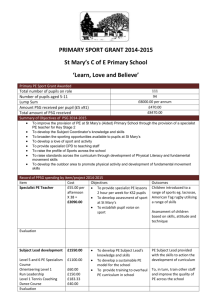
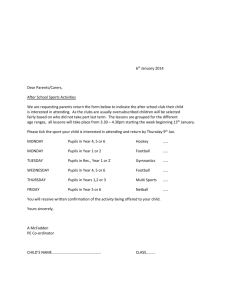
II international Congress of Physical Education Teachers
advertisement

II international Congress of Physical Education Teachers Welcoming Address of the Minister of Sports, Tourism and Youth Policy of the Russian Federation to participants and organizers of the II International Congress of Physical Education Teachers On behalf of the Ministry of Sports, Tourism and Youth Policy of the Russian Federation I would like to welcome organizers, participants and guests of the II International Congress of Physical Education Teachers. At present physical culture and sports are facing global challenges. Meeting them requires new strategic approaches. One of the priority tasks is modernization of physical education in educational institutions. In this regard exchange of best practices in physical education of schoolchildren, forming pro-active attitude, healthy lifestyle promotion are of paramount importance and up-to-date. I believe that knowledge and expertise you possess in widely-acknowledged projects are to facilitate addressing crucial social tasks aimed at advancement of physical culture and sports, forming healthy and harmoniously developed generation of younger Russians. I wish you all fruitful work and success in implementation of your plans and activities. Vitaly Mutko, Minister of Sports, Tourism and Youth Policy of the Russian Federation Welcoming Address of the Head of the Republic of Karelia Dear participants of the International Congress! Petrozavodsk, the capital of Karelia hosts the International Congress of Physical Education Teachers on June 30 – July 4, 2010. This is already the second forum of PE teachers of primary, secondary and higher education institutions, experts in physical and health education from across Karelia, Russia, near and far abroad. The capital of the Republic of Karelia is not a random choice for carrying out this significant international event. Raising healthy and physically strong generation has always been one of the priority tasks for the Karelian Government. The year of 90th anniversary of the Republic is also marked with opening of a new swimming pool in the city of Kostomuksha, a sports center in the city of Lahdenpohya, a sports gym of the Sheltozero School, stadiums in the cities of Medvezhyegorsk and Olonets. The Republic of Karelia is justly considered to be an attractive place for holding international and all-Russia sport events. 58 kinds of sports are practiced In Karelia, 45 republican sports federations are functioning. The Republic of Karelia holds the 5th place among the regions of the North-Western District of Russia on the total number of people engaged in organized forms of regular physical activities. We are proud of our compatriots, winners of World Championships and Olympics who honored Russia at various international competitions. Many athletes started their mount to the world top positions from school physical education classes. So it is a PE teacher who creates the basis of a child’s healthy lifestyle, promotes pupil’s love for exercising. Intergenerational continuity in formation of healthy lifestyle skills is a determining factor of human potential development. That is why physical and health education teachers, trainers of children sport schools bear responsibility for preservation and promotion of traditions of health saving and conscientious attitude towards one’s health among children and youth. The forum of physical and health education teachers is symbolically held within the Year of a Teacher. The government is interested in bringing up healthy young generations, and PE teachers are at the forefront of fulfilling this goal. I believe that the Second International Congress of Physical Education Teachers is to be a vivid event facilitating promotion of regular exercising, sport activities and healthy lifestyle among the population. Head of the Republic of Karelia Sergey Katanandov Congress as a form of uniting physical education teachers A.Voronov Dean, Faculty of Physical Education, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Both in Russia and many European countries approaches to promotion of healthy lifestyle among the younger generation by means of physical education are revised at present. The President of Russia has set up an urgent objective: “by 2020 every other citizen of Russia has to engaged in regular systematic physical exercising and sport activities. This figure should be not less that 80% among students”. The role of a PE teacher is of utmost importance in this regard. So a congress of PE teachers is a highly relevant event aimed at addressing the aforementioned tasks. This movement started in 2006 with the cooperation of the Faculty of Physical Culture of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy and the Association of Physical Educators in Finland on implementation of the project “Promotion of healthy lifestyle by means of PE classes in schools of the Republic of Karelia”. First pilot schools were the Lyceum #1, the School #46 and the School #48 of the city of Petrozavodsk. In 20062009 PE teachers of Karelia participated in several international courses, seminars, conferences on physical culture held in Estonia, Finland, Italy. These were organized by the Association of Physical and Health Educators in Finland under the auspices of the European Physical Education Association (EUPEA). The latter was established in 1991 for development of physical education in the whole Europe. EUPEA considers physical education to be one of the central objectives of the school educational system, as motor development and promotion of lifelong physical exercising is crucial for modern society where opportunities of these activities are shrinking. The objectives set by the Association are the following: uniting efforts of academics and teachers for development of physical culture and healthy lifestyle promotion, advancing art of teaching, sharing experience, working out new approaches to organizing physical training, and in prospect establishing unified standard of physical education in all European countries. Need in physical education quality improvement is also highlighted. The emphasis here is balanced school curricula that anticipates elevated teachers’ attention to extra motor activity of pupils including one organized within extra-curricular activities. Curricula stipulate at least 3 hours a week for physical and health education classes during the whole study period. Member of the Association are also concerned with the quality of professional training of a teacher. So for example, a primary school teacher should accomplish special training in theory and methods of physical and health education in amount of at least 1000 academic hours (60 ECTS), a PE teacher in secondary school – at least 4000 academic hours (240 ECTS). Members of the Association are convinced that unity of efforts of school teachers, parents, local communities in promotion of physical culture and healthy lifestyle are demanded. Networking of PE teachers from different countries has to be established and developed. Even though education and educational policy are filed of competence of every single country, issues of physical education are common for the whole Europe. EUPEA unites associations of PE teachers of 29 European countries. Results of its activities have been presented on international congresses, seminars and courses in Austria, Belgium, Sweden, Hungary, Italy, Estonia, Finland, etc. Unfortunately Russia is not in the list of these 29 states. Anyway it does not infer that we are not concerned with well-being of our children and youth. At our workplaces, in a sports gym or on a sports ground, everyone of us, PE teachers, tackles definite tasks, one of them is to promote love to physical exercises for every pupil, to work out such culture of behavior that everyday physical activities become an inherent part of his/he life. Anyway we have to unite in order to make results of our work more visible. Adopting experience of European associations of PE teachers and having enlisted their support we established the Karelian Regional Non-Governmental Organization “Association of Physical Education Teachers of the Republic of Karelia” in March 2008. Later the Union of Karelia, Finland and Estonia in the filed was established. The first major event organized jointly by the Association and the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy was the First International Congress of Physical and Health Education Teachers held on June 24-30, 2008 under the support of the Government of the Republic of Karelia and the Association of Physical and Health Educators in Finland. 416 physical education specialists participated the Congress representing from 15 regions of Russia, national associations of Italy, Finland, Estonia, Canada, the USA, Lithuania, Sweden, being driven by the aspiration to share experience and new ideas on physical and health education development. The Congress program involved: - Scientific-research activities (plenary sessions, presentations of new approaches to physical and health education); - Practical activities (master classes for PE teachers); - Dissemination of results of the project “Promotion of healthy lifestyle in schools of the Republic of Karelia”. 100 master classes, lectures and seminars were carried out within the week. The participants received immense amount of knowledge in the field, shared experience, learnt various methods, reenergized, got an inspiration to create at PE classes. In follow-up of the Congress a videofilm was made; collected works in two languages were published; journals “Physical Culture at School”, “Sports at School”, “Health at School” devoted their issue to the event. A foundation meeting of a new Inter-regional Association of Physical Education Teachers was held within the framework of the Congress. Representatives of 15 regions of Russia unanimously established this Association and made a decision to attract other regions to the organization. So one of the goals of the Second International Congress is promotion of establishment of all-Russia union of physical education teachers. The Organizing Committee has prepared a concept and graft regulations of the union. The union activities are to be aimed at: - Active promotion of physical exercising, Modernization of school physical education system, Activation of exchange of pedagogical experience, ideas, methods, modern technologies, information amid physical education teachers, - Improvement of physical education teaching in educational institutions, - Contribution to creation of contemporary sports facilities, working our recommendations for equipping, - Elaboration of efficient system of extra-curricular sport work, organization and holding of fitness and sport events, - Contribution to advancement of qualification, training and re-training of physical education teachers, - Promotion of a status of a physical education teacher in Russian educational system, - Elaboration of criteria for assessing work of a physical education teacher and an incentive scheme, - Development of cooperation among regional, national and international organizations of physical culture. For this end a systematic work has to organized involving holding seminars, master classes, conferences, meetings, congresses, publishing, collaboration with higher and secondary educational institutions, the Ministry of Education, the Ministry for Sports, Tourism and Youth Policy, NGOs, etc. The Union of physical education teachers of Russia should become a full-fledged member of the European Physical Education Association. It may not stew in its own juice, but adopt positive experience of European countries and promote national methods. This is particularly important in the period of integration of educational spheres. Lapta, an old Russian game E. Abramova, School №15, city of Naberezhnye Chelny The younger generation's state of health is an important indicator of the country and society's wellbeing, but spirit and traditions are also very important. No doubt, spiritual and moral health is closely connected with physical one. Insufficient motor activity and computer mania lead to decrease in both intellectual and physical working capacity of the younger generation. So, it is very important to get pupils interested in physical training. A game can be one of motivation ways. I searched for the game which could be interesting for all children, despite of the age and individual peculiarities, and could better develop pupils' motor and learning abilities. I chose a Russian national game, "Lapta". Lapta has become the most popular and favourite game at our school. To play lapta you need only a lawn or any sports field, a bat and a ball. The number of players and size of a field are not limited. Lapta is included in the programme on physical training for comprehensive schools by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Bashkortostan. Let's teach children to play lapta. Russian lapta: history and development stages Lapta is an ancient Russian game. Lapta was mentioned already in ancient Russian chronicles. It was named after a bat used while playing, "lapta". So, lapta has been played for more than a thousand years. It is necessary to mention that lapta is not only a Russian game. The Norwegian archeologists found lapta bats used by Vikings. Games similar to lapta exist in many countries: cricket in England, baseball and softball in the USA, pelota in Cuba, etc. At the time of Peter I lapta was not only a favourite game, but was also included in the program of physical training of soldiers of Preobrazhenskiy, Semenovsky and Shevardinsky regiments. Alexander Suvorov also used lapta to train soldiers. In 1926 the USSR High council on physical training tried to formulate official rules to play lapta, but lapta was not recognized as a kind of sport though it was popular with people. And only in 1957, thanks to enthusiasts' efforts, the first official lapta competition took place. The first championship of the Russian Federation in 1958 helped to develop the game more. However in the 1960-70s lapta development stopped. And only by the end of the 1980s lapta was revived by the USSR State Committee on Sport's resolution “On baseball, softball and Russian lapta development” carried in 1987. In 1994 lapta was included in the Unified Russian sports classification. In 1995 the new rules of competitions were developed. Since 1997 the inter-regional public organisation, Federation of Russian lapta, has operated. Now lapta is popular in more than thirty regions of Russia. Lapta is especially popular in Amur, Irkutsk, Tyumen, Tomsk, Saratov, Bryansk, Omsk, Volgograd, Tula, Novgorod, Moscow, Belgorod territorial units, as well as and in the cities of Krasnoyarsk and Krasnodar and in the Republic of Bashkortostan. Lapta is a dynamic kind of sports, and it develops to adapt to various situations. So, minilapta has occurred. It is possible to play it in any conditions. There is a beach lapta as well. At our school we play volleyball lapta. Lapta rules are constantly becoming simpler, and this makes it more available. I use the following rules to play lapta: Game rules Field: flat, in the open air, 30-60 m long, 20-40 m wide. Equipment: a tennis ball, a bat (length: 60-110 sm, width: 8-13 sm, a rounded handle, weight: not more than 1500 gr) Number of players: 10-30 people Game time: to the certain score. The goal of the game is to hit the ball, served by a player of the opposite team, with the bat and send the ball as far as possible, then run across the field to the kon line, and if possible to run back to the gorod line. The running player should try to avoid being hit with the ball, which is thrown by the opposing team members. For successful runs, the team earns points. A team wins by either getting more points during the scheduled time or by having all its players complete runs. Civil society opts for healthy lifestyle I.Achepovsky, honored teacher of the Russian Federation, School #48, A. Pavlov, post-graduate student, the Department of Pedagogics, KSPA, city of Petrozavodsk If you want to learn something you should do two things: meet your teacher and find a student in yourself” (ancient proverb). The key point in upbringing a new generation should be revival of traditions of Russian educational system. Children should have an opportunity to reveal their abilities, prepare already at school for living in the hitech competitive world. Current statistics of schoolchildren health is terrifying. During school study period 70% of children functional disorders turn into chronic pathology. By the time of school graduation visual organs and locomotor system diseases incidence increases in 4-5 times, digestive organs morbidity – in 3 times, number of neuropsychic disorders – in 2 times. By leaving school 80% of girls have chronic diseases, what later may affect their ability to give birth to a health baby. Academic day of a senior schoolchild lasts for 1012 hours. School study period predetermines lifelong health status of a person. Children spend a greater part of a day at school, hence pedagogues should take care of their health. Individual approach minimizing health risks within educational process has to be utilized. Participation of civil society organizations in implementation of priority national projects is one of the key ways of addressing the healthy lifestyle issue. Various mechanisms of collaboration of non-governmental organizations engaged in promotion of healthy lifestyle are being considered, as well as role of mass media. Healthy lifestyle formation is a field of mutual interests and mutual responsibility of a state, society and personality. So the central issue is the role of public organizations in elaboration and implementation of the state strategy on healthy lifestyle promotion. It is obvious that efficient collaboration of the state and the society is an essential condition for harmonious development of the both of them. What is more the population is awaiting more active and efficient work from the both of them, considering their equal partnership demanded. Various public mechanisms of development and implementation of nation health promotion programs are being discussed, involving means of creating and functioning of a uniform public information system of Russia which is aimed at healthy lifestyle image formation, promotion of healthy lifestyle and cutting edge knowledge and expertise in this field. Healthy lifestyle formation and nation health improvement should become a national purpose uniting all social classes. Governmental social strategy is needed to be elaborated and implemented. Social-economic measures on addressing demographic problems, improvement of nation physical and moral health and the quality of life have become a priority of the governmental policy in Russia. Running national projects have significantly increased state investments into human capital, meeting the population needs in health care and education. Participation of public organizations in these activities is an important characteristic of these projects. The national projects are only a first step towards continuing and systemic modernization of the social sphere. Still comprehensive solutions are needed for combating demographic crisis, increasing birth rate and lowering death rate, improving people’s health and quality of life. Only 15-30% of the newly born are healthy, what is a matter of deep concern. General health indicators of Russian children are one of the worst in Europe. Health status of grown-ups is also unsatisfactory. The alarming fact is that about half of all deaths occurs within working age. Mortality from cardio-vascular and oncological diseases, digestive organs pathology is rapidly increasing. The number of people subjected to smoking, alcoholism and drug abuse does not decrease. Physical activity and physical training of the population is still at a low level. People’s commitment to preservation of health as a basis of material welfare has not become a sustainable and comprehensive system of conduct yet. The “Nation Health” program developing ideas of the national projects should be adopted for the aims of significant improvement of physical and moral health of a person. Every level of governmental administration should have specific goals: death rate decrease, birth rate increase, lowering morbidity, prolonging life expectancy, achieving certain criteria of quality of life, environmental advancement, eliminating negative aspects of a lifestyle. Am important requirement for achieving these goals is meeting interests of all the parties: society, government, family, employers, different medical, pedagogical, sport, creativity groups. Elaboration of state educational standards for all levels of education has to be completed in the shortest time possible, as achieving these standards is a result of the educational process. Contemporary school should provide more comprehensive training of pupils on all main subjects, ensure acquisition of key social and professional competences and skills. Curricular may differ, including individual curricular adjusted to peculiarities and abilities of a child. The system of school meals is also under question. Only a small part of primary school children get wholesome nutrition at school. Nutrition culture strengthening health and assisting prophylaxis of diseases is not promoted well enough. There multiple reasons of this situation, but the solution seeks for a comprehensive approach attracting legislative and executive authorities, medics and teachers, food technologists and the general public. The work of the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Health Care and Social Development on elaboration of sanitary regulations and norms regulating educational process at school should be fairly coordinated. The issue of production of ecologically safe goods should be addressed through imposing relevant standards and state supervision system. The state should provide all the necessary conditions for massive choice for the healthy lifestyle. Social status of physical training and sport should be elevated, state and private investments attracted for establishing tourism and recreational sport infrastructure, all the public initiatives in combating alcoholism, smoking, substance abuse be supported. Physical health of a person can not be considered neglecting moral and mental health. All the mechanisms of mental, moral, patriotic, cultural and behavioral education for citizenship being at the disposal of the society should be utilized. Cultural heritage accessibility and mass media public utility are the key features for achieving this purpose. As well as collaboration in elaboration of political decisions in health care, education, demography, environmental protection, information policy is highly needed for the aims of principal nation health improvement. EFFECTIVENESS OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION IN RURAL SCHOOLS G. Akhmadyrshin, Svetlyanskaya rural school, Republic of Udmurtia Modern social life is undergoing serious changes. Health issues have always played an important role in people’s lives. Individual health is considered to be 70 % dependent on a person lifestyle. Today school has set priorities to concentrating teachers’ efforts to form healthy habits among schoolchildren. School years are favorable time for developing the necessity of physical activity. School education forms the cognitive, mental, health improving basis of further life. School education can ruin children’s health so that they will never need mathematics, Russian, physics later. But school life can also improve pupils’ health and form a positive attitude towards physical activities and sports through the effective system of physical education. According to some authors (V. Baltsevitch), fulfillment of health improving tasks is not effective at school. Mental workload, computers, a great load of homework take too much of children’s time and it results in diseases caused by physical inactivity. Starting the experiment at our school we wanted to make sure that our work would bring positive results and improve health. The work improving physical health is based on curricular and extra-curricular activities. Interconnection of these activities makes it possible to achieve good results in physical education. The lesson is the main form of organizing physical education at school. At PE lessons learn basic knowledge and they develop skills in different kinds of sports, they get interested in physical education and sports. Extra-curricular activities help to fulfill the following tasks: drawing children into sport sections and clubs, participating in sport competitions, improving sport skills, organizing leisure time. Cooperation of these activities makes it possible to achieve good results in children’s physical education and improving their health. Schools in rural areas are very specific in regard to physical education. Such features as vast territory of dwelling, when settlements are situated far apart, make teachers find out new forms of work in schools in the countryside. In my article I would like to highlight the links between curricular and extra-curricular forms of work aimed at improving physical health in rural schools. It is unlikely to find integrity in physical education at school without cooperation of these two systems. All school work is aimed at implementation of the integrated approach to physical education. Having worked at school I have always asked myself what concept of physical education should be paid more attention to: improving health, achieving high results in sports or teaching technically sound movements. Every school chooses the concept according to its resources. What results can be achieved when all the trends are being developed together? Lesson as the main form of school work. The most important task of every PE lesson is to get children interested in doing sport. At our lessons children were taught all activities given in the curriculum in track-and-field, gymnastics, sports games, skiing. Extra-curricular activities were also included in PE lessons: shot put, discus and javelin throwing. High-jumping included “Fosbury-flop” style. School championships in all these kinds of sports were held. Schoolchildren were taught to play volleyball, basketball, soccer, tennis and chess at sports games lessons. The school team was a prize-winner in these kinds of sports at the district sport competitions. Special lessons in chess were included in the school curriculum. Much attention was paid to educational process in primary school. Future results and interest in doing sports are considered to be formed at the age of 6 – 9. Children of this age group learned basic elements of many kinds of sports. Special attention was paid to technically correct doing of different elements. If pupils do not do exercises in the right way, they will be very difficult to correct later. Experiment as a way to creative work. Teacher’s job is a creative one; they can not stop working; that is why teachers have to experiment, to find out new forms of work. Experiment is carried out through the following stages: the stage of ideas, the stage of practical performance, the stage of experience evaluation. Some experimental programs give a start to new programs, some of them die out, but some others continue working. Any experiment is also difficult from the psychological point of view. New ideas are always accepted with distrust and there are always opponents to them. Great efforts should be taken to persuade parents, schoolchildren and teachers to try new forms, methods and ways. During my work at this school the following experiments were held: - making oneself fit; - developing special running abilities; - evaluating primary school children’s activity at the lessons without marks; - evaluating secondary school children without marks. The experiment “Making oneself fit”. The aim of the experiment is to improve every child’s physical health. The most important task is to reduce the number of children who very often catch cold. All the PE lessons were held in the open air at the stadium. The lessons were held indoors only in nasty weather. Only 8 lessons in gymnastics were organized in the gym, all the others were held outdoors because sports facilities at the stadium make it possible to organize gymnastics exercises according to all standards. Schoolchildren wore shorts and T-shirts until it became cold outside. Special procedures that help to make oneself fit were used at the lessons. All children did morning exercises in the open air near the school. “The Olympic hour” after the third lesson was introduced into the curriculum. At this time all children came to the stadium and did some physical exercises: they played soccer and other active games, skied, ran. The results of this experiment are convincing. While many schools in the district were closed on account of flu epidemic, children in Svetlyanskaya school missed less lesson for that reason than before. The experiment “Developing special running abilities”. The aim is to improve the general physiological endurance. The general endurance is also a priority in other kinds of sport. We organized many exercises in cross-country racing. When children practiced skiing distances were made longer. In the end of the experiment school-leavers could run a 10-km cross-country race and 20-km ski cross-country race with less effort. The experiment “Evaluating secondary school children without marks”. The aim is to evaluate children’s results in physical education from all points of view. Schoolchildren were not given marks at PE lessons; they were given points for completing standards, for achieving a certain sports category, for attending sports sections (clubs), for participating in school, district and republican competitions, for learning theoretical material on the subject. Children were encouraged to use their creative abilities. As a result, children became more interested in PE lessons; they stopped breaking discipline at the lessons and quit missing PE lessons. Pupils also achieved better results in sport, and a great number of children started training in sports sections. The experiment “Evaluating primary school children without marks”. The aim is to form a thoughtful attitude towards the learning process (knowledge for the sake of knowledge, not for the sake of marks) in primary and, as a result, in secondary school. Children are not given marks at the lessons, in the end of the school term and year. Extra-curricular activities. Extra-curricular activities should be taken very seriously. One week a month was devoted to sports and health-improving work. The program of sports events was developed in the beginning of the school year and it was given to classroom teachers. Competitions were organized so that every pupil could take part (and took part) in school sports contests 6 times during the sports week of the month. That is why every child at our school became a volleyball-player, basketball-player, chessplayer, soccer-player, skier, track-and-field athlete. As a result, every school-leaver learned about 12 – 15 kinds of sport and could participate in sports events in these kinds of sport after finishing school. The aim was to give every pupil in Svetlaynskaya school a chance to take part in official district and republican competitions. The aim was successfully achieved. 12 – 15 competitions were held at school during the year. Schoolchildren also participated in contests organized by the local administration. “Friendly matches” were held, too. On the whole, pupils of our school took part in 35 – 40 different sports events during the year. The work of sports sections was organized so that every pupil in the forms 5 through 11 could attend one of them two times a week. The results of sport meetings were announced at the Last Bell Party with parents having been invited. The best classes, parents, pupils and teachers were awarded. Teaching physical education during the lessons. Morning exercises were done by pupils before lessons. They were organized by PE leaders. In the middle of every lesson there was an interval for physical exercises. Pupils of secondary forms also organized physical exercises and games during the breaks. There was a 40-minute “sport hour” every day after the third lesson. The classrooms were aired and cleaned at this time. Sports and health-improving work among the teaching staff. The teachers of our school took an active part in school sports festivals. The teachers’ team participated regularly in local, district and republican competitions in different kinds of sport. Teachers also practiced sports in sections two days a week in the evenings. Achievements. The schoolchildren made much progress in physical education. Most of them reached high standards in PE. Nearly all children stopped smoking (there are no smoking children at school). According to the medical reports, children’s posture is constantly becoming better. Pupils did not miss PE lessons. The school was not closed on account of the flu epidemic as it happened in many other schools of the district. Pupils missed fewer lessons in case of an illness or a disease. Schoolchildren were not seriously injured during the school year. Even pupils with some problems of their health took an active part in physical activities and competitions. Children’s physical activity increased during a month: PE lessons – 8 hours; sports activities – 8 hours; “sports hour” – 20 hours; morning exercises – 15 minutes * 25 days = 6 hours; interval for physical exercises at the lessons – 3 minutes * 130 lessons = 6 hours; participation in school competitions – 1,5 hours * 5 times = 7,5 hours; participation in local, district and republican competitions – 1 hour * 10 times = 10 hours. Totally it is 45 hours of organized physical activities during every month. Sports achievements. Sports results also became better. Schoolchildren won Udmurtian republican personal and team championships in track-and-field. Pupils of our school are in the district basketball, volleyball, table tennis and chess teams. The school team won prizes for several times in team championships in track-and-field, cross-country racing among secondary schools of Udmurtia. Summary. Well-organized sports and health-improving activities help to fulfill different tasks of children’s physical education at school: - to help children make better progress in studies; - to reduce the number of smoking pupils; - to solve the problem of colds; - to organize children’s leisure; to achieve better results in sport. References 1. V. Balcevitch. Physical education for everyone. – M., PE & S, 1988 2. L. Lubysheva. The concept of formation of human’s physical culture. – M., GTIPK, 1998 3. A. Matveev. Essays on theory and methods of teaching schoolchildren in the field of physical education. – M., PON, 1997 Sports holiday dedicated to the Day of Health. «Fun races» for primary school pupils. S. Apanaeva, School №38, city of Naberezhnye Chelny To the strains of the sports march, the commands appear on the sports stage. The captains hand in the emblems of their commands to the jury. The music ceases, the physical education teacher says: «Parade, dress! Attention! Front and center!» The teacher marches to the headmaster and reports: «Dear ... (the headmaster's name)! The participants are ready for the sports holiday devoted to the Day of health. The PE teacher, Ivanov!» The headmaster greets everyone: «Good morning, children!» The pupils answer: «Good ...!» The headmaster congratulates them on the holiday, wishes them sports successes, health and a fair sports victory. The PE teacher: «To the National flag lifting! … Attention!» The flag is lifted by the captains of the commands. The children go to the flagstaff and rank in one line. The PE teacher: «Lift the flag!» The captains lift the flag. The Hymn of the Russian Federation sounds. (Flag lifting should be rehearsed under music the day before) Upon termination of the hymn, there is applause and shouts «Hurray!» The PE teacher: «Dear children, our pupils have come to congratulate you on the holiday». Sports schools representatives' performance (basketball, karate, acrobatics). The PE teacher reads a poem. «Fun races» 1 - "Relay race": the first pupil in a command runs holding a baton, overtakes a stand, comes back to the end of the command and transfers the baton through his/her legs. 2 - «Chinese sticks»: a pupil holds a ball between two gymnastic sticks, runs to the stand and transfers the ball to the next pupil. 3 - "Hockey": a pupil dribbles the ball with a stick round stands. 4 - "Tunnel": a pupil goes through a bag without a bottom, overtakes a stand and transfers the baton. The PE teacher: "Dear sports fans, a musical present for you! You are welcomed by a dancing cheer team. Your applause to the girls!" The girls dance. Calculation of preliminary results. Announcement of the results. Then «Fun races» proceed. 5 - «Potato setting»: the first participant sets potatoes (pouring out tennis balls from a bag in a hoop), the second one collects them. 6 - "Biathlon": the participant (biathlonist) puts on a number, a cap, mittens and skis, runs to a basket with balls, throws one ball and comes back. He/she transfers everything to the following biathlonist. 7 - "Erudite": each participant brings one letter to the command. Then the pupils make a word of these letters. So, «Fun races» have come to the end. The referees count the points and define the winner. The PE teacher: «Line up for rewarding of the winners!» The commands line up. The visitors are around. The photographers take pictures to prepare the holiday exhibition. The PE teacher reads a poem. The PE teacher: «Dress! Attention!» Rewarding ceremony begins. Diplomas and prizes are handed in. The flag is lowered by the winner command. The Hymn of Russia sounds. The music stops, the flag is lowered, the PE teacher says: «At ease! Dismiss!» The holiday is finished. Seasonal motor activity dynamic of 5-7 year old children with visual disorders in polar area. Elena Arsenyeva, teacher, “Northern College of Physical Culture and Sport”, degree-seeker of the Department of Adapted Physical Culture, Saint-Petersburg National University named after P. Lesgaft. Key words: children with visual disorders, motor activity, movements. Seasonal variations of physiological functions in the High North have been studied pretty thoroughly, anyway almost no research was devoted to seasonal dynamic of children physical fitness and motor activity. The relevant objective of physical education is awareness of motor activity normative criteria, ensuring sufficient all-seasonal physical fitness and labor capacity of children. Research of age motor peculiarities shows the paramount importance of a child motor activity for development and formation of the basis for further behavioral response development. Motor activity in a preschool age is the central factor for the metabolic activation. What is more, the body responds to every exercise load not merely with the compensation of the consumed energy, but with overcompensation, so excessive restoration occurs. The theoretical researches on the adapted physical culture indicate the important role of physical training in prophylactic, multimodality therapy and rehabilitation of the sight disabled. Many experts specify that motor activity, muscle work is a biological developmental factor and an obligatory condition for a disabled child development. Reluctant decrease in motor activity, muscular underdevelopment, associated illnesses, continuing musculoskeletal disorders are typical for children with vision disorders. in the High North the decrease in children motor activity is also predetermined by the climate conditions. Frost-free season accounts averagely for 83 days, the snow cover stays for averagely 218 days annually. Average annual temperature is from -4° to -5° C. The solar radiation is known to have a great health-improving impact. It raises body resistance to catarrhal diseases. In Polar regions long winter and polar night lasting for 59 days (the “biological darkness” period) lead to increase in children morbidity rate and rapid fall in their motor activity. The analysis has shown that the daily movements duration of 5-6 year olds living in the High North amounts to 4-5.5 hours, what is 80-100% of the normal rate. The motor duration of children with vision disabilities accounts for 2.5-3 hours, what is 50-60% of the normal rate. The daily movements duration of 6-7 year olds living in the High North amounts to 4-5 hours, what is 80100% of the normal rate. The motor duration of children with vision disabilities accounts for 2.5-3 hours, what is 55-60% of the normal rate. The indicator of the motor activity is the amount of movements (the number of steps) per a certain time (per day). The daily motor activity analysis has shown that the amount of movements of 5-6 year olds living in the High North accounts for 10,000-13,000 steps, what is 86-90% of the normal rate. The motor duration of children with vision disabilities accounts for 7,000-9,000 steps – 60-63% of the normal rate. The amount of movements of 6-7 year olds living in the High North accounts for 13,000-16,000 steps, what is 80-86% of the normal rate. The motor duration of children with vision disabilities accounts for 8,00011,000 steps – 50-53% of the normal rate. The analysis has indicated that life in the High North leads to motor activity decrease. The amount of movements of 5-7 year olds without vision disorders has accounted for 80-90% of the normal rate, and of ones with vision disorders – 50-60%. Negative aftereffects of the High North climate need to be overcome. The most efficient method, by our opinion, is the motor activity increase of children with vision disorders living in the High North. Hence there is a necessity to elaborate and introduce a comprehensive health-improving program for fullfledged motor activity provision for visually impaired living in the High North. General endurance at PE classes in 9-11 grades (Guidelines based on experience of Karelian teachers) Leonid Baitman, Honored worker of secondary education of the Russian Federation, Honored worker of physical culture of the Republic of Karelia, The high level of a person general endurance is extremely demanded today due to constantly accelerating pace of life. Information flow, constantly increasing intellectual load, rapidly changing pace of life and work, all these factors impose stricter requirements to a person’s physical condition. Notion of general endurance in life has been changing significantly lately. It is not simply aerobic performance, not only ability to exert monotonous load for a long time. General endurance of a person in conducting his/her practical activities is understood as ability and possibility to carry out big load, particularly of different kind and character, for example in an industry: porterage, movement with cargo, multiple repetition of strong short-term actions with short intervals, and what is the most important thing, high working capacity. So the notion of general endurance gets broader, more general. So that’s why development of this general comprehensive quality, what is a result of a healthy lifestyle, continuing training and load, is demanded. Amount of exercises on general endurance in 9-11 grades should be systematically increased applying various methods and techniques. These exercises can be carried out in any season. Taking into consideration that the 9-11 grades syllabi are based on development of physical qualities, the complex class form should be used. Circuit training is particularly suitable for achieving these goals, as it requires use of different equipment, regulation of speed and load. PE classes in the 9th grade in the beginning of a study year start with running training. Classes are conducted outdoors, at a stadium or a sports ground. Alternation of walking and running in different modes, ranging from slow to fast, at 50-200m distances. 50m smart walk, 100m slow run for 3-4 minutes, 6-8 stretching exercises: bending body, body turning, long steps. 50m smart walk, 200m slow run for 8 minutes, relaxation exercises, swings. 6-8 minute power exercises, floor dips, knee bending, stream jumping on 30-50m distances. Walk and run conjoining during September-October should be prolonged till 15-20 minute duration with making 1km distance for 5.5-6.5 minutes. In November-March all exercises of indoor complex and circuit training classes, including vigorous exercises, acrobatics, apparatus gymnastics with low bar, parallel bar, wall bars, should be repeated 4-6 times by series of 10-15 times with 2-3 minutes break. In ski training is conducted in December, January, February, then the process should be organized by the principle of interchange of 200-800m distances run with different speed and skiing modes. A pupil should cover from 6 to 10km distance within a single class. Anyway the speed of the motion should vary throughout the pace. In a fitness gym all exercises on machines should be done with 40-60% load in 4-6 series of 8-12 moves with 1.5-2 minutes break. Such exercises should interchange with relaxation exercises, body bending and arching post-legged. Continuing increase of load by duration and amount of repetition requires home task to be carried out as well. Home tasks accustom a pupil to systematic keeping fit and physical qualities development. As home tasks the following can be recommended: walking on foot only, not using public transport. But the speed walk should vary – from slow to smart walk; everyday abdominal and arm building exercises, exercises for foot, knee bending. General endurance development work should be carried out at sport games classes as well, i.e. volleyball, basketball, football. Play exercises should interchange with running. The tempo of execution of ordinary elements should be high and done in series of 15-20 repetitions. The content of a PE class remains the same in 10-11 grades, but increasing the amount and tempo of execution. All classes should contain exercises for basic groups of muscles, legs, abdominals, pectoral muscles, muscles of back and arms; they should be repeated 12-15 times, 5-6 series. Experience has demonstrated that this method of conducting classes (even if there are only 2 classes a week) contributes to significant improvement of fitness, general endurance, work capacity of schoolchildren. Now upon the introduction of the 3rd weekly PE class the load will comply with methodic and physiologic demands and principles. Thus physical education is to become the basis for creation proper skills of healthy lifestyle. Peculiarities of students psychological-pedagogical training at the Faculty of Physical Culture E. Bystritskaya, E. Tupikin, Nizhny Novgorod State Pedagogical University, Research Institute for Professional Education Development of the Department for Education of the city of Moscow Psychological-pedagogical training of physical culture faculties students at pedagogical universities has an aim to create the system of psychological-pedagogical competence. This system consists of: - pedagogical orientation of activity of a specialist in PE (system of motives, that determine personal sense of some kinds of pedagogical activity and the whole activity not specified by kind.) - the basis of pedagogical competences. (What I know, what I can, what I want and what I am able to do in my professional field.) - the system of personal characteristics that are important for the implementation of pedagogical activity in the field of physical education and sport. All the components of the system mentioned before are formed in the process of studying the subjects of psycho-pedagogical block of disciplines in the field of all the forms of student’s activity. This preparation is divided into several parts- invariant part which is necessary for every prospect teacher; variant one for every particular pedagogical specialty; personal part which depends on peculiarities of psychic setup, the personality itself, experience and conditions of life of every particular student. Such division is justified in accordance of future teachers of natural-science, mathematics, the Arts because on these lessons teachers will form the pupil’s identity in similar situations of educational activity. Psycho-pedagogical cycle, studied by the students of such specialties, consists of similar disciplines. This cycle is also fulfilled with methodological subjects. But the structure of psycho-pedagogical preparation for the teachers of Art-cultural subjects and of PE is different. They are to form pupil’s identity under the circumstances of two independent types of activity that occurs simultaneously. In a case of art or music – the types are educational and creative one. For the PE as a subject and for the physical activity as such it is intrinsic to form the body and the identity through the means of sporting and educational activity. During the education the students of the Faculty of Physical Culture are studying three types of subjects that bring the main investment into their psycho-pedagogical competence. The first group of subjects is psycho-pedagogical cycle, general for all the faculties. To this we can include general theory of education, the history of the theory of education, general psychology and the history psychology, age-specific psychology and pedagogical psychology, the course of corrective-pedagogy disciplines and others. To the second group belong such subjects, which are aimed at formation of special pedagogical competences. These competences assist the realization of professional activity in the sphere of PE – psychology of sport and the theory of education of PE. The third group is subjects of methodological block. They form physicpedagogical orientation and competences that are necessary to possess for a specialist in PE. Personality component of psycho-pedagogical competences is formed, as a rule, by accomplishment of creative student work pedagogical researches. Thereby, the main features of psycho-pedagogical preparation for the students from physicpedagogical departments flow from the special features of physical activity itself. The main pedagogical postulates, ideas, consistency and principles refracting in it, get new features. These peculiarities of the process are intensified and initialized by the originality of initialization of pedagogical activity in the sphere of PE. Let’s have a good look at these peculiarities. The PE pedagogue’s activity is aimed at the formation of terminal values. Irrelatively is this pedagogue a teacher, a trainer or an instructor, the main value is health. Meanwhile the program of general subjects is aimed at formation of values of knowledge. Other values for PE teaching are friendship and nature and many others. The aim to create a foundation of healthy life style is achieved not only by PE teachers but also by teachers of biology. But the main difference is that they are doing it theoretically and only on the courses of anatomy and physiology. And the teacher of PE does it not only in theory but in most cases in practice. They develop not only the body of their student but the identity of a person as well. Another special-purpose program of educational activity is team building. This team formation is built on the lessons of PE not only due to the pedagogical skills. On the first stages of team development - team formation is an aim of work of a teacher, but later this team is a mean of identity formation. But in the practice of a PE teacher the case is absolutely different. Here the formation of a team in a section sport games is the main aim of activity during all the time of work. At the same time this purpose is not on the first stage when we are speaking of individual kinds of sport or martial arts. The golden pedagogical rule, on which the whole base of evaluation is founded. declaims: one can not compare a student to another. One must compare the results of a student in accordance with his or her own progress. It is an interesting fact that physical activity denies this golden rule. That happens because the essence of sport lays in comparison of the results of rivals. The main motto for all the competitions is: ‘faster, higher, stronger’. However, this discrepancy is only superficial, visual. The sport activity consists of two processes – training and emulative ones. In the educational field there is no such division. In the basement of training process lays educational activity, where this golden rule is completely complied. The results of every person are taken into supervision, thanks to what every person is taken into combined team in accordance with their own growth, successes and work. Here the absolute result of individual work is of high importance. In emulative activity – during heats, games and other competitions, where not the absolute but comparative result is of high importance, the presents of rivals is one of pedagogical condition of selfappraisal and external evaluation of a sportsman or a team: ‘We performed better than on the previous competition’, or ‘We were better prepared for the competition that is why we won.’ It is to be marked that all the teachers of the Art subjects are teaching their pupils from every beginning, form zero. Let’s take for example chemistry. Children before studying it don’t make any chemical experiments and have only theoretical fragmentary knowledge. What concerns PE, the case is different. Before coming at PE lesson a pupil already has some motion experience, which is impossible not to be taken into consideration while organizing educational activity, which is reasonably called sport-educational activity. Everything mentioned before makes the creation of special pedagogical conditions on PE lessons very important. These circumstances must provide for the psycho-pedagogical preparation of future specialists in PE area in accordance with appropriate modern requirements of competence-module approach. This approach allows for the variety of forms of professional activity for these specialists. For the realization of this approach the research is held. This research is dedicated to the designing of didactic-methodological system of examination of subjects from psycho-pedagogical block. The block is based on the usage of didactical principle of substantial profiling that considers all special features of professional activity of every concrete specialist (of a sport trainer, a PE teacher in primary school, an instructor of preuniversity’s institutions etc.). The approbation of elements of this system has already given its first positive results. Military-patriotic education in Gymnasium #13 of the city of Tomsk I.Bystritskaya Gymnasium #13, city of Tomsk In later years the issues of rise of military-patriotic education of the youth has been discussed a lot. This is determined by many reasons. First of all, changes in economic, political and legal systems of Russia and civil society of the recent decade has made not only positive effects on life of the country but introduced acute challenges. These are: - Demographic crisis, - Family crisis, as many parents face problems in upbringing children, - Unwillingness of the majority of governmental and non-governmental organizations to fulfil upbringing activities, - Increase of personal and social apathy, rise in crime and drug abuse, lose of qualities of a citizenpatriot capable successfully implement own duties in peace and war time. Military-patriotic education in Tomsk region is implemented on the basis of the Regional Target Program “Patriotic Education of citizens of Tomsk region”. Central goals of the Program are: - Development and strengthening of patriotism of residents of Tomsk region, - Formation of profession related qualities, skills and ability to use them in different spheres of life, - Promotion of allegiance to constitutional, military duties in peace and war time. Moreover military-patriotic education program is needed because of some negative trends in today’s Russia. Number of misdemeanors committed by young people is rising, as number of drug addicts, moral values deteriorate, etc. Thus upbringing of the younger generation and training for the defense of the country is crucial. Military-patriotic education of the youth is carried out by a number of organizations. In the city and the region there are many clubs and associations. Nonetheless educational institutions are at the forefront of this activity. This is reasonable as educational institutions embrace the greater share of the youth under 18. Great attention is devoted to military-patriotic education in the Gymnasium #13. First of all I would like to say that the Gymnasium has worked out a Program of military-patriotic education, and almost all events held at school have patriotic emphasis. An example is annual economic game “Trinlandia”. One of its central chapters is military-applied kinds of sports. The game is aimed at adapting children to mew conditions of life in the country. Pupils earn money – trins – by establishing commercial entities. Among enterprises there can be game clubs of military-applied kinds of sports, for instance, hand-gun range, armwrestling club, fitness gym, etc. Pupils interested in history of nuclear weapon participate classes conduced by S. Ashurova and O. Pulinets devoted to research and peaceful use of atomic energy. Life safety and Basics of military service classes are integrated with chemistry, history and social studies classes in different aspects (fpr example, protection of toxical agents, history of Armed Forces of Russia, legal status of military men). Veterans of the Great Patriotic War and flash points combatants often visit our Gymnasium. The Gymnasium always participates military-sport game “Rubezh” (Frontier). It consists of three stages taking 2 days. The game involves ski accelerated march, submachine gun shooting, ceremonial review, shuttle runs. Pupils put on proudly military outer garment and show it to other schoolchildren. Almost all personnel of the Gymnasium takes part in training for the Game. Parents – military men assist render assistance with special equipment. Pupils of secondary school take part in military-sport game “Zarnitsa” (Summer lightening). In 2001 the Gymnasium team occupied the 1st place in regional competitions. Ceremonial and song reviews are constantly held for pupils of 1-8 grades. Annually on the Children’s Day competitions on military-applied sports (airgun shooting, grenade throwing, race, etc) are held as well as exhibitions of means of protection (chemical protective equipment, protective outer suits, respirators, etc) and exhibitions of patriotic literature. Gymnasium pupils take part in city military-patriotic program “Pamyat” (Memory). The program is a year long and consists of several stages. Fall and winter obstacle courses and ceremonial review are particularly popular. Program members also participate in Guard of Honor of the Post #1 by the Monument of Battle and Labor Honor of Tomsk Dwellers in Lagerny Sad on the Victory Day. During last two years they stand Guard of Honor on May, 8 by the Monument to the Hero of the Soviet Union Ivan Chernykh. In the Gymnasium there is a club of history of the Armed Forces of Russia. Recent quizzes on Stalingrad battle and Defender of the Motherland Day proved that pupils know history of the Armed Forces good enough. The Gymnasium has a magazine “Gumanitariy” (Humanitarian) with a supplement “Pamyat”. This supplement is made up of military-patriotic materials. We see the result of the military-patriotic activity of the Gymnasium that a number of school leavers entered and graduated from military higher educational institutions. For example, M. Nerovny and R. Gizmatullin graduated from Tomsk Higher Military Academy of Communicaions; V. Tchaikovsky studies at Tomsk Military-Medical Institute. All school leavers upon retiring from the Army visit the Gymnasium, meet schoolchildren, tell them about military service and their plans for the future. The process of professional activity adaptation by students of physical culture and pedagogy majors as a component of the system of psychological-pedagogical competencies E. Bystrickaya, O. Boycova, Nizhny Novgorod State University To give the generalized characteristics of teacher’s work one uses the following terminology: “professionalism”, “art of teaching“, “qualification”, “professional abilities”. For the characterization of teachers’ professional and personal qualities the notion of “professional (pedagogical) competence” is used. In different definitions of “professional (pedagogical) competence” different details are accentuated: teacher’s activity is emphasized (a teacher must possess knowledge, skills and techniques); other definitions put emphasis on teachers’ personal qualities. On the basis of the notion of the “professional (pedagogical) competence” we will rely on the following definition: Professional (pedagogical) competence is a teacher’s integrative quality including the possession of knowledge, skills and techniques, the ability to apply his/ her professional knowledge in practice and teacher professional attitude. There are six levels of professional competence. The first level is a trainee teacher: the introduction to professional work, testing one’s own abilities. The second level – a teacher: acquisition of professional basics, usage of theoretical methods and knowledge, positive efficiency and effectiveness. The main emphasis is put on knowledge, not on students’ progress. The third level – an expert: competent usage of methodology in theory as well as practically; stable high efficiency and optimality; a tendency to take students’ progress into account. The fourth level – an innovator teacher: searching for and using special methods or integrated educational systems; creativity; effective usage of innovations; orientation on students’ individuality and mental development. The fifth level – a researcher: determination and ability to learn and appraise the values of other teachers’ ideas and innovations; appraisal of efficiency and optimality. Level six – a professional: constant longing for psychological self-development; positive experience on the previous levels; a psychologist working “from a student” and “for a student”; a researcher able to evaluate the effectiveness of new ideas; an innovator; a master possessing knowledge acquainted to the cutting-edge science. Physical training specialist’s transition from one level to another can be characterized by different means of adaptation for accomplishments in their professional sphere. There are several types of professional competence. They show one’s professional adaptation degree in the professional activity: - Special competence. A good command of professional activities on high level; the ability to plan one’s professional progress; - Social competence. The ability to participate in co-operative work and be responsible for consequences of the work. - Personal competence. Ability for individual self-expression and self-development; means of counteracting professional deformation of a personality - Individual competence. Ability for self-actualization and development of one’s individuality in one’s work; readiness for professional and individual development, self-organization and self-rehabilitation. apply different kinds of professional activity, though they have much in common. The process of adaptation plays an important role in forming personal qualities of physical training teachers. These qualities are crucial for accomplishment of professional aims. The notion of “adaptation” as a psychological-pedagogical competence component is usually understood as an adjustment of one’s psyche and personality to the purposes of this or that kind of