Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological
advertisement

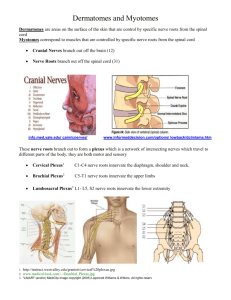
Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological Examination:Lower Limb NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION MOTOR & SENSORY FUNCTION LOWER LIMB AN ANATOMICAL GUIDE THIGH & POPLITEAL FOSSA 21.May.2014 Wednesday Testing the quadriceps is performed with the person in the supine position with the knee partly flexed. The person extends the knee against resistance. During the test, contraction of the rectus femoris should be observable and palpable if the muscle is acting normally, indicating that its nerve supply is intact. To test the hamstrings, the person flexes his leg against resistance. Normally, these muscles—especially their tendons on each side of the popliteal fossa—should be prominent as they bend the knee. LEG To test the the tibialis anterior, the person is asked to stand on the heels or dorsiflex the foot against resistance; if normal, its tendon can be seen and palpated. To test the extensor hallucis longus, the great toe is dorsiflexed against resistance; if acting normally, its entire tendon can be seen and palpated. To test the extensor digitorum longus, the lateral four toes are dorsiflexed against resistance; if acting normally, the tendons can be seen and palpated. The extensor digitorum longus extends the toes and dorsiflexes the foot at the ankle joint. To test the fibularis longus and brevis, the foot is everted strongly against resistance; if acting normally, the muscle tendons can be seen and palpated inferior to the lateral malleolus. To test the triceps surae, the foot is plantarflexed against resistance (e.g., by “standing on the toes,” in which case body weight [gravity] provides resistance). If normal, the calcaneal tendon and triceps surae can be seen and palpated. To test the flexor hallucis longus, the distal phalanx of the great toe is flexed against resistance; if normal, the tendon can be seen and palpated on the plantar aspect of the great toe as it crosses the joints of the toe. To test the flexor digitorum longus, the distal phalanges of the lateral four toes are flexed against resistance; if they are acting normally, the tendons of the toes can be seen and palpated. To test the tibilalis posterior, the foot is inverted against resistance with the foot in slight plantarflexion; if normal, the tendon can be seen and palpated posterior to the medial malleolus. http://www.youtube.com/yeditepeanatomy 1 Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological Examination:Lower Limb RegIons & MUSCLES Gluteal region superficial: Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius & minimus Tensor fasciae latae Function extends the flexed thigh Abduct and medially rotate thigh Gluteal region deep: Piriformis Obturator internus Gemellus superior Gemellus inferior Quadratus femoris Function abduct flexed thigh (excp q.f.) laterally rotate extended thigh& steady femoral head in acetabulum Anterior thigh: Ilıopsoas Quadriceps femoris Sartorius Function chief flexor of the thigh, hip flexor Extends leg at knee joint Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint; flexes leg at knee joint Medial thigh: Adductor longus Adductor brevis Adductor magnus Gracilis Function Adducts thigh Adducts thigh; flexes leg; helps rotate leg medially Pectineus Obturator externus Function Adducts and flexes thigh; assists with medial rotation of thigh Laterally rotates thigh; steadies head of femur in acetabulum Posterior thigh: Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Function Extend thigh; flex leg & rotate it medially when knee is flexed; when thigh and leg are flexed, these muscles can extend trunk Biceps femoris Function Flexes leg and rotates it laterally when knee is flexed; extends thigh (e.g., accelerating mass during first step of gait) Anterior leg: Tibialis anterior Extensor hallucis longus Function Dorsiflexes ankle and inverts foot Extends great toe and dorsiflexes ankle Extensor digitorum longus Fibularis tertius Function Extends lateral four digits and dorsiflexes ankle Dorsiflexes ankle and aids in eversion of foot Lateral leg: Fibularis longus Fibularis brevis Function Everts foot and weakly plantarflexes ankle Posterior leg superficial: Gastrocnemius Function Plantarflexes ankle when knee is extended; raises heel during walking; flexes leg at knee joint Soleus Plantaris Function Plantarflexes ankle independent of position of knee; steadies leg on foot Weakly assists gastrocnemius in plantarflexing ankle Posterior leg deep: Popliteus Flexor hallucis longus Function Weakly flexes knee Flexes great toe at all joints; weakly plantarflexes ankle; supports medial longitudinal arch of foot Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Function Flexes lateral four digits; plantarflexes ankle; supports longitudinal arches of foot Plantarflexes ankle; inverts foot Foot (Dorsum): Extensor digitorum brevis Extensor hallucis brevis Function Extends metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe, and the three middle toes Foot (Sole,1st layer): Abductor hallucis Flexor digitorum brevis Abductor digiti minimi Function Abducts and flexes 1st digit Flexes lateral four digits Abducts and flexes little toe Foot (Sole,2nd layer): Quadratus plantae Function Assists flexor digitorum longus in flexing lateral four digits Lumbricals Flex proximal phalanges, extend middle and distal phalanges of lateral four digits Foot (Sole,3rd layer): Flexor hallucis brevis Adductor hallucis Function Flexes proximal phalanx of 1st digit adduct 1st digit; assists in transverse arch of foot by metatarsals medially Flexor digit minimi brevis Function Flexes proximal phalanx of 5th digit Foot (Sole,4th layer): Plantar interossei (three muscles) Dorsal interossei (four muscles) Function Adduct digits (2-4) and flex metatarsophalangeal joints Abduct digits (2-4) and flex metatarsophalangeal joints http://www.youtube.com/yeditepeanatomy 2 Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological Examination:Lower