Key neo1 review
advertisement

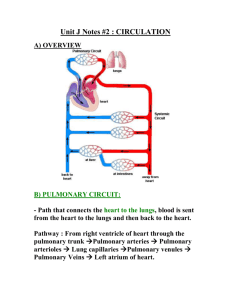
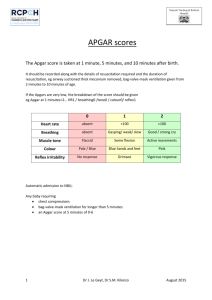
Unit 1 comprehensive Review/homework sheet Name: roster # date: 2007 1. The term infant is the one whose gestation has gone: a. More than 42 weeks b. Between 38-42 weeks c. 40 weeks d. Less than 38 weeks 2. The premature infant is the one whose gestation has gone: a. More than 42 weeks b. Between 38-42 weeks c. 40 weeks d. Less than 38 weeks 3. The SGA is an infant who: a. Is larger than he should be b. Smaller than he should be c. Just exactly right d. Has intrauterine growth retardation 4. Diabetic moms tend to have: a. SGA b. LGA c. AGA d. IUGR 5. When the mother is subjected to severe starvation or has placental insufficiency, there is a chance the infant will be: a. SGA b. LGA c. AGA d. IUGR 6. The forgut separates the primitive trachea and the esophagus at: a. 26 days b. 26 weeks c. 10th week 7. There is a beating heart at: a. 26 days b. 26 weeks c. 8th week d. 10th week 8. By week seven, the diaphragm is: a. Thin tissue b. Complete muscle 9. By week# 16 the lung devolvement is: a. Complete to the alveolar sac b. Complete to the bronchioles c. Complete to the alveolar buds 10. By week# 24 the lung devolvement is: a. Complete to the alveolar sac & alveolar ducts b. Complete to the bronchioles c. Complete to the alveolar buds 11. By week# 24 the circulation is: a. Complete at the pulmonary bed b. Is just starting at the pulmonary capillary bed c. Completely absent 12. By week # 24 in the nervous system: a. No thing is even started b. There are peripheral chemo receptors that notice hypoxemia c. The chemo receptors may or may not be active 13. The diaphragm is: a. Fully functional at 36 weeks b. Fully functional at 26 weeks c. Able to keep a FRC of fluid in the lungs d. A and c e. B and c 14. In the third trimester, the pulmonary surfactant is being produced at near normal levels by: a. Week 24 b. Week 26 c. Week 28 d. Week 36 e. Week 40 15. In the third trimester the baby is ‘practice breathing’ by: a. Week 24 b. Week 26 c. Week 30 d. Week 36 e. Week 40 16. The uterine arteries go to the uterine wall where: a. They empty into the maternal side of the placenta b. They empty into the fetal blood flow c. The placenta is attached d. A and c e. B and c 17. The umbilical cord consists of three vessels: i. Two umbilical arteries ii. One umbilical vein iii. One umbilical artery iv. Two umbilical veins a. i & ii b. iii & iv 18. The umbilical artery carries: i. Blood to the fetal heart ii. Blood from the fetal heart iii. Saturated blood iv. Desaturated blood a. i & iii b. ii & iv c. ii & iii d. i & iv 19. A function of the placenta is to: a. Secrete hormones that trigger labor b. Secrete hormones that prevent premature labor c. Send nutrients, 02 and exchange waste produces d. A and c e. B and c 20. While the material Pa02 is 80-100 torr, the best fetal P02 in the umbilical vein is: a. 26-29 torr b. 32-43 torr c. 55-65 torr d. none of these 21. The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood first to the: a. SVC b. IVC c. Liver then to the ductus arteriosus d. Liver then to the ductus venosus 22. The blood flow from the ductus venosus goes to the: a. SVC b. IVC c. Aorta d. Pulmonary artery 23. The blood flow from the SVC goes into the RA then to: a. The RV and the pulmonary bed b. The LA via the ductus arteriosus c. The LA via the ductus venosus d. The LA via the Foremen Ovale 24. The blood from the pulmonary artery will go into the –-- due to the pulmonary hypertension of the fetus. a. Foremen Ovale to the LA b. Ductus arteriosus then to the LV c. Ductus venosus then to the Aorta d. Ductus arteriosus then to the aorta 25. The most oxygenated blood enters the: a. Right subclavian and right jugular b. Left subclavian and left jugular 26. At the first breath: a. the infant’s inspiratory pressures are –80 cwp b. the infant is establishing his residual volume c. the lung compliance is low d. a, b only e. a, b & c 27.As the infant moves down the