activity. It is worth mentioning that physical culture and sport professionals. This problem can be solved taking all the basic physical culture-pedagogical majors into consideration. Nowadays in Nizhny Novgorod State University students are taught in 4 main physical physical culture-pedagogical majors: “Physical Training” (after graduation students become physical training teachers); “Physical Training and Sports” (students become heads of sports sections, clubs and other sport associations); “Adaptive Physical Training” (highly-educated specialists in physical culture and pedagogy who work with the health impaired); “Recreation and sport-recreational tourism” (professional activity in recreation rooms, recreational institutions, sanatorium-and-spa institution, travel agencies etc. All the specialists go through the following stages of adaptation for their professional activity: 1) Adjustment – is characterized by optimism, excited attitude towards the new sphere of activity; 2) Overcoming behavior (frustration phase) – so-called “shock caused by inability to solve problems in a usual way; 3) Assimilation and “recovery” – growing conflicts with the new environment and the ability of reflection; New adjustments – the last stage of adaptation process; the “usual” feeling; no anxiety; new standards of behavior and activity; occurrence of psychological neoformation; for example, professional pedagogical attitude, personal pedagogical communication style, pedagogical review, pedagogical intuition etc. All the stages are carried out in corpora; the final stage continues even when an alumnus becomes a young specialist. There are individual features of the adaptation process and also the features that depend on future profession’s specialization directly. Physical training teachers to be go through the first stages of the adaptation process at a slow pace because of the adjustment to different pedagogical activities types. For example, holding sessions for different age groups, sports’ basics teaching, class teacher duties, acting as a health-improving activity provider. This process of adjustment takes quite a long time and forms different professional adaptation directions. In comparison with physical training teachers, coaches (instructors) have got limited options of professional activity which mostly depends on the training content and competition(s). It means that the first stages of adaptation process are quite short but the frustration phase is longer. It can be easily explained by the fact that each coach works with personalities and needs to find an individual approach to each of the sportsmen on the basis of their abilities, temper and character peculiarities, willed selfregulation degree and goals. If we talk about adaptive physical training specialists, the stage of assimilation is the most important; work with the health restraint and as a consequence their psychological and personal features may lead to a longer stage of professional perplexity and shock. Judging by practical experience, this specialization is usually chosen by the people who have already got secondary medical education, experience of working with the health restraint. That’s why the first stages are usually very intensive and short and during the assimilation stage the abilities of reflection, empathy are developed; voluntary activity is growing and a teacher’s humanistic professional attitude is formed. Students specializing in “Recreation and sport-recreational tourism” usually have an active positive perception of their future work. They see it as an easy and pleasant job connected with rest, positive emotions and health improvement. But such an understanding of their professional duties is incomplete and when compared to practical experience it leads to the loss of professional motivation. Consequently the stage of active reformative behavior comes later. The stage of shock is shorter and less noticeable. That’s why the main aim of the university’s professors is to activate students’ adaptation process. All the above mentioned peculiarities of the process of students’ adaptation to professional activity cause the necessity of using efficient methods of psychological-pedagogical impact. To improve the orientating adaptation of future physical training teachers, professors should apply new methods of work. For example, methods developing thinking flexibility; judgements and deeds flexibility (problem solving, discussions etc.) Concentration, self-regulation and reflection trainings, development of empathy towards different age groups of students and other methods should be applied in the educational process. For the optimization of adaptation process of future coaches such methods as practical training, independent work (development of activity, purposefulness, endurance and stamina) are useful. Besides, it is important to hold business games increasing students’ motivation. Trainings of stress resistance and sensitivity increase are also highly efficient. A specialist who works with health restraints should possess the following qualities: high self-control degree, adequate self-acceptance, self-control, high resistance to stress, low level of anxiety and pedagogical optimism. All these qualities can be formed with the help of such methods as dialogs, discussions, psychological diagnostics and self-diagnostics. To increase the success of adaptation to professional activity for students specializing in “Recreation and sport-recreational tourism” advanced level tasks must be used. The efficient tasks are psychological case study, leadership trainings and practices etc. For specialists in the sphere of psychological-pedagogical education the process of adaptation to their professional activity is an integral part of physical training professional competence system. This process entails 3 levels: 1. Staging (more or less typical of all physical training specialists); 2. Intensity and duration of stages (typical of all the psychological-pedagogical specializations) 3. Individual features of adaptation (typical o every student and a young specialist). For shaping an adequate system of professional pedagogical competence for physical training teachers, coaches and instructors of recreation and sport-recreational tourism we should take all the peculiarities of this process into consideration and conveyed in educational net amount, content and teaching forms combination. Peculiarities of special medical group activities in a comprehensive school T. Chekhunova, Municipal Educational Institution Secondary Comprehensive school №37, city of Tomsk Nowadays upon starting school many children already have one or several chronic diseases thus falling into special medical group by their health status. During school life health indicators of the majority of pupils continue to deteriorate. The number of children of special medical group increases within school years. According to statistics about 20 % of pupils have physical development of «above the average» level, and only a few - "high", generally these are schoolchildren engaged in sports sections and clubs. The number of pupils with "average" level of physical development does not decrease, and but instead increases. Therefore it is necessary to establish the system of physical training in special medical groups (SMG) for pupils with chronic diseases. Often the problem of these children is not addressed. These pupils, as a rule, sit on a bench during a PE class or do not participate it at all. Poll of teachers of educational institutions (n = 45) was conducted for the purpose of determining reasons of no SMG physical training in a school. The analysis of its results has detected the following reasons: - a teacher does not know methods of conducting of SMG classes good enough; - no regular medical control system in a comprehensive school; - schools have in 2 – 3 study shifts what creates difficulties for the organization of SMG classes; - parents do not fully understand the importance of physical training for children with various chronic diseases; - payment system for teachers conducting SMG classes is not clearly defined; - business of sports halls; The analysis of diseases dynamics of school №37 pupils has shown that the number of pupils with different diseases has during increased in the later years, including illnesses of cardiovascular system, nasal organs, digestive system, liver, psychological diseases, and also tuberculosis. The Federal Law «On Education» emphasizes the importance of preservation and promotion of health of the younger generation and role of educational institutions in addressing this issue. So 9 groups SMG were formed in the school № 37. The following problems have encountered by conduct of SMG physical training: - Children have 2 – 3 diseases; - Study is carried out in two shifts; - children of different age, physical development, physical condition fall into one group; Therefore all pupils were divided into groups not by diseases, and by parallels (1–2 grades, 3–4 grades, etc.). SMG physical training classes were carried out in all 1 to 11 grades. The “Program of physical training for schoolchildren of SMG” has been elaborated taking into account the results of the poll. The authors are I. Slesareva, T.Chehunova. Table №3 Distribution of study time by program parts for SMG pupils Grades Part of the program Theory Gymnastics Track and field Basics of sport games Active games Total hours: 1-2 5-7 a class 34 10 14 14 8-9 34 10 28 3-4 during 34 10 10 18 72 72 72 72 34 10 14 14 The program mainly included: gymnastic exercises, active games, basics of sport games, track and field elements, respiratory gymnastics, exercises for correction of posture, strengthening of muscles of back, abdominals. Speed, strength exercises were limited, run distances reduced, the following exercises excluded: rope climbing, pull-up and acrobatics. Classes were conducted twice a week for 40 minutes. The analysis of the results indicated improvement of physical condition of SMG pupils already within a year of training (> 0.05). Medical examination showed that 2-4 pupils from everyone SMG consisting of 15 persons were transferred into a preparatory group, and 1-2 persons – into the basic one. It is should be mentioned that SMG training during three years provoked the trend to decrease of musculoskeletal diseases, the number of SMG themselves reduced from 9 to 3. Thus, three year long SMG training experience contributed to 66 % decrease of pupils falling into SMG category by their health status. Seminars for PE teachers of Tomsk and the Tomsk region on topics: “Humanization of physical training and goal-oriented development of motor skills and techniques”, "Peculiarities of special medical group (SMG) training”, “Experience of carrying out of Final Examination of pupils of SMG” were held for introduction and promotion of the experience on SMG training and the elaborated “Program of physical training for schoolchildren of SMG” had been held. In 2007 the «Program of physical training for schoolchildren of SMG» became the winner of correspondence round and was presented on internal round of the International Fair of social-pedagogical innovations in the city of Otradnoe of the Samara region. Now only few educational institutions of Tomsk have SMG PE classes. So the problem is crucial. References: 1. «Физическая культура для учащихся 4 – 10 классов и школьников, отнесённых по состоянию здоровья к СМГ», М., «Просвещение», 1981 г. 2. «Физическое воспитание учащихся 1 – 11 классов с направленным развитием двигательных способностей», В. И. Лях, Г. Б. Мейксон. 3. Материалы II научно-практической конференции «О ценности спортивного образования в физическом воспитании», Томск, 2000 г. 4. Министерство образования Российской Федерации (рекомендательное письмо) «Об оценивании и аттестации учащихся, отнесенных по состоянию здоровья к специальной медицинской группе для занятий физической культурой», М., 2003 г. Youth voluntary fire-brigade functioning within comprehensive and extended education systems integration trend T. Chekhunova Municipal Educational Institution Secondary Comprehensive school №37, city of Tomsk The youth voluntary fire-brigade of the school # 37 in Tomsk has been functioning for a long time. Youth voluntary fire-brigades are created as measures for educational purposes, aimed at preventing children’s pranks which may cause fires, helping the State fire inspection and voluntary fire society in carrying out preventive work and fire abandonment. Youth voluntary fire-brigades consist of brigades, parties and units. The school fire-brigade consists of 16 members who are divided into two parties, including 8 people, taking into consideration their age. Then the brigade is divided into 4 units. There is a special curriculum, according to which the classes are held three times a week and continue for 2 hours. The program is aimed at teaching the basis of the firemen matter to attract the students to the work on the fire prevention in the time of holidays, celebrations, summer vocations and so on. Also it is aimed at helping at fire extinguishing. Young firemen hold different propaganda classes with teens and children. They learn how to organize and hold different competition, contests and quizzes on fire safety among students of different classes. A drawing contest called “the telephone number of safety – 01” has been held for two years already. In this contest the young brigades not only organized it, but also take part in it. Older students who have received the knowledge and skills in fire precaution and how to do first aid in different situation, help in judging in the section “I am the lifesaver”, which is the ground course of the “school of the navigator” in the youth regional forum of the youth initiative, called “Russia is us” which is held annually. Annual preparation and taking part in the fire contests and competitions have become a good tradition since 1998. It is necessary to provide for the validity of the rules on the safety methods at practical classes, because the students do exercises, which are approximate fighting ones for example: “development of the fire engine”, “climbing the fire escape”, “the relay race of the firemen”. The race consists of 4 stages, the last one is connected with extinguishing a pan in fire. In 2008, at one of the annual school educational-practical conference, Levashov, Pavlov presented a report in “Is fire a friend or an enemy?”. It was considered to be the best report at the section of physical education and the basis of the fire safety. Taking part in the voluntary fire-brigades helps the children doing important and necessary thing. It gives the children an opportunity to try themselves as life-savors in practice, who help others too. The children receive organizational and communicational skills. They try different roles, learn to find out, analyze and represent information. There has been created a video film, called “make friends with sport”, to propagandize healthy life. Games in teaching track and field elements in primary school E. Chupahina, Municipal Educational Institution №23, city of Naberezhnye Chelny, Tatarstan A child can learn many things quickly by playing. Children like to play, they want to play, that’s why I use different games in my work. Playing active games they learn to value give-and-take techniques, team spirit, abide by game rules. A toy is something valuable, even domestic for primary school pupils, so I often use it in my methods. I ask children to bring a toy of particular size with which they will do exercising and then take it back home. After running I conduct a warm-up with toys addressing at once goals of general and specific warm-up. So these aims children make up two columns, everybody holds a toy or two toys. Warm-up exercises address the following objectives: development of fine motor skills, coordination abilities, strength qualities, flexibility, perseverance, hard working. Exercises: 1. Hand twisting with a plush toy rightward, leftward, arm pulling backwards and frontwards. 2. Throwing a toy up and catching with the same hand, the same with both hands, alternately and both hands. 3. Change over of a toy over the head from the initial position of arms held sideward. 4. Catching of a toy from the initial position of toys down, arms forward – a child has to catch a flying toy. 5. The same exercise but a toy is in a right hand, to catch it with a left one. 6. Toy juggling, juggling of two toys. Teaching elements of throwing. 1. Acceleration to a toy thrown over the head with two hands or one hand forward and another upward. A child has to catch a toy. 2. Pair exercises. One of children throws a toy, another one catches it. The second one has to start from various initial positions: crouch start, crouch stand, front support, etc. Shuttle run teaching. A toy of the first child standing in a column is on the finish line. By a “Go!” command a participant runs, takes his/her toy and brings it to the start line, then runs to the finish line. The second person goes the same way, but on his second way to the finish he takes the toy of the first person and brings it to the master. The last competitor takes his/her toy and a toy of the previous child and runs with both of them. Jumping exercises. 1. A toy between the knees, hands of the nape, two legs jumping forward, backward. 2. Crouch stand walk, a toy between the knees or under the knees. Arm building exercises. Arm walk from the initial position of front support, a toy between the knees. Only arm walk, straight legs, feet strained in. Posture exercises. 1. Initial position – a toy on the head, walk on toes arms extended sidewards forward or backward. 2. Stand body twisting. 3. Crouch stand walk, squatting. Nestitherapy as a method of impaired body metabolic processes restoration S. Davydov, M. Lizenko, Petrozavodsk State University In the later decades ecological disturbances, nutritional disorders, poor drinking water quality, excessive use of drug therapy have become most frequent negative factors affecting health of the population. Lifestyle change also affects health status i.e. nervous overfatigue, stresses, hypodynamia trend. All these features lead to metabolic disorders particularly impaired carbohydrate and fat metabolism, overweight, blood pressure rise, thus formation of so called metabolic syndrome. Allergic diseases have become more frequent (dermatitis, vasomotor rhinitis, bronchial asthma). All these factors lead to the necessity to revise treatment of such patients. A trend to use nonmedical therapy, eg reflexotherapy, physiotherapy, kinesitherapy, diet therapy is evolving. One of the kinds of the latter is fasting-dietary treatment, i.e. known from the ancient times hunger cure, or nestitherapy. It has been proven that shifting from exogenic (external) nutrition to endogenic (internal) is followed by regeneration of tissue structures of a human body, clearance of toxins and allergens, body systems improved functioning. Our rich experience (more than 20 years) of applying nestitherapy in clinical practice showed that all 68 persons subjected to 9-21 days of fasting demonstrated positive dynamic in such pathological processes as bronchial asthma, allergic dermatitis, lungs sarcoidosis, hypertensive disease, degenerative disk disease, psoriasis. As metabolic processes are inherent in the majority of these diseases, nestitherapy as one of sorption methods is an alternative to drug therapy. In-depth study of sanogenic impact of nestitherapy on fat metabolism embraced 88 patients suffering from bronchial asthma. 13 persons (or 14% of the total, all females from 18 to 60 years old, mean age – 41) subjected to nestitherapy; 35 persons (40%) took glucocorticosteroids, 40 persons (47%) – “usual” therapy. Lipid composition of blood serum (total cholesterin of blood serum, cholesterin of high- and low-density lipoproteins, phospholipids incl. lecithin) and red-cell membranes of every patient was measured. Nestitherapy was conducted in line with the methods of Y. Nikolaev in modification of the Saint-Petersburg Pulmonary Center of 10-14 days duration. Generally well-being of patients upon nestitherapy was improving already at the end of the first week, with choking fits ceasing upon finish of patients’ acidotic crisis. Within an observation a fact of regeneration of qualitative and quantitative composition of membrane lipids upon use of nestitherapy was indicated. The increase of total phospholipids, including first of all lecithin, which is the main component of cell membranes and lung surfactant, was determined. At the same time decrease of total lipids, mainly by cholesterin and triglycerids, is recorded. This changes were statistically valid in comparison to such figures of other patients receiving drug therapy, including systemic glucocorticosteroids. The results gained let us regard nestitherapy as a multi-purpose method of after-care: - It preserves and even increases cell membranes immunity as significantly improves the composition of their main components (increase of phospholipids especially lecithin); - Positively affects cholesterin metabolism (decreasing its level and the level of triglycerids), thus reducing the risk of atherogenesis; So nestitherapy, competently conducted, can be considered one of the promising and quite safe healthimproving aids, applicable to a range of pathological processes accompanied by metabolic disorders. Psychological aspects of female idiopathic infertility survey N. Dementyeva, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy (Petrozavodsk) – V. Behterev Research Institute (Saint-Petersburg) Among different types of female infertility patients with so called unexplained infertility fall into a specific group. According to data from different sources number of such women varies from 4 to 40% of all infertile females. The diagnosis of unexplained (psychogenic, idiopathic) infertility is made if a patient and her regular partner passed standard minimal medical examination on detection of biological reasons of reproductive disorders and it indicated that the couple was biologically fertile. There are two opposite points of view on female unexplained infertility. The first one is that there is no unexplained infertility but it is an unascertained causation what means that a woman was not fully examined or there are no proper tools for conducting such an examination. The second point of view highlights the search of psychological causes hindering and (or) eliminating impregnation possibility upon healthy reproductive system of a woman. Anyway regardless of gynecologists’ notion of infertility aetiopathogenesis, if a woman can’t get a precise answer about the infertility cause, she is stuck in a peculiar psychological situation. Occurring crisis feelings are thus targets for psychological correction. 138 women took part in the survey. 78 of them constituted basic group, 60 – control group. The survey was conducted in cities of Karelia. All survey participants had higher or secondary professional education. During the survey period the majority of them had regular job with only little percentage being housewives. Age limits of the basic group were from 25 to 41 years old. The basic group consisted of 36 women with diagnosis of primary functional sterility of explained etiology. Medical examination data ruled out any disorders according to set infertility criteria of the rest 42 women of the basic group. Nonetheless 30 out of them had no pregnancies, but 12 females formed a group with so called “secondary unexplained functional sterility” as they experienced induced termination of pregnancy. All patients filling the basic group have regular partners (in a wedlock – 63%, out of wedlock – 37%). Every infertile couple was thoroughly examined according to standard medical procedure. The control group included women of 25-40 years old all of them having a least one child and no impregnation and carrying problems in their history. The survey was held in two stages. Clinical-psychological data collection method was prevailing during the first stage, and experimental-psychological – at the second one. Experimental-psychological stage involved testing patients by: life history multimodal inquiry, ego-structure test of G. Ammon; Freiburg personality inquiry (FPI); nervous-mental tension, asthenia, low mood estimation; personal differential, mental health estimation methods; marriage contentment test-inquiry (V. Stolypin, T. Romanova, G. Butenko); graphical research methods (drawings of “My future child”, “My condition”, “My childhood”). All the data was processed with STATISTICA application program package. Several parameters were used for making social-psychological descriptions of two groups of the patients: with determined cause of sterility and with unexplained female infertility. In particular characteristics of personal meaning of infertility, peculiarities of emotional condition and personality, relations with close relatives (a spouse, parents). First of all it should be pointed out that according to experimental and clinical conversation data healthy women are distinctive from infertile ones mostly in tolerant reality attitude, broad time scope vision. They are more organized and predictable in their wishes and actions. Women with infertility diagnosis are more dependent on their emotional condition in comparison to healthy ones, they experience difficulties in handling their emotions. Infertile women suggested at a conversation that negative emotions are more typical for them, while healthy females have brighter rich emotions ranging from negative to positive. The ego structure of an infertile woman is characterized by infantilism, dependence on certain factors (mother, marital relations, work conditions, human relations, domestic comfort). Infertile woman also limits her contacts with people, avoiding new ones and experiencing no content from communication. Unlike a healthy woman, already has a child or can deliver a baby, an infertile one has to be able to work harder for preservation of her marriage. Constant and quality care of a spouse mostly at the expense of own interests, brilliant housekeeping, continuing self-fulfillment are considered as compensating factors. We suggest that any serious disease including infertility forms a new quality of life of a person. Sterility exerts significant influence on life of a woman changing self-image, creating an obstacle to her development and self-actualization. She is confronted with a new challenge to adapt to life with infertility status, find new life meanings, transform of future without loss of femininity. Patients with determined cause of sterility are fully aware of their diagnosis and peculiarities of own reproductive function. Female infertility is already an accomplished fact, a reality for them. They know its cause and possible ways to change a childless family status. Medical examination of women with unexplained infertility can’t determine their reproductive status. Patients do not get expert’s advice on family planning and possible ways of overcoming a childless family status. So women with unexplained infertility are constantly in a kind of marginal situation, awaiting a change with every monthly period and every examination, living in uncertainty. Women with unexplained infertility tend to suppress emotions, demonstrate emotional states due to a fear of not being understood but rather obtrusive, delusioned to other people. Such patients consider shame as the most recurring emotional state; compare to women with determined sterility cause who name grief, woe, sorrow. Women with unexplained infertility experience fear to people for a strange disease, to parents and a spouse for uncertainty, to oneself for being ill. A woman with unexplained infertility in comparison to those with determined cause of sterility show higher degree of critical attitude to oneself, lower self-acceptance, lower self-estimation, lower trust to one’s feelings, senses, and thoughts. They have reduced social contacts, lose professional interests, aspirations and skills, again unlike those with determined cause of sterility who fulfill themselves in occupation, hobbies. Women with unexplained infertility have enough strength for maintaining marital relations. Hence such marriages often suffer from household and sexual-personal problems. As a rule all life of these women is devoted to awaiting a pregnancy or finding out an exact cause of a childlessness. Judging on data acquired through clinical conversation and experimental-psychological methods I suggest that constant awaiting, a situation of strained uncertainty mostly influences behavior, emotional state, personality traits, and relationship system negatively. A situation of unexplained infertility with undetermined medical cause increases psychological sensitiveness of such patient, significantly changing perception and self-consciousness of a woman. She perceives herself not only as a patient with a reproductive disorder, but also as a patient with distractive mentality what may destabilize her emotional and personal status. Doctors and psychologists of maternity welfare clinics family planning centers are aware that at present the number of women with unexplained infertility despite the advancement of instrumental and laboratory examination methods stays at the same level. What is more, patients unexplained infertility are not provided with psychological guidance, consultations, psychological correction. This category of women, like many other patients with different diagnoses, is in a situation of incompleteness, uncertainty of a disease. Uncertainty factor is an extra mechanism which may hamper correct functioning of physiological and psychological resources of a patient. New efficient methods in obstetrics and gynecology enabling successful solution of childless marriages problems appeared in later years. Anyway there is a high necessity in serious psychological work with “conditionally infertile” women. Certainly psychological-correctional work should be targeted, differentiated and minimize influence of social-psychological destabilizing factors and activate adaptive mechanisms of a patient. References: 1. Актуальные вопросы акушерства и гинекологии: сб. научных трудов. Петрозаводск, 2007. 219 c. 2. Ананьев В. А. Психология здоровья. СПб., 2006. 384 с. 3. Бесплодие в супружестве / под. ред. И. Я. Юнды. Киев, 1999. 344 с. 4. Вопросы репродуктологии: сб. научных трудов. Харьков, 2003–2008. 234 c. 5. Кулаков С. А. Основы психосоматики. СПб., 2003. 288 с. Promotion of healthy lifestyle among adolescents through self-massage. Igor Divak, Massage therapist of higher category, Senior lecturer, Department of Theory and Methods of Physical Education and Gymnastics, Faculty of Physical Culture, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Everyone is aware that health is priceless fortune of a person and society as a whole. Sound health preserved and improved by a person him/herself ensures long, joyful and active life. Cultivating this need in children and teenagers is a serious pedagogical challenge. Pure theoretical knowledge are enough here. Experience of previous generations is to assist in this activity. 30-40 years ago self-massage techniques was popular and wide-spread across the country. Every person could learn it. Self-massage was particularly popular among tourists, athletes and healthy lifestyle enthusiasts. Nowadays self-massage is self-sustaining and high-efficient system of positive impact on a human body. Massage possible impacts are very broad, such ancient thinkers as Hippocrates and others wrote about necessity of using massage. Unfortunately many contemporaries do not even suggest that face self-massage contributes not only to decrease number of wrinkles, but also to prevent them and different injuries. Self-massage assists to remove or at least to relieve pain, noncontact massage – to remove fatigue and improve body condition in general. In a modern school, both sport and comprehensive one, self-massage can be used as health-improving method, as well as during tourist journeys on foot, physical training. The advantage of self-massage is that it can be performed almost in any place, its intensity depending on own well-being and feelings. Its teaching does not require any special equipment. Self-massage demands abiding by all basic rules and hygienic requirements of classic massage. Contraindications are the same of classical massage. These can be skin lesions, acute inflammatory processes, unexplained pains, etc. In some cases contraindications are temporary due to acute period of an illness or exacerbation of a chronic disease. By time passing having acquired initial technique a schoolchild is able to advance it adding various medical, sport, and ethnic massage techniques to classical one under a teacher’s supervision. Development of skills, acquisition of new knowledge and its wise utilization are extremely relevant. It should be emphasized that self-massage should be performed only after consulting a doctor. Teaching of this techniques can be organized at physical and health education classes, within extra-curricular activities, in clubs particularly sport ones. In tourism activity self-massage is highly relevant even for secondary school pupils as its applied character is obvious. Those eager to use experience of previous generations and up-to-date science achievements are to reveal a great space for utilization and advancement of infinite possibilities of a human body. Administrative project «Sports-oriented physical training as one of school priority activity areas» M. Dyuzhikova, I. Akhmetyanov, Z. Zakirova, School №28, city of Naberezhnye Chelny Our school was opened in 1976. It has magnificent sports traditions and results. The athletics Olympic champion Lilia Nurutdinova, the Olympic games participant in swimming Aleksey Zatsepin, the participants of the International competitions in judo Radik and Ramil Rashitovs, the international class masters of sports and participants of the Acrobatics World and Europe Championships E. Tsybulkina, A. Ploskova and D. Vihryanova, and many other top athletes studied at our school. Pupils of sports schools go to the 4th grade of our school every year. Additional meals are organized for such pupils, and their academic schedule is made according to their sports trainings schedule. Every year lots of our school leavers enter the Academy of physical education. Having analyzed this data, administration and school faculty decided that it is necessary to work out the administrative project called «Sports-oriented physical training as one of school priority activity areas». The project implies cooperation between Kamsk State Academy of Physical Education, Sports and Tourism, sports schools, institutions of additional education and families. The project goal is to promote pupils’ professional self-determination and their self-realisation. The project objectives are the following: 1. On the basis of teachers-innovators’ theoretical experience, to develop conceptual positions defining strategic directions of pre-specialised and specialised training of pupils. 2. To carry out the system analysis concerning professional selfdetermination, pupils’ attitude to various kinds of physical and sports activity, examination of pupils’ health. 3. To develop the program of Pre-specialised and specialised training on "Physical education", to introduce it into educational process and prove its efficiency on practice. 4. On the basis of the received results, to develop scientific and practical recommendations for teachers of educational institutions. Stages of the project implementation 1. Theoretical and search stage: working out of defining strategic directions of pre-specialised and specialised training of pupils; carrying out of an experiment to learn about pupils’ physical and mental health state, motivation for physical training, pupils’ attitude to physical and sports activity; interviewing of parents, teachers and school administration. 2. Experimental stage: working out of the program of pre-specialised and specialised training and its approbation. 3. Estimating stage: profound analysis and systematisation of the received data, presentation of the results in central press, at conferences, in scientific papers. The programme of Pre-specialised and specialised training on "Physical education" It is necessary to study pupils’ professional self-determination in the context of age processes dynamics at various ontogenesis stages (A.P. Matveev). 1) Informative stage (1-4 grades) The stage goal is to perfect the health-improving system at primary school by developing informative and activity components of physical training. The stage objectives: 1. To create propitious conditions for pupils’ health improving. 2. To advance physical education on the basis of developing of healthy lifestyle and steady interest and need for regular sports doing. 2) Investigation stage, specialised classes introducing (5-7 grades) The stage goal is to interest pupils in physical and sports activity. The stage objectives: 1. To acquaint pupils with a great number of kinds of sports to choose from. 2. To organize physical and sports training and education of pupils. 3. To acquaint pupils with the theory of physical education and sports. 3) Professional-oriented stage (8-9 grades) The stage goal is to motivate pupils for real estimation of their own abilities and achievements and for choosing a direction of physical and sports activity. The stage objectives: 1. To provide pupils with necessary conditions to promote physical and sports training values taking into account their bents, abilities, requirements, interests and physical fitness. 2. To organize physical and sports training and education of pupils. 3. To deepen knowledge in physical training and sports. 4) Professional-adaptive stage (10-11 grades) Senior high school pupils with major in sports already have high sports categories and are members of city, Republic and Russian sport teams. Due to great physical load and frequent competition trips, they miss a lot of lessons. Therefore the basic educational components for such pupils are getting practical experience in professional sphere (introduction to a profession), gaining knowledge and learning ways of its organisation, developing conditions for active self-knowledge and putting this knowledge into practice within the selected professional activity (professional test). The stage goal is to provide pupils with a rational combination of studying at comprehensive school and profound training at sports school. The stage objectives: 1. To realize education of pupils based on cooperation with institutions of additional education, colleges and higher educational institutions. 2. To deepen knowledge in physical training and sports. 3. To develop professionally important physical and mental qualities and skills. School leavers can choose the higher educational institution to study futher. They can go to the Kamsk State Academy of Physical Education, Sports and Tourism or Physical Training College. Improvement of physical fitness by means of individual practice within the physical education discipline Т. Efremova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, T. Verina, Docent, Pedagogical Institute, Southern Federal University, city of Rostov-on-Don Nowadays the matters of developing the physical culture and healthy lifestyle skills among the young people have gained particular importance and urgency. The attitude to one’s own health and physical self-perfection characterizes the level of general culture and education in the respective area among the young generation. The increase in the efficiency of the physical education process in educational institutions is closely connected with the justification of the role, place and evaluation criteria of the pupils’ and students’ independent practice. Individual practice is considered as a purposeful, active and independent students’ activity. It is selfcontrolled and analyzed by the students who organize and manage it on their own in view of individual cognitive motives and at the time which they consider the most suitable [3]. Individual practice can be exercised either under the tutor’s supervision and on his instructions or on the students’ own initiative during lecture hours and their spare time, it is also to be concluded by a certain result. In order to improve individual practice in physical education we applied the main methods optimizing the teaching process developed by Y. Babansky [1]. They presume the successive going through the following stages: goal-setting, planning and specification of aims, prognosticating the close results on basis of the initial students’ level of development estimation, the choice of the activity methods, means and contents. The choice is made taking into consideration the following aspects: the motives, the peculiarity if aims, the students’ capabilities and the studying conditions. On the program realization stage they carry out its operative adjustment. The practice analysis both by the student himself (auto-evaluation) and by the tutor is an indispensable condition of its success. The entire individual practice program realization system is attended by the evaluation and auto-evaluation of the training process, which may include operative adjustment of the practice course and the assigned tasks results analysis. When working out the individual practice system the most important matter is the one of impartial and standardized evaluation of physical fitness which is adequate for the students’ capabilities and of developing clear criteria for individual practice in the “Physical Education” discipline general evaluation. In practice we usually come across two approaches to the evaluation of physical fitness: 1 – on basis of the empirical data they determine the standards for tests or checking exercises results. The grade is given depending on the student’s results correspondence with the model characteristics of each given test; 2 – the results of the tests bank reduced to a common system and expressed in points are compared to the specific results of particular students. The analysis of scientific publications that we have done revealed that the former method frequently used in practice is not impartial enough when evaluating the pupils and students with a different level of physical development and physical fitness [2, 4, 5]. The method which is more appropriate for evaluating the level and course of physical fitness is the centile method based of the non-parametric technologies and leaving out complicated calculations. Besides, when evaluating according to this method we can take into account regional and age-related particular qualities of the pupils and students together with the development of particular physical characters. Relying on the data obtained from a three year’s pedagogic observation we have worked out centile tables of physical fitness of the students of Shakhty Medical College. By their means one can scheme the individual physical fitness profile and evaluate limiting factors and reserves of a person’s body. The evaluation of physical fitness constitutes a component part of the diagnostic module, which also includes the evaluation of physical development and the body’s functional condition. On the basis of centile analysis of a person’s physical fitness we scheme and specify the tasks and prognosticate achievable results. The student chooses the methods, means and intensity of exercise together with the tutor within the framework of practical methodological lessons in order to put the individual program of physical self-development into practice. These activities constitute the content of the theoretic methodological module. The time for individual practice is provided for at the end of lectures, within the sectional framework and during the spare time within the studying hours (studying and practical module). An integral part of the physical self-development process is auto-evaluation and the activity results control carried out by the tutor (the control module). Auto-evaluation is performed via a vivid presentation of the initial and the achieved levels of physical fitness represented in the self-control diary. The main criterion of the individual practice efficiency is the conformity of the predicted and the achieved results. Table 1 nd The evaluation of the physical development level of the 2 -year student O. Ivanova (example) Centiles 3 10 25 50 75 90 97 21,43 19,80 18,70 17,80 17,00 16,40 15,80 14.16 13.40 12.50 11,42 11.05 10.38 10.13 125 135 147 160 170 175 190 Rising the body from a lying on the back position for 1 min (number of times) 15 20 25 30 35 40 44 Rising the body from a lying on the stomach position (number of times) 14 16 20 24 27 31 40 Bending forward from a standing position (cm) -5 4 9 12 15 19 23 2 5 7 12 16 20 26 Aspects 100 m race (sec) 2000 m race (min, sec) Long jump from the spot (cm) Press-ups (number of times) Legend: 125 – initial level 135 – achieved level The effectiveness of the developed individual practice planning and evaluation system is confirmed by the data of the pedagogical experiment carried out throughout an academic year in the G. Kuznetsova Shakhty Medical College. Among the College students there were composed a control group (n=80) and an experimental one (n=78). The initial test results before the experiment do not show any reliable difference between the control and the experimental groups with the exception of some exercises (Table 2). Comparing the level of physical fitness after the experiment showed better average results in the experimental group. The result difference possess high reliability in all the given aspects (p<0,001). The control group students show positive dynamics only in two exercises which demonstrate the stamina of the abdomen and back muscles (Tables 3, 4). In other tests the members of the control group, unlike the experimental one, show either the decline of the results or minor changes (p>0,05). Table 2 Students’ physical fitness evaluation Before the experiment After the experiment EG 100 m race (sec) CG 17,79 t p EG 1,90 >0,05 18,18 CG 17,45 18,34 0,16 0,13 688,73 733,10 0,15 0,14 711,19 727,45 5,87 6,37 5,75 5,54 11,51 12,08 11,29 12,13 0,10 0,11 0,10 0,09 Long jump from the spot (cm) 159,55 154,99 165,45 155,08 1,64 1,73 1,67 1,62 Rising the body from a lying on the back position for 1 min (number of times) 29,47 27,44 34,71 28,69 0,87 0,67 0,77 0,79 Rising the body from a lying on the stomach position (number of times) 23,31 21,33 31,62 22,33 0,75 0,48 1,13 0,65 Bending forward from a standing position (cm) 12,00 10,76 14,40 10,61 0,70 0,83 0,59 0,92 Press-ups of times) 10,72 9,36 15,65 9,14 1,27 0,58 2000 m race (sec) (min, sec) (number 1,88 1,91 1,85 2,22 1,14 1,19 0,94 >0,05 >0,05 >0,05 <0,05 >0,05 <0,05 0,65 t p 4,32 <0,001 5,56 <0,001 4,46 <0,001 5,46 <0,001 7,13 <0,001 3,47 <0,001 4,66 <0,001 Legend: EG – experimental group CG – control group Table 3 Physical fitness data dynamics (experimental group) 100 m race (с) Before the experiment After the experiment ðàçí x ðàçí m ðàçí t p 17,79 0,15 17,45 0,16 0,75 0,35 0,08 4,10 <0,001 2000 m race (sec) 711,19 5,87 688,73 5,75 (min, sec) 11,51 0,10 11,29 0,10 39,32 22,46 4,45 5,05 <0,001 Long jump from the 159,55 1,64 spot (cm) 165,45 1,67 10,46 5,90 1,18 4,98 <0,001 Rising the body from a 29,47 0,87 lying on the back position for 1 min (number of times) 34,71 0,77 6,50 5,23 0,74 7,11 <0,001 Rising the body from a 23,31 0,75 lying on the stomach position (number of times) 31,62 1,13 11,32 8,31 1,28 6,48 <0,001 Bending forward from 12,00 0,70 a standing position (cm) 14,40 0,59 3,23 2,40 0,37 6,56 <0,001 Press-ups (number of 10,72 0,94 times) 15,65 1,27 6,00 4,94 0,68 7,26 <0,001 Table 4 Physical fitness data dynamics (control group) Before the experiment After the experiment ðàçí x ðàçí m ðàçí t p 100 m race (sec) 18,18 0,14 18,34 0,13 0,66 0,16 0,07 2,15 <0,05 2000 m race (sec) 727,45 6,37 733,10 5,54 22,54 5,65 2,52 2,24 <0,05 (min, sec) 12,08 0,11 12,13 0,09 Long jump from the 154,99 1,73 spot (cm) 155,08 1,62 5,88 0,09 0,66 0,13 >0,05 Rising the body from 27,44 0,67 a lying on the back position for 1 min (number of times) 28,69 0,79 4,21 1,25 0,47 2,65 <0,01 Rising the body from 21,33 0,48 a lying on the stomach position (number of times) 22,33 0,65 4,28 1,00 0,48 2,09 <0,05 Bending forward 10,76 0,83 from a standing position (cm) 10,61 0,92 3,38 0,15 0,38 0,40 >0,05 Press-ups (number of 9,36 0,65 times) 9,14 0,58 2,82 0,23 0,32 0,71 >0,05 Thus, the suggested system of planning and evaluating individual practice in the field of physical self-development allows us the following: - to determine the students’ motional possibilities and the direction of their correction, - to carry out an individual and varied approach when planning the students’ physical load and evaluating each pupil’s or student’s work; - to evaluate the physical self-development work impartially on basis of the level of physical fitness dynamics; - to finally form the skills of voluntary physical self-development exercise and managing one’s own state of health. References 1. Y. Babansky, M. Potashnik. Questions and Answers on the Optimization of Teaching Process. – Kiev: Radyanska shkola, 1984. 2. Y. Puzyr. Physical Development Control in Educational Institutions Based on the Monitoring of the Physical State: Thesis abstract. ... Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences: Moscow, 2006. 3. E. Sakharchuk, G. Sorokina. Individual practice in the system of professional training of a physical education teacher // Physical Education. Scientific and methodological journal. 2005. №4. 4. S. Simonov, P. Gritskov. Organizational and metrological aspects of building the standard background of schoolchildren’s physical fitness // “Current innovation research: science and practice” (electronic scientific edition). – 2009. - №2. 5. A. Shklyar. Typological peculiarities of a medical college students’ physical development and functional state throughout the academic period: Thesis abstract. ... Candidate of Medical Sciences: Volgograd, 2006. PHYSICAL AND SPORT EDUCATION IN ITALY Luca Eid, ANSAS (Italian National School Agency), Ministry of Education, University and Research, Milan, Italy. Nicola Lovecchio, FARC (Functional Anatomy Research Center), Morphology Human and Biomedic Science “Città Studi” Department, University of Study, Milan, Italy., Marco Busetti, MIUR (Ministry of Instruction, University and Research), Physical Education Office of Milan, Italy Italy is an European Parliamentary Republic of 60 million people, it is a over 1000 km boot shaped peninsula that, in the second half of the 20th century, improved from an economical point of view, mainly in the northern area of the country. Despite a well developed and almost cost-free social welfare, which reduced the infant mortality, the country has a limited birth rate. Nowadays, only the 20% of the population is aged below 20 years, and a 23% aged more than 60. Italy is a member of the most industrial nations group (G8 and G20 organizations) with a Gross National Product coming for a 33% from industry, for a 63% from services and for a 4% from agricultural sectors. Italy is still experiencing a significant development and richness gap between the northern industrial regions, where the unemployed rate is around the 7%, and the southern agricultural ones, where in some areas it is even over the 20%. Like in other countries, the prevalence of obesity is increasing rapidly, it is now estimated at around 14% in adults. Over half of the adult population is overweight. The consumption of alcohol appears to be increasing and the number of smokers is still relevant. It is estimated that 19% of population is practising sport like regular lifestyle, versus a 41% that never practises any sport. Sedentary habits are increasing. FIG 1: THE SHAPE OF ITALY EDUCATIONAL FRAMEWORK State schools are free, but State-authorised private schools also exist where tuition fees are required. Education is compulsory for children aged 6 to 16, involving 5 years of primary school, 3 years of lower secondary school, and 2 years of high secondary education. The university, according to Bologna Process, is generally based on two levels: a 3 years bachelor degree and a 2 years master degree with the options of further special courses. A reform has been introduced recently to achieve the EU standards. The new system is based on a minimum of 12 years education divided into two cycles: the first cycle starts at the age of six and lasts 8 years (5 years primary and 3 years lower secondary school). After the age of 14, it starts the second cycle: students can choose different tracks involving various combinations of study with, in same case, professional training. Continuation into university is direct if the student has selected a lyceum or one additional preparatory year is required if the curricula was professional. FIG 02: SAMPLE OF ANNUAL COMPULSORY AMOUNT OF HOURS IN LOWER SECONDARY SCHOOL (11-13 YEARS) PHYSICAL EDUCATION Physical Education (PE) is under the responsibility of the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR) and is a compulsory subject in the 13 years of basic education, even for the disabled people with appropriate adaptations. PE was introduced in 1859, formerly named “Gymnastics”, then “Physical Education” and now “Motor and Sport Sciences”. Physical Education in Primary School Guidelines: ‘The body as a value’. So, it is not a dress but a whole way of being and acting in the world and the society. Targets: construction of his own identity in relation to his self-knowledge and to the others and the orientation of his own life project. Contents: parts of the body, senses and perceptions, motor and postural schemes (learned through games), nutrition guidance, personal care, environmental problems and unhealthy habits (pollution, smoking, sedentariness). Evaluation: an evaluation document including a portfolio of individual skills and assembling all the documentation collected during the entire school period. Teacher: PE is taught by the general teacher. In some schools a PE specialist teacher works with the generalist teacher. Physical Education in the lower secondary school Guidelines: the national curriculum specifies the essential level that must be granted by all school, the number of compulsory hours (2 hours per week) and the quota reserved to autonomy of each school (up to a maximum of the 20% of the whole curriculum). Targets: becoming aware of his own physical efficiency through the self evaluation and basic norm for accident prevention. Contents: improvement of coordination and motor skills, self evaluation of skills and performance, highway code for cycles and motorcycles, training methods, body expression and communication. Evaluation: a mark of 6 on 10 or more allows to access to the next class; a lower score entail a ‘debt’ that will need to be fulfilled at the beginning of the new year; at the state exam (taking place at the end of the cycle) the evaluation can also involve PE with a written or oral test. Teacher: PE is taught by PE specialist teachers. PE in the higher secondary School Guidelines: more or less the same of the middle school. Targets: learning the basic principle and techniques for sport performance, well being and physical improvement. Contents: structure and rules of individual and team sports, basic principles of training theory and methodology, principle of nutrition in physical activity, doping health problems versus an appropriately physical training. Evaluation: the portfolio of the acquired skills concurs to form the final credit score that will contribute to the result of the final evaluation at the state exam (maturità). Teacher: PE is taught by PE specialist teachers. FIG. 03: TOTAL AMOUNT OF PE AND SPORT HOURS IN THE STUDENT CARRIER (FROM 6 TO 18 YEARS) IN SOME EUROPEAN COUNTRIES Total amount of PE and Sport hours in the student carrier (from 6 to 18 years) in some European countries Italia 810 Austria 1,500 Germany 1,450 Poland 1,620 France 1,680 (PE) - 2,600 (PE + Sport) (Censis Servizi su dati MUR, 2007) Extracurricular sport activities Already in primary school, the children can join physical education and introductory sport activities that are free and elective. They are supported through the funding for the widening of educational offerings. In the secondary school, school sport activities are well structured and are supported through the special funding from the Ministry of Education and the Regional School Offices for the widening of educational offerings, allowing students to train and prepare for competitions. Forms of sport integration are organised for disabled students. The sport activities concur in the definition of the student’s curriculum and acquired competences as well as in the final mark attributed at the State Exam. According to a recent monitoring, it appears that about 72% of the first-level and 76% of the second-level schools prepare their students and allow them to take part in the student sport competitions. Sport Education in Primary school No physical education teacher is required in the primary school that sees 2,6 million students with an average of 20 children per class. The play/sport programmes are defined and implemented by the local school institutions in collaboration with a number of stakeholders such as: local administrations, CONI (Italian National Olympic Committee), national sport federations and local clubs, both in the context of school activities and out-of-school programmes. This causes a wide diversity of variously co-financed initiatives that frequently lack of systematic approach and continuity, mainly because year over year budgets are not always maintained. Only recently, with the 2003 school reform, the Ministry of Education introduced a PE graduate specialist role in the primary school in order to improve action and give to sport sciences equal dignity compared to the other disciplines. Sport Education in Secondary School There are 5,2 million students in the secondary school. PE is a compulsory study involving students two hours per week, that can be individually defined for disabled. Teachers must have a master degree in Physical Education and a proper teaching habilitation. Additional hours of sport practice are included in the Educational Formative School Plan (max 6 hours not compulsory) concurring to the student’s curriculum and to the evaluation score at the end of the secondary cycle. Throughout the 8 years of the secondary cycle, school sport activities are well structured allowing students to try and participate to the various sport student competitions. The sports most widely practised are: Cross Country Races and Track Races, Swimming, Gymnastics, Alpine Skiing, Orienteering and among the team sports: Volleyball, Soccer, Basketball. Although PE teachers and school structures/administrations are the basic actors of the Student’s sport activity in the Secondary school, their effort is lacking of the necessary effectiveness because of the limited lesson time per week. They are only able to help and encourage those students that are already selfpractising sports in external Sports Clubs (in the sport federations or non-profit sport associations), with only limited success in their mission to improve the ‘sport mentality’ among the student’s population. The regular sport practice is common among the 55% of the surveyed sample aged 11-14, but many children drop-out of sport practice around adolescence (age 14), mainly because of uneasiness and problematic situations. FIG. 04: SEDENTARINESS IN ITALY (% AND AGE) Physical Education evaluation In the first cycle (primary and lower secondary school), the evaluation of pupils takes place through: An evaluation document called “the pupils Personal Record”, recording the periodic assessments and the final assessment made at the end of years 1, 3 and 5; A Summary Report reporting whether pupils has been admitted to the next class The Portfolio of Individual Competencies, which is the document where the educational team, the pupil and the family record the documentation assembled during the entire school path. For disabled pupils, an Individual Educational Plan is designed jointly by the educational team with the family and the responsible medical officer. The evaluation refers to the differentiated path the pupil must have followed with the help of support teacher. In the second cycle (higher secondary school) each teacher makes specific periodic and final assessments through a mark in tenths. A mark of 6/10 or over allows access to the next class, otherwise a lower mark entails a “debt”. The periodic assessment made by PE teachers involves the areas of motor learning and the pupil’s physical abilities. The assessment is generally organised as an integrated process combining: Observational techniques and motor tests, so as to evaluate the motor competencies attained; The written and oral tests to evaluate the knowledge of disciplinary contents. At the State Exam taking place at the end of the cycle, the evaluation can also involve movement and sport sciences. The calculation of school credits includes the sport credits acquired in out-of-school contexts and contribute to the final evaluation. Additional contexts for physical and sport activities Extracurricular Physical Activities They are school sport activities, taking place out of the school hours, conducted by PE teachers with school pupils, even with classes different from their own. They typically refer to the promotion and practice of an educational sport, which involves competition but in which competition is not seen as an aim of its own and which rather offers the opportunity to play and feel at ease with the others, promoting social cohesion. Extra-School Physical Activities The sport activities offered are various; they are sometimes offered to sport associations. In this case, families pay a share of the costs Out-of-School Physical Activities Sport associations, Federations and private subjects can organise sport centres offering introductory courses to various sports. Generally the families must bear the costs of participation. One of the activities most widely practised is soccer. Training Physical Education Teachers To be qualified as a PE teacher a University master degree is needed plus one year of teaching training (3+2+1). This is provided by Faculties of Physical Education. Sport instructors They are trained at the National Federations in a multi-level qualification path, from the initial level of Assistant Instructor to, after several intermediate steps, Federal Technicians. Access does not require any school degree. Volunteer sport operators Volunteering is a valuable asset, particularly for the non-élite sport sector. This involves many associations which are almost all non-profit, typically very small and run by volunteers. A sport association can be established without necessarily having a qualified sport technician, although those who work as instructors generally have a qualification. FIG. 05: PE AND SPORT UNIVERSITY DATA PE and Sport University Data in 2006/07 Students 24,000 Bachelor Courses 98 Master Courses 22 (Censis Servizi su dati MUR, 2007) Italian PE Teachers Association (CAPDI) Our National PE Teacher Association has more than 30 local/provincial PE Teacher Association with more than 3.000 membres. Capdi represented PE Teachers to the Ministry of Education. Capdi provides in service training for PE teachers and generalist teachers of nursery and primary school. Capdi is a member of Eupea (European PE Association). FIG. 06: DISTRIBUTION OF PE TEACHER MEMBERS OF CAPDI IN ITALY Perspectives Physical Education We are working: - to have at least one PE teacher in each primary school. Actually is not compulsory; - to keep 2 hours per week in the curriculum from 11 to 18 years; - to found Sport School Association in each secondary school. Sport The central role of Italian Olympic Committee has been reduced in various ways: there has been a reduction in the incomes and in term of responsibilities because National Federations have acquired private status autonomy and the Regions have been granted full powers. The Regions and the local bodies have become the main partners in the area of education and sport. They organise financial interventions aimed at widening sport practice and developing sport facilities. References Klein G., Hardman K., Physical Education and Sport Education in European Union, Dossier Eps, Edition Revue Eps, Paris, 2008. Eurybase. The Information Database on Education Systems in Europe, The Education System in Italy 2007/08, European Commission, Bruxelles, 2008. C.O.N.I. 1° Report Sport & Society, C.O.N.I. Roma, 2008. 