Comments/notes
advertisement
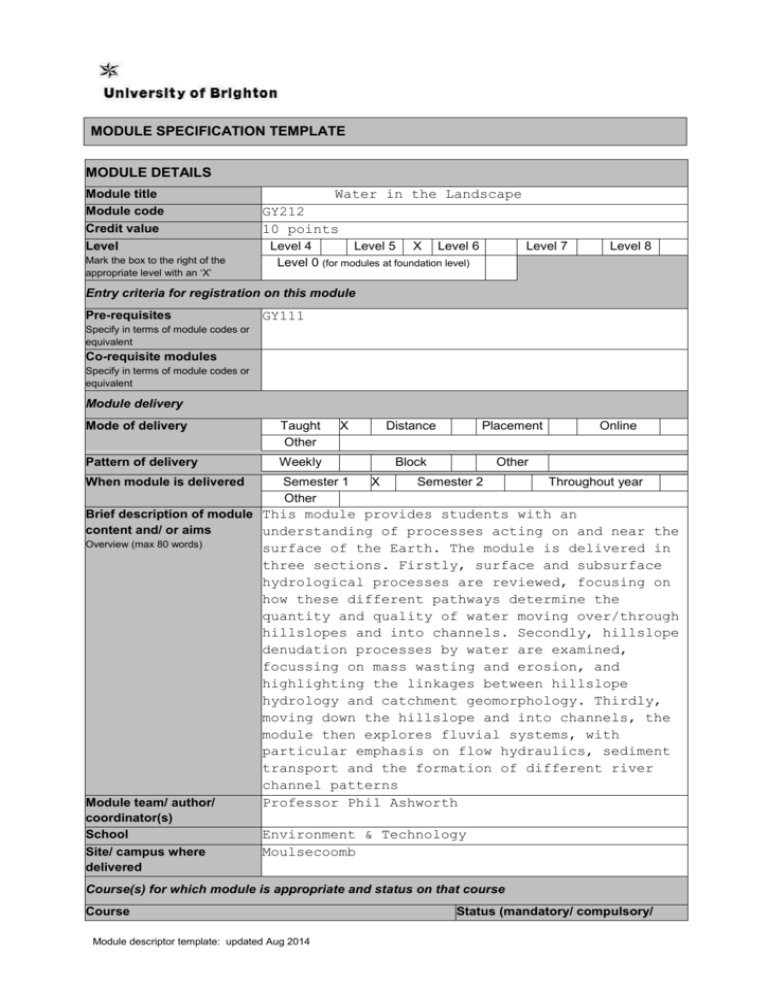
MODULE SPECIFICATION TEMPLATE MODULE DETAILS Module title Module code Credit value Level Mark the box to the right of the appropriate level with an ‘X’ Water in the Landscape GY212 10 points Level 4 Level 5 X Level 6 Level 0 (for modules at foundation level) Level 7 Level 8 Entry criteria for registration on this module Pre-requisites GY111 Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Co-requisite modules Specify in terms of module codes or equivalent Module delivery Mode of delivery Taught Other Pattern of delivery Weekly When module is delivered X Semester 1 Other X Distance Placement Block Other Semester 2 Online Throughout year Brief description of module This module provides students with an content and/ or aims understanding of processes acting on and near the Overview (max 80 words) Module team/ author/ coordinator(s) School Site/ campus where delivered surface of the Earth. The module is delivered in three sections. Firstly, surface and subsurface hydrological processes are reviewed, focusing on how these different pathways determine the quantity and quality of water moving over/through hillslopes and into channels. Secondly, hillslope denudation processes by water are examined, focussing on mass wasting and erosion, and highlighting the linkages between hillslope hydrology and catchment geomorphology. Thirdly, moving down the hillslope and into channels, the module then explores fluvial systems, with particular emphasis on flow hydraulics, sediment transport and the formation of different river channel patterns Professor Phil Ashworth Environment & Technology Moulsecoomb Course(s) for which module is appropriate and status on that course Course Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2014 Status (mandatory/ compulsory/ optional) BA (Hons) Geography, BSc (Hons) Earth & Ocean Science, BSc (Hons) Environmental Hazards, BSc (Hons) Environmental Sciences, BSc (Hons) Geography, BSc (Hons) Geography & Geology Optional MODULE AIMS, ASSESSMENT AND SUPPORT Aims To develop student understanding of the important concepts that govern earth surface evolution by water. Learning outcomes At the successful completion of the module, students will: 1. Understand the nature of hydrology, the behaviour of river catchments and the approaches to quantifying hydrological processes; 2. Understand how hillslopes evolve over time; 3. Be able to apply basic hydraulic equations and understand how rivers work; 4. Understand the linkages between hydrology, rivers and sediment movement; 5. Be able to use hydrology and fluvial geomorphology skills to answer practical, real-world problems Be able to develop a logical argument by means of appropriately referenced written work. Content This module provides students with an understanding of water-driven landscape processes acting on and near the surface of the Earth. The module is delivered in three sections. Firstly, surface and subsurface hydrological processes are reviewed, focusing on how these different pathways determine the quantity and quality of water moving over/through hillslopes and into channels. Secondly, hillslope denudation processes by water are examined, focussing on mass wasting and erosion, and highlighting the linkages between hillslope hydrology and catchment geomorphology. Thirdly, moving down the hillslope and into channels, the module then explores fluvial systems, with particular emphasis on flow hydraulics, sediment transport and the formation of different river channel patterns. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2014 Fallenmark, M. And Rockstrom J. (2004) Balancing water for humans and nature. The new approach in ecohydrology. Earthscan. Learning support Holden, J. (ed) (2009) An introduction to physical geography and the environment (2/e), Pearson. Knighton, A.D. (1998). Fluvial Forms and Processes (2/e). Arnold. Robert, A. (2003) River Processes: An Introduction to Fluvial Dynamics, Arnold. A comprehensive reading list of the latest journal articles is posted on StudentCentral at the start of the module. Teaching and learning activities Details of teaching and learning activities Normal contact time of 2 hours per week plus 4 hours directed study and assessment. Delivered as a series of lectures combined with two practicals. Students to write-up one of the practicals. Allocation of study hours (indicative) Study hours Where 10 credits = 100 learning hours SCHEDULED This is an indication of the number of hours students can expect to spend in scheduled teaching activities including lectures, seminars, tutorials, project supervision, demonstrations, practical classes and workshops, supervised time in workshops/ studios, fieldwork, and external visits. 28 GUIDED INDEPENDENT STUDY All students are expected to undertake guided independent study which includes wider reading/ practice, follow-up work, the completion of assessment tasks, and revisions. 72 PLACEMENT The placement is a specific type of learning away from the University. It includes work-based learning and study that occurs overseas. TOTAL STUDY HOURS 100 Assessment tasks Details of assessment on this module Types of assessment Standard report (50%) (LO 1-6) Standard examination (50%) (LO 1-4) task1 % weighting Indicative list of summative assessment tasks which lead to the award of credit or which are required for progression. (or indicate if component is pass/fail) WRITTEN Written exam 50 COURSEWORK Written assignment/ essay, report, dissertation, portfolio, project output, set exercise 50 1 Set exercises, which assess the application of knowledge or analytical, problem-solving or evaluative skills, are included under the type of assessment most appropriate to the particular task. Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2014 PRACTICAL Oral assessment and presentation, practical skills assessment, set exercise EXAMINATION INFORMATION Area examination board Geography & Geology Refer to University for guidance in completing the following sections External examiners Name Position and institution Date appointed Date tenure ends Dr Ian Candy (or successor) QUALITY ASSURANCE Date of first approval 2011 Only complete where this is not the first version Date of last revision Only complete where this is not the first version Date of approval for this version (KIS amended March 16) Version number 1.1 Modules replaced GY210 Specify codes of modules for which this is a replacement Available as free-standing module? Module descriptor template: updated Aug 2014 Yes No









![3: Hillslope Profile Modeling (1-D) [due: Nov. 8] Lab](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013518739_1-c195183c88225ebd79825995fa5c3633-300x300.png)