vaginal canal, he is subjected to pressures on his chest that: a. Raises the PA02 b. Raises the Pa02 in the Aorta c. Raises the mean airway pressure d. Drains the airways of excess water 28. Within the first few breaths, the alveolar 02 rises from 0 torr: a. This increases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure b. This decreases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure c. This raises the systemic pressure d. This drops the systemic blood pressure e. A & d 29. Within the first few breaths, the aortic Pa02 rises from the mid-20s to about 60-70 torr. a. This increases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure b. This closes the Foremen Ovale c. This closes the ductus venosus d. This closes the ductus arteriosus 30. The rise in --- closes the Foremen Oval: a. Pa02 in the RA b. Blood pressure of the RA c. Blood pressure of the LA d. Pa02 in the aorta e. PA02 31. The act of clamping off the umbilical cord and the placenta causes the rise in: a. Blood pressure in the systemic system b. Blood pressure of the RA c. Blood pressure of the LA d. A and c e. A and b 32. The normal blood gases for a term neonate at 1-5 hours of age are: a. PH 7.33 PaC02 47 Hc03- 23 Pa02 60 Sa02 90-92% b. PH 7.34 PaC02 35 Hc03- 19 Pa02 74 Sa02 92-95% c. PH 7.38 PaC02 36 Hc03- 21 Pa02 76 Sa02 92-95% 33. The normal blood gases for a preemie are: a. PH 7.33 PaC02 47 Hc03- 23 Pa02 60 b. PH 7.34 PaC02 35 Hc03- 19 Pa02 74 c. PH 7.38 PaC02 36 Hc03- 21 Pa02 76 Sa02 90-92% Sa02 92-95% Sa02 92-95% 34.The normal respiratory rate of the term newborn is: a. 40-60 bpm b. 30-50 bpm 35. The normal blood pressure of a preemie is: a. 46/26 with MAP of 35 b. 70-44 with MAP of 53 36. The best age to have a baby is: a. 14- 16 years old b. 16-40 years old [average 20s] c. 35-40 years old 38. Genetic defects such as cystic fibrosis: a. Can be passed onto the infant b. Can be avoided with good prenatal care 39. A woman who is G5 P2 A3 is a woman: a. With an excellent record of having babies b. At high risk for going into earlier labor 40. True/ False: A history of having babies who are SGA is significant. 41. True/ False: the socio-economic status of the mother is insignificant to the health of the infant. 42. True/ False: Ethanol abuse by a pregnant woman is a significant risk to the baby. 43. True/ False: Women who abuse barbiturates can have preemies and SGAs 44. True/ False: Women who abuse nicotine can have SGAs and increased CO levels 45. Fetal heartbeats during labor that decrease with each uterine contraction and come back to baseline are: a. Early decelerations and benign b. Late decelerations and a danger sign of fetal distress c. None of these 46. The most common deliver in the human is: a. Spontaneous vaginal deliver b. Vertex deliver c. Head first d. All of these 47. Drugs such as – can be used to slow down early labor: a. Magnesium sulfate b. Terbutaline sulfate c. both of these d. none of these 48. When the fetus is exposed to oxytocin he is getting an: a. Ultrasound b. Shake test c. Stress test 49. The APGAR Score is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 50. The Silverman Score is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 51. The Dublowz Score or Ballard’s is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 52. A baby with an APGAR score at 1 minute of 4 is: a. In serious condition b. In great condition 53. You are called to the L & D. The baby is a SVVD: a. This is a problem b. This is normal 54. You are called to the L & D for ‘fetal distress.” You seen an infant who is flaccid, his cry is weak and intermittent and he has central cyanosis and his heart rate is 118 bpm. When you suction his nares, he grimaces. : a. His APGAR score is 10 b. His APGAR score is 5 c. His APGAR score is 3 d. His APGAR score is 2 55. An infant with a APGAR score of 7 and above: a. Has a poor prognosis b. Has a fair prognosis c. Has excellent prognosis 56. Using your scale of Intrauterine Growth chart, identify the status of an 26-weeker who is 1350 grams