40° rapporto sulla situazione sociale del paese 2006, 40th report on the social situation of the country 2006 / CENSIS, Roma, 2006. Annuario statistico italiano 2006= Italian yearbook of statistics, 2006 / ISTAT. - Roma, 2006. I percorsi formativi della scuola secondaria di secondo grado statale tra corsi di ordinamento, sperimentazioni e utonomia, Educational pathways in upper secondary schools, among formal courses, sperimentation courses and school autonomy / Servizio statistico del Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione, MPI, 2007. Istruzione superiore e professioni: Guida 2006 ai corsi di primo livello= Higher education and professions. Guide to courses of the first level, 2006. / Università IUAV di Venezia; CIMEA della Fondazione Rui, MIUR, 2006. La scuola in cifre 2006= Data on the school system, 2006 / Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione, MPI, 2006. La scuola statale: sintesi dei dati - Anno scolastico 2005/2006= Public school: data in brief 2005/2006, Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione, 1, Roma, 2006. - - - - Notiziario sulla scuola secondaria di I e II grado: A.S. 2006/07= Newsletter on lower and upper secondary school, Servizio statistico del Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione, MPI, 2007. Piani di studio della scuola secondaria superiore e programmi dei trienni: Le proposte della Commissione Brocca, 2, 1083, Studi e Documenti degli Annali della Pubblica Istruzione, 59/60, Le Monnier, 1992. Rilevazione sugli scrutini ed esami di Stato conclusivi del I e II ciclo= Data on assignement of marks and on State exams at the end of the first and second cicle, Servizio statistico del Ministero della Pubblica Istruzione, MPI, 2007. Strutture dei sistemi di istruzione, formazione professionale e educazione degli adulti in Europa, Italia, Structures of education, vocational training and adult education systems in Europe, Italy, Unità italiana, di Eurydice,ISFOL, Eurydice, 2006. http://www.eurydice.org http://www.pubblica.istruzione.it http://www.cimea.it Socio-psychological aspects of pupils’ healthy lifestyle M. Elmurzaev, Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Docent, North-Western State Technical University, city of Saint-Petersburg While developing a complex human science, various methodological paradigms integrating historically developed and newest knowledge of natural, public and humanity sciences occur. In 1960s last (ХХ) century, a relatively new scientific paradigm was a paradigm of a lifestyle. In that case the lifestyle was treated widely enough. A lifestyle is a way people organize their life activities in the system of existing social and economic relations (I. Levykin, 1980). The term "lifestyle" reflects components which compose a person’s life, borders between these components, and their substantial characteristics and interrelations. Among the main determinants of a lifestyle we can state natural, economic, political, socio-historical factors, and as components - working conditions, living and leisure conditions, educational level, infrastructure development of cultural leisure institutions, etc. A lifestyle includes also social-hygienic and medical and preventive aspects of a person’s health. So, a lifestyle is defined not only by environmental factors, but also by a state of a person’s health. A person’s health is defined by their biological essence, and also by social-psychological one. A person’s health and healthy lifestyle are different terms but they have close cause-and-effect interrelation. Healthy lifestyle is a process of physical, psychological and social self-development of a person when he/she gets more universal ways of adaptation to constantly changing conditions of natural and social environment. Healthy lifestyle developing assumes also creation of acceptable, comfortable external conditions, and involving a person in such forms of activity that living a healthy lifestyle becomes his/her natural and vital necessity. "Health" is a most general, umbrella term concerning the person, has no accurate borders, and has different semantic meaning and criteria of its estimation. Therefore it is hardly probable to give any general definition of health in which the laws studied by different sciences would be reflected, or to try to study this phenomenon from the point of view of any “integrative science” that is now considered to be medicine. Nowadays representatives of human science find the medical model of health insufficient and limited. It is necessary to notice that a person, understanding the importance of health, does not have enough knowledge about its protection and promotion. The basic recommendations to live a healthy lifestyle are the following: avoiding of bad habits and stressful situations, personal hygiene rules observation, a balanced diet, optimisation of physical activity, etc. These factors allow the person to support homeostasis of his/her internal environment and his/her physical health. But all the recommendations are relative, for individuals differ on sex-age and personal characteristics, and life experience. But personality development is defined by his/her lifestyle indirectly, through psychological style of his/her lifestyle. So, criteria and norm of a person’s health can be various at each life stage. For example, children and teenagers do not have sufficient life experience to correct and regulate their state of health. The norm of health is not constant; it changes at different life stages. To be healthy means to have possibility to realize yourself. Health is mostly defined not by biological, but by sociocultural factors, and the mail factor here is the universal culture. A person can be recognized healthy only if he/she is harmoniously included in the sociocultural environment and is realized there adequately. It is impossible to imagine any area of a person’s life (education, leisure or physical education and sports activity) beyond culture. Studying of sociocultural and socio-psychological health problems and a healthy lifestyle is considered to be a priority kind of research in education and selfeducation spheres (D.I. Feldshtein, 2004). Physical education (PE) lessons take an important part in health protection and promotion. PE is a sphere which reveals a person’s lifestyle, as well as develops it. In modern scientific researches the term "physical culture" is considered to be a scientific abstraction, a name of a social phenomenon, an umbrella term. It is realized by means of its kinds – physical education, sports, physical recreation, physical rehabilitation and adaptive physical training (V.M. Vydrin, 2004; J.M. Nikolaev, 2006; R.M. Kadyrov, 2008). Physical activity is intrinsic to all physical culture kinds, but they differ on aims, display conditions and means of physical activity organization. On PE lessons at school, mainly pedagogical aims are realized, such as development of pupils’ physical qualities and physical skills. Nowadays pupils are more interested not in compulsory PE lessons, but in doing sports in their free time. In modern scientific researches physical activity in free time has been called physical recreational activity. A variety of physical recreational activity forms, their availability and freedom of choice allows to involve pupils of different sex, age and physical development level in this physical activity. Physical recreational activity in leisure sphere gives a young person lots of opportunities to display his/her personality, needs and abilities. In modern conditions physical recreation is enriched by new functions and it is considered to be a multidimensional phenomenon, an area of an objective reality where a person’s biological, psychological, spiritual and social activities are realized. Physical recreational activity is an important part of a pupil’s healthy lifestyle. Leisure has a number of functions in a modern pupil’s life. An educational function is connected with enlargement of pupils’ cognitive possibilities, developing of informal communication skills, learning skills of psychological state self-control and developing of new forms and kinds of activity. A healthimproving function of leisure combines physical, psychological and social components of pupils’ health. A sociocultural function of leisure includes social experience (socialisation) developing and cultural values (including physical culture values) learning. Cultural leisure becomes a real factor of cultural development of pupils through practical physical activity. A hedonistic function of leisure is expressed in getting pleasure and positive emotions from physical activity. Leisure is the most important sphere in healthy lifestyle development. The aim of physical recreational activity in leisure is recreational physical culture developing of a person. It includes the following components: Educational (cognitive) - steady knowledge of the health, ways of its protection and promotion. Axiological (emotional-value) - perception of health as higher human value, motivation-value orientation to health protection and promotion. Behavioral – realisation of the knowledge in practical activities. This component is expressed in labor, life and leisure culture, in attitude to his/her health and living a healthy lifestyle. Productive – achievement of satisfaction from physical activity and informal communication with people of the same age (J.E. Ryzhkin, 2008). The question of leisure and physical recreational activity interrelation is difficult. In many scientific researches and in everyday practice these two terms mean practically the same. It is possible to state that recreation is one of leisure functions; it always includes activity. Physical recreation is composed by physical activity and cognitive processes serving and regulating it. The problem of values orientation is essential in pupils’ leisure physical activity. The value of physical recreation is its entertaining (hedonistic) character. It not only lets relax and regulate pupils’ mental pressure, but also makes it possible to express lots of positive emotions. Informal leisure communication makes up for its shortage at school and is an alternative form of such social interactions as teacher-pupil, parents-teenagers, and social institutions-pupils. The main value of physical recreation is pupils’ health promotion through interaction of physical, psychological, spiritual and social components. For primary school pupils, the main value of leisure physical activity is entertaining. For teenagers, the most important is informal communication, as well as recognition and self-affirmation in surrounding society. Senior high school pupils find the following factors important: further physical development, achievement of physical perfection and the body’s beauty. They choose the forms of physical recreational activity which are connected with competitiveness, though less often with high sports result achievement. The values of pupils of different age have mainly a sociopsychological character. They make a basis of pupils’ healthy lifestyle and serve as important condition of their health developing. Estimation of respiratory system functional parameters of female students studying at the Faculty of Foreign Languages. D. Evtropkova, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Health status of students is of great concern today. Interest to students health status examination is caused by the need to define the amount of physical activity for each lesson in accordance with the requirements of the physical education syllabus[7]. Efficiency of handling a physical education process depends largely on the experience, knowledge and skills of a teacher conducting these classes. Search for prevention and correction methods of a student’ body functional condition is one of important scientific and practical tasks. In spite of the fact that students fall into relatively healthy shape of population, their way of life is associated with physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, significant neuro-psychological stress [2]. Therefore, students are often observed to have deviations of the respiratory, digestive and other systems, which proves by non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, poor work capacity, acrimony, sleep disorders, etc. [6]. Foreign researchers relate this to chronic lack of sleep, decreased interest in active sports and tourism (A. Yampolska, 1993). Such diseases as pneumonia, ear disease, dental disease and oral cavity[1] affect physical development very negatively. Correlation of physical development and academic achievements [11, 12] is of particular concern. However, there is no clear notion of this issue. Many authors see connection between students’ geodynamics disorders and the deterioration of academic performance. Performance may be affected by some other shortcomings of physical development. Thus N. Belopolskaya and co. (1975) showed that mental peculiarities of underachievers occur backed by the central nervous system disorders and a weakened somatic status. Other authors relate students progress mainly to their individual characteristics of higher nervous activity (V. Lastovchenko). Functional condition is defined as the central nervous system (CNS) background in particular conditions. In labor physiology functional status is estimated by the results of work [8] and its physiological value (level of energy demands). These figures are considered as the most integral indicator of functional condition [5, 8]. In this regard functional condition can be defined as an integral characteristic of human condition enabling assessment of efficiency and physiological cost of the proposed activity [5]. Respiratory system respond promptly to any impacts. The respiration function is characterized by its extreme mobility. Breathing capacity may change several times upon working depending on labor intensity. Prompt supply of a body with needed amount of oxygen is possible only upon reorganization of respiratorycircular system functioning, its adaptation to increased requirements [4]. The facts presented above have identified the main goal of this study - studying health status (functional condition of respiratory system) of 1st-2nd grade students of the Faculty of Foreign Languages. The following tasks have been stated in accordance with the main purpose of the study: 1. To examine functional condition of respiratory rate of 1st-2nd grade female students. 2. To compare the results obtained at 1st and 2nd grades. 3. To estimate the respiratory system status of female students of the Faculty of Foreign Languages. 4. To compare data on respiratory system status in health with the data obtained as results of the study. 5. To determine the level and harmonious physical development of the tested. The importance of functional studies [8] of respiratory system with the use of controlled activity is determined by the fact, that body abilities are fully revealed not in motionless state but during muscular activity and after it, i.e. in conditions of a body increased demands. st nd 76 students of the 1 -2 grade of the Faculty of Foreign Languages of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy are involved in the present study (38 people per grade). The study was conducted before the start of physical education classes. Serkin three-phase test was used [1] as a functional testing technique. In the first phase the time of breath-holding at breath-in in a sitting position was measured. At the second phase the breath was measured in standing after 20 squatting in 30 seconds. Then a person rests for one minute in a standing position. At the third phase of the test the time of breath-holding in a sitting position was remeasured. Also, the study used methods of mathematical statistics [1, 3]. The result of the study was the following: st st st At the 1 grade 15 girls (13%) out of 38 tested at the 1 phase can be referred to the 1 category - healthy trained people (breath-holding more than 60 seconds). 19 people (50%) as a result of breath-holding test (40 to 60 seconds) fell into the 2nd category - healthy, untrained people. And the result of 14 girls (37%) out of 38 was less than 40 seconds, what can be referred to the 3rd category - those with circulation inefficiency. During the 2nd phase of the test no one (0%) of healthy trained humans (category 1) out of the 38 girls could hold his breath after exercises for more than 30 seconds; 29 people (76%) to the healthy untrained people (2nd category) could hold breath from 15 to 30 seconds; and 9 persons (24%) out of those with circulation inefficiency – (Category 3) completed breath holding for less than 15 seconds. At the 3rd phase of the test 4 people (10%) could be referred to the 1st category (breath-holding for more than 60 seconds); 20 people (53%) - to category 2 (breath-holding from 35 to 60 seconds); and category 3 (less than 35 seconds) was the result of 14 girls (37%). st At the second year out of 38 tested persons at phase 1 of the test, 11 girls (29%) fell into the 1 category; the 2nd category - 20 girls (53%); and the 3rd Category - 7 persons (18%). As a result of the 2nd phase of the tested 2 persons (5%) were in the 1st category; 25 persons (66%) - in the 2nd Category; and 11 people (29%) - in the 3rd Category. At the 3rd phase of conducted test 3 people (8%) out of 38 belonged to the 1st category; 21 girls (55%) - to the 2nd category; and 14 girls (37%) - to the 3rd category. Thus we can make the following conclusions: the findings of our study have shown that the adaptation degree to specific living conditions is better detected by functional tests in form of graduated exercise. At the 1st phase of the test functional indicators of the respiratory system are mostly within the physiological norms; the same can be said about the 3rd phase - performance after some rest (recovery). Anyway we cannot say the same about the 2nd phase of the test, where the breath was held immediately after the load. If we compare the figures of the 1st and the 2nd grades, it is obvious that figures for the 2nd course are higher than those for the 1st grade in all 3 phases. At the second phase of the test the same trend is observed. And there is a number of tested persons (5%) at the 2 nd grade who can be referred to healthy people trained (at the 1st grade it is 0%). rd A similar situation is observed at the 3 phase - a second-year rates are higher than the first-year ones. That is the characteristic of the functional indices of the respiratory system dynamics at the 2 nd grade higher than at the 1st one. By the second year students are more trained and more accustomed to physical and neuro-emotional stress; they have higher body adaptive abilities. All this was proven in all functional parameters of the test. References 1. Аулик И.В. Определение физической работоспособности в клинике и спорте. М.: Медицина, 1999. 2. Бальсевич В.А., Запарожанов В.А. Физическая активность человека. – Киев.: Здоровье, 1997. 3. Виру А.А. Функциональная устойчивость и физиологические резервы организма // В кн.: Характеристика функциональных резервов спортсмена. Сб. науч. Тр. Л.: ГДОИФК, 1982. 4. Горанский А.И., Кирилина В.М. Адаптация дыхательной системы организма к физическим нагрузкам в условиях европейского севера // Сб. Механизмы функционирования висцеральных систем. СПб: РАН, 2001. 5. Данилова Н.Н. Психофизиологическая диагностика функциональных состояний. М.: МГУ, 1992. 6. Иващенко Л.Я., Страпко Н.П. Самостоятельные занятия физическими упражнениями. - Киев: Здоровье, 1986. 7. Ильинич В.И. Студенческий спорт и жизнь. Москва 1995. 8. Кирилина В.М., Горанский А.И. Влияние стажа работы на адаптацию системы кровообращения у мужчин-учителей разных специальностей // Успехи геронтол. 2010. Т. 23. № 1.С. 125-130. 9. Кирилина В.М., Элиляйнен Н.В. Влияние физической нагрузки на физиологические механизмы кардиореспираторной системы у учителей в условиях европейского севера. //Экология и жизнь 2000. С 17. 10. Реабилитация здоровья студентов средствами физической культуры: Учебное пособие/Волков В.Ю., Волкова Л.М. –СПбГТУ, СПб., 1998. 11. Физическое воспитание студентов и учащихся. Под ред. Н.Я. Петрова, В.Я.Соколова. Минск 1988. 12. Физическая культура студента. Учебник для студентов вузов/ Под общ. Ред. В.И.Ильинича. – М.: Гардарики, 2003. 13. Физиологические основы физической культуры и спорта: учебное пособие/Давиденко Д.Н.. – СПб., СПбГУ, 1996. – 134 с. Attitude of the 2nd grade students of the Faculty of Physical Culture to polyathlon Elena Feshina, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Polyathlon is all-round event, contributing to harmonious physical development of population. Polyathlon exerts impact on all systems of a body; it is an excellent means of developing basic physical abilities: strength, speed, endurance, flexibility and movements coordination. Polyathlon classes are aimed at improving national health status. These classes also help draftees and boys of preinduction age obtain all the necessary skills for military service. Since 2008 the "polyathlon" discipline has been introduced to the curriculum of the Faculty of Physical Culture, KSPA. In this regard, there is a need to analyze students attitude to the new subject. In order to identify indicators of students contentment with the content, exams passing requirements and subjects study results, as well as relationships with fellow students and teachers we conducted a survey of the 2nd grade students. Survey was conducted in January 2010. A month after the subject examination. In measuring the degree of students contentment or discontentment we used 7-point scale by L.Likhachev (1982). The study covered 43 students. We determined arithmetic means in points for each questions block. We found out that the characteristics of overall contentment with the study of "polyathlon" discipline amounted to 5.3 points; contentment with classes organization and conducting - 5 points. Among the factors influencing the effectiveness of students professional training, allocate them to a conscious positive attitude toward the process of obtaining knowledge and skills in specific disciplines. According to E. Ilyina (1987) and L. Likhachev (1982) a person’s interested attitude to a learning process is largely determined by the formation of his/her contentment feeling with this activity. These authors define the contentment (or discontentment) as a sustainable and long-term attitude towards performed activity (as a whole and its different aspects). The latter is called specific contentment. In this regard, we have estimated in our work peculiarities of relations between the 2nd grade students general contentment and specific contentment with the "polyathlon" discipline. We developed a questionnaire for this purpose. It focuses on students general contentment, and the following types of specific one: contentment with facilitiess, content and results of the training, interrelations with peers and teachers. Total number of contentment indicators provided in the questionnaire was 34. The degree of students contentment or discontentment was measured in a range from 1 to 7 points by the scale proposed by L. Likhachev (1979). The results of the first part are given in Table 1 (only general indicators of different types of contentment). Table 1 Indicators of the 2nd grade students contentment with “polyathlon” training Types of contentment Points 1. General 5.3 2. Facilities 5.0 3. Content 5.5 4. Results 5.3 5. Inter-relations with fellow students 5.9 6. Inter-relations with teachers 6.0 The table data shows that the characteristics of the overall contentment of the participants are not high – 5.3 points. Even less students are content with the facilities - 5 points. This is due to, primarily, the absence of premises for shooting; there is no possibility to provide students with bullets; classes are often held outdoors in bad weather. Contentment with the content of educational activities is significantly higher (5.5 points). This is due to high students contentment with content and quality of lectures (5.9 points), the classes in a range (5.0 points), gym (4.1 points), the organization of physical development and functional preparedness improvement (5,4 points). Students are less content with the results of training than the content of training activities (5,3 points). This is observed in the assessment of contentment with polyathlon practical part examination passing results (5.9 points) and its classification requirements (4.9 points). However, the results of the theoretical section, students rated highly enough – 6.2 points. Students rated contentment with inter-relations with teachers as the highest one - 6 points. They evaluated inter-relations with fellow students a bit lower – 5.9 points. Thus indicators of students general and specific contentment with polyathlon training presented in the Table 1 show that their attitude to the individual components of training activities and to all activities in general is positive. On initial level of swimming of KSPA 1st year students V. Gavrilov, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk It is known that accountancy of the initial level of swimming preparedness of students is considered among the factors contributing to the efficiency of swimming training. It, in turn, underlines the need for an objective diagnosis of swimming skills of students at the early stage of the process of swimming training. Specialists figure out such an integral index as swimming at the time. It is not accidental that the entrance examinations for the faculties of Physical Culture typically include speed swimming. In this regard, we established a goal to develop the regulatory requirements to assess the initial level of preparedness of first year students in swimming and to set the level of preparedness of first year students in swimming for Faculty of Physical Culture of the KSPA according to the results shown in a distance of 50 meters by freestyle. Swimming was conducted in 25-meter pool waterstart. The study involved students of the four first courses of the years 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009. The total number of subjects accounted for 222, including 66 girls and 156 boys. We used traditional statistical methods of calculating the average arithmetic mean, average errors, standard deviations, and a statistical criterion of differences t-Student. All calculations were made separately for each course in the men's and women's groups. To develop benchmarks for swimming for first year student there was used a standard scale, involving the calculation of an average square deviation, and using of it to establish graduation of assessments and standards. The results of this part of the study are presented in Table 1. Table 1. Benchmark in swimming at 50 m Mark Excellent Good Satisfactory Women 56 73 81 Men 43 51 56 Analysis of this table shows that the time interval between assessments "Satisfactory" and "Excellent" for men 13 seconds, while the same gap for women is twice as higher - 25 seconds. This comparison indicates that the initial level of preparedness of female students in swimming is significantly lower that the same indexes for male ones. As the result of determining of the swimming preparedness level of first year students there was found (Tables 2 and 3) that the rates of the overall success of achievement of speed standard by FPC students in the four-year period in both male and female groups have some differences. In particular, the female group of the year 2006 had an average result in swimming better for 12.63 seconds than the female students entered in 2007. In turn, the girls entered the faculty in 2009 lose 11,44 seconds by a similar indicator in comparison with female students of 2008 (in both cases, the differences of arithmetic means of the considered indicators are statistically significant at P <0.05 (Table 2). Characteristics of swimming preparedness of the FPC first year female students. Year of entrance Indicator 2006 2007 2008 2009 Time of swimming for 59,79 ± 2,30 50м (sec) 72,42 ± 4,60 58,38 ± 3,30 69,82 ± 6,78 Success rate of performance of high4,20 ± 0,14 speed standard (in points) 3,52 ± 0,24 4,15 ± 0,24 3,83 ± 0,41 In male groups, as compared with female ones performance of speed swimming remain more stable over the entire four-year period. An exception is the average rate of the high-speed swimming of students entered in 2006, which is better than the similar indicator for a group of 2007 to 5.77 seconds (P <0.05, Table 3). Characteristics of swimming preparedness of the FPC first year male students. Indicator Year of entrance 2006 Time of swimming for 44,52 ± 0,94 50м (sec) Success rate of performance of high4,21 ± 0,12 speed standard (in points) 2007 2008 2009 50,29 ± 1,16 44,45 ± 1,6 46,63 ± 1,05 3,60 ± 0,14 4,25 ± 0,15 4,00 ± 0,16 More stable performance of high-speed swimming among male groups, are proved by the arithmetic mean of the marks for initial testing of their swimming preparedness(tables 2 and 3). Only in the male group of 2007, the arithmetic mean of estimates for high-speed swimming have significant difference from the same indicator of other groups (P <0.05, Table 3). Thus, the study data indicate that the first year students of the KSPA FPC generally demonstrate initial swimming preparedness equal to standards for marks "good" and "satisfactory". On organization of school health teams O. Gavrilova, Teachers Training Institute of the Republic of Karelia, city of Petrozavodsk One of the main strategic objectives of the demographic policy of the Russian Federation is the increase of people’s motivation for healthy lifestyles and the development of the responsibility for their own health. Nowadays health is a vital value, which makes our topic really up-to-date. Schools must help pupils acquire the knowledge and develop the skills they need to lead a healthy way of life. So a competent selection and presentation of the teaching materials about healthy lifestyles is socially necessary. Not a single school can be considered successful if the educational achievements are obtained by causing health problems to children. A school is an ideal place for health education and the development of healthy habits. It has an opportunity to solve the tasks of preserving children’s health as far as all children study at school, their studies last long, and studying (at school and at home) takes most of children’s active time. However, a school is quite a conservative social institution which can not change quickly. Any change in the educational process must be carried out systematically, because a child's capacity is limited. A school can not substitute a hospital, it can not provide children with medical service, but it must create the environment that is safe and enhances health by integrating health promotion into every aspect of the curriculum, introducing healthy programmes and practices into schools' daily routines, improving working conditions. School health teams Creating a school health team (in the program "The European Network of Health Promoting Schools" they are called "school groups of health") might be one of the first steps in combining education and health promotion in order to realize the potential of both. The concept of school health teams is based on the ideas laid out by the European Network of Health Promoting Schools about 15 years ago. A positive experience of the Finnish experts in health promotion at schools is well - known in Russia. The aim of a school health team is to teach children how to keep to healthy habits and to create a responsible attitude to health. For this purpose it is necessary to solve a number of problems: o Create a team; o Identify problems and determine needs of the school to plan health promoting activities; o Assess school facilities and resources that are not used in full; o Create training materials for teachers in topics such as health education and health promotion; o Devise, carry out, evaluate and report on activities to improve school environment, to make schools better places to learn and work for pupils and school staff o Create the environment that is safe and enhances health; o Monitor the results of the activities. Health Team The team may include o Coordinator, o Headmaster, o headmaster assistant in charge of extra-curriculum activities, o physical education teacher and biology teacher, o nurse or doctor, o psychologist, o parents, o students, o teachers that have specific training, o class mistresses. The participation of the Headmaster in the activities of the Health Team makes its work important and ensures the implementation of its activities. A group might consist of 6-10 people. When it is needed, the group may also invite other participants to join - partners and professionals from medical and social institutions, youth and other public organizations, members of the municipal level and the media. School Coordinator A school health team is headed by a coordinator – a person responsible for the number of qualified personnel. A school coordinator provides the management of the school health team, helps to plan its activities, coordinates its work, communicates and cooperates with external organizations, parents, students and other partners. The role of the health team (group) School health team uses such basic techniques as o leadership o planning and evaluation, o communication, o training and education, o marketing and publishing, o supporting and organizing a network, o Influencing its actions and behaviour. Health team activity At the first meeting it is necessary to plan the activities of the Health Team. The tasks mustn’t be given to one person, it is better to divide responsibilities among all participants. Health Team work should be as open as possible, and it is necessary to announce its activities widely. Health Team needs the whole school support. Topics for reflection in the school community are: What is a safe school that promotes health? What is health? What is welfare? Who is responsible for health? How valuable is health? What would you like to change? What is a safe, healthy and successful school community/ environment? Activities for students You can propose health-related topics for students’ projects and essays about an ideal school in which they would like to study. Discussions, debates, class meetings will also help to solve this problem. Exercises in which one must find 10 criteria of a healthy school environment will be quite effective (first, the criteria might be discussed in pairs, and then as a whole class and selected the best ones by voting), short plays about school life and its problems, followed by a group discussion. You can also ask students to create multimedia materials using information and communication technologies (presentations, videos, flash animation), etc. To start working with parents organize a meeting which must result in a draft activity plan. A plan to promote a healthy school environment should be based on the needs of a school. It is better to set one goal. Example activities of a school health team 1. The organizational work (planning, determination of aims and objectives, distribution of responsibilities) 2. Cooperation with partners 3. Information activities 4. Organization of extracurricular activities 5. Consultation on the planned activities 6. Meetings & Events 7. Monitoring You can find out more details about the activities of a school health team in a teaching aid (a handout) for teachers called ' How to teach about healthy lifestyles. Responsibility for the Future ", which was created by a group of Finnish and Karelian specialists. You will also find there a checklist to identify needs and problems of educational institutions to determine areas for creating a healthy school environment. This checklist can help to include all the school staff in the activities. The most important condition for this work is motivated and experienced teachers, tutors, headmasters and interested parents who create children’s values and can influence heads of local governments as well. The composition and activities of the teams vary as much as the physical circumstances and historical and cultural traditions of the schools. It depends on the number of pupils, teaching staff, the geographical position of a school, a school building, its comfort, parents, their cooperation with teachers and many other reasons. While launching the project of a healthy school environment, it is necessary to understand that this is not a single event, but everyday work that requires constant training of those who do it. This is a multi-stage, continuous process which starts in a primary school and continues until the end of school. Certainly, this work should be supported by the government and those people who implement the work. This work can be made easier if special training courses and training activities both in topics such as health education and health promotion and in skills in such areas as communication, active teaching and learning methods are organized for school teachers. It would be helpful to visit neighboring schools, participate in seminars, conferences, exhibitions and competitions on health related topics. This work will be successful if there are a lot of educational materials on health related topics, if the activities are aimed at the development of the cognitive activity of children and adolescents and the formation of their needs and abilities in maintaining their health and keeping to healthy habits. Unfortunately, educational institutions which try to create a healthy school environment do not have necessary facilities. Despite these difficulties, we can do a lot to be sure that our children are healthy. Our task is to teach children and their parents the basics of a healthy lifestyle. Preserving the health of schoolchildren is one of the main areas of strategic policy in education, which is reflected in the national educational programme called "Our new school". Thus, to address the problem of preserving health of all participants of the educational process we need: headmaster and teachers personal interest; families and pupils personal interest; training workshops for teachers, pupils and their parents; succession of work from primary school to graduation classes including taking into account schools characteristics, its facilities and etc. Activity forms at a PE class focused on social and physical health improvement L. Gladkikh, PE teacher, Secondary School of Yubileiny settlement Having graduated from advanced training courses on the topic "Conjugate psychological and physical development of younger pupils at physical education classes" I have decided to test static exercises system with 2-4 grade pupils. Mental and physical health of schoolchildren is largely dependent on their social skills. The society is aggressive; there are a lot of misdemeanors committed by schoolchildren; the cult of physical culture was replaced by the cult of computers, videos; not only physical but also mental health issue has become a serious problem (the use of psychotropic substances, drug addiction, alcoholism, stress). Pupils with different social backgrounds study at our school. Many children come from disadvantaged families, single parent families. The feeling of anger, prejudice, jealousy makes them angry. But in wealthier families permissiveness becomes a major challenge for those children. In order to strengthen not only physical health but also somatic and mental health I use innovative means of physical education: static exercises (postures), folk outdoor games, creative exercises in which students create new combinations of motor activity, facial exercise, breathing exercises, mental qualities developing exercises, muscles tension and relaxation exercises, rhythmic exercises, relaxation exercises. The effect of special motor modes on child psychology can be very different. Much depends on type of personality, temperament and attitude towards one or another motor activity type. Use of this technique promotes physical development of children, development of their intellectual abilities and formation of social skills. I have been working in this direction for three years and I can assure the effectiveness of the work. Pupils’ morbidity rate has decreased (2-4 grade pupils). Results in mental sphere are also obvious. Training in line with this technique occupies 26% of the total hours of physical training (68 hours a year) and conducted within study of "Acrobatics", "Gymnastics". In the sports-game project "acrobatic exercises" the task: to develop the creative initiative of students. Children’s goal within these games is to be able to fulfil their potential in acrobatic exercise. The introductory phase is aimed at preparing students for upcoming workload, strengthen muscle and ligaments, circulation and respiration organs. Main phase of a class consists of is under construction sketches music. Then pupils go smoothly to final part of a class. Children do a pose of shavasana - or how I call it "dead pose". This pose is important for rest and relaxation. The second task of a pose, asana, is to depict a monkey on a rope and a ball. In the final part called "Fakir" children sit on mats or rugs cross-legged, relaxing music (3-5 min). At home: look carefully at an item, close eyes, describe it. Development of communication skills at a health class at the 4th grade called "Obstacle course" under the motto "All shall overcome!" A class includes asanas (poses), creative exercises, conjugate nature exercise. In the main part of the lesson I conduct "the ball is rolling forward” exercise in order to consolidate front roll, and "the ball is rolling backward" exercise to consolidate back roll. The obstacle course should include age relevant exercises. After the obstacle course I conduct an exercise "weightlifter": chidren tighten muscles, raise a barbell, slightly bend legs, barbell on a chest, raise above a head, straighten and bend arms, barbell on a chest and bend a body, bar to the floor. In the final part of a class I use exercises for developing communication and organizational skills. Active games are of great importance at a class. Game is the main type of activity which provides a variety of types of movements (running, jumping, crawling, throwing, etc.). Games can be divided into two groups: purpose-oriented (to maintain posture, strengthen muscles of a back) and mobile aimed at general development. Substantial improvement in posture can be reached by a combination of general developmental specific corrective exercise with massage of a back. A teacher can use these games: "Slow but steady wins the race"," Ball in a circle "," Do this - do that" and so on. The role of a class supervisor in youth physical development Yevdokiya Gudalina, Honored teacher of the Russian Federation, Municipal Institution of General Education “Lyceum # 67”, city of Tolyatti The significance of physical education during one’s school years relies upon providing the foundations for overall physical development, health improvement, and motor skills development. All this leads to the appearance of objective preconditions for one’s harmonious development. Full development of school children is almost impossible without active physical classes. It has been found out that the deficiency of motor activity causes the intense deterioration of children’s health, weakens their protective abilities, and does not provide full physical development. Our country and our society need healthy, courageous, enterprising, competent people who are ready to study and work for the welfare of their motherland and to defend it in case of need. There have been serious changes in the political, economic and social spheres of our country in the 21 st century. These changes have led to the serious exacerbation of social relations in our society and the psychological state of people. And the main cause of anxiety is the fact that such social evils as crime, drugs, and alcohol drinking attract younger people. One of the reasons is that young people have plenty of free time which has appeared as a result of the considerable reduction of sport sections and schools, various clubs and also drastic deterioration of the financial well-being of most families. Not everybody can afford paid lessons. It is not a secret that schoolchildren’s today’s state of health leaves much to be desired. According to the numerous data of medical and ecological studies the level of children’s physical development tends to fall. The facts show that a lot of illnesses have become “younger”. For instance, while in the past mainly elderly people suffered from high blood pressure, nowadays more high schoolchildren, secondary schoolchildren and even primary schoolchildren suffer from it. More and more abnormalities in the musculoskeletal system (poor posture and flat feet) and increase in catarrhal illnesses are recorded. The main reason is decrease in motor activity and lack of physical activity leading to health problems among pupils. We also know that nowadays our children get more information and that it has a negative effect on them. That is why we should think of organizing leisure time activities for children. Sometimes it is enough for a pupil to start doing sports, to become a member of a sports team working under the supervision of an experienced trainer in order to gradually become fit, polite, to study well and to get rid of bad habits. Sport can serve as an important means of moral upbringing. Such renowned traditions of Soviet athletes as deep love for the motherland, rejection of own interests and benefits in order to provide victory for your team, mutual aid, adherence to principle and honesty in competitions, respect for the rival help to form high moral qualities. Finally, sport teaches children not to be afraid of difficulties and in order to achieve their aim to overcome all the obstacles which appear in their way. It helps them to develop the will to win, confidence in their power and resistance to failures. However, they should not do useless things; they should have some reasonable goal and certain aspirations. And if a child does some activity that does not bring them any pleasure, they quit it very quickly. Thus, in order to realize all the significance of their activity, teenagers must understand its prospects. And aiming at success, they will do sports with pleasure. Aspiration to success is the main incentive. The aim of a teacher is to help all their pupils to achieve success in their activity. In sports competitions teenagers can usefully apply their energy, natural desire to compare their power with that of their friends, show their bravery and agility. Sport accustoms schoolchildren to regular physical exercises, i.e. to training which provides the development of one’s will and physical qualities. Sports classes have a great emotional influence on a child. Perhaps it is difficult to name something more exciting for schoolchildren than sport. This fact determines the choice of such important organizational types of work with children as sports events. The analysis of the educational process in the sphere of physical education of schoolchildren has shown the following: It is important to take into account the individual physiological age- and gender-specific characteristics, demands and personal qualities of schoolchildren. The formation of only physical qualities badly influences the development of a child’s personality and distorts the genuine idea of physical education. Not only motor activity but also moral, intellectual and overall cultural upbringing plays a great part in the effective physical development of schoolchildren. We should remember that physical culture is an important part of the general culture of society and its aim is not only to perfect one’s physical state. Physical education should help children to determine a permanent motivation and demands for concerning about their health and good physical state, full development of their physical and mental qualities, for the creative use of means of physical education and leading a healthy lifestyle. That is why it is very important to include physical breaks, sports competitions, sports festivals, and lessons in sports sections and clubs in a schoolchild’s daily routine. Various activities, especially in the open air, are an active type of rest after mental work at school and doing one’s homework. Such rest calms one’s nerves and strengthens the nervous system, improves a child’s mood and considerably increases their capacity for work. The aim of these activities is: to form a person’s physical culture, to prepare graduates for their future life (for socioproductive work, for serving in the army, for upbringing their own children); to make a person understand the necessity of physical activity, of having an attractive body and of optimal physical development and good health; to develop skills in using physical culture as a means of upbringing of the youth, to unite the future family and to popularize a healthy lifestyle. During A. Pushkin’s school years spent at lyceum there was no such subject as “physical education”. As a matter of fact such a concept did not also exist before the revolution. The subject “sport” was not included in the curriculum. But how did lyceum students spend their time? They got up at 6 a.m. when the bell rang. On Wednesdays and Saturdays they had fencing and dance classes. By the emperor’s order, in 1816 horse riding and swimming were included in the curriculum. Lyceum students took physical education quite seriously. For example, Vladimir Volkhovsky had wanted to become a soldier since his childhood and prepared himself for a hard life. Being weak from birth, Volkhovsky managed to reach physical perfection. He got up long before 6 a.m., sponged down and did morning exercises to warm up his muscles. He always slept on bare planks; while doing morning exercises he put heavy dictionaries on his head in order to increase the load. With these dictionaries on his head he walked about the room trying to develop the right step and a good posture. Nowadays the development of physical culture is at the most difficult stage; so much has already been missed. The number of PE lessons cannot satisfy the shortage of motion of children and teenagers. Trying to find a solution to this problem, we could include the third PE lesson in the curriculum. However, teachers face considerable problems connected with it. Firstly, there is no thoroughly worked out and well-grounded programme for this third lesson. Secondly, as a rule, there is no extra room equipped for such classes. There are many other pitfalls which are still important, though they are of secondary significance. Up-dated physical education suggests the following structure: two PE lessons oriented to education, the third PE lesson aimed mainly at health improvement, home physical exercises with the aim of upbringing, extra-curricular physical activities (health improving physical activity, school sports sections) the main purpose of which is the development of schoolchildren. We should find a special approach to the child of every age. And a homeroom teacher should know the age-related and individual mechanism of personality development of schoolchildren, problems and difficulties which appear at every stage of becoming mature. One should point out that the period of education at secondary school coincides with the stage of pubescence. This period is characterized by heightened excitability and the instability of the nervous system. The individual peculiarities of the physical development of schoolchildren are determined according to the results of medical control. Physiological abilities of the same aged children can differ a lot. That is why it is important to find an individual approach in the process of physical education. In comparison with other school subjects, physical education has its specific character and this demands special requirements for organizing and conducting PE classes. Physical education of schoolchildren plays a great pedagogical role. It encourages pupils to lead a healthy lifestyle, helps them to achieve success in the future and be ready to face difficulties. Physically educated children become healthy people and true members of our society. I have been working as a PE teacher for 48 years already and have always been a homeroom teacher. I always start getting acquainted with my class by looking through their documents. It is interesting for me to learn who and what their parents are and what hobbies they have, what illnesses their children have had and whether they have had any injuries. Then I get to know the children directly and individually. I talk with them a lot, attentively watch every pupil at PE lessons, take into account the abilities of each of them, give them and write down individual tasks. I check how they do their tasks and then advise them what sports sections to choose taking into consideration their abilities. And only a month or a month and a half after, I start getting acquainted with their parents inviting them to an individual talk. I give them advice on how to bring their children up. Afterwards I hold a parent-teacher conference aimed at bringing up the pupils of my class taking into account their state of health and abilities, help to organize their work (connected with schooling and sport). I try to do my best so that the children will not have much free time. After all, when they have a lot of spare time, they can easily get into trouble. I conduct homeroom meetings to which I invite famous athletes, mainly my former pupils (Alexandr Ryabov, a member of Russia’s Olympic team; Alexandr Gerunov, the repeated champion of Europe and the world; V.P. Kokshin; Oleg Kiryakov; etc.) At the first parent-teacher conference we agree to hold a competition called “Mother, father, and me are a sporting family”. The winners get some prizes. At weekends we often organize outings in the open air. There we play games, recite poems; sometimes we take a cross-country walk. One of the compulsory forms of physical education is a hike. We can go on a hike on the so called “health days” or after classes. Practical skills and abilities, as well as physical qualities, are developed during a hike. It helps to get to know the children better and, what is also important, to get to know their parents. And then I know what I can rely on and what support I can receive from them. I seek to encourage all my pupils to keep in touch with the heads of the sports sections they attend so that the children will not skip their lessons. I inform the trainer when somebody is ill. Visiting parents at their place, I have an opportunity to learn the whole family of my pupil, their relationships better and sometimes even to help them to save their family from breakup. After a school year, beginning in the fifth from, we go on a two-night-and-three-day hike. After such an active rest the relationships with the children and their parents improve even more. One can learn a lot about the children. Now we do morning exercises together and even some of the parents join us. On holidays we go to tourist centres or on a three- or four-night hike. So, every year we make our hikes longer. By the end of secondary school our hikes last 10-12 days. This gives us an opportunity to study the history and beauty of our native land. Besides PE classes, we have interesting homeroom meetings. We take part in all school events, attend exhibitions, performances, concerts, go to other towns/cities the culture and history of which attract us. As a result, the atmosphere in the class becomes friendly and the children feel comfortable. During all the years spent by my pupils at school, I keep in touch with the physicians of our lyceum. If initially some children have abnormalities in physical development, by the end of secondary school 90% of them become absolutely physically healthy. Moreover, many of them get more physically developed. All parents want their children to be healthy, strong, agile, fit, hardy, and to study well. The comprehensive education of a child, the development of their spiritual and physical qualities, and their personality development depends a lot on their parents. One of the main aims of family education is to take care of children’s health and their proper physical development. It is easy to imagine how happy parents are if they have no problems with their children’s upbringing. By the 11th form the children become really nice. I love them a lot and I like my job. I am glad to hear that other children want to study in my class and ask the headmaster and their parents about it. Physical education has recently become a vital problem. According to the order of the President of the Russian Federation special conditions (social and economic) must be provided to persuade people to lead a healthy lifestyle. Money is allocated for the development and reconstruction of sports complexes; television, radio and other mass media popularize a healthy lifestyle. In his speech, taking into account the results of the participation of Russian athletes in the winter Olympic Games, Dmitri Medvedev pointed out that our country possesses all the necessary resources for achieving good results in sports and involving as many people in sport as possible. He also demanded to create conditions to encourage 50% of Russia’s population and at least 80% of children to do sports. This fact shows how essential this problem is in modern Russia. Accustoming people to an active lifestyle, we will not only make our life longer, but will also promote the longevity of our country. My opinion is that being a homeroom teacher, a teacher of physical education will be more successful in making children healthy, strong, and friendly, and in helping them to become real patriots of their motherland. Prophylaxis of degenerative disc disease with dynamic and isometric exercises S. Guz Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk According to World health Organization data (2000) spinal disorders incidence reached epidemic level and became one of the central economic losses reasons even in developed countries. Epidemiologic watch indicates no difference in musculoskeletal system diseases incidence between genders. Lifespan incidence is a little higher among females than males. Musculoskeletal system diseases are more widespread among those subjected to prolonged standing or walking. It is known that pain syndrome of spinal disorders is determined by muscle and ligament dysfunction, degenerative disc disease, spondylosis, herniated discs. Disc degenerative changes are usually located in lower cervical and lower lumbar spine as these are overloaded and make greater amount of movements. Treatment of musculoskeletal system diseases is challenging. At present the majority of men suffering from these illnesses are conservative treatable. Conservative therapy is considered the basic one and includes use of medicines, orthopedic and physiotherapeutic healing methods, manual therapy, exercises therapy and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (G. Ivanov, 1994, S. Chapman, C. Defranca, 1999). Basic types of treatment at present are the following: 1. Rest, 2. Using spine immobilization bandages, 3. Special mattresses, 4. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug 5. Muscle relaxants, 6. Manual therapy and massage, 7. Reflexotherapy, 8. Traction, 9. Physical exercises, 10. Training programs in patient care, 11. Psychological correction, 12. Surgical decompression. Physical exercises are used for restoring normal muscle tension, improvement of lymph and blood circulation in a disease segment, toning up muscles of back, abdominals, and elimination of fault in posture. The initial period of exercise therapy focuses on loosening up muscles being in protective tension and improvement of anatomic relations of spinal structures thus contributing to decrease of pain syndrome. The ultimate goal of the course is spine stability increase. Spine traction is an important method of pathogenetic therapy of pain syndrome (Y. Popelyansky, 1962, B. Dubnov, 1967, E. Salganik, T. Bashkina, 1971 and others). Treatment by traction method is usually conducted through: spine relief by intervertebral distance broadening, rippling muscle disease easing, intradisc pressure decreasing, intervertebral foramen height increasing, what leads to root decompression and edema fall, eliminating intervertebralis subluxation thus making decompressing effect. Anyhow many experts suggest that the majority of methods provoke only temporary ease of pain syndrome, but do not solve the problem itself. 3 year long survey studied efficiency of dynamic and isometric exercises as means of degenerative disk disease prophylaxis. All 80 persons took part in it, mostly schoolchildren of 12-17 years old. The bulk of 45-58 year group, according to specialists’ data, had been suffering from degenerative disc disease from 7 to 15 years. Competitive sports players (20-30 year group) had had various injuries accompanied with pain syndrome in spinal zone upon physical exercising. The majority of schoolchildren of 12-17 year old participating in the pedagogical experiment had round shoulders, scoliosis, etc. The elaborated training methods included exercises for strengthening body muscles alternating with constant spine traction. Hyperextension (facedown thigh lying, legs fixed, bending of the body and trunk extension) was used as a key measure to strengthen muscles of back. The training involved as dynamic as isometric exercises. Usually training program included not more than 4 exercises each of them done the following way: first week – 2 times by 10-15 repetitions, second week – 3 times by 10-15 repetitions, third week – 3-4 times by 10-15 repetitions. The load was increasing gradually within 3 weeks (trainings were held once on 2 days). First trainings were devoted to no weight hyperextension: firstly 5-7 repetitions dynamically, then holding for 10-15 seconds body parallel to the floor, then again 5-8 dynamic repetitions. After 3 trainings (from the second week) the load was gradually enhanced to 5-10kg. The elderly were still doing no weight hyperextension in dynamic mode, but carried out 10-15 seconds body holding with the specified weight. Upon completing a set of exercises everybody had to do bar hang of 5-10 seconds duration. The exercise complex also included exercises for abdominals, muscle of back, lateral exercises. The sample program of week strength training (for degenerative disc disease prophylaxis) is shown below. It should be pointed out that all experiment participants were doing other exercise sets as well with weight aimed at development of different groups of muscles: leg, arm muscles, pectoral and deltoid muscles. Day 1 Warm up: 5min stationary cycling, calisthenics, flexibility development exercises. 1. Bench lying, leg raises – 3 * 10 2. Hyperextensions – 3 * 10 3. Sitting, vertical row to chest (lats exercise) – 3 * 8-12 4. Standing, bending sideways with a dumbbell – 3 * 8-12 5. Gymnastics – 10min. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Day 2 Warm up: 5min stationary cycling, calisthenics, flexibility development exercises. Sitting, body bending on a machine – 3 * 8-15, no weight Straight-leg deadlift (back) – 3 * 8-10 Standing, bending sideways with a dumbbell – 3 * 8-15 Hyperextensions – 3 * 10-15 Sitting, horizontal row (lats exercise) – 3 * 8-15 Gymnastics – 10min. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Day 3 Warm up: 5min stationary cycling, calisthenics, flexibility development exercises. From bar hang, knee chip-ups to chest – 3 * 5-15 Hyperextensions – 3 * 10-15 Standing, barbell on shoulders bending – 3 * 5-8 Sitting, vertical row to chest (lats exercise) – 3 * 8-12 Standing, bending sideways with a dumbbell – 3 * 8-15 Gymnastics – 10min. The survey results have indicated that almost all experiment participants experienced rapid decrease of pain syndrome, flexibility and lumbar-spine mobility increased significantly. Before the course the majority of patients of above 40 years group said that forward bend produced acute back pain. After 3 week training by the program the bulk indicated that pain syndrome had gone. Flexibility, especially active flexibility, of all participants improved. Participating schoolchildren improved their posture. Almost all pupils indicated significant improvement of well-being (insomnia, anxiety presentations, mood swings, etc decreased or disappeared) and increase of dynamic and static endurance, decrease of spine pain syndrome recurring after 6-8 school classes. Every participant upon completion of the course received a specially elaborated memo bearing description of not only preventive measures, but also exercise sets for home training. What is more the majority of them repeated the course every 6-12 months. Judging from the survey results I can make a conclusion that the proposed methods of degenerative disc disease prophylaxis and dynamic and isometric exercises, in particular, are the absolute efficient. The conducted survey has shown that this activities are promising and thus have to be continued attracting experts of health care and other fields for a comprehensive evaluation of dynamic and isometric exercises as means of degenerative disc disease prophylaxis and elaboration of specific recommendations. Health of our children is our common concern S. Ilyinova, Principal, Chupinskaya Secondary Comprehensive School, G. Pevtsova, PE teacher, Chupinskaya Secondary Comprehensive School “The only beauty that I know I know is health”, H. Heine Education is a necessary, almost vital element of social-cultural and economic development of a country. Thus one of the objectives of education is physical, psychological and moral well-being of younger degeneration. The School Development Program stipulates principle of preservation of pupils’ physical and mental health and use of health saving technologies as priority measure. In 2007 the school participated in the Republican Contest of Comprehensive Institutions introducing innovative educational programs. It was awarded the First Certificate and received state budgetary aid from the Republic of Karelia. Elaboration of health improving measures is an important part of school work. The school has set up a goal of pupils’ health preservation thus creating a mechanism of health saving environment formation. This concerns organization of the educational process and study day regimen, abiding sanitary norms and hygienic requirements to study conditions, provision of motor activity, proper medical services, and meals. Efficient and simple methods of health improvement are utilized at our school; these are vitamin therapy, iodized salt use, nearsightedness prevention by special eye exercises during a class, systematic change of pupils’ sitting order, illumination and ventilation control, wet cleaning, correct furniture arrangement. Proper motor activity amount is provided by PE classes, health-improving warm-ups and PT breaks in the first part of a day, participating sport clubs. Diagnostics of schoolchildren health status is carried out by school medical assistant and specialists of Chupa out-patient department. In-depth medical examination ensure comprehensive analysis of organs and systems condition, estimate a pupil’s individual development, determine type of a group for PE classes and further conduct monitoring of children health. Acquisition of skills a schoolchild should possess is of paramount importance for health saving environment functioning. So a range of activities aimed at combating smoking, preventing alcohol and drug abuse, venereal and infectious diseases. The “Health” program embraces and coordinates the work of the pedagogical staff on pupils’ healthy lifestyle promotion. Family of a child play an important role in this activity. The comprehensive “Health” program unites efforts of teachers, administrators, school medical assistant, pedagogue-psychologist, pupils themselves in supporting healthy lifestyle and children physical development. The goal of the program is to determine reasonable measures for preserving and improving health of schoolchildren, creating pupils favorable attitude towards healthy lifestyle as a key point for achieving success. Central objectives of the program are the following: Formation of pupils conscious attitude towards their physical and mental well-being; Formation of key social skills contributing to successful social adaptation and prevention of bad habits; Promotion of healthy lifestyle, broadening pupils’ outlook in sport and physical training. Participants of the program are: Pupils; Class supervisors; Subject teachers; School medical assistant; Pediatrist; School specialists (pedagogue-psychologist, social pedagogue). The objectives of the pedagogical staff are: 1. To create conditions for preservation of physical and mental health of pupils; 2. To form negative attitude to bad habits; 3. To develop environmental awareness; 4. To form sport-recreational system; 5. To advance field trips; 6. Master new forms of work with schoolchildren’s parents for involving them into the process of addressing the problems specified. Health saving pedagogy is not an alternative to all other systems and approaches. Its main distinction is competent care of pupils’ health as a central feature of the educational process. Regular physical training assists in preventing many diseases, fruitful work, interesting life. Physical education is obligatory not only for pupils’ acquiring motor experience but also formation of a persons’ motor activity foundation. Regular PE classes are conducted twice a week in line with v. Lyah methods implying that pupils already have basics of physical culture compounded of sound health, proper physical development, reasonable level of motor abilities, physical training skills and knowledge. In you school we teach pupils physical exercises within the system of health-improving fitness aimed at increase of body functional systems’ resources. Physical exercises of the system are divided into several groups: a. Various traditional aerobic exercises, b. Alternating continuous (stream) gymnastic exercises, c. Strength exercises, d. Relaxation and recreation exercises (for active rest and general relaxation, breathing exercises, etc). Valeological issues have been introduced partly to different school subjects in particular Life Safety. Study materials contain crucial data on health saving needed for everybody. Key term in valeology is harmony. Class supervisor collaborates with pupils also via valeological breaks, or short conversations aimed at formation of positive attitude towards one’s health and useful health saving habits. Our school participated in the “Evaluation and introduction of drug prevention model in pilot comprehensive schools” project. Our school elaborated the Program of drug prevention “Future without drugs”. The school carries out a range of mass events: Health Marathons, sports events, contests like the Best Sport Class, the Healthiest Class, Athlete of the Year, etc. Our schoolchildren perform successfully in School Olympics of the Loukhi district. In 2010 school team took the 3rd position in Ski Race within the Republican School Olympics. Sports events like “Me and my folks are sporty!”, when pupils and their parents participate joint competitions, journeys on foot, etc, have become a good tradition. An old saying reads “Let your doctors be these three: easy going manner, comfort and life confidence”, this is to be facilitated by healthy life style, physical training and sport. Basic techniques used for development of personality of students whose major is not physical training. C. Ivankov, S. Litvinov, Moscow City Pedagogical University, city of Moscow Nowadays the term “the professional development of personality” of students whose major is not physical training is often used in the teaching-methodological aids. It’s important to notice that one of the criteria of development for a person is the display of his or her personal qualities during physical training. Physical training and sport play important role in the development of a future specialist. Besides, they are the significant means for achieving goals. Different kinds of physical training might be demanded for achieving goals in other spheres of life by a future specialist. Physical training and sport give an opportunity to students not only to develop their physical qualities, but also such kinds of qualities as intellectual, moral, aesthetic, social and psychological. That’s why it’s so important to take age and individual characteristics of students into consideration. Physical education influences also the social status of a person. Breaking the personal development into stages is one of the serious problems of higher education. It consists of three stages: 1.career choice, 2. shaping professional skills and traits of character of a specialist, 3. aiming at self-development and self-improvement. It’s necessary to point out, that low level of physical education and the lack of awareness of the physical culture as a value prevents students from an adequate attitude to their health and the development of their physical qualities. As consequences, graduates that don’t get some knowledge can’t be professionally developed in a proper way. During PE lessons professional development of students whose major is not physical training is based on educational and personal development. And every student has an opportunity to display his or her aiming at individualization and self-improvement. In this case, individualization is work that is aimed at development of the personality of a student and that is connected with personal improvement. And the improvement goes along with getting knowledge about physical training and sport, about modern society, besides, it is bounded with self searching. Staging of a person forming depends on the aims of a particular student. Rating as a form of complex assessment of students’ results is of great importance. It consists of 4 components: 1. attendance, 2. evaluation of the quality of students’ unassisted work (a report, an essay) in a form of rating, 3. participation in sport activities that the department organizes, 4. rating of students’ physical skills. Tests for checking of students’ physical skills must meet some requirements such as practicality and economy; also, they shouldn’t take a lot of time for preparing and holding. As a result, tests are to be easy to interpret and interesting for students. Adoption of this system of assessment will solve the following problems: 1. The development of physical training as an educational process. 2. The motivation rise. 3. The improvement of unassisted students’ work. 4. The problem of an objective grade. To solve problems of higher education, that the students whose major is not physical training get, we should use information technologies at PE lessons that is not widely-spread nowadays. The using of information technologies includes: a preparation for lessons, an educational process, control, research and writing learning aids. Science-proven organization of an educational process at PE lessons plays important role in the professional forming of a student. Nowadays using of exercises and tests, informational technologies and rating as a form of assessment is the prerequisite for the professional forming of the students. References 1. Бальсевич В.К., Лубышева Л.И. Концепция информационно образовательной компании по развертыванию национальной системы спортивного ориентированного физического воспитания обучающихся в общеобразовательных школах Российской Федерации // Теория и практика физической культуры. – 2003. – № 4. – С.11-16. 2. Загревская А.И. Рейтинговая система оценки качества образования по физической культуре // Теория и практика физической культуры.2007.-№ 3.– С.9–14. 3. Сырвачёва И.С. Информационно-аналитическая система оценки качества образовательной деятельности по дисциплине «Физическая культура» // Физическая культура: воспитание, образование, тренировка. – 2009. - №1, - С.68 – 71. 4. Ильин Г.А. Психолого-педагогические основы профессионализации личности // Ориентир. -№4. – 2006. – С. 24-38. 5. Левитан К.М. Личность педагога: становление и развитие. – Саратов, 1991. School Physical Education in France Claude Jouber, La Rochelle, France We, the Frenchmen, are followers of the Latin saying “mens sana in corpora sano” (a spund mind in a sound body). Anyway this approach has not always been the priority, but only since 1936 when the Government of the Socialist party headed by Leon Blum and the People’s Front introduced pay leaves, attitude towards sports has changed. Nowadays sports are very popular in France; moreover they are supported by the government caring about nation health and by means of social insurance. In later years certain health problems have exacerbated naming extra weight of the younger generation, ageing of population. These have been caused by increased time of watching TV, eating unbalanced “convenience food”, use of new communication technologies, multiple stress factors. Physical Education at school. Physical education at a French school is based on the age of pupils. There are no any particular methods of PE and specially trained teachers for carrying our physical education with junior children (kindergarten from 3 to 6 years old and primary school from 6 to 10/11 years old). Primary school teachers are responsible for physical education of pupils. This practice means that if a teacher him/herself is engaged in sports, he/she attracts children to this activity. But if he/she favors “intellectual” classes, schoolchildren are not much involved in sport activities or even not involved at all. Kindergarten and primary school curricular stipulate equal share of time for sports and arts. Even though teachers tend to opt for painting or singing, but when it comes to motor development they leave pupils on their own with balls. Physical education teacher as a separate post appears only in the system of secondary education, starting from the Collège – from 6th to 3rd grade (in France the numbering is in reverse order) and further in the Lycée – from 2nd to Terminale (preparatory grade for passing Bachelor entry exams) grade. At the Collège: A PE teacher works 5 hours per week in 6th and 5th grades and 3 hours per week in 4th and 3rd grades. Notably for the first time teachers of more “intellectual” subjects did not take PE teachers seriously, but now the situation has changed. The truth is that physical activity of a pupil is often an element “restoring the balance”, eliminating such incidents of behavior as violent acts. Sports become a type of regulator of behavior: a child loosens up and gets positive motivation, stress decreases, opportunity of success increases. A PE teacher is able to view a schoolchild from a bit another point of view that teachers of academic subjects. He/she notices peculiarities of conduct in a group, a community and personal characteristics. At the Lycée: A PE teacher has the same status as other teachers, because PE can be chosen as an examination with “2” coefficient for entering Bachelor degree studies. I should emphasize that some pupils succeeded in Bachelor exams thanks to a mark for PE. Since introduction of PE exam parents’ attitude towards this subject has changed a lot. Specific scientifically based program are used since 2nd grade for preparing a pupil for the exam. These programs involve performing various kinds of sports (group and individual): handball, basketball, gymnastics, athletics, tennis, swimming, yachting. Parents watch carefully progress of their child in physical training, as credits earned in PE can compensate for subjects difficult for a pupil. The Minister of National Education Luc Chatel is engaged in elaborating a new reform. According to the central idea of the reform (presumably it is to start in September 2010) approximately 100 French Lycées will devote after-lunch time to sport activities. The President N. Sarkozy has assured that he believes in “educational values of sports”, so prelaunch time is to be for academic subjects while after lunch – culture and sports. The Ministry of Education does not supervise sport activities by networks of sport clubs and associations. This choice is up to a child and nothing is obligatory. Boys mostly choose football, rugby or handball, in brief ball games. Girls opt for gymnastics, dancing, horseriding. The choice can be determined by living conditions or where a pupil lives – in a city, in mountains, by the sea. Sport activities in clubs and associations have the reverse side: it is easy to start exercising, but soon a child is to compete wit others, he/.she has to constantly advance achievements. The training occupies more and more time. Injuries, incidents happen. When a high level of sportsmanship is achieved, doping becomes an inherent part of further progress. If only the goal of sport activities could be reaching of equilibrium between physical and moral aspects of life, harmony, well-being and freedom. But sport clubs and associations function thanks to their champions. Otherwise they would not gain any financing. Financial aspect of sport activities depend on many factors: where a club is situated – in a big city or a small village, what equipment it has, etc. Anyway parents of little athletes bear all the expenses. Training of high profile athletes: Sports elite is formed in two ways: - Within the frames of national Education system – sport sections (usually in Lycées). - “Poles of France and hopes”. School sport sections provide an opportunity for young athletes, selected by National Leagues in their events, continue school study adjusting the schedule to requirements of this particular kind of sports. In La Rochelle there is a section which has helped many its athletes to achieve the rank of national and Olympic champions. “Poles of France and hopes” is continuation of sport section at a higher level – for the “Elite” category (1625 years old). Athletes holding national and international awards fall into this group. All the activities of this group is specifically equipped and supervised. The Government and local authorities control a broad network of sport institutions and associations. Thanks to this system almost every person has an access to sport activities. Every community has its own sports gym, where clubs and association carry out various sport activities. If a community is too small, it is united with other communities. Communal budget holders are aware of how much money are to be allocated to sports in order to meet needs of the voters in these activities. That’s why sports element is usually significant. As an example I would like to tell about most popular sports among La Rochelle residents: - Yachting with our international champions and Olympic champions, as well as within traditional regatta which have excellent reputation, - “Rupella” basketball club (2nd national division), - Rugby with “Stad Rochle” (the club is in the list of 14 best French clubs who have own stadium), - November marathon (the second in France), - Swimming with “Canal Rochle” (regional level competitions). Sport life of La Rochelle involves not only excellent professionals (teachers, trainers, instructors), sports provides employment for many people: administrators, managers, businessmen, plus people engaged in organization of active leisure (entertainment parks, recreation facilities). Among entities attracting tourists La Rochelle and our Department of Coastal Charente occupy the third place in France after Paris and Mont Sant-Michelle. This is the example how sports and active leisure can become important factors of regional development. Alcohol and the youth V. Kalabin, T. Kalabina, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Fighting alcohol abuse is a crucial social and medical goal of any state. Even small amounts of alcohol can be the reasons for significant troubles: injuries, accidents, family disruptions, reproductive disorders, loss of ethical values thus as a consequence endangering national security. More and more young people are getting abused with drinking beer. As in public opinion beer is not almost alcohol, but it is cool. Need to have a drink of beer does not provoke any serious concern among the youth, as need for drinking vodka, for example. Beer abuse progresses more subtly, than vodka abuse, but its consequences are much more serious. Developing gradually it transforms into beer alcoholism. Beer drinking subculture leads to formation of an addiction what may result in degradation of the person and whole generations. Beer alcoholism afflicts brain cells more severely than vodka, thus leading to intellectual and mental disorders. Beer alcoholism forms a particular lifestyle with its rituals and habits. In this respect drinking beer can be compared to smoking: a beer alcoholic finds it extremely difficult to get rid of a habitual bottle, as a smoker — of pack of cigarettes. Moreover beer is affordable and available to all. Raising students’ awareness on consequences of drinking alcohol and its social impact is a crucial matter. Success of preventive work among schoolchildren and students depends on acute determination of prevalence of drinking beer among them. Students of the Karelian State pedagogical Academy, 54 students of 4th years of the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics (FPM) and 56 students of 3rd year of the Faculty of Physical Culture (FPC), have taken part in a survey. Despite the fact that 100 % of polled consider beer an alcohol drink and recognize all the health hazard provoked by it, it is the most popular alcohol drink among the students. The majority considers possible drinking alcohol “for the company” (FPM - 57 %, FPC - 51 %). Almost two thirds of polled consider drinking alcohol at weekends possible (FPM - 60 %, FPC - 61 %). By the age of 14 about half of polled had already tasted alcohol, the majority had done it with friends. Students of FPM of KSPA drink alcohol more often than students of FPC. This is presumably linked with doing sports and sognificant physical activity. Students of FPC are also more informed about the influence of alcohol on health, they know consequences of alcoholism. Students consider family to be a central factor influencing a person’s attitude to alcohol; a full family makes it better. It can be pointed out as a positive fact that the majority of the polled have learnt about harmful impact of alcohol from parents (FPM — 41 %, FPC - 70 %). Students are well informed about the link between alcohol abuse and rise in crime (FPM – 92.8 %, FPC -94.4 %). About one third of students answered positively the question on compatibility of alcohol and sports (FPM – 41.4 %, FPC - 37 %). The majority said that the alcohol is a factor conducing contagion with sexually transmitted diseases and HIV/AIDS (FPM - 71.4 %, FPC - 67 %). All respondents also realize the threat alcohol bears to offsprings (FPM and FPC – 100 % of replies). Last year trend is obvious: more and more students give up drinking alcohol completely, proximately 15% of the polled. 92 % of the polled consider it necessary to inform children on danger of alcohol. As the state is fighting against drug abuse a lot nowadays, alcohol abuse is neglected. So we see a lot of beer advertisements and its great consumption. Beer alcoholism is a problem frequently addressed by narcologists these days. More and more young people become addicted to beer. Anti-drugs campaign attracts a lot of attention what favors alcohol manufacturers. The results of the survey have shown that even among students of the higher pedagogical educational institution, the majority considers it possible to drink alcohol, beer in particular, pretty regularly. Therefore this problem needs its further addressing, organizing and carrying out anti-alcohol work with youth. Physical condition peculiarities of middle school age mentally retarded pupils V. Kalabin, M. Karpovich, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Mark Mark Mark Mark The data of clinical psychology prove that nowadays one of the most wide-spread forms of anomalies of the psyche in early ontogenesis is mental retardation. The number of mentally retarded children is increasing, that is why researchers are becoming more and more interested in the problem. Mental retardation is a kind of dysontogenesis which implies delayed development, and light intellectual impairment. Mentally retarded children are physically retarded as well. Musculation underdevelopment, muscular and vascular tension deficiency, and growth inhibition are intrinsic to such children. School has to correct the defects a child has. Lots of specialists believe that physical education lessons not only help to overcome mentally retarded children’s physical defects, but also reduce difficulties in mathematic education, cognitive, speech and sensory development. This work is devoted to defining of middle school aged pupils’ level of physical condition and finding out the differences in physical condition of mentally retarded children and ordinary ones. The research was done on the base of School #14, of the city of Petrozavodsk, in a standard sports hall. 23 pupils took part in the experiment: 7 mentally retarded pupils (grade 9G) and 16 ordinary pupils (grade 9A). To evaluate pupils’ level of physical condition (physical alertness, alertness&strength, tolerance) ordinary tests were used: 30/60/1000 m races and a standing long-jump. The results were processed with the help of mathematic statistics methods. Arithmetic mean value and Student’s validity coefficient were estimated. The research consisted of three stages: 1. preparation; 2. organization, technical and methodical support of control tests performing, record sheet completing; 3. mathematic processing of the results and analyzing. The results show that ordinary pupils’ level of physical condition is higher than mentally retarded pupils’ one. The difference is significant: Mean value Mean value of Mean value of Mean value of a of 30 m race 60 m race 1000 m race standing longjump Mentally 5.0 sec 3 9.6 sec 3 284 sec 2 204 sm 5 retarded pupils Ordinary 4.8 sec 4 9.2 sec 4 248 sec 4 208 sm 5 pupils So, ordinary pupils’ results are the following: alertness&strength – “5”, physical alertness – “4”, tolerance – “4”, while mentally retarded pupils’ results are: alertness&strength – “5”, physical alertness – “3”, tolerance – “2”. The difference in levels of physical condition must be taken into consideration while planning the work on physical education with mentally retarded pupils. The choice of the most effective means and methods of conducting a lesson with reference to mentally retarded pupils’ individual peculiarities implies correction and coping with defects a pupil might have. Comparative study of physical health level of the 5th and the 6th grade pupils engaged and not engaged in sport activities O. Kapustkina, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Diseases of cardio-vascular and musculoskeletal systems are on the rise, what is to a greater extent predetermined by insufficient motor activity accompanied by poor environmental conditions and imbalanced nutrition, as well as unawareness of health preservation and disease prevention issues. One of priorities of educational institutions work is provision of improved and increased motor activity of pupils, holding extra-curricular fitness and sport events, promotion of healthy lifestyle. Central goal of a school is prepare a child, an adolescent for an individual life giving him/her all the necessary skills. The issue of physical (somatic) health of children has always bothered parents and teachers. Within a school study period the number of absolutely healthy children decreases in 4-5 times, particularly in 4-5 grades when pubescence and increased educational load coincide. High intensity of school study, insufficient motor activity result in rapid decrease of emotional and mental condition and work capacity of pupils, increase of anxiety level. Nowadays demographic situation in the Republic of Karelia is negative. It is proved by worsening physical health of population, increase of alcohol abuse, smoking and drug abuse particularly among youth. In the Republic of Karelia the share of people engaged in sport activities or physical training accounts for 13.4% (101 thousand men) out of total population, while in economically developed countries this figure amounts to 40-60% (A. Voronov, 2008). Physical exercises play an important role in preservation and promotion of health of younger generation, ensuring high labor capacity. Researches of different authors prove that reasonable physical load accompanied with balanced nutrition and healthy lifestyle is the most efficient way of preventing many diseases and prolonging life expectancy (N. Amosov, 1987, A. Agadzhanyan, 1989, R. Motylyanskaya, 1990, Matveev, 1991, V. Gnevushev, 2000, V. Luk’yanenko, 2001 and others). The objective of the present research is to determine an opportunity to increase the number of PE classes and their influence on schoolchildren physical health improvement. For achieving this objective the analysis of physical health of 5-6 grade pupils was conducted (in Secondary Comprehensive School #14 of the city of Petrozavodsk where since 1982 3 additional classes of PE have been introduced to curriculum. These classes, each 45 minutes long, focus on track and field exercises). Track and field exercises contribute to comprehensive physical development, health promotion. Popularity of track and field is determined by its affordability and a wide range of exercises, easy methods, possibility to change load and train all year long. The survey of physical (somatic) health was held twice a year. It also embraced parallel study groups who had no additional PE classes for collecting control figures. Express estimation was carried out by pretty simple indicators available for any user and not requiring sophisticated diagnostic equipment. This complex program includes 5 morphofunctional indexes (of Ketle, Robinson, Skibinsky, Shepovalova, Rufie) related to level of adaptive-energetic potential of a person. Apart from general estimation of physical health the program enables evaluating of every indicator and index separately, determine weaknesses of s pupil’s body and give personal recommendations based on these estimations. The survey results have indicated (pic1) the following figures of physical health. Boys from sport class groups: 0% - low physical health level, 16% - below the average, 5% - average, 31% - above the average, 0% - of high level. Boys from control class group: 29% - low physical health, 33% - below the average, 28.5% average, 9.5% - above the average, 0% - high level. Pic1. Physical health of 10-12 year old boys The same situation is with girls. (pic2) Girls from sport class group: 12.5% - low physical health, 6% - below the average, 69% - average, 12.5% above the average, 0% - high level. Girls from control class group: 20% - low level, 27% - below the average, 53% - average, 0% - above the average and higher. Pic2. Physical health of 10-12 year old girls. The results of the research let us deduce that the level of physical health who have additional PE classes is higher than of those 5-6 grade pupils who have standard curriculum. More physical activity and greater load is recommended to children with low indicators in order to harmonize their development and improve energetic potential of a body. The results of the present research coincides with point of view of many authors that motor activity is one of the key factors of 10-12 year old children health lifestyle formation. Schoolchildren physical education at a sports ground V. Kayumova Physical education at a sports ground is an inherent element of physical education system. It is focused on children health improvement and tempering, development of their vital physical qualities and skills, fostering pupils’ interest to and habits of everyday physical exercising, formation of sanitary-hygienic and organizational skills, etc. Physical education at a sports ground bears own specific features which should be considered while organizing fitness and sport events. These are limited duration of a class at a sports ground, different age and health status, physical development and alertness of pupils, as well as more opportunities for active outdoor games, other kinds of sports. Effective tempering of children can be achieved only at a sports ground. All fitness and sport events are conducted taking into consideration age, health status, physical development and alertness of children. These events are to meet pupils’ needs and interests, promote development of their initiative and independence what are key principles of work at a sports ground. Successful physical education at a sports ground is implemented only upon active participation of a teacher. Here I propose a program of a summer event called “Runner Day”. This event can be organized in any school by PE teachers with senior schoolchildren as volunteers. The Runner Day scenario Preparation. 1. To prepare question related to the World Environment Day and A. Pushkin birthday: a. What is the day today? b. Who reads a poem by A. Pushkin? c. What fairy tales were written by A. Pushkin? 2. To prepare a venue for a competition 3. To bake a sweet award-surprise 4. To prepare indexes to direct where the award is hidden 5. To prepare costumes for a fairy godmother, angry grandpa. Holding an event. 1. Forming of participants, welcoming address, announcing the program, 2. Selecting children by age, 3. Race of preschoolers, 4. Race of 1-3 grade pupils, 5. Race of middle age children, 6. Game “Award-Surprise Stealing”, 7. Forming and awarding winners. The scenario may include sport games. In our school we have been using a plot of stealing the awardsurprise from a “fairy godmother” by an “angry grandpa”. “Spies” selected from best runners, have to guided by indexes find the award. In order to get indexes children had to fulfil particular tasks: answer questions (related to birthday of A. Pushkin (June, 6) as the Runner day was held at the beginning of June), take part in a race, do press-ups and other exercises. Upon awarding winners all the participants of the event get sweet award. Student Sports Union R. Kemza, N. Kemza, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Student sports in Russia has more than a hundred year history. Its establishing went through several stages. Contemporary stage, started in connection with the period of reforming of social foundations and economy transition to market relations, is characterized by appearing of new tasks in higher school physical education aimed not only at improvement of students physical abilities but at stimulation their interest to physical culture and sports, elaboration of values of healthy lifestyle, where physical activity is a necessary condition. In October 1993 by the initiative of State Committee on Sports, Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation and the Olympic Committee of the Russian Federation the Russian student sports union (RSSU) was established which continued activities of the All-Soviet Union Volunteer sport community “Burevestnik” discharged in 1987. The major goal of RSSU is rendering assistance to the government in youth policy strategy implementation by effective management of student sports system in the Russian Federation and development of international cooperation in the sphere. General partners of RSSU are Federal Agency on Physical Culture and Sports, Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, Olympic Committee of the Russian Federation, national unions on sports, Russian Rectors Union, Russian Students Union. Vigorous activity is being carried out to create departments of RSSU in districts and regions of Russia. We should mention the role of executive bodies in the sphere of physical culture and sports of the subjects of the Russian Federation in developing and promotion of student sports. Especially active policy is being conducted by the Government bodies of Moscow, Saint-Petersburg and the Republic of Tatarstan. RSSU unites sport clubs and organizations of more than 700 higher and 2500 secondary educational institutions in the country. Currently the Union cooperates with 15 student leagues and sports federations. About 10 thousand specialists hold regular lessons on physical culture and sports with students. In higher educational institutions more than 60 sports are being represented, the most popular of them are badminton, basketball, boxing, gymnastic, skiing, track-and-field, swimming, several combat sports, fencing, football, table tennis, chess. Since 1994 RSSU holds massive competitions on these and many other sports for students – Russian Championships among students. All-Russia Universiade-2007 included 75 sport events held in different cities and regions of the country. The program of competitions consisted of 52 sports. High skills of participants of student competitions are testified by registered in an unbiased manner results at the level of national expansion teams. Each competition became a real triumph of youth, sport and health. Since 1995 Russian students – sportsmen have successfully performed at World Universiade and in unofficial team classification they steadily enter the top three teams. In summer 2009 in Belgrade the XXV World summer Universiade was held. July 5, 2009 a student from the Karelian State Pedagogical University Alexandr Balandin won gold in exercises on the rings with total sum of points equaling to 15,675. It was the first gold won by the Russian national team at the Universiade. Except the Universiades theRussian national team defends the countries honor at the European and World Championships among students. Since 2004 3 world student championships in Russia, 3 scientific symposia have been held; from 2007 to 2008 2 world championships, 2 championships of Europe and 2 European cups among students have been carried out. One of the central projects in the sphere of student sports in Russia was nominating of the city of Kazan as a capital of the World Summer Universiade-2013. In may 2008 Kazan got the right to host this competition. Russian representatives actively participate in international sports organizations activities. The head of RSSU is a member of the executive committee of the International University Sports Federation and the European University Sports Association. In February 15, 2008 in Petrozavodsk a constituting conference on creating a sport union of the Republic of Karelia was held. During the conference a charter, a development program for student sports in the Republic were adopted. The participants of the conference elected executive committee of the Union and its president. The first competition held within the Union was a match meeting on weight-lifting between the students of the Petrozavodsk State University and the Karelian State Pedagogical University. In a hard-fought struggle the Petrozavodsk State University won. During 2008-2009 the Student Sports Union of the Republic of Karelia organized more than 20 sport competitions where 15 higher educational institutions took part. In May 27, 2009 the Student Sports Union of the Republic of Karelia work results were summarized. During the ceremony winners in 5 nominations were named: 1. Winners and awardees of student sport competitions, 2. Breakthrough of the year, 3. The best sport team, 4. The best coach-instructors 5. The most sport-oriented educational institution. The winners were awarded by a deputy Chairman of the State Committee on Physical Culture and Sports V. Filin, head of the Department of the Committee S. Malashev, Dean of the Faculty of Physical Culture of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy A. Voronov and by the President of the Union R. Kemza. The State Committee on Physical Culture and Sports provided all the competitions organized by the Student Sports Union of the Republic of Karelia with prizes for winners and awardees. The Student Sports Union of the Republic of Karelia was revived a year ago by the initiative of the State Committee on Physical Culture and Sports and the Faculty of Physical Culture of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy. It is headed by R. Kemza, a chairman of the Department of Sport Discipline of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy. He stated that during a year 20 sport competitions with participation of students from 15 educational institutions of the city were held; sport volleyball and basketball Leagues were revived, but the main point was that students had desire to do sports and coaches had a desire to train champions. Among 5 winners of the “Breakthrough of the year” there were 2 students from the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy – G. Potanin and E. Porygina. G. Potanin, a prizewinner of the competitions on weight-lifting, was awarded the title of Master of Sports. The best sport teams were three teams from the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy in five-a-side (the second rank among student teams in North-Western Federal District), female basketball team and female volleyball team, male basketball team from PetrSU and male volleyball team from the Petrozavodsk Railway College (PRC) (the winners in student volleyball and basketball leagues). Seven coaches A. Varlamov and V. Dement’ev (PRC), A. Samoilikov (Petrozavodsk Civil Engineering College), R. Matveev (Petrozavodsk Pedagogical College), V. Losev (Petrozavodsk River College), M. Krainov and O. Kruglova (Petrozavodsk Municipal Services College) were also awarded with diplomas for their work. The winners and awardees were congratulated by female gymnast from the Department of Rhythmic gymnastics of the Children Sports School #1, fitness aerobics team “Assorti” – prizewinners of 2008 Russian Championship among students, and by the “Northern region” breakdance crew. All speakers pointed out that student sports is promising, that the revived Students Union is a training pool of champions. Representatives of the State Committee promised to render support to sportsmen and wished them new records and victories. Comprehensive alertness of an athlete to achieve high sport results L. Kenareva, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Formation of a personality within sport activity is articulated in relation to practical need in psychological training of athletes. This problem was raised for the first time in 1956 at the First All-Union Conference on Sport Psychology by A. Lalayan in his report "On psychological training of athletes for a competition". Psychological training for an athlete personality formation has its own peculiarities. First of all, like all types of training (physical, technical, tactical, integrated) formation of personal qualities provides high quality training and psychological stability during competitions regardless any circumstances. Psychological process of formation and improvement of sports relevant personality traits and their underlying mental qualities has been considered by contemporary scientists G. Gorbunov (1986), Ukrainian psychologists G. Lozhkin, O. Silsenko (1992). Summarizing different approaches to this problem they have concluded that development of sports relevant personality traits and achievement of their stability makes a person able to perform tasks in full accordance with the professional skills (knowledge, skills and abilities). Another feature of the athlete characteristics’ formation is to develop qualities which provide high performance in a particular sport. Numerous studies of personal qualities contributing to success in sports show that athletes with different capabilities can achieve success. Leading scientists (N. Levitov, V. Myasischev, 1960) define human psychological phenomena and psychological readiness to compete by the following elements: - Self-confidence, - Striving for the achievement of competitive goals, victory aspirations; - Optimal level of emotional arousal; - High noise resistance; - Ability to control own actions, feelings, behavior. Thus readiness of an athlete to compete is determined by his willingness to maximum exertion of will and volitional effort in the process of competition, the existence and expression of personal and emotional qualities specific to competitive struggle. So we should point out a significant role of emotional and intellectual level of an athlete training. We can distinguish several stages of training for majorcompetition: - General psychological training involving formation and development of personal qualities and potential, - Special psychological training – formation of a complete willingness to participate in competitions aimed at maximizing physical, functional, technical and tactical abilities for sport achievement; - Correction of psychological readiness for a specific competitive stress. The most important stage of training is to create a comprehensive athlete's readiness to participate in competitions. It promotes development of skills, abilities and knowledge for efficient self-regulation in difficult conditions of a competitive struggle. They in their turn are the basis of personal qualities of an athlete and characterize potential psychological readiness. Some elite sport researchers suppose that functional readiness and efficiency of qualified athletes competitive actions are greatly affected not only by the use of various training facilities, but also the states of their performance readiness. In order to do this we must be able to analyze accurately the competitive conditions, particularly physical and mental stress, major motor qualities, specialized competitive action, commitment, and other moments that define successful accomplishment of own tasks. Thus a process of development and education of individual athlete's specific activity qualities is focused on efficient overcoming of physical and mental stress in order to achieve the highest sport results. . Importance of labor scientific management in saving health of physical education and sports institutions personnel Sh. Khubbiev, Russian State Pedagogical University named after A. Herzen, city of Saint-Petersburg The sphere of physical culture and sport (PhC&S) is undoubtedly socially important. Its material and spiritual values are popular in the modern society. Nowadays PhC&S functioning and development efficiency is being increasingly dependent on its organization and management. Sound organization and management of PC&S within the market economy can promote its progress or lead to stagnation or even recession. Certainly the society is interested in progress of PhC&S. That’s why the PhC&S institutions activities should be based on up-to-date organization theory and practice. The paramount importance here is attached to organizing and self-organizing of activities by personnel of PhC&S institutions, implying scientific management of labor (SML) of executives, their deputies, personnel of departments and agencies, teachers and students of PC&S educational institutions. Scientifically managed labor, sound communication system, management, education and sport-pedagogical activities are conditions of quality improvement of professional training of physical educators and their work in different PC&S institutions. Higher quality of educational institutions work can be enabled upon determination of a needed input of every personnel member and student into a final result of educational and sport-pedagogical activity. For these means SML mechanisms should be applied. The issue of SML in PhC is not a new one. K. Voronova (in 1974) and Sh. Hubbiev also addressed this issue in their dissertation theses. But in 80s of the 20th century this problem was neglected even though its importance is obvious. At present the solution of this problem is highly relevant. Unfortunately now there are no specific researches conducted on the matter within PC organizations modernization processes. Some aspects of SML in PhC are addressed in works of Russian and foreign authors. We have to admit that traditional approach to organization of educational, training and competitive activities of pedagogues and students is outdated. Applying of SML is to improve the situation. SML in PhC&S institutions can be defined as time and expansion regulation of content and human communications in educational, sport-pedagogical and competitive activities. Nowadays introduction of SML into PhC&S institutions activities are predetermined by a range of circumstances. Its introduction may promote health saving effect. 1. Human development principles are the basis for elaboration of SML directions ensuring systematic collaboration of all subjects of physical education and sport-pedagogical activity. According to I. Pavlov a human is a supreme product of nature, a sophisticated accurate self-regulating system. This point of I. Pavlov gained its articulation in the dissipative structures theory explaining selfregulation processes in complex systems (a human, nature, society). Self-organization programmed by nature is a mechanism of human biological and mental development. Educational and sportpedagogical activities are social phenomena complying with self-organization principles. So SML based self-organization conditions are needed for personnel efficient work in PhC&S institutions. SML regulated activities are based on principles of practicability and rationality, abiding by legal norms, resources saving, economic feasibility, time management and its efficiency, devolution of powers, work eurhythmy, healthful labor organization, devoting time also to self-education, personal development, personal health improvement, etc. so we can argue that SML contributes to health saving of personnel in line with principles of nature and social congruence. 2. Actors of PhC&S institutions are constantly formally and informally directly or indirectly collaborate. Result of their joint activity depends on labor organization, its content and communications, that is on SML. The anticipated health-improving effect of such a collaboration concerns socialpsychological factors and can be manifested in sympathies and antipathies. Relevant and precise addressed communication can contribute to social welfare, but unregulated communication – vice versa. SML creates conditions for social welfare, excluding for example emotional burnout syndrome. 3. All levels of organizational structure of a higher educational institution need SML, when a chief executive directly influences his/her deputies, heads of departments and agencies, and through them – teachers and students, and gets a feedback. This scheme enables in time informing of decisions made and controlling progress and implementation results, ensuring quality and efficiency of educational and sport-pedagogical activities. Successful functioning of different levels of a PhC&S institution’s structure creates potential for of mental and social health of executives, teachers and students. Their mental health stems from modes of thinking, concentration and memory, inner and moral aspiration to creativity, emotional stability, volitional and axiologicalmotivational attitudes to social conditions, common peace of mind, relevant behavior. Social health of personnel and students of PhC&S institutions affects personal qualities and characteristics harmonizing them with social needs, proper state of consciousness and mind, orientation to selffulfillment, conscious labor attitude, social acts of adaptation, creativity, mission, behavior, activity, live outlook. 4. Actors of physical education and sport-pedagogical activity should be aware that all the documents on decisions and orders regulate PhC&S institution functioning overlooking detailed time, place, content scheduling of every employee’s work. That’s why fulfillment of a program, a plan, an order requires actors’ organization and self-organization. This is impossible without proper SML system. Introduction of SML in PhC&S institutions favors to moral health contributing to forming of motivation and demands – values, convictions, attitudes and society behavioral motives, occupational choice, professional advancement, longevity, professional adaptation and work and study dependability, stress resistance and study and work safety. 5. Transmitted to lower organizational levels information should be detailed and relevant for use in educational and sport-pedagogical activities of personnel and students. The upward flow in information requires its processing at every administrative level for elaboration of decisions and actions. Introduction of SML in PhC&S institutions creates conditions for such information exchange and cohesion in educational and sport-pedagogical activities, minimizing unreasonable losses. As a result social, mental and physical health of educational and sport-pedagogical actors improves. 6. Introduction of SML is to contribute to stress decrease or avoidance, regulation of work and colleagues relations, all in all to mental well-being of educational and sport-pedagogical actors. 7. State policy on physical culture and sport is aimed at physical education quality and physical training improvement. Market conditions hinder spread of physical culture values and healthy lifestyle among the population. It is difficult to address these tasks without relevant SML system. Its introduction to PhC&S institutions can provide for planning of work, finding time resources for personal development and self-education, avoiding tension, overload and overfatigue, thus favoring social, mental, physical well-being of personnel and students. 8. Now PhC&S institutions are getting more state financing as well as non-budgetary investment in their development. So it is extremely important to use these funds and administer an institution efficiently, properly organize work of personnel and students life. 9. Market economy has complicated administration of PhC&S institutions multisided activities due to getting more freedom in choice of own development strategies, educational trends. Up-to-date education of specialists and sportsmen is impossible without SML introduction to decision making and implementation processes. It is worth pointing out that influence of SML on PhC&S educational and sport-pedagogical actors health saving is connected firstly with mental and social health, as well as with physical health. The aforesaid proves that SML introduction to PhC&S institutions bears not only administrative, but also health saving effect regarding all educational and sport-pedagogical actors. Degree of SML in such institutions depends to a greater extent on scientific organization of labor of a chief executive him/herself, on his/her commitment to scientific organization of educational and sport-pedagogical activities of subordinates and students. If these characteristics are adhered to then we can agree on a health saving orientation of this PhC&S institution policy. References: 1. Войнар Ю., Подготовка физкультурных кадров. Традиции, реалии, перспективы: Монография / Ю.Войнар [Текст]. – СПб. : РГПУ им. А.И. Герцена, 2000. – 228 с. 2. Пономарев Г.Н., Высшее профессиональное образование в области физической культуры: состояние, предпосылки и направления обновления: Монография / Г.Н.Пономарев [Текст]. – СПб. : Изд-во РГПУ им А.И. Герцена,2003. – 262 с. 3. Жолдак В.И., Кварталов В.А. Менеджмент спорта и туризма [Текст]. -М. : Советский спорт,2001.416. 4. Переверзин Н.И. Менеджмент спортивной организации : Учебное пособие – 2-е, перераб. и доп. [Текст]. – М. : «СпортАкадем Пресс,2002. 244 с. 5. Воронова К.А. Научная организация труда в аппарате областного (краевого, АССР) комитета по физической культуре и спорту : автореф. дис. ... канд. пед. наук / Воронова Клара Алексеевна; Гос. инт физ. культуры им. П. Ф. Лесгафта. - Л., 1974. - 21 с. 6. Теория и организация физической подготовки войск: учебник для курсантов ВИФК. – 6 изд. / Под ред. В.В. Миронова. - СПб. : ВИФК, 2006. – 594 с. 7. Щетинина А. Самоменеджмент тренера: http://lib.sportedu.ru/gettext.idc? txtid=425. 8. Коуинг: руководство для тренера и менеджера/С.Тор, Дж.Клиффорд [Текст].-СПб. :Питер,2004.204 с. 9. Жумабаев К.М., Камысбаева Д.К., Бакенов К.С., Умирбаев К.А. Физическая культура – залог здорового образа жизни: http://www.rusnauka.com/NPM_2006/Sport/1zhumabaev.doc.htmhttp://www.rusnauka.com/ NPM2006/Sport/1zhumabaev.doc. htm. 10.. И.Пригожин Самоорганизация в неравновесных системах: От диссипативных структур к упорядоченности через флуктуации [Текст]. - М. : Мир, 1979. – 512 с. 11. Психология здоровья: Учебник для вузов / Под ред. Г С. Никифорова. - СПб. : Питер,2006. - 607 с. 12. Реализация здоровьесберегающих образовательных технологий в учебном процессе http://www.orenipk. ru/kp/distant/ ped/ped/zdzb.htm 13. Васютенкова И.В. Социальное здоровье личности в поликультурной образовательной среде // Здоровье и образование: Материалы IV научно-практической межвузовской конференции/ отв. ред. Г.Е. Гун. – СПб. : ЛОИРО,2007. – 236 с. 14. В.Зорин. «Евразийская мудрость от а до Я», толковый словарь: http://terme.ru/ dictionary/470/word. 15. Колпина Л.В. Теоретико-методологические основы исследования социального здоровья личности. – М.: Изд-во СГУ, 2009. – 180 с. Track and field judging algorithm V. Kiselev, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Track and field judging is an important aspect of professional training of students of the Faulty of Physical Culture majoring in track and field. This is carried out within the following subjects: track and field, pedagogical fitness-sport advancement. At academic lectures students have to acquire specific judging knowledge: composition of a jury, duties of judges, and rules of basic track and field events. Students apply their academic knowledge at practical judging sets held at study trainings. Next stage of students’ training is carried out at pedagogical fitness-sport advancement classes, open classes, and during practical training in the Child-Adolescent Sports School #3 of the city of Petrozavodsk. Students are involved in judging competitions of an annual competition schedule of the Child-Adolescent Sports School #3. Students study judging technique in a classroom and at extra-class activities. In a classroom they acquire theoretical knowledge on rules and methods of judging, preparation of equipment, etc. during extra-class activities students acquire practical skills, participate in competitions judging. Here students may encounter difficulties in applying theoretical knowledge to practice. One of the trick a teacher may use in order to prepare a student for judging a competition can be charting by a student an algorithm of track and field judging. We see the algorithm as a sequence of actions of a judge while judging a competition. It is clearly visible that judge panel and every judge abide by a particular sequence of acts. For example, javelin judge panel firstly assesses three preliminary trials, then three final trials. Master judge approve trials by rising a white flag. An athlete makes a trial, a judge determines whether a trial is held correctly, and then measures a result. This algorithm is repeated at every trial. Such sequence of actions is defined by competition regulations and judging peculiarities of every track and field event. Judging algorithm is also affected by the level of a competition, sport facilities, number of judges and participants. Hence if a student is capable to picture to him/herself a sequence of a judge’s actions he/she can conclude a judging algorithm, thus making a shift from theoretical knowledge to practical skills. Before charting an algorithm a student has to study a competition judging sequence. He/she has to attend several competitions, watch thematic videos, define a composition of a jury and duties of every judge, discuss judging peculiarities. Then initial judging algorithm is charted, a student makes it jointly with a teacher. Firstly actions scheme of a master judge is charted. A sample algorithm is below. It is elaborated by 3rd year students of the Faculty of Physical Culture of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy. Master judge actions algorithm in javelin. Master judge «Начинаем соревнования» White flag sideward Trial Is a trial successful? «-» Red flag “NO” «+» White flag “YES” Result measuring Results announcing Then a clerk’s algorithm is charted. Clerk’s actions algorithm in javelin. Clerk Announcing of a participant’s trial Trial After 3 trials Is a trial successful? «-» «+» “Х” to score-sheet Determining finalists Writing down result 8 best results Ranking Algorithms of other judges actions are charted the same way. At this stage a teacher has to determine major mistake in actions sequence, make corrections and write additions to algorithms. For example, master judge’s algorithm is missing finals entry list checking. Clerk’s algorithm should be added with a point of changing trials sequence to an order from the worst score to the best one. A clerk has to define three awardees upon the final of a competition. A student may introduce his/her wishes to an algorithm, for example additions to judges’ actions by arrow lines, etc. Upon completion of personal algorithms of every judge a comprehensive judge panel’s algorithm is charted. A student has to combine separate charts into a single entity. 