each group. 1. 63,19,000 ; 63,00,19,251 ; 83,19,468 ; 46,10,253 2. 36,12,43,551 ; 45,16,27,142 ; 30,14,349 ; 29,18,37,156 3. 10,00,68,053 ; 39,45,12,346 ; 37,49,296; 28,21,40,183 4. 98,52,17,340 ; 40,73,89,152 ; 25,18,90,314 ; 89,25,13,704 5. 3,01,45,678 ; 4,13,08,765 ; 3,41,08,756 ; 4,30,17,865 9. Arrange the following numbers in ascending order. 1. 87,36,952 ; 87,35,952 ; 87,85,952 ; 87,65,952 2. 5,32,718 ; 67,89,542 ; 8,79,56,423 ; 12,45,78,963 3. 27,93,465 ; 2,04,05,060 ; 3,56,52,595 ; 28,63,246 4. 87,56,726 ; 8,55,77,624 ; 8,56,67,723 ; 86,75,722 10. Arrange the following numbers in descending order. 1. 25,64,056 ; 25,63,201 ; 2,56,98,530 ; 59,86,542 2. 5,26,781 ; 4,52,687 ; 45,31,071 ; 44,52,700 3. 8,78,254 ; 8,79,564 ; 82,13,475 ; 4,69,58,472 4. 76,49,866 ; 78,96,467 ; 79,84,668 ; 74,68,969 11. Write successor of each number. 1. 42,57,198 2. 17,35,000 3. 8,10,309 4. 3,16,12,319 5. 5,29,79,499 6. 9,99,99,998 7. 7,00,22,111 8. 5,12,34,000 12. Write predecessor of each number. 1. 14,32,121 2. 69,05,070 3. 8,52,008 4. 35,14,100 5. 1,00,00,000 6. 5,00,05,000 7. 9,52,34,123 8. 7,86,00,506 13. Write the greatest and the smallest 6 digit numbers (without repeating a digit) from the following digits. 1. 1,2,0,6,3,5 2. 6,3,0,1,2,8 3. 0,8,5,2,1,6 4. 7,5,8,2,9,4 5. 3,5,2,9,4,1 6. 1,9,8,7,6,3 14. Write the greatest and the smallest 7 digit numbers using all of the following digits. You may repeat the digits. 1. 7,2,0,8,9,3 2. 6,3,8,9,7,1 3. 3,8,5,2,1,6 4. 0,2,3,8,9,6 5. 3,0,1,5,6,7 6. 2,1,9,5,7,8 15 Observe the pattern and write next three numbers. 1. 3,50,172 ; 3,50,272 ; 3,50,372 ; ___________;_____________;____________ 2. 19,25,734 ; 19,35,734 ; 19,45,734;_________;_____________;____________ 3. 71,98,421;71,88,421;71,78,421 ; __________;_____________;____________ 4. 58,40,934;58,40,834;58,40,734; ___________;____________;_____________ INTERNATIONAL PLACE VALUE CHART. The international place value chart is used all over the world to maintain uniformity. In the international place value system, the periods are Ones, thousands and millions. Three digts are placed in each period. International Place Value Chart. Period Millions Thousands Ones s Places Hundre Ten Millio Hundred Ten Thousan Hundre Ten One d Millio n Thousan Thousan d d s s Million n d d HM TM M HTH TTH TH H T O 1 3 7 2 5 8 0 9 5 One hundred thirty seven Two hundred fifty eight thousand Ninety Five million So, 137,258,095 = One hundred thirty seven million, two hundred fifty eight thousand, ninety five. EXERCISE 1C 1.Write the following numbers in figures using the International place value system. a) Four hundred ten thousand seven hundred nine. b) Eight million five hundred one thousand six hundred nine. c) Sixty three million seven thousand five hundred four. d) One hundred thirteen million nine hundred seven thousand eight. e) Seven hundred nine million fifty six thousand two hundred five. f) Fifty six million. g) Twenty five million two thousand three hundred five. h) Five million two thousand thirty six. i) Sixty two million two hundred five. j) Twenty three million thirty six thousand five hundred six. 2. Write the following numbers in words using the International place value chart. a) 7,258,963 b) 1,135,429 c) 95,736,210 d) 34,568,951 e) 987,606,789 f) 247,556,398 g) 756,438,942 h) 248,631,970 3. Rewrite the following numbers using Indian place value system. a) Six hundred nine thousand five hundred two. b) Twenty five million fifteen. c) Eight million three thousand nine. d) Thirty six million one hundred twenty thousand four. 4. Rewrite the following using International place value system. a) Fifty six lakh two thousand seven hundred four. b) Twenty eight lakh twenty five thousand fifty one. c) Three crore nine lakh one thousand five hundred two. d) Nineteen crore forty lakh six. Exercise 1 D Choose the correct answer. 