Double Replacement Lab
advertisement

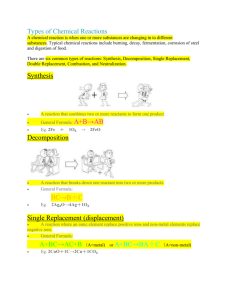
Name(s): ________________________ Double Replacement Reactions Background Information Some of the most impressive chemical reactions are double replacement reactions, also called ion exchange reactions. In a double replacement reaction, a clear solution of an ionic compound is added to a clear solution of another ionic compound. The positive ions on one compound react with the negative ions of the other compound to form a precipitate, a gas, or water. When a precipitate forms, the result can be very dramatic. The precipitate is an insoluble solid substance that may produce a sudden bright color in the remaining clear solution. In this investigation you will perform a double replacement reaction and observe and interpret the results. Problem How does a double replacement reaction occur? Materials Safety goggles Lab apron Triple beam balance (2) 250mL beakers Computer paper Lead nitrate Potassium iodide Stirring rod Graduated cylinder Procedure 1. Put on safety goggles. Place a piece of computer paper on the balance and write down its mass. Add 3 grams to the mass of the paper and move the riders on the balance to this number. Measure out 3 grams of lead nitrate and place it in one of the beakers. Discard the computer paper. 2. Add 50mL of water to the beaker with the 3 grams of lead nitrate and stir thoroughly to make sure that all the solid has dissolved. Rinse off the stirring rod and wipe it dry. 3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 using potassium iodide. 4. Pour the solution from one beaker into the other beaker and observe the results. Stir with the stirring rod and observe. 5. Place a coffee filter over one of the empty beakers and slowly pour the contents of the second beaker in the filter. Let the water completely filter through until just the solid is left. Place the coffee filter and the solid in the trash and clean everything else at your lab table and turn upside down to dry. Observations Answer each of the following with at least one complete sentence. 1. What did you observe when you mixed the lead nitrate with water? 2. What did you observe when you mixed the potassium iodide with water? 3. What did you observe when you mixed the two solutions together? 4. Did stirring the combination of the two solutions result in any change? Explain. Analysis and Conclusions Answer each of the following with at least one complete sentence. 1. What ions were present in the lead nitrate solution? 2. What ions were present in the potassium iodide solution? 3. Write an equation for the reaction that took place. Critical Thinking and Application Answer each of the following with at least one complete sentence. 1. A double replacement reaction is also called an ion exchange reaction. Describe the exchange of ions that occurred in this investigation. 2. What must always be one of the products of a double replacement reaction? 3. What must the other product(s) always be? 4. Describe what would happen if the product you obtained in this reaction were filtered through a filtering apparatus. Going Further Identify each of the following chemical equations as representing a synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, or double replacement reaction. Write a balanced equation for each reaction. 1. Carbon monoxide = Carbon + Oxygen (This problem is completed as an example of what you need to do.) 2CO = 2C + O2 Decomposition Reaction 2. Sodium + Water = Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas 3. Aluminum sulfate + Barium chloride = Aluminum chloride + Barium sulfate 4. Aluminum + Chlorine = Aluminum chloride 5. Sodium carbonate + Calcium hydroxide = Sodium hydroxide + Calcium carbonate