3rd year students make algorithms of sprint, long jump, high jump, javelin judging. While charting an algorithm a student analyses competition rules, pictures to him/herself judges actions, collaboration within a judge panel. Competition judging is made up of several stages: preliminary, competition judging itself and final. Algorithms presented above describe judge panel actions just within a competition stage. Hence it is possible to expand a chart and make more comprehensive algorithms including preliminary and final stages of judging. Basics of Tourism as a possible Physical Culture discipline content element arranged within a regional component of a curriculum E. Klochkova, Dagestan State Pedagogical University, city of Makhachkala The traditional approach to the use of tools and techniques of physical education, namely the use of model programs of physical culture in the classroom is not always sufficient to increase the functional capacity in children and effective development of basic motor abilities. Currently there is a process improvement programs for physical education students, developed its new kinds of sports, recreational and educational orientation [Y. Zheleznyak, E. Blekhman, L. Savinykh, 2002; E. Litvinov , M. Vilensky, GI fortune, 2004; B. Prokudin co-authored, 2003, 2006]. However existing publications on the use of means and methods of tourism at PE mainly relate to secondary school children and adults. Works on the foundations of physical education on the basis of tourism for the junior and middle school age on the lessons of physical culture are scarce. The efficiency of motor and functional training in the learning process can be significantly improved by streamlining procedures, using mainly means and methods of tourism. We have identified research tasks: experimental proof of the effectiveness of the developed technique of tourism on the physical education class with students of 3-6 grades of secondary schools. To solve the problems we used the following methods: the method of theoretical analysis and synthesis, teaching methods (teacher observation, teacher testing, teaching experiment), statistical methods. The study implemented in practice teaching students of a boarding school for orphans and children left without parental care in Makhachkala. The main work at the initial stage was to collect basic empirical pedagogical research, conducted in a boarding school for orphans and children left without parental care in Makhachkala. It was aimed at addressing the following objectives: to study baseline physical training, tourist knowledge and pedagogical experiment. In the pedagogical experiment 43 students 3-6 grades were attended. The study covered two groups control and experimental. In the control group there were 21 persons; and in the experimental group - 22 persons. In the control group PE lessons by the integrated program were conducted, which provides two lessons of physical education per week. In this group, we conducted anthropometric measurements, 2 times a year and organized the testing of physical skills and abilities. In the experimental group lessons were also by the program of state educational standards, 2 times a week, but with the use of tourism and tourist and local lore activities (games and exercises that do not require special expensive equipment). Assessment of results was performed using tests and measurements of anthropometric data. Activities provided for Weekend trips to the nearest natural area with the tourist relay races, festivals, tours, both in control and in the experimental groups. The experiment was composed exemplary program. This program implies a logical connection of two parts: basic and variative ones. Basic part was derived from a comprehensive program of physical education fir students 1-11klassov (2005 V. Lyakh, A. Zdanevich). The elective component of tourism is the author's design. The contents of this part of the materials on tourism in the form of partition is a special preparation of the "Fundamentals of tourist activity. A special part of the program developed and tested elements of the evaluation of the special physical and technical training, as well as the criterion requirements to the "pillars of tourism and guidance on training them. During the experiment was to record an increase in the number of children who had not suffered even once in relation to the frequently ill. And also to calculate the health index for the scheme proposed by the Laboratory "Theory and methodology of physical education" Institute of Physiology in the experimental and control groups. While the number of sick children in the experimental group decreased by 14.29%, in the control group at 9,13%, the number of students who had not suffered even once in the experimental group increased by 11,1%,and in the control group at 3, 29%. Health index in the experimental group for 20082009 proved to be 1,5 times higher than in the control group and for 2007-2008. During the teaching experiment, physical training the experimental group improved significantly compared to controls, as evidenced by the performance gains strength, endurance, agility and coordination abilities. Carried out study provides a basis to recognize the practical importance of the developed program and pedagogical experiment. Estimated distribution of teaching time for various types of program material physical education class in grades 3-6 Program chapters and 3 grade 4 grade 5 grade 6 grade topics Study hours 1. Basics Within every class 2. Physical activity types Gymnastics, acrobatics Track and field Race Active and sport games 3.Variative part Basics of tourism 4.Qualification requirements TOTAL: Totaling: 8 10 8 20 8 10 8 20 8 10 8 20 8 10 8 20 20 20 20 20 2 2 2 2 68 68 68 68 272 Tourism as the means of orphanages and boarding schools pupils’ social adaptation E. Klochkova, Dagestan State Pedagogical University, city of Makhachkala Physical training and sport are specific human activities, and their main task for a long time was healthy physical person education. At present a lot of specialists are trying to solve the problems, connected with the role of physical training in personality formation. And there is the question: how to transform physical training through pedagogical system. Modern process of personality formation is much more difficult, than traditionally based on didactic principles educational process. Initial adaptation is mostly important for every person when basic phycophysical and moral qualities are formed. Parents take superior position to their child, coming through the process of adaptation. According to Chunaev (1999), physical training appears to be the priority and value of a child’s life, it is one the opportunities of real adaptation in primary school, it is the means to enlarge the opportunity to learn languages, nature and other sciences, and also can and should become one of the main principles organizing a school. Different specialists work on this problem of adaptation of boarding schools pupils, and most means of this work are various kinds of labour education, discussions, during which there is no positive emotional disposition, also orphanages and boarding schools pupils’ consumer attitude is negative towards the outward things. The main question in this education is social adaptation demonstration, which shows following: limitation of communication with children of their age, limitation of contact room, reduced scope of information, absence of family. At the same time, as specialists think, child development goes in peculiar way when he has no family, and peculiar character traits are formed, and we can’t say they are better or worse, than the same ordinary child has, but they are different. One of the problems of personality formation at orphanages and boarding schools is communicative development. As a rule, it is expressed in two aspects: 1) “grown-up – children” communication – it is characterized with some mutilations, which show that, on one hand – children feel a need for attention and benevolence of grown-ups, positive contacts with them; and on the other hand – total dissatisfaction of these needs; very few contacts of grown-ups and children, reduction of personal treatment, their emotional deficiency and content uniformity, which mostly are directed to behavior regulations. 2) “children-children” communication – constant communication with one and the same group of children (they are mostly equal in their age or development, and they live in the same room, or area) do not have a positive influence on the “children-children” communication development (because the communication develops as in a family). At the same time, primary pupils of orphanages and boarding schools are distinguished from the children of their age by intellectual impairment and voluntary behavior underdevelopment. Sport and fitness activity supposes such situations, where traits character traits of orphanage and boarding schools pupils are critically shown; for example, greater proneness to conflicts and aggression. But for all that, some of the main targets of person development which require necessary work are: selfactualization, sustainable self-acceptance, needs for self-study, increase of self-assertion. The main factor for any pedagogical influence increase to children is motivation. Nowadays all the job with children - orphanage and boarding schools pupils – is held according to state programs, adapted to individual psycophysiological characteristics of such children. This job analysis displays that specialists (social workers, psychologists, pedagogues) show their worth by fulfilling specific tasks. But for all that, they do not solve the problem of social adaptation of pupils. But tourism and regional studies can eliminate all these negative demonstrations. As senior specialist in children’s tourism Konstantinov (2002) thinks, various forms provide with comprehensive educational and health-improving tourism and regional study activities, tourism also has wide opportunities for children’s creativity, such as sport, scientific, artistic, technical, social and even pedagogical. Motor education, health promotion, receiving and consolidation of household skills while constructing “family life” and cooking, patriot formation with regional studies, learning the history of pupils’ region, ecological knowledge formation, communication increasing, development of socially significant skills – these are the main tasks of “Social adaptation orphanage and boarding schools pupils by means of tourism and regional studies”. Considerable practice working with orphanages and boarding schools pupils allows emphasizing main courses, which involve major part of pupils and continue for a long time. Some of the most efficient courses are “Homeland” All-Russia tourism regional movement and republican actions “Namus”, “The art from the deep ages”, “Vanishing villages”. Different activities allowed attracting 80% of pupils, everyone, in spite of their age and training, could see themselves needed in different fields. Teenagers took part in weekend or two-days journey on foot to picturesque historical places of Dagestan. The competition of pictures, photos and handicrafts contributed to pupils’ creativity development. Regional studies targets were solved by looking for secret places of untouched nature, communication with Caucasus people, and also contacting those people, who have talent making unique articles from metal (Kubachi goldsmiths). Without doubt, every tourist journey has large impact on emotional, cognitive, health-improving sphere of each child, but for orphanages and boarding schools pupils it is also a good practice, when they acquire communication skills, household skills while constructing “family life” and cooking, and increasing positive motivation. Tea is finished – there is much brier, thyme, John’s wood, raspberry and mint in the mountains; got soaked to the skin – good fire will help; a child on duty oversalted porridge – next time he will do it better. What do teenagers long for during their tourist journeys? We can find the answer to this question in pupils’ replies ( from Mahachkala boarding school and orphanage # 7 from town of Izarbash): During the tourist journey I have a rest, but I also have to work a lot… I would like to say, that the best memories about journeys are… sitting around the night bonfire and singing merry songs and playing the guitar…I would like to learn to cook… just because of nature… I would like to swim in a waterfall… I would like to know more about history of our ancestors and examine my self and my potential… you can learn to do lots of things in a trip… Social pole of orphanages and boarding schools pupils showed that they realize necessity of tourism for forming life necessary skills and personal traits. Striking example of complex solution of educational tasks on the basis of sport and physical training, where priority was given to sport, fitness-recreational and patriotic activities, is the project – 12-days historical-ethnographical travel on foot Mahachkala - Kolo-kareish - Kubachi – Amusgi – Itsari – Derbent. So, evident positive motivation of most boarding schools pupils to different sport and fitness activities in complex with other means of development assumes significant focused activity efficiency enhancement to formation socially demanded personal traits. References 1. Комков А.Г., Лубышева Л.И. Социологические основы здорового образа жизни и физической активности детей школьного возраста // Физическая культура: воспитание, образование, тренировка. 2003, №1. 2. Константинов Ю.С. О проблемах развития туристско-краеведческой деятельности в общеобразовательных учреждениях // Теория и практика физ. культуры. 2002, №11. 3. Лубышева Л.И. Социология физической культуры и спорта: Учеб. пос. - М.: Издательский центр "Академия", 2001. - 240 с. 4. Чунаев А.А. Физические упражнения в формировании личности ребёнка в начальной школе // Физическая культура: воспитание, образование, тренировка. 1999, № 3, 4. Schoolchildren health-improving physical training A. Komkov, E. Kirillova Saint-Petersburg Research Institute of Physical Culture Health-improving physical training is an educational component of physical education syllabus for 1-11 grades of a comprehensive school. It stipulates fulfillment of core requirements of physical education syllabus by schoolchildren. Is also assists teachers in their activity of preparing pupils for passing evaluation in accordance with the state educational standard and of formation of pupils’ sound health and physical condition. The better way to promote schoolchildren’s lifelong sound health is to conduct physical education in schools properly. Health-improving physical training syllabus is aimed at improving school physical education, up-to-date training of PE teachers for creating uniform approach to physical education focused on health promotion within the program of health-improving physical training. Health-improving physical training program is elaborated first of all for updating knowledge of PE teachers on the basis of efficient strategies for pupils’ acquiring knowledge, forming skills, conducting evaluation and strengthening commitment to lead active health lifestyle. Its content is about use of PE methods of teaching which ensure addressing age peculiarities and adaptation requirements and different games and motor activities. The goal of the health-improving physical training program is to assist schoolchildren in acquiring knowledge, developing skills and techniques, and promote positive attitude towards physical culture and commitment to active healthy lifestyle. The objectives of the program are: - Stimulating the process of physical activity not emphasizing the level of physical condition of a pupil, - Define the goals stimulating physical activity and achievable by schoolchildren. - Form basic motor skills so that pupils feel themselves competent and confident in carrying out motor activity, - Informing pupils about their achievements thus contributing to increase on their commitment to physical activity, - Convincing schoolchildren to conduct physical training by themselves as well and learning techniques of self evaluation of one’s physical condition, - Utilizing physical condition testing results for defining a pupils’ individual development, - Attracting parents thus creating a comprehensive approach to preservation and promotion of health of pupils. Technology of physical activity commitment formation is essential for managing this process. This feature is divided into the following successive stages which constitute health-improving physical training program: - The first stage (1-2 grades) - regular physical exercises contributing to a habit of exercising and getting pleasure out of it, - The second stage (3-5 grades) – physical training assisting in learning criteria of its health-improving value and setting reasonable personal goals, - The third stage (6-7 grades) – doing personal sets of physical exercises aimed at making a personal choice of motor activity types and its evaluation, - The fourth stage (8-9 grades ) – self-evaluation of own fitness-sport activity linked with testing own physical condition and interpreting of tests results, - The fifth stage (10-11 grades) – addressing own problems and implementing these decisions what are the basis of individual program planning and learning information needed for these aims. 1. The program emphases positive impact of physical activity, not diseases prophylaxis, 2. We offer emotional reasonable program of health-improving physical training enabling pupils to use the acquired knowledge in their daily life, 3. Pupils learn basis motor skills which are needed for use of full range of motor activities and movements. Health-improving physical training should be targeted at a definite age group and an individual pupil. For example, group study and formation of basic general motor skills, especially elementary locomotion, is suitable and relevant for 1-4 grade pupils. 5-9 grade schoolchildren should be focused on formation of special skills and strategies enabling motor activity efficiency increase. Actual elaboration of detailed individual plan of physical training is relevant for 10-11 graders. Health-improving physical training is different from traditional physical education by the features aimed at providing the following effect: Educational – pupils learn to apprehend why physical activity is so important and it benefits them now and within the life span; Health-improving – emphasizes health related physical training in addition to tradition approach of motor skills formation; Personified – pupils are not regarded in comparison to each other but rather individual development of every one is in focus. Thus ensuring self-fulfillment of each pupil. At the same time traditional physical education provides the same guidance for all schoolchildren; Sufficient – pupils are evaluated by personal self-fulfillment not by his/her competitive achievements or the age normative standard. Use of testing results in the health-improving physical training program implies assisting pupils in better understanding health issues of training and shaping personified goals of physical advancement. Traditional physical education uses testing results for giving marks; Pleasing – physical activity is understood as an activity type which gives pleasure to a pupil and provides him/her with a opportunity to make a choice every time possible. Traditional physical education utilizes the same exercises and games regardless of pupils’ wishes and not giving them an option; Realistic – pupils learn many different health-related types of physical activity and improving physical condition so that they could use these skills in real life. Traditional physical education offers a strict syllabus often repeating the same exercise for years without proper successive development of skills. Health-improving physical training program is complemented with two elective courses for 8-9 and 10-11 graders. The offered elective course of bodybuilding is focused on elaboration of values related to healthy lifestyle formation, body physical advancement, as well as elimination of negative features of life the youth, especially bad habits. It is for male pupils of 8-9 and 10-11 grades. If this course is taught in school with physical culture major the it is focused on developing pupils skills in carrying out individual fitnessrecreational and sport activity. The goal of the course is purposeful physical training in bodybuilding the results of which can be used in future education, occupational choice, professional work, military service. The second goal of the course is organization of individual exercising by making bodybuilding exercise sets aimed at promotion of health and healthy lifestyle. The program is based on learner-oriented educational approach. This means that bodybuilding training considers a pupil’s individual characteristics, physical condition, health status, as well psychological development peculiarities. The fundamental experience of J. Vader system is practically applied in this course. The elective course program enables implementation of health-improving – corrigent approach. The way it is organized provides transition from basic (fundamental) physical qualities development to specific ones thus ensuring practical application of acquired knowledge and skills. Practical content of the course consists of physical exercises set integrated with basics of bodybuilding knowledge and physical characteristics of an adolescent. The initial stage is devoted to motivation preferences in fitness-sport activity and interest of senior schoolchildren in bodybuilding classes. The introductory phase consists of basic means and methods of strength training, as well as its principles and patterns. Variety of training management techniques depends upon knowledge of body physiological processes and peculiarities of load performance. The first phase includes basics of bodybuilding, safety instructions, description of goals and objectives of bodybuilding. Specific objectives of the course are formation of positive attitude towards bodybuilding, importance of vitamins and minerals in nutrition, auto-training skills. The information on pharmacologic drugs for restoration of physical fitness and impermissibility of hormonal agents and other prohibited drudg is provided. The second phase illustrates types of physical activity in bodybuilding. Particular methods for determining physical qualities (strength, endurance, power endurance) are used, as well as apparatus movement technique and weight assessment. Methods are predefined by constitutional peculiarities. The content of program involves considering the following aspects: purposefulness of a class, characteristic of load, number of classes per week, duration of a class, number of repetitions, load intensity, load power, methodical principles, basic types of physical activity (strength exercises, stretchers). Elective course of rhythm plastics is for girls and is considered as a system of athletic, dance calisthenic routine and conscious actions transforming within motor activity for comprehensive harmonious body development, what is particularly important for female students of higher educational institutions. The goal of the course is formation of physical culture of a female student by which she is able to function is the society confidently, to express and fulfill herself in different activities. The content of the program has interconnected components: a basic one, ensuring formation of physical culture basics, and a variative one, enhancing the basic one and considering individual peculiarities of a female. The offered content of the course is aimed at stimulating and regulating of student activities by means of cognition and self-actualization, control and self-control. The part of special training consists of exercises of rhythm plastics, focusing on targeted teaching of choreographic and dance elements, ensuring full body-control. The program also includes elements of implementation of the course contents in real educational process. So this program may be a tool for fulfilling educational goal. The concept which has been the basis for the program is aimed at reaching reasonable level of physical health via traditional and non-traditional measures used at PE classes and within individual work of a female student. The program is based on the system by N. Droen, consisting of conscious dance actions and breathing transforming within form building, motor activities advancement with regard to type of a constitution. The program involves various exercises of Oriental gymnastics, choreography, folk, modern, ball dances, sports acrobatics, bodybuilding, stretching, callanetics, respiratory gymnastics and shaping elements. It also includes some elements of classic and folk dances, rhythmic gymnastics accompanied with music. After first stage of general and dance-gymnastic training exercises are getting more personified; more difficult coordination exercises are introduced. This approach emphasizes problem method of teaching, development of creativity within group and individual exercising. References 1. Alexander Komkov, the Federal State Institution “Saint-Petersburg Research Institute of Physical Culture”, Deputy Director, Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences, Professor. 191040 Saint-Petersburg, Ligovsky Ave., 56E. Ph.: (812) 600 41 15 2. Elena Kirillova, the Federal State Institution “Saint-Petersburg Research Institute of Physical Culture”, Senior Research Fellow, Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Docent. 191040 Saint-Petersburg, Ligovsky Ave., 56E. Ph.: (812) 600 41 15 Implementation of the “Schoolchildren Health and Behavior” international program A.Komkov Saint-Petersburg Research Institute of Physical Culture Cooperation in the field of sports organized by the Council of Europe is carried out in partnership with governmental and non-governmental organizations within the Committee for the Development of Sports (CDDS), established in 1977. The International Council on Sports Sciences and Physical Education (ICSSPE) is a link between Sports Sciences and Physical Education. Main objectives of the Council are to promote apprehension of human values inherent in sports; to promote improvement of health status and increase of physical activity; to promote development of physical education and all over the world. Children and teenagers are predisposed to physical activity, it is necessary for them to gain experience of motor activity in the childhood before they become adults. These facts form the basis for perfection of physical education process contents. Children should understand that learning by doing is the best way of study. Efficient physical education has the following characteristics: child oriented approach, not sports oriented. Working out of an international obligation, capable to ensure such a practice that all children would receive praise, training and support needed for active healthy lifestyle. International documents depict that despite convincing academic evidence about significance of physical activity and the fact that in 1978 UNESCO entrenched them in the Charter of Physical Education as a fundamental human right, physical education is endangered in all regions of the world. Some national governments have either excluded physical education from national curriculum or reduced its time within a curriculum. Shortcuts of budgetary financing have negative impact on time and resources necessary for qualitative physical education. Unfortunately physical education is not considered as a priority within the educational sphere. At present it is under serious threat has to compete for study hours within a school curriculum. The International Council on Science, Sports and Physical Education has elaborated proposals including the following: development of a system of permanent monitoring and evaluation of progress of different countries in implementation of measures and recommendations of international summits on physical education; expansion of physical education best practices exchange; establishment of programs of research of physical training value evidence and exchange of academic research results in the field; working out of guiding principles for creation of representative organizations on physical education and propaganda materials; elaboration of international criteria for school PE educational programs quality for guiding local and national authorities in their working out and implementing of their policy. Great importance in improvement of physical education of children of school age is being attached to social-pedagogical monitoring which is understood as a form of the organization, collection, storage, processing and distribution of information about pedagogical system and social infrastructure providing continuous tracing of educational process conduct and living conditions, and enabling prediction of their development. The specified approach is carried out jointly by participation in the «Health and Behavior of Schoolchildren» international project implemented under the aegis of the World Health Organization and the European Regional Bureau the WHO. Participation in working out of a standard version of a questionnaire for carrying out of sociological survey within the program provides an opportunity to accumulate foreign scientific experience in addressing schoolchildren health promotion and applying sociological and behavioral sciences’ methods in these purposes. International research within the project is aimed at addressing the following issues: improvement of awareness and regular monitoring of children health and health-related; revealing of interrelations of school, family and other social institutes and pupils lifestyle; assistance to development of social programs and implementation of children health promotion policy; expansion of interdisciplinary health and health lifestyle research via an international network of researchers. The specified research activities imply the following actions: discussion of their importance in regard to health; the description of some health and behavior related measures; display of similarities and differences between countries and regions, age groups and genders. Research activities within the Health and Behavior of Schoolchildren project were initiated in 1982 and have been carried out every 4 years. 3 countries participated in the first survey, while 42 states in the current one (2010). Every country conducts project surveys in accordance with the quality standards specified in the research protocol (the Russian Federation has participated in the program since 1990). The central elements of the technology are: 1300 children of every age group (11, 13, 15 years old) are examined in every participating country; random sampling representativity is defined by schools and grades within a country and a region (with population of no less than 1 million); data is collected on a no name basis by filling in a questionnaire during a class in accordance with polling requirements; international standard questionnaire is utilized in all participating countries; survey results are processed and undergo formatting for putting into an international databank. The questionnaire composed by the international program members consists of standard (permanent within the program lifespan) questions and specific (added and altered every 4 years by a new survey round). Physical activity question block elaborated by the Federal State Institution “Saint-Petersburg Research Institute of Physical Culture” includes the following aspects: values (motives, needs and interests); physical activity (study, sport, play, active leisure); attitude to a PE class (importance, contentment, knowledge); doing sports (kind of sports, sports achievements); self-evaluation of physical condition (in general, physical qualities); self-evaluation of physical development (weight, height, form). Data of social-pedagogical monitoring should be used not only for addressing academic issues, but also on increase of the educational process efficiency, advancement of pupils’ fitness-sport needs, motives and interests. Social-pedagogical surveys are divided by territory and content principles. Social-pedagogical monitoring of pupils’ physical culture indicators is aimed at performing the following functions: pedagogical awareness of the content, forms and methods of physical education; promoting health and cultural development of children; studying of psychological-pedagogicla peculiarities and conditions of physical culture formation; defining interests and needs in physical training. Representation of children interests in physical education advancement is based on collection of information about their needs via mass sociological polls, diagnostic and prognostic surveys. The collected data is used for informing administrative and pedagogical staff on schoolchildren physical activity degree, for healthy lifestyle promotion, providing physical activity opportunities. It can be also used in socialpedagogical and social-psychological education services, specialized children institutions, NGOs and various foundations, municipal bodies and agencies, valeological, fitness-recreational and rehabilitation centers. Practical implementation of social-pedagogical monitoring concept is based on scientific study and information analysis, administrative, social-pedagogical maintenance. General model of social-pedagogical technology can be described as follows: 1. Socially oriented evaluation of basic peculiarities of formation of a pupils’ personal physical culture; 2. Social-pedagogical supervising of individual physical self-advancement of pupils of different gender and age groups; 3. Conclusion on a social-pedagogical problem related to pupils physical education advancement; 4. Predicting development of social-pedagogical processes and conditions of pupils’ physical activities organization. Information analysis system is set as a result of social-pedagogical monitoring performance. It includes database on quantitative and qualitative characteristics of pupils’ physical activity, self-evaluation and lifestyle indicators, as well as social factors determining formation and effectiveness of physical activity. Information analysis system containing pupils mass poll database enables conduct of a multifold analysis of social-pedagogical conditions of pupils of different age physical activity formation. Physical activity is an important factor of health improvement of not only younger generation but the whole nation. The survey has indicated key physical activity factors. It is also indicated that physical activity level decreases by age, particularly this affects females. Factors related to physical activity of children, adolescents and youth have been determined: demographic (greater activity in the early age especially of boys),psychological (self-evaluation of own competence and getting pleasure), social (approval of parents, relatives and peers), environment (available infrastructure and programs). In the later years the issues of intensity and scope of physical activity for mass event have been widely discussed. The bulk of these discussions has concerned adults not teenagers, but the acquired results can be applied to both of these groups. It is emphasized that physical activity of moderate intensity carried out for pretty log time can affect health positively. In 1997 a group of international experts retested recommendations for adolescents and offered two key provisions. The first one is: youngsters leading sedentary lifestyle should devote at least 30 minutes per day to physical activity. Moderate intensity has been defined as physical activity equivalent to smart walk when a person feels warming and mild dyspnoea. The second, and the most important one is: all youngsters should theoretically be engaged in such activity for 1 hour a day. Twice of three times a week a person should do exercises for muscle strength, dorsal spine mobility and locomotor apparatus. There are obligatory criteria for examining school within the Health and Behavior of Schoolchildren project: the amount of time a school may devote to physical exercising, acceptable amount of questions and necessity of logical coherence with other questionnaire chapters. So it means that physical activity related questions should be limited in number. Collected data enables objective evaluating of efficiency of running and elaborating of a new syllabus of “Physical Education” subject, as well as adjusting social-pedagogical technology of this process. The result of social-pedagogical monitoring is determination of actual level of physical activity of schoolchildren from different Russian regions, near and far abroad countries. Sociological surveys database handling system has been created. It has become the foundation of information analysis system. Standard tools for mass schoolchildren poll conducting has been experimentally tested for the aims of studying social-pedagogical conditions of formation of schoolchildren physical activity. The results of the survey contributed to elaboration of the elements of social-pedagogical technology of handling the process of physical activity formation, physical education syllabus advancement, increase of PE teacher activity efficiency. Persons engaged in elaboration of a strategy should handle up-to-date data on key health evaluation criteria. Mass media as well as specialized media has great influence on the society thus on decision makers and public institutions. They are particularly important for this survey by disseminating the results and promoting it to the public. The conditions for increase of physical activity should be provided thus positively influencing health of children, adolescents and youth. Decision makers have to be aware of major hindrances and available evidence of intervention efficiency. Politicians have to devote more attention to addressing social problems like affordability of teaching aids. On the results of forecasting and planning of study-training, recreational and sport activities aimed at tourism development in the Petrozavodsk State University Y. Lanev, Head of the “Sampo” tourist club, master of sports, city of Petrozavodsk The profession of a teacher is the ..easiest one in the world. It is the most natural occupation. As every human being is a teacher from his/her birth to some extent. We all have fundamental pedagogical skills/sense. It is one of our abilities, like hearing, voice, thinking. This pedagogical sense is the basis of human communication, universal communication which continually transfers knowledge, expertise, wisdom, benignity. The humankind would not have survived without it. So we, the pedagogues, have taken this joyful duty to simply manage this wonderful sovereign process of knowledge and expertise transfer. Pedagogues have been lucky to carry out humanistic activities even in harsh times – to educate and show the way to life. Any lesson is by itself throwing a lifeline to every pupil, incentive to create his/her own future without fear, as you, the pedagogues, are always by their side. I was about 26 when they offered me a position at the Department of Physical Education at the Petrozavodsk University. It happened in 1964. So I have devoted already 46 years to physical training of students, faculty members and university employees. “Sampo” tourist club has become a great part of my life. The point was not merely to create a game, but put all the efforts to let all the students understand its rules. The most important result of this game is viable well-being. So that during every single journey on foot students could apply and advance their skills and techniques. The beginnings of active tourism encountered the necessity to clarify the priorities. Indeed travelling as an ancient amusement of the humankind. But a pedagogue has to take into consideration the need to constantly address various serious challenges. In 1964 the University had no tents, sleeping bags, any other touristic equipment. I guess many beginners were shocked with the first tasks set by the pedagogue: 1. To train a master of sports within 10 next years, 2. To conduct first club journey on foot in Kamchatka in the following 10 years, 3. To go international and carry out first international journeys on foot during the next 10 years. Now I do realize that the pedagogue indicated precise challenging goals not only for the students, but first of all for himself. Moreover we had to develop our internal ideology only relying on the term “life success”, without great achievements in our archives. Our aim has been to educate students achieve highest results even in harsh circumstances, act reasonably and decisively, thus collecting journey on foot expertise for decades, as well as transfer this expertise from generation to generation. Surprisingly, these tasks were completed ahead of schedule. Two first master of sports received the honors in 1972. The first journey on foot (of the 5th category of difficulty, leader – Vareliy Vlasov) was conducted in 1978. The first international ski journey (10 citizens of the USSR, 10 Finns, 800km distance, 16 days: 8 days in Russia, 8 days in Finland) was carried out in 1990. Meeting these challenges proved that the bulk of the “Sampo” club members were professionally excited and able to address difficult, but amazing tasks. During these years we have succeeded in teaching our students to handle their life energy, reveal inner reserves both physical and intellectual. Everyone has great life energy potential. Nonetheless one has to pursue his/her life journey with reasonable caution. I recall it very clearly how happy students were upon completing their first 50 km ski distance. Later another student group completed 70 km way. The distance of the 1977 ski marathon was 102 km per day. Males completed 150 km and females 120 km within another 20-hour ski trip. We skied for 176 km per 24 hoursin our joint endeavor with Kondopoga fellows. We were planning to go from Medvezhyegorsk through Tolvuya, Kizhi to Petrozavodsk covering the distance of 204 km in 26 hours. Unfortunately that year not the whole Onego lake was in ice, that’s why we had to cancel this journey. 25 ski marathons lasting for several days and covering distances from 500 to 2,000 km were conducted during these years in the “Sampo” tourist club. It is not accidental that Finnish skiers participating 800 km journey from Russia to Finland emphasized excellent physical condition of the students of the Petrozavodsk University. Olympic champion, Vyacheslav Vedenin, also pointed out the same feature while taking part in one of our Russia-Finland ski endeavors. The “Sampo” tourist club has carried out about 900 classified ski, on foot and by water journeys. The aim was to train activists overcome major difficulties. So we were fostering philosophy of a winner in them, enriching training with proficiency aspirations and energy promoted by the slogan “Beyond!” we also had to educate students work for the present moment and for the future sharing responsibilities and elevating self-esteem. Training of active commercial and sport tourism professionals is implemented in 2 directions. These are training of “Tourism of Russia” badge awardees and training of tourism instructors. This system has assisted the “Sampo” tourist club in promoting tourism among Karelian schoolchildren, students, faculty members and employees of the Petrozavodsk University for 45 years. During last 9 years (2001-2009) the “Tourist of Russia” title was awarded to 3,747 persons at our university (according to data available on January, 1 2010). This achievement contributed to successful provision of recreational journeys on foot in the Petrozavodsk State University. 160,700 persons participated weekend campaigns during the 10 years (1998-2008). Sport classification stipulates stricter requirements for training of tourism instructors. 2005 persons have been trained in the “Sampo” tourist club for 45 years, including 13 masters of sports, 30 Candidates in Master of Sports, 118 sportsmen of first degree, 437 sportsmen of second degree, 1407 sportsmen of third degree. 858 classified journeys on foot including 321 – of first category of difficulty, 289 – of the second category, 132 – of the third, 64 – of the fourth, 44 – of the fifth have been conducted during all the described time. The administration and the Department of Physical Education of the Petrozavodsk State University, the “Sampo” club activists have created the atmosphere and conditions for tourism development ensuring that tourism classes and outdoor activities are useful and interesting for Karelian schoolchildren, students, lecturers and university employees. Polyathlon as an affordable physical training event O. Lisov, Vice-President of All-Russia Polyathlon Federation, Internationally Certified Judge, city of Ryazan Polyathlon is a complex all-round aimed at endurance and strength development. Its distinctive features are affordability, health improvement, availability for all ages. There two types of polyathlon – summer and winter one. Winter polyathlon can be a double-event or triathlon. Summer one - double-event, triathlon, quadrathlon or pentathlon. It is worth pointing out that polyathlon popular in the CIS states is getting an international kind of sports. Polyathlon is interested and useful not only for athletes but also for amateur people who lead or try to lead healthy lifestyle, as well as for those who want to try several kinds of sports. The Russians know polyathlon as a follower of a patriotic complex of GTO (Russian acronym translated into English as “Prepared for Labor and Defense”). Polyathlon is by its essence a successor of GTO complex practiced in the USSR since 1930s. The content of the complex is the following: shooting, throwing, swimming, strength exercises, cross and short distance race. Let us track the history of polyathlon. All-USSR sport complex GTO was established March 11, 1931 and used to be a state system of national physical training standards. It implied comprehensive physical development of a person, preservation and promotion of health, training for high-performance labor and defense of the country, contributed to formation of a moral image of a Soviet citizen. Norms and standards of GTO changed several times, for example, in 1934, 1940, 1947, 1955, 1959, 1965. Last PT complex GTO was adopted by the decree of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union and the Council of Ministers of the USSR in 1972. It involved 5 stages defined by age limits with particular standards for every age: first stage – 10-11 and 12-13 year olds, second – 14-15, third – 1618, fourth – 19-28 and 29-39 males and 19-28 and 29-34 females, fifth – 40-60 males and 35-55 females. In 1948 there were 139 physical culture associations and 7.7 million physical culturists, in 1977 –already 219 thousand PC association and 52.3 million physical culturists. In 1972-1975 more than 58 million people fulfilled GTO norms. According to level of accomplishment a person could have been awarded with golden or silver badges of GTO, a person who had fulfilled norms for several years in a sequence – with a badge of “GTO Honorary Lapel Button”. Physical culture associations of employees of various plants, agencies, etc could have received a badge “For achievements in GTO”. Since 1974 All-USSR GTO competitions were held. For example, in 1975 37 millions took part in mass starts, about 500 persons – in finals. GTO PT complex was interconnected with the Uniform All-Union Sport Classification. Sport categories and titles were awarded upon fulfilling GTO norms by athletes. In 1980s GTO complex was altered again, so that every trainee could opt for a set more suitable for him/her. GTO all-round was preserved during the years of the USSR dissolution. Development of polyathlon is connected with the name of Gennady Galaktionov. In 1989 he was elected the President of All-Union GTO All-Round Association. In 1992 after the USSR collapse first CIS GTO winter all-round championship was held. In CIS states GTO all-round were kept alive under the aegis of the International Polyathlon Association. Mr. Galaktionov was elected the President of this Association in February 29, 1992. The same year GTO winter all-round was renamed into polyathlon and the first international winter polyathlon championship was held. Next year, in 1993 the first World Championship on summer polyathlon was held in Chernigov, Ukraine. 324 athlete took part in it representing 11 states. Since 1994 World Cups on summer, and later winter, polyathlon have been conducted. Since 1997 World Championships among men and women on summer polyathlon have been held. Nowadays calendars of international and national polyathlon competitions consist of about 10 winter events and 20-25 summer ones for all ages. In Russia since 1993 sport classification on polyathlon (till Master of Sports of International Class) has been in operation. Since October, 2004 All-Russia Polyathlon Federation’s head quarters has been situated in the city of Ryazan. Polyathlon is practiced in 47 regions of Russia. Race distances are 2000-3000m for men and 1000-2000m for women. Running is an inherent part of training of every athlete. It is one of the most affordable physical activities which can be performed in any park, for example. Ski race distance are 10km for men and 5km for women. Grenade throwing is a military-applied standard. In Russia it has almost a hundred year history and plays important role in schoolchildren training for military service. By time passing grenade throwing has developed into a full-fledged sport event with its specific methods and records. Swimming distances are 50 or 100m (depending on a competition level, the higher level – the longer distance). Usually a competition is held in a standard 25m swimming pool, but sometimes in open water as well. Strength exercises are pull-ups (for men) and push-ups (for women). On the one hand, pull-ups and pressups are not a separate kind of sports but on the other hand, these are an inherent part of every athlete training process. Moreover almost no equipment is needed for performing these exercises. This event has its won champions and leaders. For instance, recently Daria Vas’kina from Ryazan set the Record at the Championship of Russia on winter polyathlon accomplishing 164 press-ups within 4 minutes. Sprint in polyathlon is 50-60m race (indoor) or 100m (outdoor). As this is a short period race the utmost importance is attached to fast start and good reflexes of an athlete. 10m air rifle is carried out to a 5cm of 25cm target by 5 or 10 shots. Air rifle develops a person’s psychological stability, self possessing abilities. Polyathlon results assessment sheets enable objective tracking of physical development as results achieved by a person are transferred into scores. Individual performance progress is clear by considering results of different years/time periods. Modern youth is eager to lead healthy lifestyle. In particular this proves the fact that young people want to do physical exercises and sports thus improving their physical capabilities and enriching their leisure with useful and interesting activities and competitions. Polyathlon addresses these issues. Thus polyathlon has an important applied significance for athletes not engaged in other kinds of sports – it contributes to sport longevity and achievement of high results also in several sport events at once. Relying of polyathlon programs, our human resources and organizational potential the All-Russian Polyathlon Federation is ready to contribute to the state’s activities in addressing national issues such as training of the youth for military service, population physical health testing, combating bad habits, comprehensive physical training of all sections of population. Finnish-Karelian project on Health Education in schools of the city of Petrozavodsk and the Republic of Karelia Nikolay Listkov, Teacher-supervisor, Honored worker of education of the Republic of Karelia, Lyceum #1, city of Petrozavodsk Finnish-Karelian project on Health Education in schools started in 2006 with approval of pilot schools in the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Karelia. These were Lyceum #1, Comprehensive School #46 and Comprehensive School #48. First seminars conducted by Pertti Helin and Vladimir Kuivanen were held in Lyceum #1, then shifted to School #48. All seminars were carried out in business-friendly atmosphere. Some time later Comprehensive Schools #39 and #42, Lyceum #13 joined the project. Thanks to these seminars the majority of city school learnt about the project and its progress. The same year the first seminar for PE supervisors of the Republic of Karelia was held in School #48, event being organized by a representative of the State Committee of the Republic of Karelia on Sports S. Malashov. Information about the project was presented by N. Listkov and I. Achepovsky to representatives of 16 districts of the Republic who transmitted it to PE teachers of their home cities. Later the First International Congress of Physical Educators held in Petrozavodsk in July 2008 welcomed speeches by PE teachers of the Republic and Petrozavodsk: G. Subbota, T. Surina, I. Krotova, E. Korsakas, G. Pevtsova, N. Listkov, N. Savolainen (Lyceum #1), I. Achepovsky, I. Pavlov (School #48), N. Skibina (School #46), Z. Chekunova (School #39), S. Cheremukhin (School #33),on their work within the project. In August 2009 at its meeting Methodic Association of Teachers of Petrozavodsk reached a decision of attending advanced training courses, held within the project and organized by the Faculty of Physical Education and its Dean A. Voronov, by all PE teachers of the city. In 2009 due to this courses many city schools joined the project, its representatives successfully completing the training. PE Teachers Association of the Republic of Karelia, established in May 2008, also made a contribution to the Health Education project: its representative delivered lectures within the advanced training courses on topics of “School health teams: principles, goals, forms of work” and took part in polling held by Finnish party to the project and the Faculty of Physical Culture. Many republican and Petrozavodsk schools established their own forms of work with the project. Here I bring to your notice a healthy lifestyle monthly plan implemented in the Lyceum #1. Monthly plan of action dedicated to healthy lifestyle Grades Event Responsible persons Data/time/ venue Extra info 5–6 Exhibition of drawings of 5-6 grades on Health Lifestyle Class supervisors, March 1–24 Works arts teachers, preparation in social pedagogue line with study schedule 8–11 Social advertising contest Organizing pedagogue, March 1–24 Best works to be honored at social pedagogue the final ceremony Russian language March 1–24 and literature teachers, social pedagogue Best works to be at exhibition “Health of Karelia – 2010” 5–9 Essay on Healthy Lifestyle 8–9 Making media Life safety presentations on “My teacher, social dream school” pedagogue March 1–24 Authors of best works to make presentations in other class groups, final ceremony 5–7 Learning songs Elena dedicated to healthy Vladimirova lifestyle March 1–24 Best teams to perform at the final ceremony 8–11 Photo-cross Organizing March 20, pedagogue, Drevlyanka social pedagogue district 7–9 “healthy morning” journey on foot Class supervisors, March 27, organizing pedagogue, social pedagogue, life safety teacher, specialists of “Bogatyrskaya Zastava” teenagers’ club Class Training-seminar for supervi class supervisors on sors secondary and senior school 7–9 Trainings on healthy lifestyle Specialist of the Center of Family Planning and Reproduction March 29– 30 Social pedagogue, volunteers At school classes Topics: “Sexual and reproductive health and rights of a teenager”; “Prevention of bad habits” 8 7–8 Lection-conversation Specialists of on drugs Republican Narcological Dispensary At school classes Lection-conversation Specialists of Clinic Friendly to Youth March 16– 18 Ceremony of announcement of results of contests held within the monthly plan March 25 Topic «Hygiene. Мy body» Optimization of the physical education process for primary school pupils with health disorders L. Lushpa, A. Lushpa Kuzbas Regional Institute of Advanced Training and Re-training of education workers, city of Kemerovo, Kemerovo State University, the city of Kemerovo The period of school study creates the basis for comprehensive personal development and formation of adaptive abilities. As the school age is a foundation for further development of psychomotor qualities of a child which represent themselves the basis for sustaining of physical and mental health. At once for the period from 1998 to 2008 the rate of pathologic prevalence (total prevalence rate of functional deviations and chronic illnesses) among primary school pupils has increased by 54,5%, including 59,8% growth of spread of functional deviations and 31,8% growth of frequency of chronic illnesses. One of the reasons for that is generally declining level of motor activity of a child after starting the school education. Deficit of motor activity accounts for 35-40% already in primary school. PE classes hardly compensate for (at 10-18%) the deficit of motor activity. That is not enough for prevention of health disorders (V. Kuchma, L. Suhareva and co-authors, 2009). The purpose for physical education in schools is to promote comprehensive personal development by forming pupils’ own culture of physical activity. The components of the physical culture are sound health, good level of physical development, proper amount of motor ability, knowledge and skills in the sphere of physical culture, motives and acquired techniques of carrying out of health and fitness activities (J.Kuramshin, 2004).Out of this definition, the process of physical education cannot be limited with school lessons only but it demands the particular system of teaching of pupils, especially those with different health deviations. We took the comprehensive school #94 of the city of Kemerovo, which bears rich expertise in work with children who fall into special medical group (SMG) due to their health status, as the platform for our research (G. Tushina, E. Kazin anc co-authors, 2004). The number of SMG pupils has increased during recent 10 years from 2% to 16% out of the aggregate quantity of pupils. The educational institution is addressing the following matters in order to more efficient pedagogical impact aimed at health support and promotion, provision of psychoemotional well-being and comprehensive development of a child who has continuing or temporary health deviations: 1. Carrying out of analysis of medic-biological, psychological and social-pedagogical factors affecting physical and mental health and development of a child; 2. Introduction of measures for improvement of physical development, correction of risk factors and gradual control of the level of physical and mental health of pupils; 3. Formation of the philosophy of healthy lifestyle and commitment to it among pupils and their parents. The school has the following facilities which are utilized for addressing the aims mentioned above: a swimming pool, a correctional gymnastics gym, a sports gym, a functional diagnostics office, center of medical control, dental office, physiotherapy office, relaxation room. Forming of special medical groups is carried out jointly by a school doctor, a psychologist and a P.T. teacher. They take into consideration health documentation and results of psychophysiological testing which indicates the level of anxiety, fatigability, and individual characteristics of a child. Due to a small number of pupils with similar illnesses the groups are formed by age criteria, regardless of a type of illness, for example, out of pupils of 1-2 and 3-4 grades. The number of pupils in a group is about 10-15. The following techniques and methods are used for work with children with health deviations: Participants of the educational process learn about the health status of school pupils; Provision of convenient learning environment including control of the study load, schedule of study with respect to efficiency and fatigability of a pupil, use of P.T. breaks during classes and afterschool, introduction of dynamic breaks; Conducting Health Classes and Weeks; Carrying out of individual and group work with parents; Provision of active rehabilitation and diagnostic activities aimed at forming of physical and mental health of a pupil and its gradual control; Health improvement of pupils during vacations in the Health and fitness center of the school. Children from special medical group have two P.T. classes per week which are conducted by the special elaborated program, including the following components: breathing exercises, corrigent gymnastics, antistress gymnastics, motor education, body-conditioning. If a SMG pupil has no contraindications he/she can also go in for recreative swimming to the school swimming pool. The basis of P.T. classes for SMG pupils is type of illness of a pupil, functional capabilities of his/her body, peculiarities of physical development and physical condition, what helps to take correct exercises and determine the load. Medically fragile pupils can be overloaded physically, that’s why a pupil is supervised by a teacher and controls his/her pulse and respiratory rate. Testing is conducted in order to get information on pupils’ health. Testing is carried out via particular exercising permissible for such pupils. P.T. teachers and specialists of Health and fitness center systematically supervise the functional health status and physical development of a child. The use of automated cardiorhytmographic program in the diagnostics office ensures conducting evaluation of the efficiency of an impact motor activity on pupils, determining of “physiological value” of the study process. We have found out that schoolchildren with reduced functional capabilities need more personalized mode of motor activity that pupils with satisfactory level of adaptiveness. Change of the mode of study activity, control of the impact of motor activity, correctional work with a psychologist, constant iatric advice – all these measures help schoolchildren in easier adapting to school study, and further in compensating for significant overload when leaving primary school and entering a secondary one. The schedule of the study process can be organized in a cycle mode for the aims of prophylactic of overfatigue of schoolchildren and teachers, increase of work capacity, nonspecific resistance of a body. Every cycle includes 3 parts: traditionally organized educational process (duration – 4 study weeks); intensive process creatively arranged (duration – 1 day); rehabilitation part (duration – 1 day). This cycle mode also includes 1 hour per week dedicated to health of a teacher. During study in primary school the number of SMG pupils with harmonic physical development has increased at the expense of decrease of the quantity of children with extra weight and underweighted, the physical condition of pupils has improved. Positive impact of motor activity on somatic status of a child leads to changes in psycho-physical development. According to the conducted survey the indexes of personal and state anxiety have significantly decreased, memory and concentration have improved. This has contributed to higher level of qualitative achievements. During the observation period the infection rate of schoolchildren has decreased, including decrease in number of upper respiratory diseases and cases of exacerbation of chronic illnesses. To sum up, according to the conducted research change of the mode of study activity, special organization of motor activity, psychological correction assists to increase of adaptive-compensatory capabilities of a person and as a consequence it assists the improvement of health of pupils from special medical group. References: 1. Курамшин, Ю.Ф. Теория и методика физической культуры / Ю.Ф. Курамшин – М.: Советский спорт, 2004. – 464 с. 2. Кучма, В.Р. Школы здоровья в России / В.Р. Кучма, Л.М. Сухарева, И.К. Рапопорт и др. – М.: Издатель Научный центр здоровья детей РАМН, 2009. – 128 с. 3. Тушина Г.И. Основы валеопедагогического руководства физическим воспитанием школьников / Г.И. Тушина, Э.М. Казин, Л.