1. 10 millions = ________________ crore. (a) 1 (b) 10 (c) 100 1 2 3 4 5 (d) 1000 2. 1000 = __________________ hundreds. (a) 1 (b) 10 (c) 100 (d) 1000 3. 1 lakh = ________________ thousand. (a) 1 (b) 10 (c) 100 (d) 1000 4. Face value of 9 in 94,58,63,215 is _____________. (a) 9 (b) 90 (c) 9000 (d) 90,00,00,000 5. Place value of 0 in 70,86,24,314 is _______________. (a) 10 (b) 1,00,00,000 (c) 0 (d) 1,00,000 6. Place value of 3 in 3,24,89,652 is ______________. (a) 3 (b) 30,000 (c) 3,00,000 (d) 3,00,00,000 7. Standard form of 9,00,00,000 + 8,00,000 + 50,000 + 3,000 + 20 + 3 is (a) 90,00,85,323 (b) 9,85,03,023 (c) 90,08,53,023 (d) 9,08,53,023 8. Difference between the place value of two 3’s in 31,16,365 is (a) 29,99,700 (b) 30,30,700 (c) 29,29,700 (d) 29,00,700 9. The greatest 4 digit number using the digits 4,7,6 and 2 only once is (a) 4762 (b) 6427 (c) 7624 (d) 7642 10. The greatest number among 37,189 ; 37,918 ; 37,819 and 37981 is (a) 37,189 (b) 37,918 (c) 37,819 (d) 37,981 11. The smallest number among 6,17,081 ; 6,18,701 ; 6,17,801 and 6,10,781 is (a) 6,17,081 (b) 6,18,701 (c) 6,17,801 (d) 6,10,781 12. The suceessor of 17,28,999 is (a) 17,28,000 (b) 17,29,000 (c) 17,29,999 (d) 17,39,000 13. The predecessor of 4,36,000 is (a) 4,36,001 (b) 4,35,990 (c) 4,36,999 (d) 4,35,999 14. The smallest 7 digit number using the digits 6,2,0,1,9,4,8 only once is (a) 98,64,210 (b) 20,14,689 (c) 10,24,689 (d) 10,04,689 15. The greatest 7 digit number using the given digits 5,4,9,2 is (a) 99,99,542 (b) 99,95,542 (c) 95,55,542 (d) 99,55,542 16. Three hundred sixty four thousand two hundred four can be written as (a) 3,16,204 (b) 3,61,204 (c) 6,13,204 (d) 3,64,204 ANSWERS EXERCISE 1A A. CRORES LAKHS THOUSANDS ONES TC C TL L T.TH TH H T O 3 5 2 4 6 7 8 9 7 1 6 0 2 0 3 0 1 6 2 5 4 3 4 3 4 1 5 4 2 8 9 3 5 6 4 2 5 3 6 2 5 1 7 6 2 8 7 5 3 0 0 0 7 3 8 3 5 2 8 7 8 3 1 8 0 9 7 9 1 0 2 9 6 6 10 8 5 4 3 9 6 3 4 B.1. Seventy two lakh thirty eight thousand six hundred eighteen. 2. Sixty seven lakh eighty one thousand two hundred eighty five. 3. Thirty eight lakh fifty two thousand nine hundred six. 4. Two crore six lakh six hundred twelve. 5. Two crore seventy four lakh thirty eight thousand sixteen. 6. Forty three crore eleven lakh sixty four thousand six. 7. Two crore twenty six lakh eighteen thousand three hundred ninety six. 8. Sixteen crore seventeen lakh ninety thousand thirty four. 9. Seventy four lakh twenty five thousand six hundred thirty seven. 10. Forty three lakh sixty eight thousand two hundred fifty eight. 11. Three crore sixty nine lakh forty seven thousand eight hundred ninety one. 12. Two crore eighteen lakh forty five thousand six hundred seventy nine. 13. Thirty five lakh eighty four thousand two hundred seventeen. 14. Six crore twenty five lakh thirty thousand one hundred forty nine. 15. Eight crore twenty four lakh sixty two thousand one hundred fifty seven. 16. Thirty two crore fourteen lakh sixty two thousand one hundred ninety. C. 1.72,37,479 (2) 37,28,272 (3) 92,78,318 4. 5,39,27,217 (5) 43,72,38,527 (6) 7,55,30,933 7. 67,00,00,090 (8) 50,00,90,075 (9) 70,05,00,000 10. 9,19,80,000 (11) 7,71,00,101 (12) 2,00,05,117 13. 5,50,50,050 (14) 81,60,307 (15) 6,06,60,066 16. 