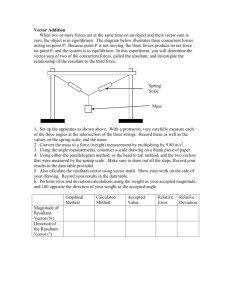
Practice – 3-2 Vector Addition and Subtraction – Graphical Methods

Name: ___________________________
Practice - 3.2 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods
1. Find the following for path A in figure. All blocks are 120 m on a side
A. The total distance traveled.
B. The magnitude and direction of the displacement from start to finish.
2. Find the following for path B in figure.
A. The total distance traveled.
Figure for Problems 1, 2 and 3.
All blocks are 120 m on a side.
B. The magnitude and direction of the displacement from start to finish.
3. Find the following for path C in figure.
A. The total distance traveled
B. The magnitude and direction of the displacement from start to finish.
4. Suppose you walk 18.0 m straight west and then 25.0 m straight north. How far are you from your starting point, and what is the compass direction of a line connecting your starting point to your final position?
(If you represent the two legs of the walk as vector displacements A and B , as in the figure to the right, then this problem asks you to find their sum R = A + B .)
5. Parallelogram Method
To add A and B using the parallelogram method, place the tail of B so that it meets the tail of A. Take these two vectors to be the first two adjacent sides of a parallelogram, and draw in the remaining two sides. The vector sum (i.e. resultant), A + B, extends from the tails of
A and B across the diagonal to the opposite corner of the parallelogram. If the vectors are perpendicular and unequal in magnitude, the parallelogram will be a rectangle. If the vectors are perpendicular and equal in magnitude, the parallelogram will be a square.
A. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the parallelogram method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A
B
Vector
A
Magnitude Direction
B
Resultant
B. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the parallelogram method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A
B
Vector
A
B
Resultant
Magnitude Direction
C. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the parallelogram method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A
B
Vector
A
B
Resultant
Magnitude Direction
D. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the parallelogram method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A
B
Vector
A
B
Resultant
Magnitude Direction
6. Head-to-Tail Method
To add A and B using the head-to-tail method, place the tail of B so that it meets the head of A without changing the orientation/direction of either vector. To find the resultant, connect the tail of A to the head of B.
Example: A = 3.0 m/s @ 45 deg, B = 5.0 m/s @ 135 deg = 5.83 m/s, 104 deg
B
A
B R
A
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
A. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the head-to-tail method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A:
B:
5.0 m/s @ 45 deg
2.0 m/s @ 180 deg
Magnitude Direction
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
B. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the head-to-tail method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A: 6.0 m/s @ 225 deg
B: 2.0 m/s @ 90 deg
Vector
A
B
Resultant
Magnitude Direction
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
C. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the head-to-tail method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A:
B:
5.0 m/s @ 45 deg
2.5 m/s @ 135 deg
Magnitude Direction
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
D. Add these two vectors using your ruler, protractor and the head-to-tail method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A: 5.0 m/s @ 0 deg
B: 2.0 m/s @ 90 deg
Vector
A
B
Resultant
Magnitude Direction
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
GRAND VECTOR CHALLENGE:
Add these three vectors using your ruler, protractor and the head-to-tail method on the axes below, and determine the resultant.
A: 2.0 m/s @ 315 deg
B: 5.0 m/s @ 180 deg
C: 2.0 m/s @ 60 deg
Vector
A
B
C
Magnitude Direction
Resultant
Scale: 1 cm = 1 m/s
Solutions:
1. A. 480 m
2. A. 1200 m
B. 379 m @ 71.6
o
B. 379 m @ 71.6
o
3. A. 1560 m B. 120 m @ 0 o
4. 30.8 m @ 125.8
o (NW)
5. A. 4.6 cm @ 27 o
C. 3.6 cm @ 79 o
C. 5.6 m/s @ 72
6. A. 3.9 m/s @ 67 o o
B. 2.1 cm @ 87 o
D. 2.6 cm @ -71 o
B. 4.8 m/s @ 208
D. 5.4 m/s @ 22 o
GRAND VECTOR CHALLENGE: 2.6 m/s @ 173 o o