Г. Лушпа // Валеология. – 2004. – № 4. – С. 56-60. Paintball, a sport game V. Malinen, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk In the twenty-first century most people lead very busy lifestyles. Permanent rush and hard work result in individual and emotional stresses. This condition can originate as if from nowhere, in circumstances where no activity is done. But its consequences - a change in the status of an individual and the emergence of aggressive reactions - can be quite real and serious, not only for individuals but also for social communities and even for a society. However, such tensions may last long, without showing itself, and one day it may suddenly explode in conflict on some at first glance insignificant reason. The state of stress results in depression, hysteria, nervous breakdowns, as well as in quarrels, hurt feelings, decreased performance and unintentional aggression toward people. Sport fits perfect to combat these negative trends. Sport is one of the main sources of vivacity and energy. Many sports fans have experienced a state of euphoria, causeless joy after exercise. It is also a kind of stress management. We can say that people who do exercises regularly, boost immunity to stress. It is well known that physically active people are less prone to various diseases than sedentary people. One of many sports used to combat stress is paintball. According to a widely accepted definition, paintball - is a "sport and technical extreme game, simulating transient firing contacts in a limited space." The basis of this game is engagement of people in some extreme situations, in which they must get rid of negative emotions. At the same time it is not dangerous for players. Paintball, like any other sports game has not only supporters, but opponents. It might be explained by the fact that paintball competition does not seem likely to any other known sporting event. Besides the usual balls, much smaller than say in football, paintball assigns a big part to use of firearms. Despite the fact that these arms shoot not with bullets, but with quite edible balls, yet some people associate this game with bloodshed and violence, and opponents of paintball make more than rigid and clear statements: "This is legalized bestiality," "What can be good in a game where you have to "kill" rivals?", "Is it good for children? It causes cruelty! "," This game is promotion of violence! " And if there is a huge number of examples of antisocial behavior as a result of distortions of personality under the influence of computer games or watching fighters and horror movies - you can not say anything like this about paintball, which in addition to its safety has also confirmed rallying effect. There are no examples of serious crimes related to paintball. All sports involve injury in a varying degrees: bruises, sprains, abrasions - sometimes something more serious, it is part of the sport. Accident in rugby can lead to paralysis or even death, in hockey it can be a traumatic brain injury. As for paintball - there is no direct physical contact. Only a ball can touch the other player. Physical contact puts a player under exclusion and team penalties. In addition, there are plenty of evidence that paintball promotes harmless release of negative energy and aggression. Turning to psychology, paintball contains two types of stress management: firstly, it provides an arena where players are free to express their accumulated aggression, releasing physical and mental stress, and secondly, it gives you an opportunity to evaluate the reaction, accompanying high-stress situations. Paintball increasingly begins to occupy the leading position among the active forms of collective recreation. Recently only certain categories of people could do this sport, now paintball is available for all sectors of society due to opening of numerous paintball clubs, providing rent of special equipment at a low price and inexpensively sell balls with paint (consumables). Many consider paintball a kind of simulator for employees of companies serving the alarm systems, or special forces soldiers. But the popularity and availability of it is much wider. First, it is difficult to find a more exciting game, which is so rich in new experiences and adventures. Each new match differs from a previous one. It's impossible to predict how new rivals will behave, and how you will play with a new team. In addition, the relaxing effect of paintball after a week in the office at the computer is incomparably richer than the rest on the sofa watching television. Secondly, what can rally the team better than paintball? Team play helps to know the staff from a new point, gives an opportunity to feel the corporate spirit, to see and estimate friends in different circumstances. The success of a team depends on the ability to feel teammates in the game. The goal is not only to attack and defeat the enemy team. It is also necessary to keep enemies away from the symbol of a team - its flag. Protection of objects is a very difficult task, and only a consolidated team can cope with it. Another important fact is that paintball is able to remove tension and negative emotions accrued during the work, thus bring a person out of stress. A single session of the game is enough to replace irritation, aggression, and depression with good mood, optimism and a new charge of vivacity and health. Influence of fresh air, physical activity, vivid impressions after the victory over the enemy team is huge. But losing a game does not deject spirits as well. It's just a funny collective game for adults, behaving as children, stained with paint and allowed not to limit their emotions. But how pleasant feeling of relaxation after physical fatigue is! Problems and troubles seem to be all gone, and undermined relations with colleagues are improved, and the world looks not so gray and gloomy, and you consider your friends as the most reliable. Another proof that paintball can be considered as an alternative to aggression, is that children and wayward teenagers who join the game change for the better. They do not become more aggressive and warlike, as it would be if paintball promoted cruelty and violence. Their behavior, on the contrary, improves. The game unites and captures children so that they are trying hard to show their the very best qualities only, which subsequently help them to go through difficult life journey. Health saving technologies in higher education Tatiana Martirosova, Siberian State Technological University, Docent, Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Department of Physical Culture and Valeology, Lyubov Yatskovskaya, Siberian State Technological University, Docent, Candidate of Pedagogical Sciences, Department of Physical Culture and Valeology, Siberian State Technological University, city of Krasnoyarsk The health saving educational technology is a system creating optimal conditions for preservation, improvement of health and ethical, emotional, mental, personal and physical development of all the parties of the educational process (students, teachers, etc). Utilization of health saving technologies in higher education, which qualitative component – education and development – does not affect negatively students’ health, is one of the key objectives of all parties involved. Central components of the health saving technology are: - Educational component, divided into 3 group: o Organizational-pedagogical technologies which determine the structure of the educational process, partly stipulated by the Sanitary Regulations and Norms, prevent overfatigue, hypodynamia and other disadaptive conditions; o Psychological-pedagogical technologies which determine the way a teacher conducts a lesson, and the impact a teacher makes during this lesson on students. o Educational technologies which include health education and students health culture formation programs, motivating them to healthy lifestyle, prevention of bad habits, extracurricular activities. - Axiological component, which implies awareness of students of the paramount importance of their health, conviction to healthy lifestyle enabling fulfillment of one’s goals and utilization of mental and physical abilities. Carrying out of the axiological component is done through formation of outlook, inner convictions, determining reflection patterns and acquisition of a particular system of ethical, vital, medical, social and philosophical knowledge relating to physiological and neuropsychological age peculiarities; learning laws of a human mental development. Thus education is aimed at forming of value system of health, health saving as an inherent part of an outlook. - Epistemological component, which means acquisition of needed health saving skills and techniques, self-actualization, learning own potential abilities and capabilities, own health awareness, learning literature on health issues, health-improving methods. This process is focused on forming of scientific and practical knowledge system, every-day healthful skills. This is resulted in one’s care about his/her health, leading healthy lifestyle, foresee and prevent possible negative aftereffects. - Health saving component, involving values and mental sets shaping a system of healthful skills and habits necessary for a body functioning, as well as for community and environmental well-being. The particular attention within this component is paid on day, dietary, work and leisure regimens what contributes to prevention of bad habits, functional disorders. The component includes psychohygiene, psychoprophylaxis of the educational process, utilization of environmental healthimproving factors and some specific health-improving methods. - Emotional-volitional, covering expression of psychological mechanisms – emotional and volitional. The preset condition for preservation of health is positive emotions, experiences which make a person lead a healthy lifestyle. Will is a mental process of cognitive control of activity of overcoming difficulties and obstacles for achieving a goal. A personality through the will can perform control and self-control of his/her health. The will is very valuable particularly at the beginning of health-improving activity, when healthy lifestyle has not become an internal need of a personality and qualitative and quantitative indicators are not obvious yet. The emotional-volitional component aims at acquisition of experience of personality – society interrelations. It forms such personal qualities as self-management, discipline, duty, honor, dignity. These qualities enable a person’s viability in a society, preservation of as individual as collective health - Ecological component, noting that a human being as a biological species lives in a native habitat, which provides his/her with specific biological, economic and productive resources. Moreover it ensures physical well-being and ethical development. So we see the dependence of physical and mental well-being on ecological conditions. Hence formation of skills and techniques of ecological adaptation is an inherent part of health saving education. Unfortunately ecological environment of - - - - educational institutions is not always favorable for students’ health. Natural habitat surrounding a school is a powerful health-improving factor. Fitness - health-improving component means knowing how to increase motor activity and avoid hypodinamia. Moreover this component ensures body conditioning and advanced adaptive capabilities. Medical-hygienic component concerns human health, competences of health professionals, quality of health care system. Even though the “health” term is a cornerstone of medical sciences, medics deal with various diseases, not health promotion and health improvement. The proposed approach of priority of prophylaxis over treatment is still vain wishes. One may try this by simply asking a physician on how to promote health. The answer would to be like: eat healthy food, spend more time outdoor, avoid stress. But provision of health promotion programs in educational institutions is of paramount importance, even compulsory. Medical-hygienic technologies involve control and provision of proper hygienic conditions in accordance with the Sanitary Norms and Regulations. A medical station carries out vaccination and sanitary-hygienic education of students, provides consultations and emergency care, watches students health status dynamic, conducts prophylactic measures expecting an epidemy (of flu), as well as other activities related to its competence. A doctor of a medical technician participates psychological-pedagogical consultations dealing with a particular student health issues, especially of those of special medical group. Establishment of a dentist’s, a physiotherapist’s offices for rendering every-day assistance for lecturers and students, creation of juice bars, conducting exercise therapy classes are the elements of this component. These two mote groups of technologies which are traditionally implemented our of a higher school, but now more and more often they are introduced to extra-curricular activities. Social adaptation and personality development involve technologies forming and strengthening students’ psychological well-being, advancing personality psychological adaptation resources. These include various social-psychological trainings, social and family pedagogical programs what implies attracting not only students but also their parents and pedagogues. Medical – health-improving technologies are medical-pedagogical knowledge. These involve medical pedagogy and exercise therapy what influence students’ physical health resumption . Elaboration of health saving technologies within the system of higher education took several stages. The first one was from 1996 to 2000 when a new subject of valeology was introduced to the State Educational Standards for Higher Professional Education (Order of the State Committee of the Russian Federation on Higher Education № 380 of March, 4 1996). So departments of valeology have been founded in different higher educational institutions. But the elaboration of health saving educational technologies was hindered by the absence of uniform notion of valeology as a teaching subject and significant differences in running educational programs. Some programs emphasize basic of medical knowledge (E. Vainer, 1993), others – family and healthy life style issues (L. Pankova, 1994) or psychophysiological and pedagogical basics of human health (G. Zaitseva, V. Kolbanov, M. Kolesnokova, 1994). If we compare different approaches, methods and techniques of health saving technologies the most important and efficient is fitness – health-improving technology which is precisely aimed at physical development of humans, eg body conditioning, power, endurance, speed, flexibility training. The aforementioned technologies are interconnected. So if a study schedule is compiled incorrectly neglecting health requirements, it is almost impossible for students to avoid overfatigue and maintain to high work capacity. Comparative characteristics of contemporary school physical education syllabuses A.Matveev At present the content of an educational program of the Basic Curriculum is determined by so called didactic lines. The physical education subject matches up with two main didactic lines, these are the line of professor V. Lyakh (with biological orientation of study content) and the lone of professor A. Matveev (with of culturological study content). Every line is embodied in relevant syllabus naming “Comprehensive Program of Physical Education for 1-11 grade pupils” (V. Lyakh) and “Educational Program of Physical Culture for Primary, Basic, Senior and Specialized Schools” (A. Matveev). These programs are recommended by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation as alternative, reflecting different approaches to elaboration and contents of the subject of physical education. So for practical application teachers should know provisions of these programs and how differ from each other, what are the theoretical and methodical basics of them. The first distinction is difference of conceptual foundations of programs. The Comprehensive Program of Physical Education is based on the concept of sensitive periods focused on purposeful physical qualities development in definite age periods. In its turn the Educational Program of Physical Culture is worked out in compliance with basic provisions of the concept of a leading activity type in ontogenesis. In accordance with it program content considers and is relevant to developmental peculiarities of a pupil. Summarizing two concepts it should be concluded that the first program worked out by V. Lyah is focused mostly on physical training of schoolchildren, while the second one, by A. Matveev, on fostering pupils’ interest to physical exercising. The second distinction is the ultimate goals of the programs. One of the central objectives of the State Standard on Education Content is promotion of health 0f students. The Comprehensive Program by V. Lyakh addresses this issue through physical education process, when acquisition of study material at PE classes implies pupils’ health improvement as well. In its turn the Educational Program of Physical Culture by A. Matveev is aimed at purposeful teaching schoolchildren of skills to personal health improvement. This is realized by means of particular content of an educational process involving physical exercises themselves, related knowledge and techniques of individual activity. The third distinction is difference in structure of the subject. The Educational Program by A. Matveev includes an extra chapter “Individual activity techniques”. It describes not only main ways of pupils’ health improvement within individual exercising but also provides understanding of own peculiarities of physical development and physical condition. This chapter is focused on development of self-reliance and creativity of schoolchildren, formation of skills of team activity and communication. The distinctions figured out characterize specific features of these didactic lines and hence differences in program contents, as well as choice of particular methods and forms of teaching. So main means of learning within the Comprehensive Program are mostly physical exercises aimed at physical qualities development. While the Educational Program involves apart from physical exercises knowledge and skills of individual physical activities. That’s why successful completion of the Educational Program requires study books and other extra methodical and visual aids. PE study book is utilized at PE classes and at home for doing homework related to physical qualities and motor development. Study books are not so necessary at PE classes within the Comprehensive Program. This is reasonable because repeated typical assignments and time-proven content do not a lot in common with the study book material; moreover they do not require much individual work and creativity from trainees. The Comprehensive Program stipulates rather tough structure of a PE class divided into 3 obligatory parts. Every part of a class is related to a particular phase of physical workability. Preparatory part correlates with warm-up phase; main part – sustainable workability phase; final part – temporary decrease of workability. Such structure of a PE class reminds the structure of a workout session where a trainee has to complete a significant physical load. The Educational Program by A. Matveev offers different forms of structuring a PE class. It proposes in line with classes of training type, classes of educational focus which can be multicomponent thus escaping dynamics of physical workability. Speaking about classes of educational focus it should be pointed out that their content involves teaching of not only particular physical exercises movements, but also skills and techniques of individual physical activity. Educational focus classes where pupils are separated into groups and assigned different tasks are the most efficient. Tasks not pupils distinguish by the difficulty level. This approach of multilevel organization of classes facilitates a teacher’s pedagogical activity, provides more attention to more complicated tasks leaving control of easier ones to children. Utilizing group organization of classes a teacher divides each group in pairs or in threesome where one child performs exercises and another one controls and analyses it. Pupils’ control and analysis of exercises performance is conducted on the basis of material of the study book and any other didactics. We have to admit that methodical support of educational focus classes is not sufficient yet, in comparison to training type classes. That’s why many teachers conduct classes in conformity with the Comprehensive Program of V. Lyah. Anyway State Standards on Education more emphasize culturological line providing an opportunity for schoolchildren to elevate own creative activity on health promotion and leading healthy lifestyle. Theoretical-methodical foundations of school physical education contents A.Matveev Introduction. Domestic science teacher, whose role has always increased at a crucial stage of development of society, proposed a number of methodologically sound regulations and conceptual solutions to reform school. Basically, they all reflect the common need of society in the formation of diverse personality able to realize the creative potential in a dynamic socio-economic conditions, both in their own vital interests and the interests of society. In accordance with the general target setting, formulated objective of general secondary education in physical culture, which orients its objective content on the formation of versatile physically developed personality, able to actively use the value of physical training to strengthen and maintain long-term health, optimizing its own work in a dynamically evolving socio- economic conditions. Problem. It is no secret that during the pre-historic stage of physical education as a cultural phenomenon, seen mainly in the society from the standpoint of pragmatic units set up by the system of physical education and obeyed in its development of its decision purely utilitarian task to improve the "biological nature of man. Developing in the assignment of this system, physical culture, in fact, "losing" their own socio-cultural forms and functions, and salute in the mind of man as the essence of the identity of the process of physical training that relates to "direct" only with the practice of "preparing to work and defend the homeland." Such transformation of physical culture of the phenomenon of culture-based holistic development of personality, one of the means of physical preparation has identified the problem today of content of the national standard of education in physical culture, the possibility of a full realization of its objective in the modernization of national schools. Adoption of the new target set for the education of physical culture, predetermined objective "translation" of the vector of content of the school subject physical education with the paradigm of education in the paradigm of education. As a consequence, as the basic grounds of content of the school subject of physical culture are established, which are determined from the target plant, ie "Education", "personality", "physical culture". And of course, before you work out the structure and content of physical education as a subject, it is necessary to analyze the substance of the basic concepts presented in the general pedagogy, and theory and methodology of physical education. The analysis of the key concepts for education (education, personality, physical education), allowed us to conclude that the problem is structural and of content of the subject of physical culture in schools is related, including, and with today's development of categorical system of pedagogical sciences, in the first place , an integral part of the theory and methodology of physical training: 1.B general pedagogy category "education" is revealed through the processes of learning, education and development, ie in the same design and with the same filling as the concept of "holistic pedagogical process", which by definition includes training, education and development (JK Babansky, 1989). Hence, education and holistic pedagogical process are identified, i.e. are like the essence of one and the same and, therefore, targeting an objective of education is equally true of the very process of education and a holistic educational process. 2. In modern pedagogy, the notion of "education" as disclosed in the so-called "Broad interpretation", ie as a system organized social phenomenon, under which, inter alia, is incrementally younger generation to an active life. This training is provided in a variety of organizational forms of education, upbringing and education, which are saturated with relevant content, age-biological, psychological and social characteristics of students (VA Slastenin, 1987). Consequently, in this case, education is viewed through the prism of education, training and development, but appears as a socially organized system, it focuses on training people (graduate school) to participate actively in social processes. Thus, in modern pedagogy, education, or is associated with a holistic educational process and empowers learning, educating and developing functions or relates to the social system designed to prepare people (graduate school) to an independent life. Own the same generic function of the process of education, its place, role and impact on the effectiveness of holistic teaching process in pedagogic practice is not disclosed. 3. General pedagogy does not considered the term of "education in the field of physical culture". Instead it uses the concept of "physical education" which is revealed not in the paradigm of proper upbringing, but through the processes of health and physical development. As a consequence, physical education outside the educational structure and outside the focus of its targets, is perceived as an independent phenomenon, developing in accordance with its rules, laws and set targets. 4. In the modern theory and methodology of physical culture the term of "education of schoolchildren in the field of physical culture", its objectives and forms are not considered. As a consequence we see that the problem of education emphasis on formation of a pupil’s personality and the problem of content of this process are addressed in the theory. 5. "Physical education” is a basic category in physical culture theory and methodology; it is defined as a synonym for physical training and is characterized by processes of learning motor actions and physical qualities fostering. In this case the last one is viewed as a "... combined anatomical and morphological properties of a human ..." (i.e., bones, muscles, etc.) and a factor contributing to "... development of a pupil’s personality...." Hence the purposeful development of students’ "biological nature" is identified in the physical culture theory and methodology with the process of forming pupils’ personalities. 6. Despite the fact that secondary school curriculum involves the "physical culture" subject the study process is carried out in line with the physical education programs, which are, essentially and by definition, physical training programs (V. Lyakh, 1993-2003). As a consequence the basis of the physical culture subject is physical training, i.e. fitting a pupil’s physical condition to the relevant specified samples (standards), rather than a person’s active work in order to improve his/her own physical condition. Thus modernization of a national school within the education paradigm and relative insufficiencies of the existing physical culture theories and methods to be actively involved in the modernization process have led to an objective need to develop a concept based on the structure and content of schoolchildren education in physical culture. The purpose of this article is presenting to broader discussion the concept and approach to the definition of the basics of school physical culture education content, the validity of their use in the elaboration of the state secondary education physical culture content standards. Determination of basics of schoolchildren education in physical culture structure and content of was carried out through the analysis of the pedagogical theory basic conceptual categories and provision and was correlated with the existing notions of physical education pedagogy. The initial reasons for working out of the physical culture structure and content were the following: - pedagogical process as a prerequisite for a personality development; - a pupil as an active subject of pedagogical process; - a school subject as a means of pedagogical process focused on personality formation. Pedagogical process is a comprehensive entity which includes the unity of the processes of teaching, upbringing and education. Each of these structural components of the pedagogical process basics is determined by its own functional orientation, content and technology of impact on physical, mental and social sphere of a student: - Teaching - basic (generic) function is revealed through the formation of meaningful socio-historical experience and reflected in acquiring appropriate knowledge and skills; - Upbringing - basic (generic) function is revealed through the formation of socially significant attitudes, concepts, principles and values; it is manifested in the acquisition of personal philosophy and outlook, stable character traits and ways of interpersonal communication; - Education - basic (generic) function is revealed through the development of creativity and thinking; it is manifested in acquisition of cognitive and substantive activities, the development of skills for active selfrealization for individual and public interests. In a comprehensive educational process none of its components (teaching, upbringing, education) can not be isolated from one another. Socialization of a schoolchild underlies the formation of his/her personality and is characterized as an active process of his/her inclusion in a variety of social relations which may manifest themself in several interrelated images: - Identification - the process of entering into real activities measured by identifying with other people and entering into relationships with them; - Individualization - a process of self-development in a real activity measured by the acquisition of distinctive characteristics and abilities, the active inclusion in interaction and cooperation with others on the basis of shared interests, purposes and acquired quality properties; - Personalization - a process of self-realization in real creative work within the integrity of the acquired variety of quality properties and abilities, expressed in social attitudes of other people, active influence on them even outside their direct interaction. In comprehensive pedagogical process each of its components through its own generic functions stimulates a particular focus in a pupil’s socialization. Learning tasks focus stimulates the identification process; upbringing issues focus - the individuation process; education issues focus - the personalization process. Dominating pedagogical founding principles can be determined by the basic concepts of ontogenesis leading activity revealing age-specific manifestation of students activity at different stages, as well as identify the characteristics of the relationship between the components of the pedagogical process and identity formation (Table 1) . Table 1 Dominating pedagogical founding principles by education stages Indicators Activity types Structural components of pedagogical process Socialization components Primary school Basic school Senior school Study Socially useful Prefessioal-study Teaching Upbringing Education Identification Individualization Personalization The teaching subject of physical culture at school is culture sphere the basis of which lies is activities aimed at transforming (improving) a person's own physical nature. Like any activity physical (motor) activity ensures development of a human him/herself, his/her way of thinking and creativity, uniqueness of individual qualities and abilities, except for the transformation of the object to which it is directed (in this case, the physical nature of a human). Fitness activities, as well as any activity type, has a complicated systematic structural organization of its foundation, including information, operation and motivational components: - information component combines the knowledge of physical nature of a human (medical and biological basics of activity), the mental nature of a human (psychological and pedagogical grounds of activity) and social nature of a human (historical and sociological grounds of activity); - Operational component is means, methods and forms of organization activities, methods and forms of planning, monitoring and regulation of the transformation process; - Motivational activity components include samples of movements and motor actions, types and variety of athletic activities. Each of these components is made of structural components of the physical culture discipline and is described by existing training content: Physical culture knowledge - the content is being selected and grouped by three grounds of cognitive activity: natural studies, human studies, social studies. Ways to activities organization - the content is being selected and grouped on three grounds of substantive activities: means, ways (methods), types and varieties of activities. Physical improvement - content of three types of athletic activities: physical culture, sports and applied one. Every form of athletic activities includes physical exercises, motor skills selected on the basis of three value orientations: subject-generic, personally relevant, socially relevant. Such a selection of components of study discipline and its content focus in correlation with the basic provisions of the ontogenesis leading activity let us suggest that priorities of physical culture content on different education stages (Table 2). Table 2 Priorities in study content orientation by education stages Subject’s Structural components Primary school Basic school Senior school Knowledge Natural studies Human studies Social studies Means Ways Forms and types of activity Subject-generic values Personally relevant values Socially relevant values Personal activity Physical improvement (fitness – health-improving, sport – healthimproving и applied activities) Structure and orientation of physical culture content can be presented in a matrix focused on formation of a pupil’s personality within study of physical culture at different education stages (Table 3). Table 3 Conceptual grounds of structure and content of schoolchildren education in physical culture Basics Primary school Basic school Senior school Personality formation Identification within fitness activity Individualization within fitness activity Personalization within fitness activity Pedagogical process Teaching Upbringing Education Goals of pedagogical process Introduction to fitness activity Self-determination within fitness activity Self-realization within fitness activity Interaction principles within pedagogical process Learn from a teacher Learn with others Study subject and its values: Physical culture knowledge Ways of personal activity Physical improvement Learn to be a teacher Physical culture as means of physical development and health improvement Planning, control and handling by simple workout forms Fitness activity with general developing applied focus Physical culture as means to foster personal qualities and physical improvement Planning, control and handling by a system of purposeful workouts Fitness activity with health-improving and sport focus Physical culture as means of a human lifestyle Planning, control and handling by different forms and types of fitness activity Fitness activity with individual and applied focus Development and promotion of health saving skills of school, lyceum and gymnasium pupils. L. Muratova, post-graduate student, senior lecturer, N. Arnst, Docent, A. Komarov, Docent. Siberian State Technological University. The Krasnoyarsk territory, the city of Krasnoyarsk. the Department of Physical Culture and Valeology, The Health of the nation has been emphasized for the later years. It is highly important that every person is aware of healthy lifestyle and health promotion. Educational system should contribute to this as well as provide health education. The central role in this process rests to schools, as health status of schoolchildren deteriorates gradually during the school years due to decrease in motor activity, insufficient knowledge about health, healthy lifestyle, etc. Effective addressing this problem requires improvement of schoolchildren physical education system, as well as pre-university training. Hence as a consequence of the concept of continuous comprehensive and professional education innovative educational institutions appear: gymnasiums, lyceums, colleges which assist in solving aforementioned problems and conduct occupational guidance of schoolchildren. Physical and valeological education enhances specific knowledge and a skill of pupils, increases conscientious attitude towards one’s healthy lifestyle, facilitates preservation and improvement of one’s health. Moreover physical education enriched with valeological component positively affects self-esteem of schoolchildren, formation of their psychological health, occupational choice. The present status of youth physical and moral health has fallen to the critical level. The most crucial and urgent problem is poor physical condition and physical development of schoolchildren. For the time being there is significant lack of data on pre-university training systems, which should be focused on not merely “stuffing” a pupil for entry exams, but first of all on personal development of a prospective student. Improvement of adolescents’ bodies functional capabilities is the key goal of physical education. Appropriate motor activity accounts for 3 hours a week for lyceums, schools and gymnasiums pupils. Upon this amount schoolchildren show the highest indexes of mental work capacity, and it is more stable within a day span, academic achievements improve, as well as immune defense and adaptation to physical load. What is more motor activity provision needs taking into consideration age peculiarities of pupils, their physical condition, school facilities for carrying out sport and fitness events, motor activity intensity and duration balance within a day and a week. Calisthenics of 5-7 minutes duration are recommended for preparing pupils for learning activity before a class. Once in 2-3 weeks exercise set should be renewed. P.T. breaks during various classes have proven to be very efficient for improving well-being. These exercises should include movements for muscles differing from those of subjected to learning static load. Exercises and active games during breaks are aimed at decreasing and prevention of learning fatigue. Carrying out of the physical activities mentioned above within a school day promotes increasing of pupils’ motor activity at least at 1.5 hour a week. Creative activity of a schoolchild is also gaining more attention. Now universities are looking for prospective students with a range of different qualities. Political, economic and social changes of our country could not help but affected the system of education a lot. That’s why currently the emphasis is put on a learnercentered approach the outcome of it being a personal creative development. The inherent characteristics of creativity are: novelty, individual and creative actions, combination and modification of knowledge and skills, overcoming stereotypes, adequate self-esteem, self-assertion, ambitions, etc. For example, competitive exercises contribute to moral development of a child. As competition rules are based on fair play and competitiveness. Noone is looking for an easy victory, as moral rules of a group become strict models of behavior. However the following conditions and means should be taken into account upon fulfilling of the aim of schoolchildren creative development: 1. Particular content of the pre-university training which ensures senior schoolchildren creative development, 2. Determined methods and forms of senior schoolchildren creative development within differentiation of teaching, based on individual and collective activity types, 3. Elaborated model of senior schoolchildren creative development explaining its structure, content, methods, forms based on theory and practice interconnection. Nowadays the education is one of the most rapidly changing spheres of life of our county which is characterized by extremely complicated contradictory processes determined by the impact of multiple objective and subjective factors. Different regions of Russia re testing new models of conducting State Uniform Examination; many discussions at different levels are held on the education modernization issues. Interrelation of physical and general valeological education contribute to improvement of particular knowledge, conscious attitude to one’s health and promotion of healthy lifestyle, as well as to occupational choice. References: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Кофман Л.Б. Настольная книга учителя физической культуры. – М.: Физическая культура и Спорт, 1998. – 496 с. Чесноков Н.Н. Довузовская подготовка как этап непрерывного физкультурного образования. М., 1997. – 126 с. Абульханова-Славская К.А. Деятельность и психология личности. – М.: Наука, 1980. – 333 с. Лубышева Л.И. Концепция формирования физической культуры человека. – М.: ГЦИФК, 1992. – 120 с. Лях В.И. Развитие и совершенствование координационных способностей школьников от 7 до 17 лет в процессе физического воспитания // Физиологические особенности организма школьника и физическое воспитание: Сб. науч. тр. Свердловского пединститута. Свердловск, 1988, с. 81-87. Давыдов В.В. Проблемы развивающего обучения. – М.: Педагогика, 1986, - 240 с. Виленский М.Я. Формирование физической культуры личности учителя в процессе его профессиональной подготовки. – М., 1990, - 54 с. Endurance sports as means of healthy lifestyle promotion and self-management skills constructing Vyacheslav Ogarev, PE teacher of higher qualification, kettlebell lifting trainer, Vytegra Polytechnic School, The city of Vytegra, Vologda region Since 2006 I have been working as a PE teacher specializing in kettlebell lifting in the Vytegra Polytechnic School in the settlement of Belousovo of Vytegra district of Vologda region. I have been engaged in kettlebell lifting since 1976. Since 1993 I have been a head coach of the regional youth team in kettlebell lifting. I have elaborated a particular training methods with a person-oriented approach as its essence. I describe it below. Workout should be conducted individually because, firstly, of personal technique building process, secondly, a person’s capacity to do a particular number of repetitions varies a lot as everybody has a different weight and physical condition. Workout starts with a warm-up, then a newcomer takes a 8kg kettlebell and does as many repetitions by each arm as he is able to, but no more than 50 repetitions. If he has completed 50 swiftly, 2 extra kilos are added and a person goes through the same procedure. If a person can make only 8 repetitions, he should continue with general physical training. If from 10 to 50 then next time a trainer should give an assignment in such a way that the total sets would make up for 50 repetitions, while every set consisting of no more than 30% of the record repetitions made. For example, 30 record repetitions in the first time mean that next time a person should do 3 sets of 10 repetitions. At the same time a trainer has to carefully watch the training process controlling the technique, as it is easier to teach that to correct a mistake in technique. After 6 workouts (3 times per week) and if 50 repetitions are not a challenge for a boy, he should continue with a 10kg kettlebell the same way. Upon 50 repetitions of 10 kg kettlebell rise by every arm training continues with 12kg kettlebell, then – 14kg, then – two 8kg kettlebells arm thrust. Since this moment sets of the main part of a workout are measured in minutes not repetitions. Next workout is compiled of 3 1-minute arm thrust sets and 6 1-minute jerk uprise sets (jerk uprise is exercised in the same way as arm thrust). Next time – 6 1-minute arm thrust sets and 3 1-minute jerk uprise sets and then alternating the number of sets at every workout. After 6 workouts and if the total accomplishment is more than 100 repetitions (in jerk uprise and in arm thrust), a trainee may switch to bigger load (extra 2kg to a kettlebell). A boy has to keep a diary and do homework (exercises for abdominals, muscle of a back, leg and races). A trainee should have a choice out of 4-5 types of exercises on every muscle group. Every workout finishes with exercises for abdominals and football playing, basket throwing or slow running. Some auxiliary exercises contributing to mastering of double-event technique may be included in a workout, for example, kettlebell swing, kettlebell breast up, mobility exercises, and to increase muscle strength engaged in double-event performing, foe instance, half-knee bending with kettlebells on shoulders, abdominals exercises, various swings. Upon a trainee may perform 100 16kg arm thrust and jerk uprise, workout plan changes significantly. If at the first workout a trainee performs 9 arm thrust sets, then he has to do 3 10minute jerk uprise sets. The second workout – 6 sets in arm thrust and 6 sets in jerk uprise. The third workout – 3 3 arm thrust sets and 9 jerk uprise sets. The number of workouts per week is 4 now. Upon accomplishing advanced degree a trainee starts to use kettlebell of different weight in arm thrust and jerk uprise, for example, first set with 8kg kettlebell, second – 10kg, third – 8kg (pyramid, as weightlifters call it). Upon a trainee may perform 100 24kg rises one more workout a week is added. Upon accomplishing Master of Sports of Russia degree the number of workout is 6 a week. Here is a raw method of arm thrust and jerk uprise training. Every trainee requires personal approach so the number of minutes in a set and the number of repetitions per a minute may vary according to the objectives stated. Cross-country race or cycling, or skiing are particularly important in achieving high results. In 2006 D. Benidze, who has been training in line with the method described since 2001, at the age of 15 accomplished Master of Sports of Russia qualification at the All-Russia Junior Championship and took 3rd award. A year later he won the Cup of Russia accomplishing at the same time qualification of the Master of Sports of International Class. Preparing for World and Europe Championship D. Benidze was training by the caterpillar method, 6 workouts per week. Training plan was concluded on a weekly basis. At the first week on Monday – 3 sets by 1 minute by 18-22 repetitions each 16, 20, 24kg kettlebells. Tuesday – 6 sets (two series of 16, 20, 24kg kettlebells). Wednesday – 9 sets (3 series). Thursday, Friday, Saturday repeated Monday program. At the second week every set lasted for 1.5 minutes. The third week was the repetition of the first one. At the fourth week every set lasted for 2 minutes. The fifth week repeated the second one. At the sixth week every set lasted for 2.5 minutes. The seventh week repeated the fourth one. At the eighth week every set lasted for3 minutes. The ninth week repeated the sixth one. After the eighth week the caterpillar started to go down. At the tenth week every set lasted for 2 minutes, eleventh – 2.5 minutes. At the 12th week every set lasted for 1.5 minutes. At the 13th week every set lasted for 2 minutes and sets were performed in inverted sequence - 9, 6, 3, 9, 6, 3. After two days rest competitions are to start. Apart from all these exercises every training was accomplished with half-knee bending with kettlebells on shoulders by the scheme 3, 6, 9 sets of 12-18 repetitions in each one. 9 sets fall into the workout with 3 sets of 2 kettlebells arm thrust. Weight of kettlebells was 36, 40 and 44kg. Abdominals exercises were also performed. Jerk uprise was performed at every workout for 10 minutes. The initial kettlebell weight was 20kg, then gradually increasing at 2kg. At a competition D. Benidze was doing jerk uprise for all the 10 minutes with 32kg kettlebell thus setting the Records of Russia, Europe and the World in weight category below 63kg. D. Benidze was covering 10km race every day for a month before a competition. The Cup of Russia 2009, Europe and World Championships were won with the Records of Russia, Europe and the World. Here are four training methods in kettlebell lifting used: 1. Percentage out of the maximum rises completed (no less than 30% and no more that 70%) which is described in powerlifting guidance books. 2. Short 1-minute circuit, i.e. first workout – 3 1-minute sets, second – 6 1-minute sets, further alternating the number of sets (mostly used by lifers of mass qualifications). It appeared after time limit introduction. 3. Long 10minute circuit, i.e. first workout – 3 1-minute sets, second – 6 1-minute sets, third – 9 1minute sets, further alternating the number of sets. It is mostly used by lifters of 1 st grade and Candidate to Master of Sports. It appeared after time limit introduction. 4. Caterpillar. It is used by Master s of Sports. Efficient for working with high-profiled athletes. Avoiding overtraining is the central feature. I never use now any kinds of kettlebell presses, as I found out during my training experience that these exercises decrease flexibility, increase body weight thus prolonging the way to excellence. I neither use specific hand strength exercises. I suggest that jerk uprise is enough. During training kettlebell weight should be at lest 4kg less than at competitions in order to avoid injuries and increase strength endurance. Half-knee bending with kettlebells on shoulders, abdominal exercises are performed too. Running is important as well. Taking into consideration personal characteristics of a trainee these simple methods produce good results. Sometimes a trainee is not focused on high achievements but simple wants to keep fit. So the first and the second methods are better for him. Summarizing my experience I have made a conclusion that my method of kettlebell lifting training is relevant, as it has produced high results: 1. Strength and endurance for draftees, 2. Promotion of healthy lifestyle among kettlebell lifters, 3. Self-management skills, 4. Providing conditions for trainees’ higher accomplishments. I have trained 8 Masters of Sports of Russia (Sergey Shuvalov, Anatoly Kuznetsov, Alexey Arsenyev, Alexander Ermolin, Denis Anikin, Alexander Ogarev, Jonny Benidze, Elena Yurysheva), 1 Master of Sport of Russia of International Class (Jonny Benidze) more than 30 Candidates to Master of Sports of Russia. Lifters from our club take awards at annual regional competitions. More than 80 Records of the Region, 15 Records of Russia, 9 Europe Records and 4 World Records have been set. Records of Russia, Europe and the World, apart from 2 Russian ones, have been set in later years. Sociological analysis of Lyceum pupils’ attitude to physical training and healthy lifestyle D. Morozov, V. Panachev, Lyceum №1, Perm State Technical University, city of Perm Scientists started paying attention to mass schools pupils’ state of health in XIX century. Doctors found that children suffer from shortsightedness, posture fault and neurasthenia, and the situation got worse from class to class, for these diseases were inevitable consequence of school training. The diseases were named «school diseases». At that time their principal causes were defined as well. They are overloaded programs, a great number of lessons a day, static position of a child’s body for a long time not corresponding to children's age features. The causes of school diseases have not disappeared, their quantity has gone up instead, due to increase in information stream, computerization, TV domination, and motor inactivity. At the same time pupils of specialized schools, gymnasiums and lyceums suffer from diseases more often than pupils of comprehensive schools, and their health gets worse faster. Pupils’ health deterioration is influenced not only by negative economic, socio-cultural and environmental factors in the country, and intensification of educational process (when pupils’ physical abilities are not considered), but also by breach of hygienic educational norms, and insufficient training of teachers in pupils’ health protection. The aim of any educational institution is not only to teach children, but also protect and strengthen their health. Health schools, combining educational and health-improving processes, help to solve this problem. Lyceum №1 has been engaged in this work since 1989. Since 2000 our Lyceum №1 PSTU has been a health school. We consider important not just to copy experience of other schools, but to study various factors influencing the lyceum pupils’ attitude to health promotion at school to make the Lyceum’s activity purposeful, system and planned. Various factors influence a pupil in educational process, and they all to some extent influence his/her psychosomatic state. From the point of view of health improvement we can single out the following influences: background, pedagogical, health-improving, juvenile, family and administrative. Background influence is a constant throughout a certain period of time (for example, a lesson, a school day, an academic year) influence of organizational and material environment of an educational institution on a pupil. Optimization of the Lyceum’s operating mode is important. It includes introduction of trimesters instead of quarters, dynamic breaks, obligatory staying of pupils in the open air, etc. Besides, it is necessary to beautify the yard, to maintain housing utilities working well, to develop recreation rooms, to prevent posture faults, to provide security for pupils. Such actions have long-term health-improving background influence on pupils and create a positive spirit. The concept of Russian education modernization and some other documents are concentrated on a problem of improvement of lyceum students' training quality according to the modern requirements of the State educational standard. Modern society needs healthy specialists with developed creative abilities, able to make right decisions in non-standard situations and apply the fundamental knowledge received at school. Physical education is one of our culture components. The main objectives of physical education are to improve pupils' health and cultivate a healthy lifestyle among them (the Concept of development of physical training and sports in the Russian Federation). In the last years Russian children and the teenagers' state of health has deteriorated. Medical examinations testify that during studying at school children's health gets 4-5 times worse. The existing system of physical training at schools does not provide pupils with good enough health. So, there is obvious contradiction between the society's requirements and pupils' training conditions. Modern pupils do not think Physical education lessons are necessary. It is important to find out the reasons for such attitude and try to change it to a positive one. To solve this problem we questionnaired the lyceum pupils and PE teachers conducting lessons at 10-11th grades. The questionnaire contained 10 questions for teachers and 15 questions for pupils. The analysis of pupils and teachers' attitudes to physical training revealed discrepancy between them which starts with motives. Pupils attend PE lessons because it is their duty, and teachers think that pupils do it to keep fit and stay healthy. This pupils' attitude influences their physical fitness deterioration. Most teachers (98,4%) consider that lyceum pupils are happy with PE lessons, while 13% of pupils do not like them. The majority of teachers think that the most popular kinds of sports among pupils are sport games, specifying that basketball takes the first place, volleyball - the second one and football - the third. Though, the lyceum pupils put basketball on the third place; the first and second places, in their opinion, take football and volleyball. In general, according to the lyceum pupils, sport games do not take the leading position. Swimming is the most popular with pupils. The lyceum pupils stated that they often miss PE lessons due to some illness. This once again proves the importance of PE in health improving. Comprehensive monitoring of schoolchildren psychophysical health and adaptation in educational environment by “Diakoms” and “Sociomonitoring” methods V. Panov “Presnenskiy” center of psychological-pedagogical rehabilitation and correction, Moscow One of the factors foreseeing child abilities to study without affecting negatively his/her psychological and somatic well-being is the scope of his/her adaptation in an educational environment. A pupil’s health is the outcome of integration of all aspects of social life a child involved. Preservation and promotion of pupils’ health is the central objective of any educational process. Psychophysical health level as one of the key criteria of pupils wellbeing and development within an educational process is considered as a starting point in elaboration and organization of an educational process at all stages of education. Present surveys indicate that 53% of pupils are medically fragile, 2/3 of above 14 have chronic diseases, only 10% of graduates are healthy. Up to 80% of school leavers are limited within their occupational choice due to health status. Health and physical development of more than 40% of below the draft age boys do not meet military service requirements. Preservation and promotion of health of pupils, formation of health and healthy lifestyle values, choice of proper educational technologies have become a priority goal within the educational reform and introduction of new educational standards. Successful solution of these issues requires applying of innovative methods of pupils health examination meeting the following criteria: - Firstly, as the majority of modern examination methods tests structural state of various inner organs primarily, a new approach should evaluate them in terms of their functional activity, so it should be more “functional”; - Secondly, as every modern examination method tests only a single or maximum several organ (systems) of a body, a new one should examine all organs and systems at once, so it has to be “systemic”; - Thirdly, as all modern methods are sensitive to one or several inner or outer factors influencing a person’s health, thus the speculated method should reveal and evaluate impact of all factors at once, so it has to be “universal”. “Diakoms” health express diagnostic and “Sociomonitoring” program-methodical set provide a comprehensive solution to the challenges. They enable all-up examination of pupils psychophysical welbeing, interpersonal relations, educational activities implementing, children behavior handling. obtained and estimate indicators undergo double statistical processing and are represented in percentage and sigma. “Diakoms” chart interpreting enables pretty precise evaluation of pupils psychophysiological condition by the following indicators: 1. Mental tension – increment of activity of lymphatic system (LS) >+45%. Mental state determined by anticipation of a negative or unfavorable for a person situation. It can be accompanied by a general sense of discomfort, anxiety, sometimes fear, but unlike anxiety it implies readiness to handle a situation, find a way out. 2. Proneness to conflict, aggression – increment of activity of meridians upon proneness to conflict – stomach>+20%, upon aggression – liver>+20%. Proneness to conflict is a discrepancy between the expected and the experience. In classical psychology it is a confrontation of opposite incompatible tendencies in a person’s mind. At school this can be in form of a conflict, proneness to arguing. Aggression is an increased soreness, anger expression provoked by encroachment to an item of affection of a person or spontaneously upon ingenerate aggressiveness as a trait of character what can a feature of a choleric temperament. Left branch of a meridian shows personal peculiarities, right branch – environment interaction response. 3. Anxiety (interpersonal, self-evaluation) – decreased activity of meridians of liver (Lv) and stomach (S) simultaneously or separately less than 30%. Correlation studies conducted in pilot school indicated that aggregate and interpersonal anxiety is accompanied by decreased activity of a liver meridian, selfevaluation anxiety – decreased activity of a stomach meridian. 4. Proneness to phobias – decrement of an indicator of ergo-trophotrope activity less than 30%. It matches expressed introversion in psychological terms. Introverts are prone to self-analysis, anxiety, hypochondria. If introversion develops into a severe state different phobias occur, for example carcinophobia, claustrophobia. 5. Proneness to exhaustion of central nervous system (CNS), attention concentration decrease, quick attention exhaustion – decrement of activity of meridians of LS and Tl <-30%. Inhibitory processes in the central nervous system predominate excitative processes. Determination of the cause of CNS exhaustion can be fulfilled by functional loading: upon ingenerate defects or organic disorders LS and Tl state does not change after loading. It should be pointed out that main causes of CNS exhaustion are computer games, longitude computer activity without break, watching TV, listening to music or foreign language in headphones in motion. All these may further lead to immunity deterioration, functional imbalance of the whole body. 6. Hypermotivity of CNS, attention switch problems, attention deficit - increment of activity of meridians of LS and Tl >30%. %. Excitative processes in the central nervous system predominate inhibitory processes. This is often ingenerate peculiarity of CNS especially if a fetus experienced anxiety. Such babies are born with nervous hypersthenia, they are hyperactive, anxious and watchful towards the outer environment. CNS increased excitability can be a consequence of a disease, head injury, surgery under general anesthesia, and can be accompanied with increment of intracranial pressure, headaches. 7. Tendency to decrement of adaptation – decrement of activity of meridians PS and MP <-20%. In this case even a tendency to decrement of these meridians is already negative sigh. Social disadaptation is understood as rejection of social environment, search for meaning of life in regard to one’s aspirations what may lead to unpredictable behavior and asocial acts: alcohol and drug abuse, criminal conduct. Such state may lead to decrease of immune of a human, proneness to serious diseases increase. 8. Decrement of volition - <-30% decrease signifies of immature emotional-volitional sphere, that is reluctance to make serious decisions, irresponsibility, inability to defend one’s opinion and show initiative, easily subjected to suggestion. 9. Decrement of motivation to study – decreased activity of the antagonist pair – of colon and kidneys – on 10%. Data acquired from the “Diakoms” survey in pilot school indicated that decrease on motivation to study is accompanied by decrement of activity of this pair of organs. According to a theory inclined in the program colon activity is linked with psychological moral sinew, while activity of kidneys – with interest and attention to the external world. Thus it is clear that the higher the moral sinew and the greater interest to the external world of a person the bigger motivation to study he/she possesses. 10. Adaptation syndrome – cumulative adaptation responses of a body. At school adaptation syndrome is pretty frequent in multinational groups. What is more this indicator is often traced in Asian children and during mass virus diseases. 