13,12,11,101 EXERCISE 1B Q:1 a) 40,00,000 (b) 20,000 (c) 80,000 (d) 900 e) 4,00,00,000 (f) 3 Q:2 a) 60,00,00,000 (b) 6,000 (c) 6,00,000 (d) 600 e) 6,00,00,000 (f) 6,00,000 Q:3 7999200 Q:4 a) 3,00,000 + 80,000 + 2,000 + 800 + 60 + 5 b) 70,000 + 8,000 + 300 + 60 + 5 c) 1,00,000 + 70,000 + 8,000 + 300 + 20 + 8 d) 6,00,000 + 70,000 + 8,000 + 300 + 50 + 6 e) 3,00,000 + 50,000 + 6,000 + 200 + 10 + 8 f) 2,00,000 + 80,000 + 3,000 + 800 + 60 + 7 g) 20,00,000 + 8,00,000 + 30,000 + 1,000 + 600 + 20 + 8 h) 1,00,00,000 + 60,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 20,000 + 4,000 + 900 + 70 + 8 i) 4,00,00,000 + 20,00,000 + 9,00,000 + 700 + 80 + 1 j) 10,00,00,000 + 2,00,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 70,000 + 3000 + 400 + 70 + 1 k) 30,00,00,000 + 90,00,000 + 4,00,000 + 10,000 + 300 + 60 +7 l) 70,00,00,000 + 4,00,00,000 + 50,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 90,000 + 1,000+100+40+ 6 Q:5 a) 72,00,819 (b) 47,34,825 (c) 28,70,027 d) 80,00,789 (e) 37,98,071 (f) 8,79,86,897 g) 2,70,05,876 Q:6 a) < (b) > (c) < (d) > e) > (f) > (g) < (h) < 5 8 6 8 5 Q:7 a) 31,20,567 (b) 17,38,758 (c) 45,69,308 d) 11,29,80,164 (e) 25,71,01,294 Q:8 a) 46,10,253 (b) 30,14,349 (c) 37,49,296 d) 25,18,90,314 (e) 3,01,45,678 Q:9 a) 87,35,952 < 87,36,952 < 87,65,952 < 87,85,952 b) 5,32,718 < 67,89,542 < 8,79,56,423 < 12,45,78,963 c) 27,93,465 < 28,63,246 < 2,04,05,060 < 3,56,52,595 d) 86,75,722 < 87,56,726 < 8,55,77,624 < 8,56,67,723 Q:10 a) 2,56,98,530 > 59,86,542 > 25,64,056 > 25,63,201 b) 45,31,071 > 44,52,700 > 4,52,687 > 5,26,781 c) 4,69,58,472 > 82,13,475 > 8,79,564 > 8,78,254 d) 79,84,668 > 78,96,467 > 76,49,866 > 74,68,969 Q:11 a) 42,57,199 (b) 17,35,001 (c) 8,10,310 d) 3,16,12,320 (e) 5,29,79,500 (f) 9,99,99,999 g) 7,00,22,112 (h) 5,12,34,001 Q:12 a) 14,32,120 (b) 69,05,069 (c) 8,52,007 d) 35,14,099 (e) 99,99,999 (f) 5,00,04,999 g) 9,52,34,122 (h) 7,86,00,505 Q:13 a) 653210 , 102356 (b) 863210 , 102368 c) 865210 , 102568 (d) 987542 , 245789 e) 954321 , 123459 (f) 987631 , 136789 Q:14 a) 9987320 , 2003789 (b) 9987631 , 1136789 c) 8865321 , 1123568 (d) 9986320 , 2003689 e) 7765310 , 1003567 (f) 9987512 , 1125789 Q:15 a) 3,50,472 ; 3,50,572 ; 3,50,672 (b) 19,55,734 ; 19,65,734 ; 19,75,734 c) 71,68,421 ; 78,58,421 ; 78,48,421 (d) 58,40,634 ; 58,40,534 ; 58,40 434 EXERCISE 1 C Q:1 a) 410,709 (b) 8,501,609 (c) 63,007,504 d) 113,907,008 (e) 709,056,205 (f) 56,000,000 g) 25,002,305 (h) 5,002,036 (i) 62,000,205 j) 23,036,506 Q:2 a) Seven million two hundred fifty eight thousand nine hundred sixty three. b) One million one hundred thirty five thousand four hundred twenty nine. c) Ninety five million seven hundred thirty six thousand two hundred ten. d) Thirty four million five hundred sixty eight thousand nine hundred fifty one. e) Nine hundred eighty seven million six hundred six thousand seven hundred eighty nine. f) Two hundred forty seven million five hundred fifty six thousand three hundred ninety eight. g) Seven hundred fifty six million four hundred thirty eight thousand nine hundred forty two. h) Two hundred forty eight million six hundred thirty one thousand nine hundred seventy. Q:3 a) Six lakh nine thousand five hundred two. b) Two crore fifty lakh fifteen. c) Eighty lakh three thousand nine. d) Three crore sixty one lakh twenty thousand four. Q:4 a) Five million six hundred two thousand seven hundred four. b) Two million eight hundred twenty five thousand fifty one. c) Thirty million nine hundred one thousand five hundred two. d) One hundred ninety four million six. EXERCISE 1 D Q:1 (a) Q:2 (b) Q:5 (c) Q:6 (d) Q:9 (d) Q:10 (d) Q:13 (d) Q:14 (c) Q:3 (c) Q:4 (a) Q:7 (d) Q:8 (a) Q:11 (d) Q:12 (b) Q:15 (a) Q:16 (d) Ch-2 OPERATIONS ON LARGE NUMBERS Addition : Rule : (1) Arrange the given numbers in columns and add from extreme right. (2) Take the carry over if any to the next column to the left and add it along with the digits in that column. Terms used in Addition a) The numbers to be added are called addends. b) The result of addition is called the sum. 71 Addend + 25 Addend 96 Sum EXERCISE 2 A Q:1 a) 585874 b) 3612375 +345678 + 5732163 c) 123456 789987 +654321 d) 1122334 4556677 +8899112 e) 4056708 9102340 + 218795 f) 2626520 5252620 + 456789 g) 3045678 2908754 + 321987 h) 234567 765432 + 123456 Q:2 Arrange in the columns and odd. a) 36,75,218 + 18,76,984 b) 62,57,173 + 47,53,619 c) 7,54,36,948 + 39,67,489 d) 3,82,56,714 + 27,84,236 e) 1,34,52,672 + 2,43,64,739 + 93,18,453 f) 4,74,36,127 + 2,36,55,438 + 53,16,883 + 20,71,631 EXERCISE 2 B Q:1 Ram bought two houses, one for Rs. 6,16,435 and other for Rs.4,58,236. How much money did he spend altogether? Q:2 Find the sum of the largest 7 digit and the largest 6 digit number. Q:3 A bulb manufacturer produces 1,99,725 ; 10,25,950 and 4,55,950 bulbs in three months. How many bulbs does he produce in these three months? Q:4 The population of town A is 82,57,865, the population of town B is 50,39,831 and the population of town C is 4,38,651. Find the total population of the three towns. Q:5 In a public library there are 72,19,256 books on Literature, 6,19,005 Mathematics and 25,16,856 books on other subjects. Find the total number of books in the library. Q:6 People of three Villages had collected Rs.96,43,210 ; Rs.12,45,896 and Rs. 75,42,639 for earthquake victims. Find the total money collected. SUBTRACTION If we have to determine the difference of two numbers, we always subtract the smaller number from the bigger number. To find the difference we proceed as follows. i) Arrange the given numbers in columns. ii) Go on subtracting column wise from ones column,borrowing if necessary from the next column to the left. Terms Used in Subtraction 1.Minuend : The larger number from which we subtract the smaller number is called minued. 2.Subtrahend : The smaller number which is subtracted from the larger number is called Subtrahend. 3.Difference : The result we obtain after subtraction is called the difference between the given numbers. 8 7 Minuend - 5 6 Subtrahend 3 1 Difference EXERCISE 2 C Q:1 a) 8005007 b) 5030469 -3026024 -2982149 c) 8234962 - 2458654 d) 970 0770 - 8888888 e) 8912345 -6789123 f) 3003003 -1234567 g) 10000000 - 1234567 h) 98765432 -12345678 i) 81008108 -12345678 j) 1010101010 - 101010101 Q : 2 Arrange in the columns and subtract. a) 36,98,367 from 65,47,812 (b) 27,85,745 from 78,56,429 c) 63,54,724 from 74,56,789 (d) 3,65,84,722 from 5,68,42,189 e) 5,86,92,456 from 7,58,96,125 (f) 4,85,96,235 from 9,85,64,723 g) 9,58,47,624 – 4,58,62,375 (h) 56,89,237 - 1,24,568 i) 5,69,85,245 – 2,45,89,626 (j) 60,22,55,524 – 7,89,54,222 EXERCISE 2 D Q : 1 There were 5,47,546 mangoes in a godown. If 3,12,764 were rotten, How many mangoes were good? Q : 2 An exhibition had two gates A and B. In a month 6,78,54,923 people entered through gate A and 9,35,48,697 people entered through gate B. How many more people entered through gate B than gate A? Q : 3 In an examination 5,67,53,951 candidates appeared. Out of these 2,98,54,632 passed. How many candidates failed in the examination? Q : 4 Total population of a town is 18,39,150. If the number of females is 8,00,637. Find the number of males in the town. Q : 5 A factory produces 57,86,321 gas stones in a particular year and 7,89,75,324 in the following year. Find the increase in production of gas stoves. Q : 6 Mrs. Patnaik bought a computer for Rs. 32,555 and a refrigerator that was priced Rs.7920 less than the computer. How much did she pay for the refrigerator. Q : 7 A merchant had 78,543 sacks of potates. On Monday he sold 3748 sacks and on Tuesday he sold 5637 sacks. How many sacks did he sell in all these two days? How many sacks were left? MULTIPLICATION Following terms are used in Multiplication. 1.Multiplicand : The number to be multiplied is called the multiplicand. 2.Multiplier : The number by which we multiply is called the multiplier. 