Lab #5: Chicken Wing Dissection
advertisement

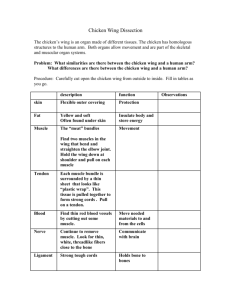
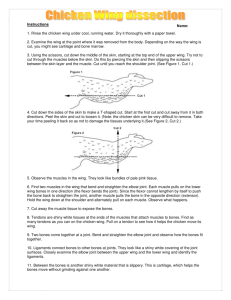
UNIT 3 SPA: Chicken Wing Dissection –Skeletal and Muscular Systems Procedures: 1. Obtain a chicken wing and dissecting equipment. 2. Rinse the chicken wing under cool, running water and thoroughly dry it with a paper towel. 3. Pick up the wing and imagine it is still on the chicken. Answer Observation Question #1. 4. Imagine that the wing is your arm. Move the joints, look at Figure 1 and answer Observation Question #2. Figure 1 5. Examine the skin covering the chicken wing. Fill in #1 on the Observations Table. 6. At the cut end of the upper wing slip the tip of the scissors between the skin and the muscles underneath. Answer Observation Question #3. 7. Cut the skin lengthwise along the entire length of the chicken wing to the joint between the upper wing and the lower wing. Try not to cut through the muscles below the skin. 8. Remove the skin from the joint between the upper wing and lower wing. Be sure not to cut any tendons or ligaments. This is difficult. It works best if you slide your finger around under the skin to break some of the connective tissues then grab the skin, cut and pull hard from top to bottom. 9. Notice the yellowish tissue found in small clumps on the inside of the skin. This is called “fat tissue.” Fats are a kind of molecule we will learn more about in digestion. All cells contain some fats but “fat cells” are filled with the stuff. A bunch of “fat cells” together make “fat tissue.” Fill in #2 on the Observation Table. 10. Remove the skin on the lower wing in the same way that you removed the skin on the upper wing. Leave the skin on the wing tip. 11. Observe the muscles on the wing. They are bundles of pale pink tissue. Fill in #3 on the Observation Table and answer Observation Question #4. 12. Use a blunt probe to separate the individual muscles from each other WITHOUT tearing them. On the back of your lab or separate sheet of paper draw you chicken wing showing its separate muscles. Label each muscle. 13. Observe the shiny tendons. Fill in #4 on the Observation Table. 14. Notice the white ligaments at the joint. Fill in #5 on the Observation Table. 15. Find a thin reddish-brown strand of tissue. Pull it aside with the dissecting needle. This is a blood vessel. Fill in #6 on the Observation Table. 16. Straighten the chicken wing and hold it horizontally above the tray. Pull on each of the muscles and note the movement that each muscle causes. Answer Observation Question #5. 17. Turn the wing upside down and bend the joints. Again pull on each muscle and note how the bones move. Answer Observation Question #6 18. Find a tendon and use it (pull on it) to move the chicken wing and see how it helps the chicken move. 19. Cut through the middle of a muscle that you have identified as a FLEXOR for the upper wing. Answer Observation Question #7 20. Cut through the middle of a muscle that you have identified as an EXTENSOR for the upper wing. Answer Observation Question #8 21. Remove the muscles and tendons from around joint A. Answer Observation Question #9. 22. Try to pull the bones apart at joint A without twisting them. 23. If you did not succeed in pulling the joint apart, twist it apart. Inspect the joint area and answer Observation Question #10. 24. Throw the chicken remains away. 25. Wash all equipment (not in the back sink) in hot, soapy water, rinse it and put it in the appropriate place to dry. 26. Wash your hands with hot water and soap. 27. Finish answering the Observation Questions. Note: if you do not finish Procedures #1-23 in one period then you must write your names and block on a piece of tape and put it on a bag. Then put your chicken wing in the labeled bag and put the bag in the fridge (where specified) and clean up. You may have the next period to finish up your observations. Observation Table # Tissue 1. Skin 2. Fat 3. Muscle 4. Tendon 5. Ligament 6. Blood Vessel Description (color, texture, etc.) Your Chicken Wing Tissues it attaches to: Name ____________________________________ Date __________ Period _______ UNIT 3 SPA: Chicken Wing Dissection –Skeletal and Muscular Systems Observation Questions: 1. Do you think your wing is from the right or left side? Explain why. 2. Joint questions: a. Which joint in the human body (shoulder, elbow, wrist or finger) is the equivalent to Joint A? b. Does Joint A move more like a ball and socket joint or more like a hinge joint? c. Which joint in the human body (shoulder, elbow, writs or finer) is the equivalent to Joint B? 3. What skin layer are you underneath? 4. How many different groups of muscles are attached to the bones that connect at joint A? 5. On your drawing, outline in RED each muscle that FLEXES a joint. 6. On your drawing, outline in BLUE each muscle that EXTENDS a joint. 7. What happens to the ability of the wing? 8. What happens to the ability of the wing? 9. How many ligaments hold joint A together? 10. Explain whether or not you caused each of the following types of injuries when you pulled the wing apart at Joint A: Sprain Fracture Dislocation Analysis Questions: 1. For each of the following chicken parts identifying the types(s) of tissue(s) that make up the part. Write “C” for Connective, “E” for Epithelial, “M” for Muscle and “N” for Nerve on the appropriate blanks tendon_________ nerve________ fat________ blood vessel____ skin________ ligament_____ bone_______ muscle______ 2. Why are tendons important to a muscles ability to move a bone? 3. What type of tissue actually moves the chicken’s wing? 4. What tissue of the chicken wing is commonly referred to as the meat?