11. Decrement of intellectual activity – on 30%. It may be a sign of intellectual overload or decrease of interest to any purposeful activity. This decrement does not imply mental disorders. “Diakoms” chart interpreting enables evaluation of psychophysiological condition of every pupils as well as health profile of the whole study group. Bar chart 1. Health profile of a study group The “Sociomonitoring” program-methodical set provides comprehensive evaluation of interpersonal relations, as well as: - Detection and prevention of mass and individual school (social) disadaptation; - Diagnostics, planning and support of developing potential of social environment of a group, the whole institutional social environment; - Defining personal effects and changes under developing pedagogical technologies, correctional technologies, rehabilitation projects, trainings, etc; - Study of motives and causes of aggressive, stress, suicide and other types of abnormal behavior of children, adolescents in any educational institution; - Study of gender relations in educational institutions, causes of gender transformations; - Study of hidden factors determining formation of children and adults behavior in any educational institution. Right columns indicate the level of own social activity of a pupil which he/she is ready to express in collaboration with group members for achieving optimal psychic comfort. Left columns show the degree of demand of a child by a social class environment within educational activities (or social recognition of a person by a group). The scale is from +3 to -3. Bar chart 2. Aggregate impact of partners We have carried out monitoring of psychophysical condition of final grades of primary school of progymnasium №1768 and secondary school №59 of the Central Administrative District of Moscow within the frames of experimental research. The study covered 6 groups of the 4th grade totaling 136 pupils. The results indicated decreased intellectual activity (50-75%), significantly decreased adaptation activity (30-70%) in 4 groups, pretty high level of self-evaluation anxiety (30-70%) in 4 groups, in 3 groups – CNS arousal (40-55%), in 2 groups – high level of psychic tension. So general psychophysical health status of pupils is characterized by higher claims for attention, difficulties of interpersonal relations, psychic tension and constant expatiation of troubles, anxiety. Psychological profile of a pupil indicates decreased interest towards school study, its content and obviously teaching methods. Our recommendations to teachers and school administrations assist in considering peculiarities of introduction of new state educational standards for primary school, determine risk zones and educational process negative factors. Physical training for students of extended education institutions E. Pasalsky, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Changes in the Russian society predetermine alterations in schoolchildren physical education. One of the ways of addressing the issue of pupils’ insufficient motor activity is a pretty new approach of senior schoolchildren’s sport majoring within PE classes; the basis of this approach is integration of basic and extended physical education. So children sports collective groups should be established in order to provide them with an opportunity to choose interested kind of physical activity and get pleasure out of training. Hence most efficient forms of sports and physical activity are to be promoted. It is obvious that the regular pedagogically organized physical exercising produce better result. Moreover students get greater health-improving effect out of matching exercises, not a number of unrelated ones. Anyway the emphasis should be out on health-improving aspect of physical education. Motor development should not be an end in itself. And physical education should pursue achievement of quality indicators, not quantity ones. The basis of physical education is ideally adaptation of efficient sport techniques and methods to peculiarities of students physical education. Available resources of secondary education system are not enough for overcoming lack of motor activity. So scope of physical training opportunities has to be enhanced, utilizing facilities of extended education system. Within this system physical-sport activities are provided in specialized extended education institutions (Child-Adolescent Sports Schools) and in non-specialized Youth Creativity Centers and clubs. The central goal of extended education is formation of spiritually rich, physically healthy , socially active, creative personality. This goal is achieved by means of healthy lifestyle promotion, creation of educational programs of new generation, scientific-methodological provision of extended education. Pedagogical process in extended education institutions is different from that in schools by firstly voluntary class attendance. Hence motivation issues stems from that; these should be taken in consideration like health improvement issues. Health improvement emphasis means that training is aimed at not achieving high sport results but promotion of regular exercising, increasing of students’ health status and physical condition, developing of individual and collective qualities. Hence children collective groups’ activities should be regarded as promotion and formation of bright emotional healthy lifestyle, what is a key feature in education of a harmonic personality. Poor facilities of non-specialized extended education institutions are to be considered as well. These are lack of equipment, apparatus, etc. Hence we encounter the issue of collaboration of a school and a sport extended education institution. Experts emphasize this feature what is to contribute to enhance and diversify motor activity of pupils. Anticipated results are physical condition and health improvement, positive changes of a schoolchild him/herself, i.e. expanding circle of peer contacts, learning new skills, self=actualization and socialization. Many experts point out necessity to create conditions for a free choice of a sport event by children, time management in order to avoid overfatigue, negative emotions, boredom, but instead of that for stimulating eagerness to exercising, commitment to healthy lifestyle by clear vision of one’s progress. Main principles of extended education institutions work are mass scale and affordability of exercises based on voluntary children associating by interests, development of children leadership skills and self-reliance. Experts are convinced that nowadays issues of health status and physical condition of younger generation are of utmost importance for the whole society. So social significance of physical training and healthy lifestyle is addressed, as lack of motor activity is one of the causes of poor well-being. Central means of health improvement of schoolchildren is active physical exercising. It contributes to sound functioning of body organs systems and physical abilities development. Anyway exercises used should be safe and comply with norm of physical load suitable a particular student. Several years long studies indicated that: - Recreational bodybuilding is an efficient means of advancement of senior schoolchildren physical condition. Systematic exercising provokes positive changes in physical development, physical and functional condition of pupils, increases work capacity. - Increased need in communicating with peers during workouts, commitment to healthy lifestyle. - Use of relaxation exercises increases functional and adaptive capabilities of schoolchildren, contributes to proper organization of PE classes. - Analysis of physical condition changes proves high efficiency of health-improving bodybuilding activities in non-specialized extended educational institutions. High degree of students’ contentment with these activities is also emphasized. Bud’te zdorovy! Be healthy! A. Pavlov, post-graduate student, the Department of Pedagogics, KSPA, I.Achepovsliy, honored teacher of the Russian Federation, city of Petrozavodsk It is important to remember that the knowing of own roots, history of the ancestors, respect for cultural heritage of the people is one of the ways of displaying internal personal culture, convictions, attitude to what’s going on in the state. For this reason we should study not only grammar and lexis rules of the mother tongue, but also be interested in its origin and development, as many usual, at first sight, words may have a latent meaning attached to it by our ancestors. The present work focuses on the origin of one of the most widely used and popular words of the Russian language – "zdravstvuite" (hello). People of different ages, genders and social statuses use this word several times a day. Since the early childhood parents teach the children to be polite, thus first of all acquainting them to the word "zdravstvuite" (“hello”). Meanwhile not many people think about the genuine meaning of this word given to it by our ancestors in very ancient times. "Zdravstvuite" is a word used as the salutatory form in Russian upon meeting someone. However its genuine meaning is wishing health. This expression originates from the word "zdravstvovat’" - to be healthy/well, to exist safely. This national greeting wish differs the Russians from many Europeans, who wish pleasure, happiness and the good in their greetings. A Russian has always seen health in everything. Thus, it is possible to draw a conclusion that the initial meaning of the word "zdravstvuite" is a wish of health, what is also proved by its radical – "zdrav", what means “health”. Our ancestors considered it necessary to wish each other good health when meeting what was, in their opinion, the most important matter in life. That is the same reason why such phrases as "bud’ zdorov” (be healthy), “zdraviya zhelayu” (wishing you health), “zhelayu zdravstvovat’” (I wish you to be well), “dobrogo zdoroviya” (to good health), etc are still used in everyday communication. In modern speech the word "zdravstvuite” gradually loses its initial meaning. It is a part of etiquette and is used only as a greeting. Thus almost no one considers health issue. Greeting formulas have great importance in a communication process. Greeting is one of the most important forms of speech etiquette. People come into contact through it, define human relations. Not knowing greeting formulas means being unable to communicate. Greeting formulas connect people, strengthen contacts, give joy of human dialogue. Any language is historical memory of a nation embodied in words. Thousand-year spiritual culture is reflected in a language. So the culture of language, culture of word is considered as continuous bond of generations. Mother tongue is a soul of a nation, its supreme and most apparent characteristic. Such important and features as national psychology, national character, habit of thought, originality of art creativity, morality and spirituality find their expression in and through language. Knowing mother tongue, correct use of its forms and speech tokens is obligatory for every self-respecting person. References: 1. Введенская Л.А., Павлова Л.Г. Культура и искусство речи.- Ростов-н-Дону, 1995.- 345 с.; 2. Граудина Л.К., Ширяев Е.Н. Культура русской речи и эффективность общения. – М.: Наука, 1996.; 3. Сопер П.А. Основы искусства речи.- М., 1999.- 359с. 4. Янышев В.Г. Речь и этикет.- М., 1993.- 451 с. Role of animation activities in formation of adolescents’ and youth healthy lifestyle. V. Plotnikova, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Several President’s Addresses to the Federal Assembly, in particular in 2001 and 2008, touched upon the issue of the health status of the nation. Many academics also raise this problem, as deterioration of nation’s physical, mental and moral health in circumstances of rapid technology development and ecological disturbances is obvious. In Russia only 5% of school leavers comply with the norms of physical development and health. So the most crucial issue of the country’s nowadays development stage is preservation and promotion of nation’s health. In the Address to the Federal Assembly 2008 the President stated that: “System of education forms a personality and as a whole lifestyle of the nation. Revival of the Russian educational system is of utmost importance for formation of new generations”. The President pointed out sound health of schoolchildren as the key trends of national policy emphasizing priority of healthy lifestyle in an school’s educational environment. In this regard one of the central directions of state policy in addressing social problems related to the population health is development of physical education and sport nationwide. Physical exercising, recreation sports and tourism are efficient means of preservation and promotion of health; they decrease risk of non-infectious diseases (cardio-vascular diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis, obesity, etc) and have proved to be efficient measures for prevention deviant behavior, alcoholism, smoking and drug abuse. Formation of person’s healthy lifestyle is positively affected not only by good living conditions and, physical training, but also cultural and leisure events which are important for morality, physical and mental wellbeing. Lately leisure and recreation activities, and entertainment are being called as animation. While people engaged in these activities called animators. The term animation means stimulating full-scale recreation, social-cultural leisure activities for a human through affecting his/her stamina. Animation activity is an innovation activity aimed at involving participants of educational, social and cultural process into active, creative, mutually beneficial interpersonal relations. Sport animation is a specific type of animation activity. Sport animation is an innovation activity aimed at involving its participants into active, creative interpersonal relations aiding to health improvement. It includes as entertaining events, as various sport games, exercises and competitions thus enriching the content of its programs also with health related goals. Sport animation has a particular theoretical basis as its inherent part. Below I examine the logic structure of animation activity: its subject, object, topic, forms, means, actions based on particular methods, and result. A subject of sport animation is a leader, a manager of sport animation. A collective subject can be such group of people or the society in general which are united by similar goals, acting in the same direction for achieving a result suitable for all. An object of sport animation is groups or individuals for whom a program is prepared. This is a central element of a system of satisfying their cultural and physical needs. Factors as age, health status, attitude to leisure, physical training and sport should be taken into consideration. A topic of activity is a matter at which subject’s activity is focused on. Topic of sport animation is animation programs. Sport animation programs are based on healthy lifestyle. Preservation and promotion of health are central functions of sport animation. According to the definition by the World Health Organization, health is a state of full physical, mental and social well-being. Comprehensive viewpoint on health can be represented in a 4-component model, consisting of somatic, physical, mental and moral health: 1. Somatic health – current condition of organs and organ systems of a human body, based on individual biologic development program, implying use of sport-recreation and tourist-recreation active animation programs. 2. Physical health – level of development of body organs basing on body functional reserves, implying application of medium active animation types such as sport-entertaining and contest-playing. 3. Mental health – condition of a mental sphere based on peace of mind, ensuring relevant behavioral response. It is satisfied by sport-entertaining programs. 4. Moral heath – complex of motivations and needs based on a person’s values. It is satisfied by sportcognitive and teaching programs. Every aforementioned type of animation programs may be a combination of different forms of animation activity. Forms of animation activity: Sport-recreation and tourism-recreation programs – aimed at sport and active leisure enthusiasts; focused on restoration of strength and health by means of physical activity on fresh air; such kinds as journeys on foot, sport events, camps, festivals, etc. Sport-entertaining programs – aimed at participants of any age and their involving into active movements through alluring funny contests, active games, etc. For example, pirates and caves visiting role plays, etc. Sport-cognitive programs – based on promotion of moral values through active leisure. These are journeys on foot, excursions, short educational programs focused on learning different skills of various crafts. Upon participation in such program its attendees point out they have learnt to communicate on local language, learnt national musical instruments, dances, etc. So here more attention should be devoted to relaxed, casual atmosphere. Means. Among central means of animation activity are the following: participants inclusion into action, diversification of animation programs. Action. In animation activity it consists of three stages: elaboration and preparation stage, implementation stage and analysis and control stage. The following means are utilized: illustration, drama performance, games, competition, rhythmic movements, etc. A result is the final phase of activity, proving that the goals set have been correct. A result of animation activity may be the following: - Harmonic physical and functional development; motor, strength, mobility, agility development; - Development an strengthening of a human physical resources during leisure time, relieving of fatigue, revival, psychological safety valve by games and entertainment; - Broadening and deepening of knowledge on physical training and sport, their role in diseases prevention and nation health status increase; - Promotion of positive attitude towards physical training by fostering interest and habit of regular exercising; - Use of physical training and sports as an important component of moral and mental development, cultivation of patriotic and civic values, creative development; - Involving of all groups of population to physical training; use of physical training and sports in social adaptation of the disabled, orphans; promotion of healthy lifestyle. References 1. Гаранин Н.И., Булыгина И.И. Менеджмент туристской и гостиничной анимации. – М.: Советский спорт, 2003 – 156 с. 2. Курило Л.В. Теория и практика анимации: Ч.1. Теоретические основы туристкой анимации: Учебное пособие, М. Советский спорт, 2006. – 195 с. 3. Новиков А.М., Д.А. Новиков Обучение основам методологии // Педагогика. 2009, №7, с.1117. Professional formation of adapted physical culture prospective teachers O. Pokhorukov, Kuzbass State Pedagogical Academy, city of Novokuznetsk Modern situation in the education let us state the uncertainty of the requirements from the society’s and governments’ sides. According to the modern analysis, we suppose that professional training of a modern teacher of physical education is aimed at acquirement of professional activity, in which objective knowledge are very important. It Is aimed at his or her being ready to consistent teaching activity, but not its separate pieces or forming the system of pedagogical knowledge and skills. Professional and competent is the kind of teacher’s work, in which pedagogical activity is being carried out. The word competent comes from Latin «competens (competentis)» - meaning having some experience and knowledge in some sphere, and being able to judge according to it. The necessity in the competency approach in educational process is because of the requirements of the modern society. The European Union and Russian conception of modernizing educational system are those, who implement th competency approach. Bolotov, Lednev and many others emphasize the practical approaches of the competences. Zimnyaya stresses that White in his work, called «Motivation reconsidered: the concept of competence» (1959), fills competence with personal components, including motivation. This fact shows that in the 60-s of the last century there has already been the understanding between competence and capacity. The capacity approach in domestic psychology is introduced in the works of Bodrov, Klimov, Kuzmina, and others. The capacity approach means integration of the theoretical and practical background in the process of education, which provides the adaptation of a graduate to the labor market. The specific character of this kind of approach in education is based on the knowledge and facts, which are gained by the student him (her)self, because he (she) through finding solution to different problems. The student becomes the subject of the educational process. This fact contributes into the forming (building) of a steady cognitive process as a tool of increasing the quality of the proficiency of the specialist. Changes in education made the high schools prepare specialists of high proficiency. Though these changes are already noticeable, they are not enough spread. The graduates of the physical departments are not enough prepared to propaganda of a healthy lifestyle and they do not show a good example themselves. Moreover the curriculum is not aimed at the children’s interests and gives only the school program for studying. Modernization of the physical education is made for overcoming difficult situation in which there is a contradiction between requirements of the society and the proficiency of the teachers. The aim of the modernizing is in building up devices of steady cognitive process of developing the system of education of the professional training. The realize the mission of a teacher, a newly-made teacher must be an example for the students and act according to the received knowledge and skills. Under these circumstances the social importance of physical education and forming a thoroughly developed individuality of a student is increasing. Fitness Aerobics classes for preschoolers and primary school children E.Ponomareva, Elets State University named after I. Bunin The program is concluded in accordance with key provisions of the Concept of Preschool Education where the goal of the educational process is stipulated as strengthening health, physical and mental development via fitness aerobics means. We have opted for fitness aerobics as this kind of sport is affordable, popular, diverse and spectacular. It is a modern and powerful tool in promoting healthy lifestyle. Physical exercises as the essence of physical education is the central means of targeted impact on physical development. Systematic muscle training requires taking into consideration the following aspects: alternating muscle tension and relaxation weary less that static tension. Taking into account quick fatigue a person should avoid extreme physical load while exercising and alternate activity types every 20-30 minutes. Types of PE classes (by N. Kozhuhova) Teaching-training classes. Implying formation of motor skills, physical qualities development, and advancement of skills typical for fitness aerobics. This type of classes should account for at least 50% of the total. Comprehensive classes. Aimed at synthesis of different types of activity addressing objectives of physical, mental, moral development. Play classes. Based on various active games, shuttle runs, etc. motor skills advance, physical qualities develop, interest to physical exercising, sport competitions and team spirit is breaded. Choreographic class. The central objective is formation of correct posture, development of muscles, flexibility. Class structure The structure is based on recommendations by M. Levin adapted to fitness aerobics peculiarities. There is a typical class structure, nonetheless it is just a basis for addressing the objectives. Preparatory phase of a class. Introduces children to planned activities, establishes a contact between a teacher and pupils. A child body is being prepared for upcoming exercising of the central class phase. The first phase involves marching exercises, smart walk, slow run, jumps in place and forward, response and alertness drill, etc. The objective of this phase is to arrange children in a group, pupils’ acquiring collective action skills; these exercises promote discipline and attentiveness. Central phase of a class. The objective is to let children acquire basic and specific skills needed in fitness aerobics. The phase also focuses on movement coordination, time and space orientation, self-reliance, and other psychophysical qualities. This part of a class involves as traditional (walk, run, jump, breathing and balance stand exercises), as specific fitness aerobics exercises such as classic aerobics, step aerobics, funk/hip-hop aerobics, fitball aerobics. Wall bar, gymnastic bench, barre exercises are inherent part of such class. This phase is to be finished with emotional active games primarily competitive ones. Final phase of a class. Its duration is about 5-10 minutes. The objectives to meet are to complete a class by gradual decrease of load, let children calm down by means of slow walk, breathing exercises. Annual training plan (3 classes per week) № Types of physical training Age group 5 – 6 year old 6- 7 year old 1 2 3 4 5 Teaching-training classes Comprehensive classes Choreographic classes Play classes Control class 64 hours 23 24 23 6 Total hours At the end of each semester 140 144 Monthly plan 1st week 1 Choreographic 2 Teaching-training 3 Comprehensive 2nd week Teaching-training Play Teaching-training 3rd week Choreographic Teaching-training Comprehensive 67 hours 23 24 23 7 4th week Teaching-training Play Teaching-training ( at the end of semester - control) Training equipment Standard equipment + step platform, fitballs, etc. The structure of class topics Theory History of physical culture and sport Practice Managerial skills Техника основных движений Use of marching exercises Hygienic knowledge and skills Basics of choreography Conduct of active games Basic of body constitution and functions Basic steps and elements of fitness aerobics Team interaction The terms used (fitness aerobics) Standards’ control Initial referee skills Games Medical supervision References 1. Аэробика. Теория и методика проведения занятий. Учебное пособие для студентов вузов физической культуры/ Под ред. Е.Б. Мякинченко и М.П. Шестакова. – М.: СпортАкадемПресс, 2002. – 304с. 2. Болонов Г.П. Физическое воспитание в системе коррекционно-развивающего обучения: Программа закаливания, оздоровления, организации игр, секций, досуга. – М.: ТЦ Сфера, 2003. – 160с. 3. Буцинская П.П., Васюкова В.И, Лескова Г.П. Общеразвивающие упражнения в детском саду. – М.:1990. 4. Кожухова Н. Н., Рыжкова Л. А., Борисова М.М. Теория и методика физического воспитания детей дошкольного возраста :схемы и таблицы. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 2003. – 192 с 5. Левин М.В. Гимнастика в хореографической школе. – М.: Терра-Спорт,2001. – 96 с., ил. ( Русская театральная школа) 6. Левченкова Т.В., Сверчкова О.Ю. Малыши на мячах. – М.: Центр Фитбол, 2005. – 130с. 7. Лисицкая Т.С., Сиднева Л.В. Тестирование физической подготовленности в аэробике. – М.: 2001. – 16 с. 8. Спортивная аэробика в школе. – М.: СпортАкадемПресс, 2002. – 84с. 9. Спортивные игры на уроках физкультуры/ Под общей редакцией О. Листова. – М.: СпортАкадемПресс, 2001. – 276с. 10. Шебеко В.Н., Ермак Н.Н., Шишкина В.А. – Физическое воспитание дошкольников. – М.:1999. IAAF Child track and field Viktor Predbannikov, Senior teacher, Russian Gymnasium, city of Iyhvi, Estonia, Track and field coach of 4th category, IAAF lecturer Having worked for more than 20 years as a PE teacher at school I can tell for sure that general level of physical condition of pupils has been decreasing in the later years. We should be aware that sound physical development of children depends to a greater extent on motor activity. The nature itself has given children an essential need in motor activity. It is determined by age peculiarities not depending on their consciousness. In this regard the paramount role for children may and should play track and field during PE classes and out-of-school time. The International Association of Athletics Federations has studied the current situation with the popularity of track and field among children and considered it necessary to make a proposal adapted to real state of affairs. Backed by this study IAAF experts have elaborated a form of training for children which meets contemporary requirements; its goal is promotion of track and field training among junior children ultimately aiming at making track and field #1 sport in a comprehensive school. IAAF Child track and field involves a system of training in form of instruction cars and team competitions. Having completed training at the international course for lectors of IAAF I have learned this program and now use it in practice. Having organized and implemented IAAF program competition I claim that the program is really interesting. New events and multifold motor tasks conducted in a team give pleasure to children. Moreover this competition enables participation of a big number of children in limited space any time. Team work is the central principle of IAAF Child track and field. All races are conducted in form of either relay of a team competition. All technical events (jumping, throwing) are classified the same way – by summing results of all team members. As all participants compete as members of a team, even less capable children can take part. Every individual performance is an input to a team performance thus empowering the concept that every child’s participation matters. Every team member takes part in different events of every group of events (sprint, jumping, throwing). As well as long distance race. This strategy prevents early majoring and provides multifold and diverse approach to track and field development. All teams within IAAF Child track and field program are mixed (always made up of girls and boys). All events are carried out as team events. IAAF Child track and field is for 3 age groups: Group 1: 7-8 year olds Group2: 9-10 year olds Group3: 11-12 year olds. Amendments can be introduced but corresponding basic principles of IAAF Child track and field: - Mixed teams competition - Competition in simple and available events - Brief competition organized in accordance with IAAF recommendations - Immediate results and their obviousness within a competition process - No child in any event can be given 0 result - No direct conflict, no qualifications. Competition forms recommended for children by IAAF should meet these principles in order to stay true to the spirit of the Child track and field program. No new decisions can be made if they counteract these principles. Cmpetitions are conducted by a schedule to ensure that various events, constituting events groups: race, jumping, throwing, are practiced in three different places. Long distance race is carried out for everyone simultaneously. The classical formula for IAAF Child track and field competition is 9 teams made up of 10 persons, 9 groupsstations (3 for race, 3 for jumping, 3 for throwing events + endurance). There can also be 6-8 participating teams of 8-10 members. Upon defining the number of teams, events for competing should be determined. IAAF proposes the following events for Child track and field. Events of IAAF Child track and field: Race events - 8 minute free run - Shuttle-race (hurdling – flat race) - Circuit relay race “Formula 1” - Speed ladder - Hurdling sprint and slalom relay - Hurdling relay - 1000m race Throwing - Foam javelin throwing - Kneestand medicine ball throwing - Discus throwing by exactitude - Overhead medicine ball throwing - “Ludi” discus throwing in a limited zone - Javelin throwing - Target tennis ball throwing over an obstacle Jumping - Long pole jump - Standing frog long jump - Triple jump - Long jump by exactitude - Rope jumping - Crossed jump. Teams should be distinctive differing by some elements (t-shirt, cap, etc) in order to make a competition successful. A team should also have a name. Competition venue should be determined far beforehand a competition date. A sports ground should be safe, jolly and adapted for a competition. The ideal size is 60m * 40m. The basic rule is to distribute stations by events ensuring safety of a competing process. Particular equipment has been elaborated and proposed for training and conducting of IAAF competitions. Its key characteristics are simplicity, bright and catching shape, utility and safety. Child track and field and school Why do I recommend Child track and field to my colleagues? Probably everyone knows that track and field exercises are the best among various types of physical exercises in promoting physical development. Different types of race, jumping and throwing are really part of every PE class. IAAF Child track and field proposes an optimal way of educating a pupil track and field exercises. Our rapid changing environment calls for school classes to change as well. Thus track and field exercising makes benefit for a person and promotes this engrossing kind of sports. Training system with instruction cars and practically tested team competitions elaborated by experienced professionals is offered to PE teachers for aiding them in their work. It provides the content of a training and methods for its practical application. Proposed competitive events give children an opportunity to acquire a range of motor actions. Preparation of such competitions make children work in a particular mode adapting to requirement to their age group. In summary. IAAF Child track and field is a great aid for physical education at school. Due to its goals it can be incorporated into the study process and children comprehensive training. The essence of track and field exercises is provide all junior athletes with basic physical education, a “platform” for their future physically active life, as well as ensure access to means of physical socially recognized expression. Adapted Physical Activity in Finland Pauli Rintala, professor in Adapted Physical Activity, University of Jyväskylä Finland The term of Adapted Physical Activity (APA) is defined in Finland as follows: “physically active lifestyle which is available for people with different disabilities, long-term illnesses or those whose functional capacity is either physically, mentally or socially such that they are not able to participate in general physical activity provision and whose participation needs modifications and special expertise”. From the 1970’s the English term ’Adapted Physical Activity’ has been an umbrella term worldwide (DePauw & Sherrill 1994). It is considered to cover both the traditional rehabilitation and physical education and it means: (Adapted) = adaptations which can be educational (e.g., teaching methods), technical (e.g., assistive devices) and/or administrative (e.g., facilities); (Physical) = physical activity experiences and participation; and (Activity)= education, therapy, leisure time activity, and/or competition (Doll-Tepper 1995). In Finland the term is also understood as described above. The number of participants in APA has been growing rapidly in recent decades being now over one fifth of the population in our society. In terms of equal opportunities, progress has been made with local sport provision, the activities of specialized organizations, education and training in the field of sport and physical activity, and international contacts. The latest Sport Act from 1999 calls for more attention to providing opportunities for special groups in sports and physical activity. All this should be done in partnership between sport, social welfare, public health and education authorities. Definitive steps forward have been taken for instance in the following: local authorities have hired sport instructors for special groups, the financial support of specialized organizations has grown, the sport, social welfare and public health systems have intensified their information, research, training and publication relating to APA, and sports facilities and recreational areas have been renovated with a view to adapted physical activity. Finnish sport culture accommodates fairly well to the needs of special groups. About 5% of the state funds in Finland is allocated for physical activity and sport to promote exercise for individuals with disabilities and long-term illnesses, but also elderly population. Organizations concerned with exercise for the disabled are represented on the decision-making bodies for the administration of physical exercise; sport organizations for disabled persons receive state aid on the same basis and in the same proportions as other sports organizations. In the future, the focus will remain on improvement of training for physical exercise, teaching, and health care personnel. Physical activity has a direct impact on prevention and cure of some illnesses. However, as the result of many illnesses and impairments there can be a situation that the existing facts cannot be influenced any more by exercising. In this case, physical activity can be used to delete or at least diminish the consequences caused by the impairment. Many forms of physical activity do not directly have any specific effects to different functions of the body, but they indirectly diminish the existing disabilities. Physical activity can adhere to any phase of the rehabilitation process and many times it influences at the same time on the different levels of illness, impairment, disability, and handicap. The city of Jyväskylä provides an outstanding example and prototype of the continuum from special programs in segregated facilities to fully integrated physical, recreational, and sport opportunities. In addition it shows how diverse laws - both Public Health Act and Sport Act - and activities sponsored and supported by different agencies can work together, complement and supplement one another. Dominant factors in this process are interests and needs of each participant as an individual. The city of Jyväskylä is a university and school town in Central Finland, surrounded by several lakes. A total of 23 % of the surface area of the city is covered by lakes. The number of inhabitants is about 130 000 and the image is youthful. There are tens of public schools, vocational schools and institutes, the University of Applied Sciences and the University of Jyväskylä, where the only Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences in Finland is situated. The total number of students in Jyväskylä is close to 30 000. Jyväskylä is also known as a sports city. More than 70 different sports, including summer and winter sports, can be carried out in our city. There are nearly 240 constructed sports facilities and 120 sports clubs. Many kinds of adapted physical activity services complete the image of a sports city. The adapted physical activity programs organized by the network are intended for persons who, for reasons of disability, chronic illnesses, advanced age, diminished physical capability, or social situation are unable to benefit from the usual range of physical activities available to the public. According to legislation which came into force in 1980 and was renewed in 1999, the main duty for the provision of adapted physical activities falls on the municipal departments responsible for physical activity services in general. However, in practice, the provision of services for special groups is the result of cooperative efforts involving other departments and agencies. The main responsibility for planning and coordinating adapted physical activity services in the city of Jyväskylä belongs to the Department of Sports and Physical Activity Services and to the Center for Social Welfare and Health Services (Figure1). These two departments take care of e.g., planning activities and courses, coordination, major part of implementation, organizing transportation for the groups with severe handicapping conditions. They do vast cooperation with other administrative agencies and organizations, associations of the disabled, pensioners and war veterans. They also take care of training and consulting of instructors, and information of the services. Information about the special programs available is sent to every household in the form of a newsletter. Also an annual Calendar of Adapted Physical Activities (2010) is published in the web. Department of Sports and Physical Activity Services Center for Social Welfare and Health Services Physical education teacher in charge of special groups Physical activity advisor in cooperation with physiotherapy unit HEALTH RELATED AND ADAPTED PHYSICAL ACTIVITY PROGRAMS • planning •coordination •implementation (major part) •cooperation with other agencies •information services Workers` institute & open colleges UNIVERSITY OF JYVÄSKYLÄ UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES Figure 1. MODEL OF NETWORK Disabled & pensioners associations Dept of Education Church organizations Sport associations Although the main responsibility for adapted physical activity services lies with the above-mentioned municipal departments, these services are also provided by the associations for the disabled, pensioners, war-veterans, the church, municipal school administration, workers' colleges and open folk colleges and, to some degree also by sports clubs. The Faculty of Sport and Health Sciences of the University of Jyväskylä provides a great amount of know-how for the development of adapted physical activity. Many research and development projects over the years have been carried out in cooperation with the university. The adapted physical activity groups also offer many opportunities for practice and employment for students of the University of Applied Sciences and the University of Jyväskylä. This innovative cross - administrative cooperation has enabled us to combine resources and, as a result of many years of development work, to create excellent adapted physical activity services in Jyväskylä. References 1. Calendar of Adapted Physical Activities (2010). City of Jyväskylä. See: http://www.jkl.fi/liikunta 2010. 2. DePauw, K. & Sherrill, C. (1994). Adapted physical activity: Present and future. Physical Education Review, 17(1), 6-13. 3. Doll-Tepper, G. (1995). International perspectives on adapted physical activity. In H. van Coppenolle, Y. Vanlandewijck, J. Simons, P. Van der Vliet, & E. Neerinckx (Eds.), First European Conference on Adapted Physical Activity and Sports: A White Paper on Research and Practice (pp. 45-51). Leuven: Acco. Role of physical education in formation of children abilities for music A. Ryazantsev, Acting Associate Professor of Astrakhan Institute of training and retraining, Candidate of pedagogical science, city of Astrakhan The modern concept of physical education is aimed at enhancing the role of educational focus as the defining condition of success of the formation of physical culture of a student. The national educational initiative ‘Our new school’ says, ‘School education should be constructed so that graduates can independently set and achieve important goals, skillfully respond to different life situations’. This is only possible while preserving and strengthening their physical and mental health. For this purpose, in 2010 a new standard of physical training was introduced, not less than three hours a week taking into account the individual characteristics of children. But, even this progressive innovation does not completely solve the problem of low motor activity of modern youth. The data of numerous studies suggest that the body's needs for school-age children in an organized motor activity are 12-16 hours per week. Increasing the number of classes by itself can not solve the problem of their effectiveness because the question is not so much the quantity, but more what content is like, what their focus is. The focus here must be on the educational objectives, the successful implementation of which could help prepare children for self-improvement of their own physical condition in the process of self-study and other forms of physical training outside of school. Particularly this problem is relevant to children starting to play music. These children of 7-8 years old spend about 2 hours a day playing the instrument, and students-musicians of 11 years old are engaged in the piano up to 6 hours daily. Students carry these additional loads in the inactive position already having the deficiency of motor activity and the large amount of homework in secondary school. I investigated the physical readiness of children of 7-15 years in 12 educational institutions in Astrakhan, regularly involved in music from 5-6 years (242 boys and 341 girls). Physical readiness was determined by tests recommended by the curriculum for physical education. The analysis of the results of testing of schoolchildren has shown that since 3 years of primary school (9 year old children) there is a significant lag in the development of physical qualities (for all indicators, except for dynamometry) for boys and girls involved in music as compared to children not involved in music and sports ( p <0,005). Each year, the lag increases and by the time of admission to musical educational institutions (15-16 year-old students) becomes very significant. In physical education of students regularly engaged in the music, it is necessary to use various forms of overtime work (exercises before classes, homework in Physical Education, outdoor games and physical exercise during the breaks, and physical warm-ups in class). Some of them should be recommended for introduction in the learning process in children's music school. Teachers- musicians, guided by the planning documents and guidelines of the teacher of physical culture, taking into account the age and the psychological characteristics of a person should be the organizers of athletic events in music schools. All exercises should be aimed at the prevention of hypodynamia and should develop professionally important qualities and functions, depending on the chosen musical instrument. That will show the level of competence of a teacher of Physical Education and Music. Parents of future musicians need to monitor homework in Physical Education and the necessary hygienic and preventive requirements during individual music lessons at home. Both parents and teachers, and especially the students themselves should be able to monitor the state of the organism dosing loading while working out. Here one must once again return to the issue of the educational focus of physical education class at school and the increased role of a teacher of physical culture. Following the principles of the extensive search engine, support and maintenance of talented children, this is only possible by bringing together teachers of different school subjects and their parents. The pedagogical experiment carried out in three music schools of Astrakhan, showed that motivational and emotional components are needed at the initial stage of introducing the elements of physical culture in the process of learning music. Motivation for the children is that physical exercises help them in mastering the future music profession and provide an opportunity to study together with their peers of physical condition. The emotional component is that all the outdoor games, rhythmic exercises and choreography are held with music. Fit ball and inflatable car tires are introduced as optional equipment. Exercises with the transferring and catching the ball cause not only positive emotions and effectively restore the mental work, but improve the function of vision. In addition to exercises for the development of large muscles of the torso and limbs exercises for smaller muscles of the hand, fingers must be included in training, because they not only develop the small muscles of the hand and improve fine motor coordination, which is very important for a musician, but are also conducive to the development of children's speech. For the prevention of myopia it is necessary to perform eye movements, fixing eyes on the hand or an object in his hands, when performing a particular exercise, especially related to the movement of hands. Working with students involved in music, it is necessary to avoid exercise in hanging and setting against gymnastic apparatus, as well as exercises, under which some group of muscles can overload, causing tension and convulsions. All this information and much more must be reported to pupils during physical education classes with educational and cognitive orientation, which is reflected in interdisciplinary results. The recommendations given in this article may be useful not only for music school students, but also for all children who have "sedentary" lifestyle, including students with "computer syndrome". Role of physical education in modulation of emotion A. Ryazantsev, Acting Associate Professor of Astrakhan Institute of training and retraining, Candidate of Pedagogical Science Astrakhan Very often in the process of studying a number of students experience significant neuro-psychological tension, state of ‘emotional stress’. This condition may be called "emotional tension", ‘stage fright’ among musicians, "anxiety of expectation" or "start fever" among athletes. Having different forms (poor body coordination, "failures" of memory, deterioration of physical condition and performance, profuse sweating, dryness in the throat, hand tremor, significant vegetative and bioelectric changes in the central nervous system (CNS), this mental state, especially ‘emotional tension ‘, has a huge impact on the effectiveness of educational and vocational activities (3). Rather typical case of "emotional tension" is the one that occurs in humans in the examination situation. The exam is the critical moment in a person’s principal activity, which largely determines his further life Examination situation is characterized by well-known uncertainty of the outcome. All this makes the exam situation a very strong emotional factor (3). Taking into account the fact that not only the numerous examinees are prone to the phenomenon of "emotional tension", but also people of practically all professions, this problem must be acknowledged more than actual. The first attempt to solve the scientific issue was taken by scientists and practitioners involved in musical performance. Among professional musicians, whose work involves constant public performances, increased level of "stage fright" occurs twice as often as among those with other occupations (4). Individuals experiencing negative emotions of public speaking need to know that these factors not only violate the peace of mind, but also lead to diseases (neurasthenia, mental disorders, etc.). Musicians recommend various options for autogenic (AG) and psychoregulatory training (PRT) and some medicines at various stages of psychological preparation for performance. But in my view, the practice of training athletes for competitions and important performances accumulated a lot of positive experience, which can be used to eliminate the negative effects of anxiety, on the condition of taking into consideration specific musical performing and training activities. Literature describes several methods of self-regulation of mental activity: with the help of other emotions, by changing the posture, AG and PRT, the use of verbal and musical psychoregulation, normalization of sleep. In this paper, I will highlight the pedagogical methods and especially the means of physical culture. Noting the relevance of psychological readiness for exams, tests and presentations, it should be noted that, in the first place, it is a pedagogical process. In order to influence the person directly and effectively it is necessary to know a lot of his individual characteristics: anatomical, biochemical, physiological, psychodynamic, psychological, personal, social, etc. In this process, the role of the teacher has a huge significance and it determines the level of his competence. The problem of mental states is also important for educational practice. Influenced by "emotional tension" the student can not show the level of knowledge and skills, which he really has. The subject of observation and analysis in a situation of anxiety for many teachers is the display of the functional, mental states and personality traits: complexion, condition and movements of eyes, facial expressions, changes in gait, habitual postures, pace of walking, sleep, daily routine, interests, desires, habits etc., as well as the extent and nature of communication, where the central place is occupied by the form and content of speech. To worry less before the examination and performance a person should be more self-confident, and this can only be with a better preparation. The teacher should closely monitor the behavior of the student: categorically prohibit symptomatic "walking around the room”, and offer to sit quietly, doing nothing. In addition, the teacher should offer to use a simple method of breathing exercises: slow and deep breathing in through the nose, a small "breathholding" and quiet and slow breathing out through the mouth. Then some rest and repetition of the exercise. The exercises should be repeated several times, each time extending the rest time between them. Every teacher and student should know that broad, free movements of hands are incompatible with a sense of depression, stiffness. Pupils shouldn’t be calmed down by the phrase: "Do not worry!" or the requirements: "Pull yourself together!". In neither case the teacher achieves the desired result, and often encounters the irritated response. It would be better to say: "Quiet" and even "Worry", reminding him thus, that excitement before a performance is an assistant. Mental stress should not be managed directly. Let me examine some facts of scientific research, noting the importance of physical culture and sport in eliminating the negative aspects of "emotional stress". While teaching at the same educational institution it was revealed that there is a significant difference in initial values and in the manner of vegetative changes on the tests among athletes compared with students who were not involved in sports. (2). This is explained by the fact that systematic training and participation in competitions make people more emotionally stable and vegetative indicators of tension were decreased because of the weak value of the subject. As a result of many studies it was proved that regular exercises can serve as an excellent natural tranquilizer. Besides the fact that during exercise the negative emotions evaporate together with the energy expended, there are positive biochemical changes in the body. During exercise endorphins which contain morphine are released. They reduce sensitivity to pain and stress, cause the state of lightness throughout the body. Regular aerobic exercises can help counter stress, or reduce it to a manageable level (1). It was found out that there is a decrease in anxiety regardless of the sport after training sessions. Even under the influence of a one-time physical activity (not including competitive exercise) students get the reduced level of situational anxiety (5). I should note the positive role of various physical exercises as a means of creating a kind of distraction. Psychophysical mechanism of these devices consists in the increased intake of the information to the CNS and this information has a competing, distracting character. The flow of nerve impulses from these distractions can be stronger than the negative influences that are caused by fear, excitement or anxiety of a student, a musician or an athlete. The use of special exercises (facial, respiratory, etc.) affects the regulation of the mental state also through targeted control of release of certain hormones into the blood. For example, a gloomy face promotes increased production of adrenaline, leading, in turn, to anxiety, depression, insecurity, as well as serotonin, which affects the development of the phenomena of internal inhibition. A smile helps to release serotonin and causes feelings of self-confidence, passion and enthusiasm. Obviously, at the same time, production of certain fractions of endorphins is increased, which reduces the internal stress, it becomes easier to bear pain and other feelings of physical and mental discomfort. Other exercises also have such an effect that allows to influence the organism as a whole with the help of the mechanism of stimulation of biologically important points and the entire zones (5). CORRELATRION BETWEEN ANTHROPOMETRIC AND KINEMATIC DATA IN SPRINT FOR STUDENTS IN THE COLLEGE OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Ben Saeed N., King Saud University College of Physical Education & Sport. Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Introduction: The anthropometric data play an important role in the performance. To achieve a high performance the athlete must have adequate anthropometric data 2,3,4,5. Specialists often try to determine the ideal anthropometric characteristics that support performance in different sports. Medved pointed out the importance of body height in basketball and volleyball. Larin 3 confirmed the influence of anthropometric data on the quality of execution of certain technical elements. Yaguello V. and Yaguello M. 6 have reported the importance of anthropometric characteristics as being factor of differentiation between athletes and sedentary. Hoffman noted the strong relationship between the height, length of lower limb and average length of stride as important in achieving a performance in the Sprint. Bulgakova 2 demonstrated the importance of limb length in swimming performance. Thus anthropometric data is presented as an important factor in the selection and in the achievement of a performance. The performance in sprint depends on three factors 1,7: the first is the stride frequency, the second factor is the amplitude, the third is the reaction time. The goal of this research is to determine the character of the correlation between anthropometric data and kinematic factors determining performance in sprints. To do this we need to determine the anthropometric data of the subjects and kinematic parameters of the 100 m race. To achieve our goal we used the following methods: the chronometry, the pedometry, the anthropometry and mathematical statistics methods. The subjects of our research were represented by 26 students of the College of Physical Education & Sport belonging to various sports clubs aged 20-24 years. During our research we have fulfilled longitudinal and weight measurements. Based on longitudinal measurements (height-H, lower limb length-Lmi and the length of the thigh-LC), we determine the following indices: The index of the lower limb: I1 100 length of lower limb . height The index indicates the ratio between the length of the thigh and the length of lower limb: I 3 100 The index I 4 100 length of the thigh length of lower limb indicates the ratio between the length of the thigh and height: length of the thigh height We determine also the body mass (Mb) and the height-weight (ponderal) index of Livi (I2): I 2 10 body mass height We have calculated the mass of segments using the formulas derived from the radioisotopic method of Zatsiorsky and Selouianov 7, and we determined the mass of the thigh (Mt), leg (Ml) and lower limb (Mlower.limb): the mass of the thigh: Mt = 2649 + (0.1463 x weight) + (0.0137 x height), the mass of the leg: Ml = 1592 + (0.03616 x weight) + (0.0121 x height), the mass of the lower limb: Mlower.limb = Mt + Ml + Mf. Mf = -0829+ (0.0076 x weight) + (0.0073 x height). The second part of the experiment concerned determining certain kinematic parameters of sprint such as amplitude and stride frequency and the average speed of 100 m, the average speed of the first 10 meters (V1) and acceleration during the first 30 meters. Results and Discussion: According to data presented in table 1, the height (H = 177.5cm 7.79). The average value of the index of the lower limb (I1) is 49.26 1.99, that states that the subjects have the short lower leg ( I1 55 ). On the other hand, the value of the index of Livi (I2) is 23.40 0.58, that indicates that the subjects has middle weight development (23.0 I2 23.9). Table 1: Values of anthropometric data. anthropometric data M 177.5 87.67 45.52 72.42 3.17 10.37 14.57 49.26 0.52 0.25 23.40 H (cm) LMI (cm) LC (cm) Mb (Kg) Ml (Kg) Mt (Kg) Mlower.limb (Kg) I1 I3 I4 I2 e 7.79 6.12 3.76 9.06 0.40 1.41 1.94 1.99 2 1 0.58 statistique variables V% Min 4.39 166 6.98 76.5 8.26 38.5 12.51 59 12.62 2.55 13.60 8.26 13.31 11.64 4.04 43.46 3.85 46 4 23 2.48 21.98 Max 194 99.5 52.5 93 4 13.45 18.69 53.53 55 27 24.32 Extended 28 23 14 34 1.45 5.19 7.05 0.07 9 4 2.34 According to the data represented in table 2 the average speed of first 10 meters (V1) is equal to 4.49 m/s. This value demonstrates the reaction time and speed at the start. The acceleration (a) expresses the change in velocity versus time during the first 30 meters, its average value is equal to 1.34m/s². The average mean of velocity (V) is 7.62 m/s, standard deviation indicates a low dispersion, it means that the average speed is low. Table 2: Values of kinematic parameters of sprint Kinematic characteristics statistique variables M 4.49 1.34 195 3.91 7.62 V1 (m/s) a (m/s2) LF (cm) FF (F/s) V (m/s) e 0.35 0.11 8 0.22 0.32 CV 7.79 8.21 4.10 5.63 4.20 Max. 5.23 1.61 213 4.39 8.29 Min 4.05 1.24 178 3.54 7.10 Extended 1.18 0.37 35 0.85 1.19 The analysis of data presented in table 3 showed that the correlation between height and acceleration is positive (rH-a = 0.34). We also note a positive correlation between the length of lower limb and the acceleration, and a negative correlation between lower limb length and average speed V1 (-0.398). Regarding the length of the thigh we note a positive correlation with the average speed V1. The index of the lower limb (I1) has a positive correlation with the acceleration and the speed V1 (0.459). Table 3: Values of the correlation between anthropometric parameters and longitudinal kinematic sprint. Longitudinal anthropometric data statistique variables LF FF V a V1 H -0.04 0.20 0.22 0.34 0.013 Mlower.limb 0.04 0.09 0.17 0.32 -0.398 Lc 0.12 0.06 0.20 0.26 0.319 I1 0.07 -0.008 0.07 0.29 0.459 I3 0.20 -0.03 0.16 0.02 0.231 I4 0.22 -0.06 0.14 0.19 -0.11 According to data depicted represented in Table 4 we see a strong negative correlation between weight and speed V1 (r =- 0.873). This correlation is significant at P <0.001 which allows us to deduce, that the weight inhibits progression speed on start . On the other hand, a strong positive correlation (r = 0.739) between the mass of the thigh and the speed V1 is significant at P <0.01, we can say that more the mass of the thigh, we can develop a better speed on start. It is important to note the presence of a strong negative correlation between the weight index of Livi (I2) and acceleration (-0.873), it is significant at P <0.001. It means that for two individuals who have the same height, that who has a lower weight, may develop a better acceleration. This reflects that it is better able to improve his speed over time. Table 4: The correlation between anthropometric parameters weight and sprint kinematics Weight anthropometric data Mb Mmi Mt Ml I2 LF -0.21 -0.19 -0.19 -0.18 -0.28 FF 0.20 0.21 0.20 0.21 0.04 statistique variables V a 0.05 0.001 0.07 0.04 0.06 0.03 0.09 0.08 -0.25 -0.87 V1 -0.873 0.069 0.739 -0.354 -0.392 Conclusions: Basing on the gathered material, we can draw the following conclusions: The speed of the first 10 meters (V1) and acceleration (a) are strongly correlated with anthropometric data (body mass, mass of the thigh, weight index of Livi). These correlations are realized in the strong negative correlation between (V1) and the weight on one hand and the acceleration with the weight index of Livi (I2) on the other. The two kinematic parameters (V1) and (a) are weakly correlated with longitudinal anthropometric data. Our results accord with the conclusions of Selouyanov and all that signal the presence of correlations between performance in sprint (the 100 m race) and factors descripting modification of circumferential data, the mass and height. The absence of significant correlations correlation between the anthropometric data and the length and stride frequency. Thus, we can deduce that the anthropometric data (particularly the weight anthropometric data) have a great importance to developing good speed at the start and its evolution during the actuation. References 1. Arakilian E. et al.: The biomechanics of the actuation. G.C.O.L.I.F.K. edition Moscow 1986 2. Bulgakova N.: The selection and preparation of young swimmers. Vigo 1990 Paris edition 3. Larin Y.: The preparation of sporting yachtsmen .