Operations Management
advertisement
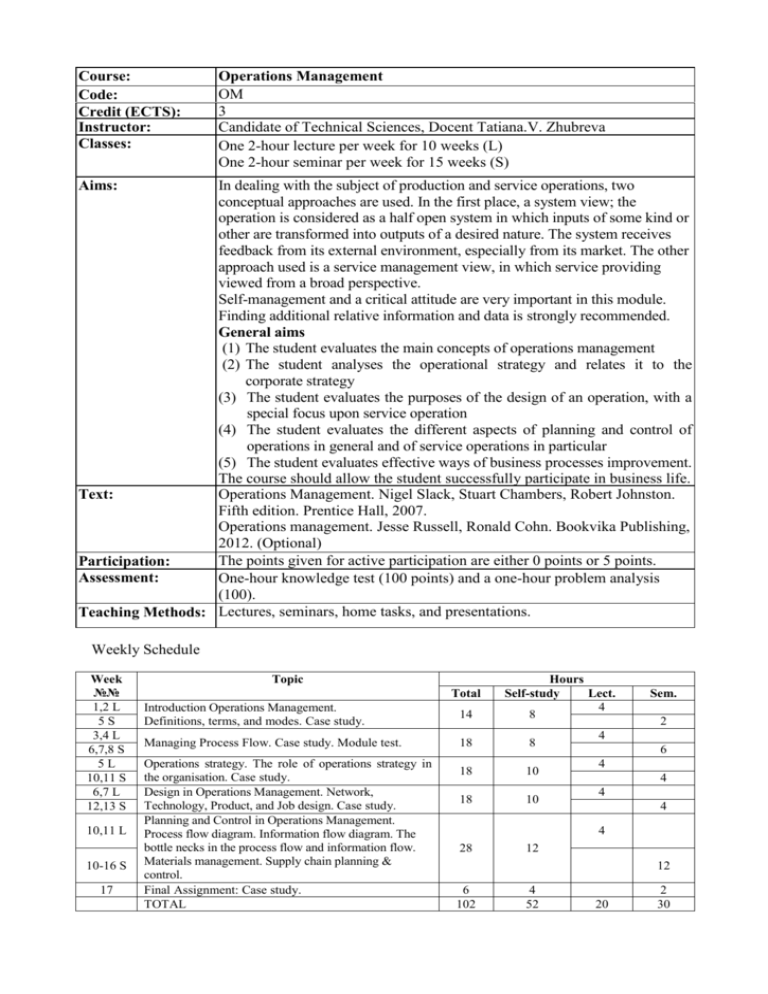
Course: Code: Credit (ECTS): Instructor: Classes: Operations Management OM 3 Candidate of Technical Sciences, Docent Tatiana.V. Zhubreva One 2-hour lecture per week for 10 weeks (L) One 2-hour seminar per week for 15 weeks (S) In dealing with the subject of production and service operations, two conceptual approaches are used. In the first place, a system view; the operation is considered as a half open system in which inputs of some kind or other are transformed into outputs of a desired nature. The system receives feedback from its external environment, especially from its market. The other approach used is a service management view, in which service providing viewed from a broad perspective. Self-management and a critical attitude are very important in this module. Finding additional relative information and data is strongly recommended. General aims (1) The student evaluates the main concepts of operations management (2) The student analyses the operational strategy and relates it to the corporate strategy (3) The student evaluates the purposes of the design of an operation, with a special focus upon service operation (4) The student evaluates the different aspects of planning and control of operations in general and of service operations in particular (5) The student evaluates effective ways of business processes improvement. The course should allow the student successfully participate in business life. Operations Management. Nigel Slack, Stuart Chambers, Robert Johnston. Text: Fifth edition. Prentice Hall, 2007. Operations management. Jesse Russell, Ronald Cohn. Bookvika Publishing, 2012. (Optional) The points given for active participation are either 0 points or 5 points. Participation: Assessment: One-hour knowledge test (100 points) and a one-hour problem analysis (100). Teaching Methods: Lectures, seminars, home tasks, and presentations. Aims: Weekly Schedule Week №№ 1,2 L 5S 3,4 L 6,7,8 S 5L 10,11 S 6,7 L 12,13 S 10,11 L 10-16 S 17 Topic Total Introduction Operations Management. Definitions, terms, and modes. Case study. Managing Process Flow. Case study. Module test. Operations strategy. The role of operations strategy in the organisation. Case study. Design in Operations Management. Network, Technology, Product, and Job design. Case study. Planning and Control in Operations Management. Process flow diagram. Information flow diagram. The bottle necks in the process flow and information flow. Materials management. Supply chain planning & control. Final Assignment: Case study. TOTAL 14 18 18 18 Hours Self-study Lect. 4 8 8 10 10 Sem. 2 4 6 4 4 4 4 4 28 12 12 6 102 4 52 20 2 30