3.Product : The result we obtain after the multiplication is called the product. E.g.: 6 2 Multiplicand X 5 Multiplier 3 1 0 Product Properties of Multiplication 1.Order Property : The product of two numbers do not change when the order of the number is changed. For Eg. 5 X 8 = 40 and 8 X 5 = 40 So, 5 X 8 = 8 X 5 2.Multiplicative property of 1 : The product of a number and 1 is the number itself . For eg. 27 X 1 = 27, 159 X 1 = 159 , 1234 X 1 = 1234 3.Multiplicative property of 0 : The product of a number and 0 is 0. For eg. 199 X 0 = 0, 5432 X 0 = 0 EXERCISE 2 E Q : 1 Using the properties of Multiplication, Fill in the blanks. a) 783526 X 7158 = 7158 X ___________. b) 781352 X 0 = ____________. c) 735616 X 1 = ________________. d) 536 X ______________ = 7182 X 536 e) 683516 X _________________ = 683516 f) 715898 X _______________ = 0 g) _____________ X 53899 = 53899 Q : 2 Multiply. a) 756 X 60 d) 32,156 X 70 g) 7,30,421 X 50 j) 4,32,904 X 20 (b) 3874 X 80 (e) 86,435 X 50 (h) 3,55,321 X 40 (c) 43,256 X 30 (f) 1,56,752 X 30 (i) 1,12,657 X 90 Q : 3 Multiply. a) 21,355 X 300 d) 30,652 X 400 g) 18,553 X 900 (b) 92,321 X 700 (e) 93,256 X 600 (h) 20,658 X 800 (c) 19,225 X 500 (f) 25,252 X 200 Q : 4 Multiply. a) 3261 X 4000 d) 3956 X 6000 g) 3525 X 7000 (b) 2876 X 9000 (e) 5648 X 2000 (h) 8259 X 3000 (c) 3381 X 5000 (f) 4268 X 8000 EXERCISE 2 F Q : 1 Find the product. a) 3804 X 26 d) 27806 X 989 Q : 2 Find the product. a) 7225 X 167 d) 8326 X 778 g) 6009 X 475 j) 6019 X 247 b) 1267 X 157 e) X 53805 458 (b) 1624 X 333 (e) 7059 X 263 (h) 2709 X 819 (k) 5250 X 318 c) 3924 X 641 f) X 87012 825 (c) 2697 X 812 (f) 6240 X 742 (i) 4709 X 358 (l) 2688 X 282 EXERCISE 2 G Q : 1 Cost of a table is Rs. 5,975. What is the cost of 864 such tables? Q : 2 A truck can carry 4582 Kg of tomatoes. How much can 758 such trucks carry? Q : 3 A bundle to rope measures 4,587 meters. How much rope will be there in 562 such bundles? Q : 4 A Shopkeeper sells 459 toys every week. How many toys will be sold in 397 weeks? Q : 5 A factory produces 4,527 bolts in a day. How many bolts will be produced in a normal year? DIVISION Terms used in Division : 1.Dividend : The number to be divided is called the dividend. 2. Divisor : The number by which we divide the dividend is called the divisor. 3. Quotient : The result of division is called quotient. 4. Remainder : The number which is left undivided is called the remainder. Divisor 9 5|47 -45 02 Quotient Dividend Remainder PROPERTIES OF DIVISION 1.The following relationship holds good in a division : Dividend = Quotient X Divisor + remainder This relationship is used to check the division. 2.When a number expect 0 is divided by itself the quotient is 1 For Eg : 25 / 25 = 1, 339 / 339 = 1 3. When a number is divided by itself, the quotient is 1. For Eg : 29 / 1 = 29 909 / 1 = 909 4. When 0 is divided by a number expect 0, the quotient is 0. For Eg : 0 / 23 = 0 0 / 157 = 0 5. A number cannot be divided by 0. EXERCISE 2 H Q : 1 Fill in the blanks. a) 43 / 43 = _________________ c) 1234 / 1 = _________________ e) 182115 / 1 = _______________ g) 781266 / 781266 = ____________ i) 156826 / 156826 = ____________ (b) 126 / 1 = ___________________ (d) 0 / 9456 = __________________ (f) 0 / 6549 = __________________ (h) 0 / 987654 = ________________ (j) 3672681 / 1 = _______________ Q : 2 Write down the quotient and the remainder without actual division. a) 2600 / 100 (b) 2,54,789 / 10 c) 5,12,689 / 1000 (d) 2,34,509 / 100 e) 65,000 / 1000 (f) 7,53,021 / 10 g) 62,15,873 / 100 (h) 58,962 / 1000 i) 86,742 / 10 (j) 2,36,589 / 1000 k) 1,90,029 / 100 (l) 12,056 / 1000 Q : 3 Find the dividend. a) Quotient = 938 ; Remainder = 25 ; Divisor = 55 b) Quotient = 5105 ; Remainder = 59 ; Divisor = 126 c) Quotient = 445 ; Remainder = 1 ; Divisor = 19 d) Quotient = 998 ; Remainder = 43 ; Divisor = 26 e) Quotient = 3020 ; Remainder = 18 ; divisor = 33 f) Quotient = 135 ; Remainder = 47 ; Divisor = 84 EXERCISE 2 I Q : 1 Divide and check your answer a) 1800 / 12 (b) 5328 / 51 (c) 1825 / 23 d) 14202 / 16 (e) 30395 / 27 (f) 87,486 / 26 g) 45,238 / 18 (h) 53,805 / 58 (i) 63,000 / 66 j) 87,012 / 45 (k) 75378 / 71 (l) 89380 / 59 (m) 39476 / 69 (n) 51615 / 55 EXERCISE 2 J Q : 1 45,000m of wire is to be packed in bundles. If each bundle contains 50m of wire. How many bundles will be made? Q : 2 14850 books are packed equally in 25 boxes. Find the number of books in each box. Q : 3 The cost of 35 boxes is Rs.52500. What is the cost of one box? Q : 4 A contractor paid Rs.11340 equally to 84 workers. How much money did each worker received? Q : 5 The cost of 25 games is Rs. 1,23,125. Find the cost of one game? Q : 6 75 Biscuits are to be packed in a polypack. How many poly – pack are required to pack 2,22,075 biscuits? EXERCISE 2 K Choose the correct answer. 1.10,10,940 + ___________ = 10,10,940 (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100 2. 13,56,478 + ______________ = 13,56,478 (a) 1 (b) 10 (c) 0 (d) 100 3. 4,81,50,951 + 1000 = ___________________. (a) 4,84,60,951 (b) 4,81,51,951 (c) 4,81,50,851 (d) 4,81,50,961 4. 7463 X 1000 = _______________ (a) 74600 (b) 74630 (c) 746300 (d) 7463000 5. 7,45,986 X ______________ = 7,45,986 (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100 6. _____________________ X 48975 = 0 (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100 7. 47 X 63 = _____________ X 47 (a) 69 (b) 39 (c) 36 (d) 63 8. 896 X 100 = ______________ (a) 890 (b) 8960 (c) 89600 (d)896000 9. 73508 / 100 gives (a) Q = 735, R = 80 (b) Q = 735, R = 8 (c) Q = 7350, R = 8 (d) Q = 37, R = 508 10. 800196 / 1000 = _________________ (a) Q = 80, R = 196 (b) Q = 8001, R = 96 (c) Q = 800, R = 196 (d) Q = 8000, R = 196 11. 19254 / 19254 = _____________ (a) 1 (b) 1 (c) 19254 (d) none 12. 0 / 73 = _______________ (a) 1 (b) 1 (c) 73 (d) 37 ANSWERS EXERCISE 2 A Q : 1 a) 931552 d) 14578123 (g) 6276419 Q : 2 a) 55,52,202 d) 4,10,40,950 EXERCISE 2 B 1) 10,74,671 4) 1,37,36,347 (b) 9344538 (e) 13377843 (h) 1123455 (b) 1,10,10,792 (e) 4,71,35,864 (2) 1,09,99,998 (5) 1,03,55,117 (c) 1567764 (f) 8335929 (c) 7,94,04,437 (f) 7,84,80,079 (3) 16,81,625 (6) 1,84,31,745 EXERCISE 2 C Q : 1 a) 49,78,983 (b) 20,48,320 (c) 57,76,308 d) 8,11,882 (e) 21,23,222 (f) 17,68,436 g) 87,65,433 (h) 8,64,19,754 (i) 6,86,62,430 j) 90,90,90,909 Q : 2 a) 28,49,445 (b) 50,70,684 (c) 11,02,065 d) 2,02,57,467 (e) 1,72,03,669 (f) 4,99,68,488 g) 4,99,85,249 (h) 55,64,669 (i) 3,23,95,619 j) 52,33,01,302 EXERCISE 2 D 1) 2,34,782 (2) 2,56,93,774 (3) 2,68,99,319 4) 10,38,513 (5) 7,31,89,003 (6) Rs. 24,635 7) 9385 ; 69,158 EXERCISE 2 E Q : 1 a) 783526 (b) 0 (c) 781352 (d) 7182 e) 1 (f) 0 (g) 1 Q : 2 a) 45360 (b) 309920 (c) 1297680 (d) 2250920 e) 4321750 (f) 4702560 (g) 36521050 (h) 14212840 i) 10139130 (j) 8658080 Q : 3 a) 6406500 (b) 64624700 (c) 9612500 (d) 12260800 e) 55953600 (f) 5050400 (g) 16697700 (h) 16526400 Q : 4 a) 13044000 (b) 25884000 (c) 16905000 (d) 23736000 e) 11296000 (f) 34144000 (g) 24675000 (h) 24777000 EXERCISE 2 F Q : 1 a) 98,904 (b) 1,98,919 (c) 25,15,284 (d) 27,50,0134 e) 2,46,42,690 (f) 7,17,84,900 Q : 2 a) 12,06,575 (b) 5,40,792 (c) 21,89,964 (d) 64,77,628 e) 18,56,517 (f) 46,30,080 (g) 28,54,275 (h) 22,18,671 i) 16,85,822 (j) 14,86,693 (k) 16,69,500 (l) 7,58,016 EXERCISE 2 G 1) 51,62,400 (2) 34,73,156 (3) 26,00,829 4) 1,82,223 (5) 16,52,355 EXERCISE 2 H Q : 1 a) 1 (b) 126 (c) 1234 (d) 0 e) 182115 (f) 0 (g) 1 (h) 0 i) 1 (j) 3672681 Q : 2 a) Q = 26 R=0 (b) Q = 25478 R=9 c) Q = 512 R = 689 (d) Q = 2345 R=9 e) Q = 65 R=0 (f) Q = 75302 R=1 g) Q = 62158 R = 73 (h) Q = 58 R = 962 i) Q = 8674 R=2 (j) Q = 236 R = 589 k) Q = 1900 R = 29 (l) Q = 12 R = 56 Q : 3 a) 51615 (b) 643289 (c) 8456 d) 25991 (e) 99678 (f) 11387 EXERCISE 2 I a) Q = 150 R=0 c) Q = 79 R=8 e) Q = 1125 R = 20 g) Q = 2513 R = 4 i) Q = 954 R = 36 (b) Q = 104 (d) Q = 887 (f) Q = 3364 (h) Q = 927 (j) Q = 1933 R = 24 R = 10 R = 22 R = 39 R = 27 k) Q = 1061 R = 47 m) Q = 572 R=8 EXERCISE 2 J 1) 900 