PHS224 - Mineral Area College
advertisement

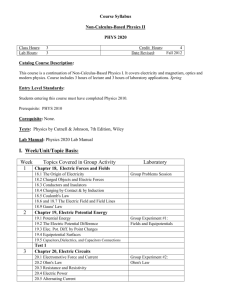
Instructor: Office Hours: Office: Phone: e-mail: Department Chair: Prerequisites: GENERAL PHYSICS II PHS2240 AA01 Mineral Area College FALL 2015 4 credit hours Dr. George Saum 1:00 M W F 9:00 T R AS223A or Physics Lab AS223 573-518-2174 gsaum@mineralarea.edu Dr. Margaret Williams General Physics I 518-573-2195 FO 29 mwilliam@mineralarea.edu PHS 2230 Textbooks: PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS, ninth edition R.A. Serway and John W. Jewett, Thomson Brooks/Cole Publishers, 2014 ISBN 978-1-133-94727-1 Laboratory experiment handouts will be provided in class The course meets for four hours of lecture and problem session, and two hours of lab each week. Lecture/Problem MTWF 11:00-11:50 Lab R 10:00-11:50 Supplementary Material: Mathcad and Excel will be used in solving and analyzing laboratory and classroom problems Other Materials: Scientific calculator. Attendance/Absence Policies: Disciplined attendance is strongly encouraged. A student missing a total equivalent of two weeks of class work will be dropped. School policy requires dropping students with poor attendance. Poor attendance will severely impact your classroom performance. Grading policy/scale: The grading for the course will be as follows: A 90-100 % B 80-89 C 70-79 D 60-69 F <60 You must notify in advance if you cannot make class on test day. The test must then be taken on the next class day. Only one late test will be allowed. Non-Discrimination Policy – Mineral Area College does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, gender, disability, age, religion, creed, or marital or parental status. ADA Policy If you have special needs as addressed by the Americans with Disabilities Act and need any test or course materials provided in an alternative format, notify your instructor immediately. Reasonable efforts will be made to accommodate your special needs. Special Needs Services is located in ( ) , 518-2152. If you are a handicapped person and cannot attend the on-site examinations, please contact the instructor to make special arrangements. Dishonesty policy: “…College discipline shall be exercised when student misconduct adversely affects the college’s pursuit of its educational objectives. Misconduct for which students are subject is defined as follows: Dishonesty, such as cheating, plagiarism, or knowingly furnishing false information to the college” (Mineral Area College Board Policy Manual, section 5.72, IA., p. 99). Honors Option: The honors option is offered in this course. 1 This is the second semester of the introductory calculus based physics course designed to meet the needs of physical science or engineering students. Principal categories covered are: Electromagnetism and Optical Wave Phenomena Topics to be covered: Electrostatic field , Coulomb's law, Gauss's law Electrical potential Electric fields and potentials from distributed charges Capacitors and Ohm's law Direct current circuits Magnetic forces and Ampere's law Faraday's law and inductance Alternating Current circuits Maxwell's equations Wave properties of light Reflection and refraction of lenses and mirrors Interference and diffraction Optical instruments Tentative sequence of tab experiments: Mapping Electric fields and potential fields Dc currents and potentials Measuring resistance Resistivity Joule heating Earth's magnetic field Electromagnetic induction Reflection and refraction Mirrors and lenses Wavelength of light Evaluation: Grading Scale: 90-100 80-90 70-80 60-70 < 60 Homework Lab reports Exams (5) 10% 20 % 70 % A B C D F 2 PHYS 2240 HOMEWORK PROBLEMS AND TEST SCHEDULE FALL 2015 DATES Aug 17 18 19 21 24 25 26 28 31 SEPT 1 Chap 23 Electric Fields Problems 23.1,2,3 23.4 23.5 23.6 23.7 Coulomb’s Law Electric Field Electric Field of Continuous Charge Electric Field Lines Motion in a Uniform Field 9,11,13,15,17 25,29 37,39 Chap 27 Current and Resistance 27.1 27.2 27.3 27.4 27.6 Electric Current Resistance and Ohm’s Law Model for Conduction Resistance and Temperature Electrical Energy and Power Chap 24 Gauss’s Law 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 24.5 24.6 Review TEST 1 Electric Flux Gauss’s Law Applications of Gauss’s Law Conductors in