at birth. a. SGA b. AGA c. LGA Unit 1 comprehensive Review/homework sheet Name: roster # date: 2007 9. The term infant is the one whose gestation has gone: a. More than 42 weeks b. Between 38-42 weeks c. 40 weeks d. Less than 38 weeks 10. The premature infant is the one whose gestation has gone: a. More than 42 weeks b. Between 38-42 weeks c. 40 weeks d. Less than 38 weeks 11. The SGA is an infant who: a. Is larger than he should be b. Smaller than he should be c. Just exactly right d. Has intrauterine growth retardation 12. Diabetic moms tend to have: a. SGA b. LGA c. AGA d. IUGR 13. When the mother is subjected to severe starvation or has placental insufficiency, there is a chance the infant will be: a. SGA b. LGA c. AGA d. IUGR 14. The forgut separates the primitive trachea and the esophagus at: a. 26 days b. 26 weeks c. 10th week 15. There is a beating heart at: a. 26 days b. 26 weeks c. 8th week d. 10th week 16. By week seven, the diaphragm is: a. Thin tissue b. Complete muscle 6. By week# 16 the lung devolvement is: a. Complete to the alveolar sac b. Complete to the bronchioles c. Complete to the alveolar buds 7. By week# 24 the lung devolvement is: a. Complete to the alveolar sac & alveolar ducts b. Complete to the bronchioles c. Complete to the alveolar buds 8. By week# 24 the circulation is: a. Complete at the pulmonary bed b. Is just starting at the pulmonary capillary bed c. Completely absent 9. By week # 24 in the nervous system: a. No thing is even started b. There are peripheral chemo receptors that notice hypoxemia c. The chemo receptors may or may not be active 10. The diaphragm is: a. Fully functional at 36 weeks b. Fully functional at 26 weeks c. Able to keep a FRC of fluid in the lungs d. A and c e. B and c 13. In the third trimester, the pulmonary surfactant is being produced at near normal levels by: a. Week 24 b. Week 26 c. Week 28 d. Week 36 e. Week 40 14. In the third trimester the baby is ‘practice breathing’ by: a. Week 24 b. Week 26 c. Week 30 d. Week 36 e. Week 40 15. The uterine arteries go to the uterine wall where: a. They empty into the maternal side of the placenta b. They empty into the fetal blood flow c. The placenta is attached d. A and c e. B and c 16. The umbilical cord consists of three vessels: i. Two umbilical arteries ii. One umbilical vein iii. One umbilical artery iv. Two umbilical veins a. i & ii b. iii & iv 17. The umbilical artery carries: i. Blood to the fetal heart ii. Blood from the fetal heart iii. Saturated blood iv. Desaturated blood b. i & iii c. ii & iv d. ii & iii e. i & iv 18. A function of the placenta is to: a. Secrete hormones that trigger labor b. Secrete hormones that prevent premature labor c. Send nutrients, 02 and exchange waste produces d. A and c e. B and c 19. While the material Pa02 is 80-100 torr, the best fetal P02 in the umbilical vein is: a. 26-29 torr b. 32-43 torr c. 55-65 torr d. none of these 20. The umbilical vein carries oxygenated blood first to the: a. SVC b. IVC c. Liver then to the ductus arteriosus d. Liver then to the ductus venosus 21. The blood flow from the ductus venosus goes to the: a. SVC b. IVC c. Aorta d. Pulmonary artery 22. The blood flow from the SVC goes into the RA then to: a. The RV and the pulmonary bed b. The LA via the ductus arteriosus c. The LA via the ductus venosus d. The LA via the Foremen Ovale 23. The blood from the pulmonary artery will go into the –-- due to the pulmonary hypertension of the fetus. a. Foremen Ovale to the LA b. Ductus arteriosus then to the LV c. Ductus venosus then to the Aorta d. Ductus arteriosus then to the aorta 24. The most oxygenated blood enters the: a. Right subclavian and right jugular b. Left subclavian and left jugular 7. At the first breath: a. the infant’s inspiratory pressures are –80 cwp b. the infant is establishing his residual volume c. the lung compliance is low d. a, b only e. a, b & c 1. 