4) Rs. 135 EXERCISE 2 K 1) a 6) a (l) Q = 1514 (n) Q = 938 (2) 594 (5) 4925 (2) c (7) d R = 54 R = 25 (3) Rs. 1500 (6) 2961 (3) c (8) c CH-11 ROMAN NUMERALS * There are seven distinct symbols in Roman system. They are Roman Numerals I V X L C D Hindu Arabic Numerals 1 5 10 50 100 500 (4) d (9) b (5) b (10) c M 1000 There is no zero in the Roman System. This system has no place value system. RULES 1) Repetition of a symbol means addition. For Eg. 111 = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3 XXX = 10 + 10 + 10 = 30 CC = 100 + 100 = 200 Repetition is not allowed more than 3 times. V , L & D are never repeated. 2) If a smaller number is written to the right of a greater numberal then the smaller is added to the larger one. For Eg. VII = 5 + 1 + 1 = 7 XI = 10 + 1 = 11 LXXX = 50 + 10 + 10 +10 = 80 CLX = 100 + 50 + 10 = 160 3) If a smaller numeral is written to the left of a larger numeral the smaller is always subtracted from the larger one. For Eg. IV = 5 – 1 = 4 IX = 10 – 1 = 9 XL = 50 – 10 = 40 XC = 100 – 10 = 90 The numerals V , L and D are never subtracted. I is never written to the left of L, C and D. ROMAN NUMERALS FROM 1 TO 200 1 I 51 LI 2 II 52 LII 3 III 53 LIII 4 IV 54 LIV 5 V 55 LV 6 VI 56 LVI 7 VII 57 LVII 8 VIII 58 LVIII 9 IX 59 LVIX 10 X 60 LX 11 XI 61 LXI 12 XII 62 LXII 13 XIII 63 LXIII 14 XIV 64 LXIV 15 XV 65 LXV 16 XVI 66 LXVI 17 XVII 67 LXVII 18 XVIII 68 LXVIII 19 XIX 69 LXIX 20 XX 70 LXX 21 XXI 71 LXXI 22 XXII 72 LXXII 23 XXIII 73 LXXIII 24 XXIV 74 LXXIV 25 XXV 75 LXXV 26 XXVI 76 LXXVI 27 XXVII 77 LXXVII 28 XXVIII 78 LXXVIII 29 XXIX 79 LXXIX 30 XXX 80 LXXX 31 XXXI 81 LXXXI 32 XXXII 82 LXXXII 33 XXXIII 83 LXXXIII 34 XXXIV 84 LXXXIV 35 XXXV 85 LXXXV 36 XXXVI 86 LXXXVI 37 XXXVII 87 LXXXVII 38 XXXVIII 88 LXXXVIII 39 XXXIX 89 LXXXIX 40 XL 90 XC 41 XLI 91 XCI 42 XLII 92 XCII 43 XLIII 93 XCIII 44 XLIV 94 XCIV 45 XLV 95 XCV 46 XLVI 96 XCVI 47 XLVII 97 XCVII 48 XLVIII 98 XCVIII 49 XLIX 99 XCIX 50 L 100 C 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 CI CII CIII CIV CV CVI CVII CVIII CIX CX CXI CXII CXIII CXIV CXV CXVI CXVII CXVIII CXIX CXX CXXI CXXII CXXIII CXXIV CXXV CXXVI CXXVII CXXVIII CXXIX CXXX CXXXI CXXXII CXXXIII CXXXIV CXXXV CXXXVI CXXXVII CXXXVIII CXXXIX CXL CXLI CXLII CXLIII CXLIV CXLV CXLVI CXLVII CXLVIII CXLIX CL 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 CLI CLII CLIII CLIV CLV CLVI CLVII CLVIII CLIX CLX CLXI CLXII CLXIII CLXIV CLXV CLXVI CLXVII CLXVIII CLXIX CLXX CLXXI CLXXII CLXXIII CLXXIV CLXXV CLXXVI CLXXVII CLXXVIII CLXXIX CLXXX CLXXXI CLXXXII CLXXXIII CLXXXIV CLXXXV CLXXXVI CLXXXVII CLXXXVIII CLXXXIX CXC CXCI CXCII CXCIII CXCIV CXCV CXCVI CXCVII CXCVIII CXCIX CC EXERCISE 11 A Q :1 Write the Roman numeral for each of the following Hindu-Arabic Numeral. a) 200 (b) 197 (c) 184 (d) 171 e) 136 (f) 115 (g) 109 (h) 105 i) 99 (j) 85 (k) 63 (l) 42 m) 37 (n) 29 (o) 19 (p) 13 Q : 2 Write the Hindu – Arabic Numeral for each of the following Roman numerals. a) CXCIX (b) CXCVIII (c) CLXXVI (d) CLXII e) CLVIII (f) CXXXIX (g) CXVI (h) CIV i) LXXXVI j) XCVIII (k) LVII (l) XLV Q : 3 Fill in the blanks with > or <. a) XL __________ XXXIX c) XLII _________ LXI e) LXXV ___________ LXIX g) C ________L i) C __________XC Q : 4 Match 1. 19 2. 27 3. 32 4. 63 5. 85 6. 99 7. 152 8. 189 9. 161 10. 134 (b) LX _________ XL (d) XLIX _________ LIX f) LXXIX _________ XLVIII h) XC ____________ LXXXVIII j) XC ____________ XLIX a. LXIII b. LXXXV c. CLII d. XIX e. XCIX f. CLXI g. XXVII h. CXXXIV j. CLXXXIX j. XXXII EXERCISE 11 B Q : 1 Choose the correct answer. 