Equilibrium Experimental Verification Formal Derivation of Gauss’s Law Selected Answers 51,53,55 3,5,11 17,21 26,27,29 39,47,51,53 3 1,3,5 19,21 27,29,35 37,55 1435 C Sept SEPT Chap 25 Electric Potential 2 25.1 25.2 Potential Difference and Electrical Pot Potential Difference – Uniform Field 3,5 9,11 4 25.3 25.4 LABOR DAY 25.5 25.6 Electrical Potential - Point Charges Electric Field form Electrical Potential 13,21,23 39,41 Electric Potential due to Continuous Chg. Electrical Potential due to Conductor 44,45 50 Chap 26 Capacitance and Dielectrics 26.1 26.2 26.3 26.4 26.5 Definition of Capacitance Calculating Capacitance Combinations of capacitors Energy Stored in a Capacitor Capacitors with dielectrics Chap 28 Direct Current Circuits 28.1 28.2 28.3 28.4 28.5 28.6 Review TEST 2 Electromotive Force Resistors in Series and Parallel Kirchhoff’s Rules RC Circuits Electrical Instruments Household Wiring 7 8 9 11 14 15 16 18 21 22 3 7,9,11 13,15,19 31,33 43,45 4 1,3 9,15,19 23,25,29 37,39 1513 kV, k[L-d ln((d+L)/d)] 0, 1.17 kV, 1.67 kV Sept Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields 29.1 29.2 29.3 29.4 29.5 29.6 Chapter 30 Magnetic Field and Forces Motion of Charged Particles Applications Force on Conductors Torque on a Current Loop The Hall Effect Sources of Magnetic Fields 7,9 13,21 27 33,35 48,51 54 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.5 30.6 30.7 Chapter 31 The Biot-Savart Law Magnetic Force Between Two Conductors Amperes Law Magnetic Field of a Solenoid Gauss’s Law in Magnetism Magnetism in Matter Magnetic Field of the Earth Faraday’s Law 3,5,7 21,25 30,31,33 41 48 500 amps 5 6 7 9 12 13 31.1 NO SCHOOL 31.2 31.3 31.4 31.5 31.6 Faraday’s Law of Induction 5,9,14 .0142 cos( 120 t) Motional EMF Lenz’s Law Induced EMF and Electric Fields Generators and Motors Eddy Currents 25,27,37 39 14 16 Review TEST 3 23 25 28 29 OCT 30 2 5 45,49 4.27 cm, 1.79x10-8 s .0054 A m2, .0043 N m .0377 T, 4.25 x 1025 /m3 19 20 21 23 26 27 28 30 Nov 2 3 4 Chapter 32 32.1 32.2 32.3 32.4 32.5 32.6 Inductance Self – inductance RL circuits Energy in a Magnetic Field Mutual inductance Oscillations in an LC circuit The RLC Circuit 3,5,9,13 15,17,31 33,39 41,43 48,49 57,58 Chapter 33 33.1 33.2 33.3 33.4 33.5 33.6 33.7 33.8 33.9 Alternating Current Circuits AC Sources Resistors in an ac Circuit Inductors in an ac Circuit Capacitors in an ac Circuit The RLC Series Circuit Power in an ac Circuit Resonance in an RLC series circuit Transformers and Power Transmission Rectifiers and Filters 1,7 9,11 21,23 24,29,31 36 43 49,51,57 53 Chapter 34 34.1 34.2 34.3 34.7 Review TEST 4 Electromagnetic Waves Displacement Current Plane EM waves Energy in an EM wave The Spectrum of EM waves 3 9,12 21,27 51,57,65 6 608 pF 146, 213, 179, 34 V Z =500, 8 W .733 T DATE Nov 6 9 10 NOV 16 17 18 20 23 DEC Light and Optics 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 35.6 35.7 35.8 Nature of Light Speed of Light Ray Approximation Reflection, Refraction Hurgens Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection 11 13 Dec Chapter 35 24 25 26 27 30 1 1,3 5,7,11 37 42,45 27o, 37o, 49.8o 9,11,13 29,35 41,42,43 5/4 f, -.25, inv, real 68 800, inv VETERANS DAY Chapter 36 Geometric Optics 36.1 36.2 36.3 36.4 36.5 36.6 36.7 36.8 36.9 36.10 Flat Mirrors Spherical Mirrors Images from Refraction Thin lenses Aberrations Camera Eye Magnifier Microscope Telescope Chapter 37 Interference of Light Waves 37.1 37.2 37.3 37.4 37.5 37.6 37.7 Conditions for Interference Young’s Double Slit Experiment Interference Intensity Distribution of Double Slit Change of Phase Interference in Thin Films Michelson Interferometer Chapter 38 Diffraction and polarization 38.1 38.2 Intro to Diffraction Diffraction with Narrow Slits Thanksgiving Thanksgiving Resolution of Slits and Apertures Diffraction Grating X-rays Polarization of Light 2 4 38.3 38.4 38.5 38.6 Review 8 TEST 5 ( FINAL ) 10:00 11:40 7 3,5,9 31,33,40 97.8 nm, ¾, 5/4 etc 3,5,6 15,17,24 25,33 45,49 105 m LAB EXPERIMENTS MCAD/EXCEL FIELDS AND POTENTIAL OHM'S LAW RESISTIVITY SERIES/PARALLEL RESISTANCE KIRCHOFF'S RULES RC TIME CONSTANT HELMHOLTZ COILS DIODES ANALOG OSCILLOSCOPE TRANSFORMER R-L-C CIRCUITS DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPES TRANSISTORS LENSES GRATINGS/ SPECTROSCOPY 8