8. As the infant moves down the vaginal canal, he is subjected to pressures on his chest that: a. Raises the PA02 b. Raises the Pa02 in the Aorta c. Raises the mean airway pressure d. Drains the airways of excess water 9. Within the first few breaths, the alveolar 02 rises from 0 torr: a. This increases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure b. This decreases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure c. This raises the systemic pressure d. This drops the systemic blood pressure e. A & d 10. Within the first few breaths, the aortic Pa02 rises from the mid-20s to about 60-70 torr. a. This increases the pulmonary capillary bed pressure b. This closes the Foremen Ovale c. This closes the ductus venosus d. This closes the ductus arteriosus 11. The rise in --- closes the Foremen Oval: a. Pa02 in the RA b. Blood pressure of the RA c. Blood pressure of the LA d. Pa02 in the aorta e. PA02 12. The act of clamping off the umbilical cord and the placenta causes the rise in: a. Blood pressure in the systemic system b. Blood pressure of the RA c. Blood pressure of the LA d. A and c e. A and b 13. The normal blood gases for a term neonate at 1-5 hours of age are: a. PH 7.33 PaC02 47 Hc03- 23 Pa02 60 Sa02 90-92% b. PH 7.34 PaC02 35 Hc03- 19 Pa02 74 Sa02 92-95% c. PH 7.38 PaC02 36 Hc03- 21 Pa02 76 Sa02 92-95% 14. The normal blood gases for a preemie are: a. PH 7.33 PaC02 47 Hc03- 23 Pa02 60 b. PH 7.34 PaC02 35 Hc03- 19 Pa02 74 c. PH 7.38 PaC02 36 Hc03- 21 Pa02 76 Sa02 90-92% Sa02 92-95% Sa02 92-95% 1. 15. The normal respiratory rate of the term newborn is: a. 40-60 bpm b. 30-50 bpm 16. The normal blood pressure of a preemie is: a. 46/26 with MAP of 35 b. 70-44 with MAP of 53 17. The best age to have a baby is: a. 14- 16 years old b. 16-40 years old [average 20s] c. 35-40 years old 18. Genetic defects such as cystic fibrosis: a. Can be passed onto the infant b. Can be avoided with good prenatal care 19. A woman who is G5 P2 A3 is a woman: a. With an excellent record of having babies b. At high risk for going into earlier labor 20. True/ False: A history of having babies who are SGA is significant. 21. True/ False: the socio-economic status of the mother is insignificant to the health of the infant. 22. True/ False: Ethanol abuse by a pregnant woman is a significant risk to the baby. 23. True/ False: Women who abuse barbiturates can have preemies and SGAs 24. True/ False: Women who abuse nicotine can have SGAs and increased CO levels 9. Fetal heartbeats during labor that decrease with each uterine contraction and come back to baseline are: a. Early decelerations and benign b. Late decelerations and a danger sign of fetal distress c. None of these 10. The most common deliver in the human is: a. Spontaneous vaginal deliver b. Vertex deliver c. Head first d. All of these 11. Drugs such as – can be used to slow down early labor: a. Magnesium sulfate b. Terbutaline sulfate c. both of these d. none of these 12. When the fetus is exposed to oxytocin he is getting an: a. Ultrasound b. Shake test c. Stress test 13. The APGAR Score is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 14. The Silverman Score is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 15. The Dublowz Score or Ballard’s is used to assess the baby’s: a. Signs of life b. Signs of respiratory distress c. Signs of physical and neurological maturity d. Size 16. A baby with an APGAR score at 1 minute of 4 is: a. In serious condition b. In great condition 5. You are called to the L & D. The baby is a SVVD: a. This is a problem b. This is normal 6. You are called to the L & D for ‘fetal distress.” You seen an infant who is flaccid, his cry is weak and intermittent and he has central cyanosis and his heart rate is 118 bpm. When you suction his nares, he grimaces. : a. His APGAR score is 10 b. His APGAR score is 5 c. His APGAR score is 3 d. His APGAR score is 2 7. An infant with a APGAR score of 7 and above: a. Has a poor prognosis b. Has a fair prognosis c. Has excellent prognosis 8. Using your scale of Intrauterine Growth chart, identify the status of an 26-weeker who is 1350 grams at birth. a. SGA b. AGA c. LGA