Limb REGIONS & Nerves (Motor INNERVATION ONLY) Shoulder: supraclavicular nerves (medial,intermediate,lateral) the skin as far as the middle line, the skin over the pectoralis major and deltoideus, the skin of the upper and posterior parts of the shoulder, inferior part of the deltoid muscle (axillary nerve) Anterior arm: inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm (radial nerve) lateral and anterior aspects of the lower part of the arm medial cutaneous nerve of arm back of the lower third of the arm, extending as far as the elbow superior lateral cutaneous nerve of arm (axillary nerve) the skin over the lower two-thirds of the posterior part of the deltoid muscle, as well as that covering the long head of the triceps brachii Anterior forearm: medial cutaneous nerve of forearm medial surface of the forearm down to the wrist lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm (continuation of musculocutaneous nerve) lateral half of the anterior aspect of the forearm Posterior arm & forearm: radial nerve posterior aspect of the arm and forearm (posterior cutaneous nerve of forearm), lower lateral surface of the arm, medial cutaneous nerve of arm medial side of the distal third of the arm Hand: superficial branch of the radial nerve dorsolateral aspect of the palm and the dorsal aspects of the lateral three and one-half digits distally to approximately the terminal interphalangeal joints ulnar nerve medial side of the palm, medial half of the dorsum of the hand, the 5th finger, and the medial half of the 4th finger, anterior surfaces of the medial one and a half digits median nerve thumb,index,middle fingers,lateral side of the ring [distal parts on the dorsum of the hand], palmar surface of the lateral three and one-half digits and over the lateral side of the palm and middle of the wrist Gluteal region: Upper lateral quadrant of the gluteal region is supplied by the lateral branches of the iliohypogastric (L1) and 12th thoracic nerves (anterior rami). Superior clunial nerves L1-L3 posterior rami Skin overlying superior and central parts of buttock Medial clunial nerves S1-S3 posterior rami Skin of medial buttock and intergluteal cleft Inferior clunial nerves Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh (S2-S3) Skin of inferior buttock (overlying gluteal fold Thigh: obturator nerve superior medial thigh, genitofemoral nerve middle anterior thigh, posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh posterior aspect of the thigh, intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh (femoral nerve) variable area on the medial aspect of the thigh, the medial cutaneous nerve of the thigh (femoral nerve) medial aspect of the thigh Leg: saphenous nerve (femoral nerve) medial aspect of leg, posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh upper part of the leg superficial fibular nerve anterolateral leg, sural nerve posterolateral leg Foot: Medially saphenous nerve, which extends distally to the head of 1st metatarsal. Superiorly (dorsum of foot) superficial (primarily) and deep fibular nerves. Inferiorly (sole of foot) medial and lateral plantar nerves; the common border of their distribution extends along the 4th metacarpal and toe or digit. (This is similar to the pattern of innervation of the palm of the hand.) Laterally sural nerve, including part of the heel. Posteriorly (heel) medial and lateral calcaneal branches of the tibial and sural nerves, respectively. http://www.youtube.com/yeditepeanatomy 3 Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological Examination:Lower Limb Sensory Innervation of the Lower Limb Iliohypogastric (L1; occasionally T12) superolateral quadrant of buttock Ilioinguinal (L1; occasionally T12) Skin over medial femoral triangle Genitofemoral Lumbar plexus (L1-L2) Femoral branch supplies skin over lateral part of femoral triangle; genital branch supplies anterior scrotum or labia majora Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh Lumbar plexus (L2-L3) Skin on anterior and lateral aspects of thigh Anterior cutaneous branches Lumbar plexus via femoral nerve (L2-L4) Skin of anterior and medial aspects of thigh Cutaneous branch of obturator nerve Lumbar plexus via obturator nerve, anterior branch (L2L4) Skin of middle part of medial thigh Posterior cutaneous nerve of thigh Sacral plexus (S1-S3) Skin of posterior thigh and popliteal fossa Saphenous nerve Lumbar plexus via femoral nerve (L3-L4) Skin on medial side of leg and foot Superficial fibular nerve Common fibular nerve (L4-S1) Skin of anterolateral leg and dorsum of foot, excluding web between great and 2nd toes Deep fibular nerve Common fibular nerve (L5) Skin of web between great and 2nd toes Sural nerve Tibial and common fibular nerves (S1-S2) Skin of posterolateral leg and lateral margin of foot Medial plantar nerve Tibial nerve (L4-L5) Skin of medial side of sole, and plantar aspect, sides, and nail beds of medial 3½ toes Lateral plantar nerve Tibial nerve (S1-S2) Skin of lateral sole, and plantar aspect, sides, and nail beds of lateral 1½ toes Calcaneal nerves Tibial and sural nerves (S1-S2) Skin of heel http://www.youtube.com/yeditepeanatomy 4 Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Neurological Examination:Lower Limb reflexes Tendon Reflexes and the Segmental Innervation of Muscles of the Lower Limb Patellar Reflex The quadriceps femoris is innervated by the femoral nerve. A tap with a tendon hammer on the patellar ligament therefore tests reflex activity mainly at spinal cord levels L3 and L4. Calcaneal Tendon Reflex The ankle jerk reflex, or triceps surae reflex, is a calcaneal tendon reflex. It is a myotatic reflex elicited while the person's legs are dangling over the side of the examining table. The calcaneal tendon is struck briskly with a reflex hammer just proximal to the calcaneus. The normal result is plantarflexion of the ankle joint. The calcaneal tendon reflex tests the S1 and S2 nerve roots. If the S1 nerve root is injured or compressed, the ankle reflex is virtually absent. http://www.youtube.com/yeditepeanatomy 5