1. LXIX is equivalent to (a) 49 (b) 59 (c) 69 (d) 79 2. CXLV is equal to (a) 150 (b) 145 (c) 445 (d) 175 3. Which of the following is incorrect? (a) XV (b) VX (c) XXV (d) XXXV 4. In Roman numeral 137 is written as (a) CVIIXXX (b) XXXVIII (c) CXVIII (d) CXXXVII ANSWERS EXERCISE 11 A Q : 1 a) CC e) CXXXVI i) XCIX m) XXXVII Q : 2 a) 199 e) 158 (b) CXCVII (f) CXV (j) LXXXV (n) XXIX (b) 198 (f) 139 (c) CLXXXIV (d) CLXXI (g) CIX (h) CV (k) LXIII (l) XLII (o) XIX (p) XIII (c) 176 (d) 162 (g) 116 (h) 104 i) 86 Q : 3 a) > f) > Q : 4 (1) d (6) e (b) > (g) > (2) g (7) c (j) 98 (c) < (h) > (3) j (8) i (k) 57 (d) < (i) > (4) a (9) f (l) 45 EXERCISE 11 B (1) c (2) b (3) b (4) d (e) > (j) > (5) b (10) h CH : 21 BASIC GEOMETRICAL CONCEPTS 1. POINT : A small dot made by a sharp pencil on a piece of paper represents a point. A A point has no length no breath and no thickness. It has only position. It is represented by capital letters such as A, B, C, X, Y, Z etc. 2.LINE SEGMENT : The straight path between two given points is called line segment. A line segment has a fixed length. A line segment AB is denoted as AB. Points A & B are end points of AB. Line segment AB is same as BA. 3.LINE : A line segment extended endlessly in both the directions is called a line. It has no end points. It is denoted by AB. AB is same as BA. A line has no definite length. 4. RAY : A line segment extended endlessly in one direction is called a Ray. It has one end point. In the fig.A is the end point of Ray AB. It is also called the initial point of AB. It is denoted as AB. It has no definite length. Ray AB is different from BA. 5. INTERSECTING LINES : When two lines meet at a point, then they are called intersecting lines and the point at which they meet is called point of intersection. Here AB and CD are intersecting Lines and O is the point of intersection. 6. COLLINEAR POINTS: When three or more points lie on the same line, then they are said to be collinear. In the fig A, B, C are collinear but D, E, F are not collinear. EXERCISE 21 A Q : 1 Classify the following as Point, Ray, Line and Line Segment. Q : 2 Name the points marked between X and Y. Q : 3 Name all the line segment in the following figure. Q : 4 Name the line segments in the following figure. Q : 5 In the figure name the following. a) 4 line segments b) 3 rays c) 2 lines d) 4 collinear Points Q : 6 In the figure name a) 2 Pair of intersecting lines b) 4 collinear points c) 3 non collinear points. Q : 7 Fill in the blanks. 1) A line segment has _____________________ end points. 2) A ray has ___________________ end point. 3) A ____________________ has a fixed length. 4) A ________________________ have no fixed length. 5) A __________________________ can be extended on both sides. 6) Point at which two lines meet is called _________________________. EXERCISE 21 B A. Measure each of the following line segments. B. Draw line segments of following lengths. 1) 2.3 cm (2) 4.7 cm 4) 9.7 cm (5) 5.8 cm 7) 8.3 cm (8) 3.4 cm C. Choose the correct option. 1. A line has _______________ end points. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) no 2. A ray has _______________ end points. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) no 3. Which of the following has a definite length? a) Point b) Line c) Line segment d) Ray (3) 10.7cm (6) 8 cm (9) 7.9 cm 4. A geometrical figure which has no size but has position is: a) Line b) angle c) Point d) ray 5. A Line Segment has __________ end points. a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ANSWERS EXERCISE 21 A Q : 1 a) Point L (b) Line segment XY (c) Point R d) Line RS (e) Line MN (f) Ray AB Q : 2 P,B,Q,D & F Q : 3 PQ, PR, PT, PS, QR, QT, QS, RT, RS, TS Q : 4 i) AB, BC, CD, DA ii) PQ, QR, RS, ST, TP iii) MN, NO, OS, SP, PQ, QM Q : 5 a) HF, FD, CD, DE (b) FH , CA, CB Q : 6 a) (XW and PS) (QR and TU) (b) X, P, Q and W Q : 7 a) two d) Line and Ray EXERCISE 21 B A. 1) 8 cm 4) 3.6 cm C. 1) d (2) a (b) one (e) Line (c) Line segment (f) Point of intersection (2) 4.8 cm (5) 12.9 cm (3) c (3) 6.4 cm (4) c ************** (5) b (c) B, C, D, E (c) T, Q, R