- M.: Terra.Sport, 1999. -192p. 4. Platonov V.: The general theory of the preparation of Olympic athletes Olympic edition literature MOSCOW 1997. 5. Selouyanov V., Godina E., Khomyakov I., Feyofilaktov V.: The distribution of muscle mass in segments as a basis for assessing the level of physical and functional status. 12-th International Congress "the Olympic and Paralympic sport and modern sport" Moscow 2008 - p.73-74 6. Yaguello V. Yaguello M.: The somatic aspects of athletic performance among women practicing fencing. 12-th International Congress "the Olympic and Paralympic sport and modern sport" Moscow 2008 - p.8283. 7. Zattsiorsky V. : Metrology sport. edition of Physical Culture and Sport, Moscow 1984 The stressors Galina Saunina, lecturer, the Department of Physical Culture, Vologda Institute of Law and Economics of the Federal Penitentiary Service of the Russian Federation, city of Vologda The mankind is living now in such a period when work efficiency is determined by first of all techniques of operating sophisticated machines and technological processes, creative thinking and acting, handling rapidly growing information flow. A human has to live at the limit of his/her capabilities in rapidly changing environment. Unstable social-cultural and economic situation in the country only highlights this fact. So one of the central trends of the national security state policy (the “Protection and Promotion of Health of The Healthy” State Program for 2003-2010) is provision of health and healthy lifestyle. In this regard the key goal is elaboration and introduction of labor organization rules and forms providing both maximal efficiency of mental work and preservation of health. Rational mental work organization should contribute to development of moral courage, endurance and stamina, mental abilities of a modern human. And it is highly relevant to create a basis of this skills and techniques during a person’s school age. Contemporary living conditions, rapid pace of science and technology development, study and work processes advancement, cadet regiment, increasing amount of information acquired make influence on a cadet’s body. Flexible functional systems of a young man enable pretty quick adaptation to a range of various impacts of the environment. However military discipline, study load, motor activity exerting extra stress on a young body may lead to functional disorders and later to diseases. Big study load, unbalanced physical and mental work and leisure alternating, sport exercises, insufficient sleeping time may result in overfatigue of a student. That’s why particular conditions eliminating negative influence of the factors mentioned above on health should be created at home and in an institute. A survey on stressors was conducted among 1, 2, 3 year cadets of the Vologda Institute of Law and Economics of the Federal Penitentiary Service of the Russian Federation. The analysis of the collected data showed that students encounter many factors negatively affecting their work abilities in everyday study process. The survey methods include questions to students to assess how mentioned factors hamper their work capacity and progress. The questionnaire was divided into 4 parts: proneness to conflict, overload, field of activity, tension in relations with the administration. Part #2, mental and physical overload, got the highest score. Part #4, tension in relations with the administration, took the second place. Part #1, proneness to conflict, was the third in popularity. And part #3, field of activity, was the last one. Questions to students from the part #2 were the following: “Do you experience overload?”, “Don’t you have enough time to prepare your study assignment well?” Positive answer was complemented with a scale of intensity of 1-5 points. The conducted survey among 237 students gives evidence of a big amount of stressors in students activities. The stress is considered a frequent phenomenon. Minor stresses are inevitable and harmless, nut severe stress makes problems and difficulties in completing the set tasks both for a personality and an educational institution. Stress theory originates from the works of internationally recognized Canadian physiologist G. Selye (19071982). He created a universal concept of stress. A stress by its essence is a way of achieving sustainability of an organism in response to negative factors. Stressors are negative significant in their impact and duration external an internal influences leading to stress conditions. The term of “a stress factor” (a stressor) is traditional for different concepts of stress and is defined as a cause provoking a stress condition. Comprehension of stress development mechanisms, emotional and behavioral responses can not be achieved without understanding of stress factors. For example, stressors of a communicative stress are predetermined by relevant stressful situation – a conflict in a study group, oral presentation at a seminar, an examination, a conference. For many students stay in the higher educational institution of a federal law enforcement agency (living in barracks, duties, fatigue duties, etc) and impelled communication with strangers, public presentations are stressful. Stress factors can be conditionally divided into two big groups: objective (information difficult for comprehension, presentation time limit, etc) and subjective (personal peculiarities). Senses of shame and guilt as social emotions are important emotional expressions of a communicative stress. There are passive and active types of emotional responses within a communicative stress development, mostly depending on a temperament. Communicative stress also changes action patterns of a person. This depends on experiencing either communicative eustress or communicative distress. Behavior of a person often changes right-about in comparison to his/her ordinary quiescent state. Stress may occur as a result of a definite social impact. According to a theoretical thesis of H. Heine a stress gives a body “an opportunity to free itself from some types of behavior and develop new ones”. This point is in line with a theoretical assertion of A. Maslow about “deficiency conditions and motivations to growth”, as well as J. Nutten’s - about “stressors’ motivation function is not only initial need reduction but also creation of new tensions”. Here social transformations and alterations of human relations can become means of protection from stress. All in all the issue of communicative stress is multifaceted and deserves in-depth and comprehensive study among youth. Stress is a very sophisticated phenomenon. It may lead to contraction of a mental disorder or a disease. But stress is also an important tool for training and conditioning as it promotes body resistance and adaptation capabilities. Health promotion and healthy lifestyle matters are addressed in the educational process of the Vologda Institute of Law and Economics. One of the most efficient measures of health promotion and improvement of body stress resistance capabilities is physical training, i.e. “removing” of a mental stress by a physical one. Physical exercises and sport are the best means of preventing negative aftereffects of stress. The importance of physical training and sport and their promotion to daily life of the majority of the population is increasing, particularly for the aims of promotion of health of the nation, harmonious development of an individual, preparing youth for professional work and defense of the Motherland. We are convinced that the matter be organized in the way of making every person aware and caring of his/her health and physical advancement since childhood, possess hygienic and medical aid knowledge and skills, lead a healthy lifestyle. References: 1. Василюк Ф.Е. Психология переживания. Анализ преодоления критических ситуаций. -М. 1984. 2. Жириков Е.С. Психология управления. Книга для руководителя и менеджера по персоналу. М. 2002. Конфликтология / Под ред. В.П. Ратникова.- М. 2002. Маслоу А. Мотивация и личность. -М. 1998. Менеджмент. Под ред. М.М. Максимцова - М. 1998. Менеджмент. Под ред. Ф.М.Русинова - М.: Изд. ФБК-ПРЕСС- 1998 Нюттен Ж. Экспериментальная психология. -М. 1975. Ожегов С.И. и Шведова Н.Ю. Толковый словарь русского языка. Российский фонд культуры. М. 1995. 9. Хайне Х. Биология стресса. Т.1. 2002. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. On experience of pedagogical practices modernization and state qualifying attestation conduct at the Pedagogical Faculty of Physical Culture of the Udmurtia State University G. Severuhin, Udmurtia State University, city of Izhevsk In the light of market service system established in our country brand new requirements for educating professionals arise. Independent institutions of higher education are competent enough for applying new flexible educational technologies and making the process of education approach international standards. Curricula must take into consideration a lot of strategies, aspects of values and motivation concerning obtaining knowledge, abilities and skills. This enables teaching staff, faculty councils to utilize their potential in search for ways to improve the efficiency level of educating future physical education instructors. The majority of specialists reckon that the weakest link of the old system of educating students is the lack of professional and methodological equipment. That is, in comparison with other pedagogical branches PE teacher holds practical lessons using basic sport rules for accomplishing tasks of health, education and development according to biological, psychological and pedagogical laws. It by no means belittles the value of theoretical basics and teaching methods how to pass knowledge on to pupils in the framework of modern ideas of physical education for children and young people (V. K. Balsevich, V. I. Lyah, L. I. Lubysheva, A. P. Matveev). On the contrary, it highlights the specific character of a PE teacher’s job. Therefore we can single out some contradictions in studying teaching methods, basic sport pedagogical subjects, student teaching at schools and requirements of monitoring and final assessment of students that influence the way future graduates obtain the basics of the job: - Curricula of sport pedagogical subjects are basically aimed at obtaining the basics of theory and practice of sport, physical exercises, in order to get a pass for teaching methods students have to conduct a lesson in their academic group, the exam is based on teaching practice at school, the chair is hardly connected with schools because another chair of theory and methods of physical training deals with student teaching. - Ways of student teaching do not consider peculiarities of teaching methods, the grade is made upon the completion of tasks defined by the curriculum. - Theoretical form of the final exam is unable to evaluate the readiness of graduates for the job and does not motivate student teaching practice. Taking into account all these contradiction the department of physical education in Udmurtia State University has defined the ways to make the requirements tougher: 1. Special attention must be paid to making cross-curriculum connections, improvement of student teaching according to the requirements of monitoring and final assessment of students. 2. Enhancing motivation must take place for students to be more active in obtaining professional knowledge, skills and abilities. 3. All chairs must take responsibility for their contribution to the system of student teaching. 4. The system of student teaching must be looked upon as a specific process of giving students all chances to get first-hand knowledge based on laws of education but at the same time having its own peculiarities concerning organization, management, equipment and motivation. 5. The main criteria in current and final assessments should be the level of professional awareness of students. The analysis of ways the student teaching is organized in other departments was followed by the decision of Faculty Council to change the system of student teaching and to create rules for the final state examination held in the form of a PE lesson in a comprehensive school so that the graduate could demonstrate his professional abilities including gnostical, organizational, communicational, constructive and planning abilities, knowledge of PE theory and practice, particular sport and pedagogical subjects and also knowledge of pedagogics, psychology, physiology and hygiene of PE. Student teaching sessions must get a student ready for his future profession as a PE teacher which is the basic one for a graduate of the department of Physical Education. It does not contradict the requirements of final assessment that are aimed at defining how well a student knows theory and practice according to state educational standards. Not ignoring main goals of student teaching process which is not simultaneous with studies, the faculty demands four directions of student teaching typical of republic of Udmurtia: gymnastics, skiing, track and field athletics and sport games. Practice of gymnastics has a priority because students have to learn how to manage pupils (basic commands, terminology, strong voice, arranging pupils in order, taking precautions etc). On top of that, what is more important, a lesson in a gym excludes negative factors like those in the stadium, school ground or park. There is a set of general and particular requirements getting tougher for each student teaching session. The level of difficulties enhances, the list of tasks is getting longer, professional level of students should be getting higher resulting in independent and creative approaches. The complication scheme is the following: - From observations to actions according to the plan; - From group work to individual work; - From being an assistant to becoming a teacher. Each sport-pedagogical subject is followed by a student-teaching session. The grade for teaching methods applied at the lesson is essential for taking an exam and influences the final grade for sportpedagogical subject. Chairs of gymnastics and theoretical basics of PE prepare students for their first student teaching session. Other chairs are responsible for reviewing lectures before all kinds of student teaching sessions. It is connected with the fact that we’re working in a “human-human” system hence all chairs must take charge for students being ready for student teaching at school and decrease possible negative impact on educational process at school. In order to get chairs more involved responsibilities of professors have been changed. General managing of student teaching was taken by the chair of theoretical basics of PE. It contains faculty and group instructors who manage students practicing in this or that school according to all rules. They are responsible for individual work with students in fulfilling all tasks including those that used to be controlled by pedagogical chairs (consulting, control, meetings), controlling how students have learnt means of analysing a lesson, leading conversations, school activities. Professors from those chairs act as teaching methods specialists who educate and consult students about how to write lesson plans and conduct lessons using sport methods, observation, analysis, evaluation of a lesson, i.e. they control methodological knowledge, abilities and skills. On completion of student teaching a student gets 2 grades: the first one is given for knowing teaching methods, the second one evaluates all fulfilled tasks. All grades are given by the “Expert Council” (instructor, teaching methods specialist, PE teacher). In case of an unsatisfactory grade for teaching methods a student won’t be allowed to take a current exam. The new way of studying sport-pedagogical subjects: - Obtaining theoretical and methodological knowledge of the subject, sport techniques; - Learning basics of teaching methods in a student group; - Learning teaching methods and skills during student teaching; - Taking an exam in sport-pedagogical subject considering the grade for student teaching. Student teaching sessions are held in the following order: - 4th year students: gymnastics (November, December – 4 weeks); skiing (January, February – 4 weeks); - 5th year students: track and field athletics (September – 4 weeks); sport games (Oktober – 4 weeks). On the whole student-teaching sessions prepares students for the final state examination in the form of a PE lesson at school that consists of different parts and motivates students and enables to evaluate the contribution of all chairs into students’ professional level. Exam is taken in the second half of May. To hold the exam the university makes a contract with two best schools in Izhevsk where student teaching sessions take place then a draw is held for defining a school and a class. Before the exam students are given about 3 weeks to get acquainted with the school, its facilities, traditions, to make contacts with teachers and pupils. Two days before the lesson the second draw is held where a student picks up a card with the type of the lesson written on it. Before the day of the lesson he is obliged to hand in the lesson plan made according to the example and conduct the lesson with the state certification commission present which consists of the chairman, representatives of different chairs and a PE teacher of highest rank. Criteria of assessment singled out in the statute of the complex interdisciplinary examination. 1. The readiness for the lesson. - Lesson plan: a) correspondence of lesson tasks and the content of the card; b) consistent, concrete and decent lesson aims; c) teaching methods should not contradict lesson aims and consider age peculiarities and lesson conditions; d) lesson plan should be written according to standards. - Preparing conditions for the productive lesson: place, equipment, stock, visual aids, audio-visual aids, pupils’ coming on time prepared for the lesson, the appearance of the teacher. 2. Lesson conduct - Organization: a) lesson starts and ends in time; b) making pupils occupied with setting the equipment, c) frontal, group and individual kinds of work; d) teacher’s behavior, his abilities to locate pupils rationally, being tactful and resourceful in finding solutions; e) managing pupils’ activities; knowledge of terms, timely commands, demands for abiding by the rules; f) providing safety, aid. - Educative work: a) ability to set, clarify and explain aims, give necessary knowledge; b) following main didactic principles, connection with labour, moral, intellectual and aesthetic education; c) using verbal, visual and practical methods; d) the ability to find out and tackle general and individual mistakes in education, to assess progress and behavior objectively; e) the ability to solve new problems and choose suitable patterns of behavior; f) the ability to allocate time and load, considering pupils’ potential; g) using class assets. - Productivity of pupils’ activities: a) how involved, active, interested and responsible pupils are; b) how they treat the teacher, discipline issues; c) the ability to control emotions, actions, reflect on the results of work, independence in taking decisions; d) mutual control and help, productivity of assistants’ work and work of those who have been temporarily excused from PE lessons because of health problems; e) how well pupils have studied the material and how satisfied they are with their activities and teacher’s evaluation. The faculty has been working according to this scheme of student teaching and conducting state examinations for 20 years. It is approved by all chairmen of state certification commission and the methodological Panel of the department of PE. We were interested in our graduates’ opinions who’ve been through this new system of student teaching sessions and taking final state examination. 123 people were surveyed. 95% believe that such a division of student teaching sessions promotes professionalism of future PE teachers. According to 63% of graduates, focusing on practice instead of theory during final state examination enhances the readiness, to 72,4% - it promotes more mature attitude to obtaining professional skills and abilities. The affirmative answer to the question of readiness for PE teacher job was given by 80% of respondents. Some aspects of KSPA students’ attitude to psychoactive substance abuse L. Sevryukova, L. Ivanova, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk Health is mostly determined by life style. In the list of factors that negatively influence health and ruin it first places take hypodynamia, smoking, alcohol and drug abuse. These ways of behavior have become a special sphere of social pathology that represents social and biological danger, they are of global scale and besides they are a threat for the national safety of Russia. In Russia the percentage of smokers is the highest in the world. More that 50 % of population in Russia smoke: 63 % of men ( about 44 mln.) and 9,7% of women( about 8 mln.). In Russia about half a million persons dye in a year and 40% of the men’s’ death the reason of that were cardiovascular diseases were caused by smoking. The amount of people that drink alcohol is increasing. Now there are 18 liters of alcohol per capita in Russia and 20 liters in Karelia. As World Health Organization say, 8 liters per capita in a year is a limit that threatens gene pool of any nation. Officially there are 2 millions alcoholics in Russia. The amount of the sold alcoholic drinks is 80% higher than the amount of produced drinks, this indicates the usage of counterfeited drinks, that are increasing up to 40-50%. They are the reason of poisoning, that often leads to death. According to the official statistics of the 2009 there are 50 thousands drug addicts in Russia, that are on regular medical check-up and the real amount, according to the mythology of U.N.O., is more than 2,5 mln. Every day more than 250 persons in Russia become drug addicts and 80 persons dye from using drugs. In our country 4,5 tons of drugs are sold every day and 820 in half a year. For the last years the amount of synthetic drug consumers has increased from 28% to 74%. This tendency shows that many drug addicts become incurable. The issues of the problems developing are: -the increasing of the usage -decreasing of the first time taking -feminization Young people are especially prone to these disgusting things. As it said in the Ministry of Public Health, the number of smokers is getting bigger on 10% thanks to teenagers. More than 80% of children under 14 at least once tried alcoholic drinks. Children in the age from 10 to 14 started to drink more alcohol and 11 thousands suffer from alcoholism. Youth’s beer abuse causes a lot of anxiety. Beer leads to alcoholism. The increase of beer usage in the country occurs thanks to teenagers and women of childbearing age. Beer alcoholism quickly damages brain, leads to intellectual disorder, psychotopological changes. For the last 10 years the teenagers’ death rate in Russia caused by drugs has become 42 times bigger. The number of drug addicts has grown up to 3,5 times higher. Taking into consideration, that most of them are in the age from 12 to 20, we can say that the future generation of our country is under threat. Specialists think that nowadays teenagers can be divided into two groups: those who tried drugs and those who didn’t, but later the division will be impossible. Students are a special sociological category. Every year teacher’s staff of personal and social safety department makes researches on these problems. The respondents are the KSPA students. Under our supervision a group of second-year students of historical and philological department takes part in these researches. The aims of these researches are studying the following: -The extent and activity of taking psychotropics. -Students’ attitude and knowledge concerning these problems. Type of the research is anonymous questionnaire. Here’s the data of the sociological research that was made in 2010 among the first and second-year students of historical and philological department of KSPA. 80 students (66 girls and 14 boys) were questioned on the theme of Youth’s smoking and health. Almost every third student ( 34 person) smokes, out of them is the every fourth girl ( 17 girls ) and every second boy ( 7 boys ), 7 girls and 3 boys smoke only sometimes. Out of those who smoke systematically , half of the girls started smoking at the age of 13-14 and the other half did at the age of 15-16, boys – at the age of 15-16. Smoking activity: 1-2 cigarettes smokes every third student (10 persons) 3-5 cigarettes smokes every fourth student (9 persons) 6-7 cigarettes smokes every third student who smokes systematically (8 persons) There cases when students smoke up to 10, 15 and 20 cigarettes. Motives of smoking are the following: relaxing, calming down, girls also say that they smoke to keep smb.'s company and just for fun. Students mention about negative smoking effects only on the respiratory apparatus, cardiovascular and nervous systems, appearance. But they don’t mention the other systems that shows that they have a lack of knowledge concerning this issue. The parents of those girls who smoke systematically are both smokers. Those who smoke occasionally have siblings-smokers. Almost all students are aware of second-hand smoking (78 persons).There are those who tried to give up smoking, 17 respondents failed and 5 succeeded. There were 64 persons that were questioned on the problem “Youth and alcohol”, 54 of them were girls. 61 respondents ( 51 girls) take alcoholic drinks, more often wine (25 persons) and beer (32 persons), and some of the respondents drink vodka ( 4 boys). Every third respondent ( 21 persons) drinks once in a month, every fifth drinks more often and 14 students use alcohol more seldom than once in a month. Every fifth student (12 persons) took alcohol for the first time at the age of 7-10, every third (20 persons) did at 13-14 years, every fourth (17 persons)- at 15-16 and 10 persons -at 17-18 years old. More than a half of respondents took alcohol for the first time with parents. All respondents’ (64 persons) parents take alcohol on holidays. Most of the students get the information about smoking effects from TV programs, school discussions and parents. But not all the students are aware of the organs and systems that are influenced by smoking: they mention only cardiovascular, digestive and nervous system. Almost all ( 60 persons) know about the smoking effects on descendants and they are sure that taking alcohol is a factor that supports sexually transmitted diseases and AIDS. There were 103 respondents on the drug addiction and toxicomania problems, and the majority of them were girls ( 80%). One-third of the respondents (34%) tried drugs and 12,7% tried inghalts, more that the half who tried drugs (24,3%) used them again. Most of the students think that drug addiction and toxicomania means taking drugs. But only 44,7% of the respondents know about the peculiarities of the disease. Mostly students get the information from their parents (49,5%), TV programs ( 41,7%), and unfortunately only one-third of them gets it from the discussions in school. It’s strange that the students of the historical and philological department name literature as the information source last of all ( 13,6% ). There students don’t get any information about the problem (6.8%). The majority of the students (65%) consider that they don’t need any extra information. Mostly the information that they get arouses negative attitude to drugs (78,6%), 17,5% are not influenced, but 3,9% get a desire to try it. Only 17,5% of the students don’t know where they can buy drugs. Half of the students (51,5%) name disco club as the place of drug distribution, 40,8% name the institute of higher education, 28,2% - dormitory. So, our research proves the contemporary tendency of the problems, shows that young people have a lack of information about the characteristics and consequences of the abuse. So, the abuse preventing work can not be reduced, but activated. It’s necessary to form a culture of healthy life style among young people and responsible attitude to their health and health of the people around them. In KSPU the abuse preventive works are the following: - lectures - seminars, for that students prepare their essays that are discussed - courses ‘ Preventing socially dangerous diseases and their consequences on teenagers and young people’ - conducting the groups that have the problems - conducting students’ term papers - preparing students for their reports on the theoretical and practical conference in KSPU that are accompanied with multimedia presentations. Physical education issues in modern socio-cultural context A. Shahriev, M. Aliev, Daghestan State Pedagogical University, city of Makhachkala Education is a unique public phenomenon defining the progress of human civilisation. Education plays an important role in a person’s development. Nowadays physical education at higher educational institutions is considered to be the main resource of training of highly skilled experts in physical training and sports. To train competitive experts it is important improve physical education (PE) teachers-to-be training quality. This improvement depends not only on presence of well-equipped material base and higher institution mental potential, but also on skilful construction of teaching and educational sports work in the humanistic education context, on its humanisation and democratization. Problems of humanisation and moral education are becoming extremely important today. Modern society needs a physically and intellectually developed, humane person. To teach such a person is one of major goals of education. However, aspects of humane traits of character developing are poorly presented in the scientific methodical literature devoted to humanisation and democratisation of education at institutions of higher education. Pedagogical recommendations on humanisation and democratisation have not been developed so far. Most teachers use an authoritarian education method putting heavy demands on students. This negatively affects sportsmen’s behaviour and does not give any positive result. A teacher has a great influence on education of a humane person. A teacher has to develop students’ outlook, their thinking, activity and communication abilities, for humane education assumes selfdevelopment and self-improvement. Teachers of higher education institutions are to create humane, student-focused environment for education of a humane person, to give proper attention and pedagogical support to students. The research done allows to draw the following conclusions: 1. Physical training and sports have great educational and developing potential. Higher education institutions provide not only physical training, but also develop humane and moral traits of character (kindness, mercy, humanity, sympathy). In sports activity humanity is developed through kind and compassionate attitude to other people, sympathy, putting adequate demands, and personification of education. 2. Realisation of humanisation in sports education allows to provide favorable conditions for development of a sportsman’s personality, personification of education and recognition of a person as an individual, as well as develops humane traits of character. Higher education institutions should be directed not only on achievement of high sports results, but also on developing of moral socially significant traits (purposefulness, responsibility, independence, kindness, mercy). 3. Ignoring of humanisation can make PE lessons become a source of negative traits development, such as egoism, arrogance, aggression, cruelty, and disrespectful attitude to contemporaries. To avoid this situation, a teacher should work with a student individually using a humane education method. 4. A teacher should refuse to use an authoritarian education method. A teacher should decide on a democratic style of communication without suppressing students’ initiative and independence. It helps to develop cooperation and benevolent attitude to them. 5. Questionnairing of students of the Daghestan State University revealed that the most popular teachers are those who assist and support students, establish a kind rapport with them, are able to ease tension and put interesting ideas forward. More than 60 % of respondents consider that cooperation, mutual understanding and mutual respect between a teacher and a student are essential. 6. Developing students’ positive motivation for studying, developing humane traits (kindness, mercy) and kind and confidential relations between participants of pedagogical process are any teacher’s major goals. This promotes creation of favorable conditions for humanisation of a person in educational process. 7. In modern life, inhumane and immoral traits are intrinsic to many young people (cruelty, roughness, violence, cynicism, nihilism, unbelief). It is caused by absence of accurately considered sociallyoriented youth policy on moral education. Educational work at pedagogical universities should be directed on overcoming of these negative phenomena. 8. To prevent the negative phenomena, it is necessary to develop the state target program on moral education of the studying youth based on humanisation and democratisation. 9. Sports activity gives any person possibility to show his/her worth by constantly improving personal results. Besides, sports activities establish importance of team spirit, mutual assistance and mutual respect, develop students’ will, character, discipline and humane traits (kindness and mercy). Influence of health and fitness activities on indicators of preschool children physical development in Northern regions E. Shaposhnikova, A. Talankina, V. Korchin, Surgut State Pedagogical University, city of Surgut. Analysis of the health status of children and adolescents in Russia in recent years indicates that even at preschool age a large amount of children (58 - 70%) have multiple functional disorders, and 15 - 26% of children have chronic diseases. Preserving and strengthening the health of the child population in northern Russia nowadays acquire significance. Today, the northern regions are allocated in a particular area that requires careful attention as the proportion of chronic diseases among children and adolescents of the North which has a tendency to a sharp increase with advancing age, determines the relevance of prediction and qualified prevention measures at the population level. Physical development is one of the key indicators of child population health. The level of physical development significantly affects the flow of all major functions of the organism, their economy, and defines the limits of their adaptive capacities. Growth and development are key indicators of child health. General biological significance of growth is to achieve a level of development of the organism, which is required for its reproductive, intellectual and social excellence. Growth of children is not the same at different stages of age development. The most intensive increase in body length is observed in the first year of life. In addition, there are distinguished half-growth and puberty growth spurts. The first one coincides with the age of 5 - 7 years; the second one is realized from 11 to 15 years. Objective: To study anthropometric indicators of preschool children living in the northern region. The object of study. There were explored 102 children living in the largest industrial city of Tyumen region Surgut: 57 (55,9%) of them attended kindergarten "Romashka" and amounted to Group I (experimental) and other 45 (44.1%)children attended kindergarten "Teremok" and amounted to Group II (control). Among children from group I there were examined 20 (35.1%) boys and 37 (64,9%) girls, and from Group II - 19 (42,2%) boys and 26 (57,8%) girls. Methods of research. We studied three main anthropometric trait - body length (BL), body weight (BW) and chest circumference (CC) in three dimensions. Measurements were made in the first half of the day according to generally accepted standardized methodology of Aron - Slavitskaya using standardized, methodologically proven tools. Statistical data processing was performed using the program Statistica 6.0. and MICROSOFT EXSEL. The significance of differences was determined by the method of Fisher-Student. Digital material was processed at the IBM PC / Pentium IV. Results. Anthropometric indices in both groups of surveyed children at the preschool age of the city of Surgut were in the range of physiological variables specific to children of appropriate age (Table 1). Average values of body length for boys and girls of the experimental group were slightly higher than those in the control group, but did not differ significantly internally. Average values of body weight for children of experimental group differed credibly from the indicators in the control group: the boys - P <0,001, the girls - P <0,05. In the group of boys in all three positions of chest circumference indices in the experimental group were credibly (P <0,001) higher than similar values of the control group. Comparative characteristics of anthropometric indicators of 6-year- old children, attending pre-school educational institutions of the city of Surgut. Index BL, cm M±m BW, kg M±m Boys group I Boys group II Girls group I Girls group Il 121,4±1,2 118,9±0,8 121,6±0,7 119,6±0,8 22,7±0,8 18,9±0,6*** 22,3±0,9 19,5±0,6* CC, cm M±m pause 61,7±0,7 57,7±0,6*** 61,5±0,8 57,8±0,6** breath 64,9±0,7 61,4±0,4*** 64,9±0,8 60,6±0,6*** exhale 59,7±0,6 56,6±0,5*** 60,1±0,8 56,8±0,6** Note: credible difference between groups of girls and boys: * - P <0.05, ** - P <0.01, *** - P <0,001 Among the surveyed girls as well - the results of chest circumference on all indicators were credibly higher compared to figures for the control group: pause and exhale - P <0,01, breath - P <0,001. Research of the ratios between the basic indicators of physical development of children in the experimental and control groups (based on scales of regression of body length and age) found that the body weight of the half boys of the experimental group was in accord with body length. Minor deficiency (up to 1 kg) found in 1 (5.0%) boy, and in 3 (15.0%) boys - 2 degree underweight (up to 3 kg). Slight 1 and 2 degree excess of body weight was found in 3 boys in both cases: 15,0%in each group. A completely different picture was presented in the study of the same indicators in boys of the control group. Physiological suitable ratio of length and weight were found in 4 (21,0%) boys of a control group. In 5 (26,3%) of observations there was revealed a slight deficit of body weight in relation to its length. In the vast majority of cases - in 8 (42,1%) boys – there was found moderate underweight, and 1 (5,3%) frank underweight found. For the majority of girls in the experimental group - 26 (70,3%) - body weight was adequate to its length. In one case - 1 (2,7%) – there was detected a slight excess of body weight relative to the physiologically optimal values. In 5 (13,5%) girls of the group there was recorded a minor underweight and in 5 (13,5%) moderate underweight. In the control group of girls the optimal ratio of length and weight was recorded more than 2 times less than in the experimental group - in 8 (30,8%) girls. Excess body weight of various severity was detected in 2 (7.7%) girls, the 1 degree deficit of body weight was found in 2 (7,7%) girls of the control group, 2 degree deficit - in 10 (38.4%) girls, and 3 degree deficit - in 4 (15,4%) girls. Thus, the surveyed preschool children of the city of Surgut who attend a pilot group of kindergarten "Romashka" showed the optimal ratio of length and weight, compared with the control group of preschool children who attend kindergarten "Teremok". In the kindergarten "Romashka" healthy lifestyle is paid much more attention. In addition to traditional health improvement activities exercises on Biofeedback machinery are regularly conducted. These exercises help to improve muscle tone, strengthen muscular corset, and develop good posture. P.E. pedagogue teaches children the skills of relaxing diaphragmatic breathing. In pre-school educational institution "Romashka" there function sensory integration room and a cabinet of psychological rehabilitation; a work on wellness tempering and corrective gymnastics is also being held. In addition, seminars, conferences, lectures and discussions on issues of healthy lifestyle are regularly conducted for parents with the participation of teachers, doctors, scientists, Surgut State Pedagogical University. Thus, the joint efforts of educators, doctors, parents and teachers of high school have been crowned with success: the surveyed preschool children of the city of Surgut who attend a pilot group of kindergarten " Romashka " showed the optimal ratio of length and weight, compared with the control group of preschool children who attend kindergarten "Teremok". Estimation of physical fitness level of Petrozavodsk comprehensive schools pupils Y. Shlykov, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk In the present work preliminary results of studying of Petrozavodsk comprehensive schools pupils’ physical fitness level are presented. This is a 5-year-research. It began in 2006 and will finish in 2010. For estimation of the pupils’ general level of physical fitness, the test system of the «Presidential competitions» program was used. The survey was done annually in May. Petrozavodsk comprehensive schools pupils of the 4th, 9th and 11th grades (12 schools in total) took part in the research. One of the goals of the research is to study whether the pupils’ motor age corresponds to their biological age. Nowadays the society is anxious about pupils’ health deterioration. Half of them have chronic diseases and cardiovascular system diseases. One of the reasons is the lack of motor activity. Hypodynamia (physical inactivity) is widely spread among children and teenagers. According to experts’ research, only 1020% of comprehensive school leavers can be considered almost healthy that is a consequence of an inactive lifestyle. 1. Estimation of the 11th-grade pupils’ general level of physical fitness (table 1). Table 1 Sex; years Estimation, % Super Excellent Good Satisfactory Poor Dangerous Boys 2006 0.92 47.8 51.3 - Girls 2007 1.05 1.32 27.85 47.90 21.88 - 2008 2.55 3.70 35.51 35.0 22.22 - 2009 3.76 14.9 40.34 25.77 15.13 - 2006 39.26 60.74 - 2007 3.85 41.25 31.20 23.70 - 2008 0.62 9.17 44.67 24.65 21.49 - 2009 3.8 17.70 36.95 19.21 24.27 - The results of physical fitness level shown in different years are not the same. It is caused by the fact that there are new pupils in the presented classes every year. At the same time every year the majority of results are within the zones of “Good” and “Satisfactory”, in a range accordingly from 27.85 to 44.80% and from 19.21 to 60.74%. Percent of pupils with the results “Super” and “Excellent” is very small. So, only 1.05-3.76% of the boys and 0.62 to 3.80% of girls have “Super” results. “Excellent” results showed only 0.92 to 14.9% of boys and 3.85 to 15.70% of girls. The percent of pupils, both boys and girls, showing “Poor” results is considerably high (15.13 – 24.27). Pupils of 9th and 4th grades showed the similar results. 2. Estimation of the pupils’ level of physical fitness in individual kinds of «Presidential competitions» (Table 2). The best results of the 11th-grade pupils are in the test «Standing long-jump», the majority of boys and girls showed “Good” results, that is accordingly, in 2006 – 92.1 and 88.4%, in 2007 – 89.3 and 92.3%, in 2008 – 72.7%. The pupils showed very low results in 1000 m race. In 2006 the percent of satisfactory results reached 87.5% (boys), and 67.7% (girls). Good and satisfactory preparation showed both boys and girls in the “Lifting of the body” exercise within 30 seconds: in 2008 33.3% of boys showed “Super” results, 51.9% - “Excellent” ones, and 52.6% of girls showed “Excellent” results. It is necessary to state low preparation in performance of «Bending ahead» exercises by boys: the percent of “Poor” results reached 62.5%, as well as in performance of «Bent suspension». 3. Pupils’ motor age, 2008. Studying of the results of estimation of the pupils’ general level of physical fitness showed inhomogenuity in pupils’ physical fitness. Only a few pupils have high level of physical fitness. Most pupils are quite good in some kinds of sports and bad in other ones. So, we consider it important to study whether the pupils’ motor age (their physical fitness) corresponds to their biological age (Table 3). Table 2 th Estimation of the 11 -grade pupils’ level of physical fitness in individual kinds of «Presidential competitions» Kinds 1000 m race (sec) Press-up suspension Lifting of the body (30 Standing long-jump sec) 2007 2008 2006 2007 2008 2006 2007 2008 Bending ahead 2008 Bent (sec) 2006 Year Estimation% BOYS Super Excellent Good Satisfactory Poor Dangerous GIRLS Super Excellent Good Satisfactory Poor Dangerous 2006 2007 2008 2006 2007 2006 2007 2008 12.5 87.5 - 57.3 41.3 1.4 - 36.4 54.6 9.1 - 62.5 37.5 - 2.7 12.0 66.7 18.6 9.1 72.7 9.1 9.1 - 68.7 31.3 - 13.3 2.7 41.3 42.7 - 18.2 36.4 45.4 - 50.0 50.0 - 8.0 37.3 54.7 - 33.3 51.9 3.7 11.1 - 7.9 92.1 - 8.0 89.3 2.7 - 9.1 72.7 18.2 - 6.25 12.5 18.75 62.5 - 8.00 1.30 17.3 14.7 58.7 - 36.4 36.4 27.2 - 32.3 67.7 - 33.8 36.2 30.0 - 31.6 42.1 20.4 - 7.7 7.7 38.5 46.1 - 2.2 15.2 28.2 37.0 17.4 - 15.8 31.5 42.1 5.3 5.3 - 3.8 11.6 84.6 - 4.3 6.5 27.4 61.6 - 21.1 15.8 63.1 - 61.5 38.5 - 18.1 65.2 16.7 - 5.3 52.6 21.0 15.8 5.3 - 3.8 88.4 7.6 - 1.5 92.3 4.2 - 73.7 10.5 15.8 - 11.6 53.8 23.0 11.6 - 1.5 15.9 38.4 24.6 19.6 - 5.3 31.6 26.4 36.7 - Table 3 Estimation of pupils’ motor age in 2008, % Grades Motor age 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 11th grade boy 12.5 25.0 12.5 12.5 25.0 12.5 - girl 9th grade boy 8.3 25.0 16.7 25.0 16.7 8.3 - 3.0 21.2 6.1 27.3 27.3 12.1 3.0 girl 4th grade boy girl 2.4 12.2 7.3 29.3 19.5 7.3 17.1 4.9 - 9.1 4.5 13.6 31.8 4.5 9.1 27.4 - 9.4 12.5 9.4 9.4 21.8 12.5 9.4 15.6 - The analysis of results testifies a wide range of motor age in each class. So in the 11th grade the level of physical fitness is very low, those pupils’ motor age corresponds to 10-13 years among boys and to 9-12 years among girls. The situation is slightly better in the 9th grade, where 69.7% of boys prove that their physical fitness corresponds to the biological age. There is a wide range among girls - their physical fitness corresponds to the age from 6 to 14 years. The situation in the 4th grade is quite good. Boys and girls’ physical fitness corresponds to their biological age in 86.7 and 78.1% cases. In conclusion it is necessary to notice that the 11th-grade pupils’ level of physical fitness does not meet the requirements of a modern life. It is necessary for schools to widely use all forms of physical activity. ''Fitness'' extended education program for 5th to 7th grade pupils. M. Shtoda, M. Rostovtseva, Russian Fitnees-Aerobics Association, city of Moscow The federation of the fitness-aerobic in Russia prepared ''An approximate program of the additional education for the students from 5th to 7th grade ''Fitness'' in 2008. The program was evaluated and nowadays is successfully used in many schools of Moscow. The program calls the students for physical development, preventive measures and correction of the body posture. And also the program helps to form the positive attitude towards physical training, sport and healthy way of living. This program is very up-to-date. According to the statistics the physical development and children's health have declined because of many reasons. 2 P.T. Lessons per week for children in order to develop them physically is not enough. That's why it is very important to arrange the additional programs concerning physical training. There is a certain novelty in this program because nowadays there are not many programs of that kind, devoted to fitness. In those extracurricular activities can be involved music in order to develop physical qualities of the students. The aim of the program is to form the positive student's attitude towards P.T. as an extracurricular activity to raise the level of health and also to inform students about physical training and sport in general. The tasks of the program are: 1)Educational -to raise the level of rhythmic training by using music tracks -preventive measures and correction of the body posture -the development of strength and flexibility with the help of using stretching 2) developing -to teach how to organize the activities of daily living in harmony with healthy way of living (physical activity, giving up bad habits, the day's routine etc.) -to raise the level of student's health -to enlighten the students concerning the basics of anatomy, the relation of music and movement 3) upbringing -a student's ability to deal with a group of people -to raise children's interest to the P.T. The major functions of the program are: -the use of music on P.T. lessons -a wide range of methods that are used on those lessons -the educational effect of the program is that the students broaden their knowledge of anatomy and physiology. The lessons consist of 70 hours. They are held from September to May and end with the competitions between the teams from different schools. These classes are extracurricular activities and are held 2 times per week. The structure of academic activity: The students sequentially study different topics. Every lesson consists of the exercises focused on durability development, development of strength and flexibility. The structure of the program ''Fitness'' The program consists of the following parts: Part1) Classical aerobic and dancing aerobic Part2) Fitness-aerobic (aerobic and hip hop aerobic) Part3) The program ''Healthy back'' Part4) Power training (with and without equipment) Part5) Stretching Part6) Feetball Part7) Training is aimed at development of strength and flexibility Part8) Training with the pauses Part9) Theory courses The whole program is aimed at 5th-7th grades but,nevertheless, there are some differences concerning physical exercises. Boys and girls are highly recommended to exercise together. In this program are used such kinds of exercises as front-face exercises, combining the instructor's explanation and visual methods. The instructor does the exercises with the students. He or she uses verbal and visual techniques. The rhythm of music depends on the rhythm of the movement. The results of the program: -Fitness-aerobic increased the rhythm of children, music hearing and health. Furthermore, there is a certain progress in durability, flexibility, strength, coordination. In order to define the effectiveness of the program there were held some tests and competitions. During the year of studying the tests were held 3 times: in the beginning (September-October), in the middle (December-January) and at the end (April-May). More over, in May there were held final competitions on fitness-aerobic between the teams of different schools ''Aerobic'' and ''Hip hop aerobic''. Ski training of children and adolescents with metal disorders in Kolar polar region A. Smetanina, Child-Adolescent Sport-Adapted School #15, city of Murmansk Development of a human being proceeds in accordance with his/her intellectual, social and motor capabilities. Mental retardation is the most frequent and severe development defect by its social consequences out of all functional health deviations. The importance of adapted physical culture for schoolchildren with mental disabilities can not be overestimated. Here we see that physical training has no parallel comparable to its efficacy in different types of rehabilitation of the disabled. Adapted physical culture classes account for the major part of corrective work with a person. Apart from solving traditional tasks – health improvement and conditioning of a child body, ensuring of correct physical development, teaching of motor skills and techniques – PE classes in special (correction) school of 8th type assist to addressing correction tasks through overcoming of physical development defects and motor disorders of mentally retarded pupils. At present the PE syllabus for special (correction) schools of 8th type includes the following basic training: track and field, gymnastics, sport and active game, skiing. Skiing is not included into PE syllabus for children with moderate or severe mental retardation studying in Murmansk boarding schools, special (correction) schools of 8th type, rehabilitation centers. But it is recommended for senior schoolchildren as extra classes in health-improving clubs. At the same time skiing classes make significant health-improving, healthful impact as an outdoor activity hence assisting to health promotion and body conditioning. Skiing contributes to better development of muscular system, blood circulation and respiratory organs of a child. Hence skiing can be successfully used in all kinds of adapted physical culture for mentally retarded. The conducted analysis of scientific literature indicated that ski classes for mentally retarded are aimed, first of all, at correction of basic motor disorders. They contribute to correction and overcoming of motor physical development disorders, stimulate mental and motor activity of mentally retarded, develop abilities of undertaking motor activities of different complexity by him/herself. Skiing contributes to development of social activity of the mentally retarded even out of sport activity sphere. They get sick more rarely, express less aggressive or detrimental behavior. Regular ski classes, as well as other types of physical activity, contribute to and favor formation of positive social-emotional traits, socialization and normalization of life cycle of the mentally retarded. Living, study and leisure conditions of children residing in Polar regions are influenced by a range of extreme environmental factors not inherent in mid and low latitudes which have effect on child body development. Extended period of low temperature, extreme weather volatility, strong winds, rapid change of atmospheric pressure, negative annual balance of solar radiation and its misdistribution during a year due to long polar day and polar night periods, proximity of permafrost to the ground surface, great geomagnetic perturbation, regional compulsive hypokinesia as a result of mixed influence of environmental factors (extreme environment) and artificially created living quarters comfort zone - all these factors exert negative impact on a body development. The bulk of experts (E. Lapitskaya, S. Lapitskaya, E. Sivkov, V. Lyah, L. Tarasov, S. Pushkarev) emphasize the leading role of physical training in proper development of a motor function, physical viability of a child. Outdoor activities with use of aerobic training (skiing) contribute to improvement of functional abilities of a child body. Scientific reasoning of educational methods used at PE classes is of great importance in preparing and conducting physical training in north regions. Extreme climate and geographical peculiarities of high latitudes determine specific living conditions and adaptation mode of a child to education. The climate of Kolar polar region provides a unique opportunity for use of skiing and via it a broad range of health-improving nature factors for adapted physical activity. Ski walk and ski training may compensate for the needed volume of movements. Exercising every day keeps you healthy all the way! Short-time limited-variety physical exercises at school and home Irina Smirnova Senior teacher, Petrozavodsk Pedagogical College Nowadays physical education is being reorganized. V.I. Lyah thinks that it is necessary to transfer the emphasis from physical training to healthy lifestyle developing by means of Physical Education (PE) lessons. Potential possibilities of personal physical culture developing depend on the content and organisation of physical training at home, school and pre-school educational institutions. One of the objectives of health-improving education is using small forms of physical training both at school and at home to ease the tension. It is very important to combine learning and health improving during the educational process. We should introduce additional kinds of motor activity, such as "Hour of your health", daily dynamic, motor and physical training breaks, introductory gymnastics and others. The goals of "Hour of your health" are active rest, increase of working capacity, perfection of physical development, and health improving. This hour is always various in forms and content, and never repeats PE lessons. The most widespread variants of "Hour of your health" for primary school are action-oriented games, relay races and walking in the open air; for secondary school - rhythmic gymnastics, sports and national games, cycling in summer and sledging in winter; for senior high school pupils – competitions on various kinds of sports, sports entertainment or skating. «Motor breaks» are aimed at maintenance of working capacity, easing the tension and dealing with exhaustion. Games are chosen depending on the age of children. All the games have to be finished 3–4 minutes prior the lesson. Additional kinds of motor activity are also used in the first grade. It is a so-called daily dynamic break lasting not less than 40 minutes. Children usually walk in the open air, play outdoor games, take part in mini relay races. Physical training breaks at lessons help to restore intellectual working capacity, prevent increase of exhaustion, and ease the tension. Physical training breaks are essential for primary school and middle school aged pupils. Each system consists of 4-5 exercises repeated for 4-6 times. It is better to choose easy exercises, such as stretching, bending, half-bending, and knee bending. Physical training breaks are to take place at each lesson between the 20th and 25th minutes and last for 1.5-2 minutes. Introductory gymnastics usually consist of 5-8 easy gymnastic exercises without any sport equipment which last for 5-7 minutes prior to the beginning of the lessons. It activates functional systems of a child's body and helps to study effectively. Morning exercises are one of the most popular forms of physical training at home. Its main goal is to optimise transition from long rest (dream) to daily activity. Besides, it is possible to develop a normal posture and maintain level of development of some motor skills. Morning exercises include gradual stretching in bed or in a standing position, gradual knee bending, bending or twisting of the body, turns, jumping, running for 3-5 minutes, walking, etc. Morning exercises usually last for about 10-15 minutes. Short-time limited-variety physical exercises differ from long-time various ones mostly in rather narrow orientation of activity and rather small duration. These forms are additional but very significant. 8th-10th grade pupils’ attitude to extracurricular physical education lessons O. Stepanenkova, I. Achepovsky, N. Listkov, city of Petrozavodsk To organize extracurricular physical and health education lessons for pupils effectively, the authors prepared an anonymous questionnaire for the pupils. The aim was to learn the pupils and their parents’ attitude to extracurricular physical exercise, as well as their favourite kinds of sport. 300 8 th-10th grade pupils of Petrozavodsk state schools took part in the questionnaire. The research showed that 40% of respondents think that the amount of compulsory PE lessons is not enough to be fit and healthy. The result proves that pupils need extracurricular physical and health education lessons. The pupils’ favourite kinds of sport include the following: - sport games: volleyball, basketball, football – 50%; - fitness-aerobics: hip-hop, fitball, yoga, step, dance – 43%; - martial arts, extreme sports: climbing, parachuting, snowboard, skateboard, surfing – 14%; - athletics – 11%; - skiing with possibility to rent high quality sports equipment- 8%; - athletic gymnastics – 7%. The Federal law “Self-financing in education” made it necessary to find out whether parents are ready to pay for extracurricular lessons on the chosen kinds of sport for their children. 42% of the respondents are ready to pay for extracurricular lessons. 31% of the pupils find it necessary to organize a fee-paying rent of high quality sports equipment. 34% of pupils’ parents are willing to do healthy gymnastics and some other physical activities in a sports club. 18% of pupils want to do sports together with their parents. Wishes on organization and conducting of the lessons and extracurricular activities differ among pupils of different ages. The 8th-grade pupils suggest doing sports in the open air; they would like to play various exciting sport games more often, to have more lessons in a swimming pool and fitness gym. In winter they are eager to ski and skate, in summer they want to cycle and rollerblade. Besides, the 8th-grade pupils would like to have more competitions between schools and classes, to have a fitness gym and a treadmill. The 9 th-grade pupils would like to have more lessons on sport games and muscle-strengthening exercises, to use fitness machines more often, to include all year round swimming, step-aerobics, yoga, and skiing and skating in winter. The 10-thgrade pupils’ main wish is to cancel standard control tasks and marks. They would like to do aerobics, to play sport games (volleyball, basketball, football) and to have free extracurricular lessons. The research revealed next organizational actions on introducing of extracurricular lessons for pupils and their parents in a sports club. Games with elements of Kalmyk national wrestling as means of preparation for martial arts school course V. Tsandykov, State Educational Institution Children Recreation-Educational Center “South-Eastern”, city of Moscow Modern teaching methods utilized in many sports imply use of preliminary exercises at different stages of training. These exercises are aimed at reaching several goals: development of physical qualities needed for the chosen kind of sports, learning of specific motor activities and creating background for further sport specialization. Unfortunately today school curriculum foes not include preliminary exercise for martial arts course in senior school. Anyway I suppose that this preliminary phase should be introduced as this is determined by the specific character of this kind of sports requiring abilities to concentrate the maximum efforts at a particular moment, resist adversary’s actions and respond to them, act in tough circumstances, etc. Solution of these problems requires to my mind applying various games with martial arts elements to physical training classes prior to Martial Arts course. As this feature is to contribute to better pupils’ learning of the course mentioned. Different researches prove that skills learnt within a game are everlasting and rooted. A game smoothly mobilizes body latent recourses. Pupils repeat many times study material while playing even without realizing it. The goal of the present article is to render methodical support to PE teachers and experts in enhancing their expertise in games with martial arts elements in particular Kalmyk national wrestling for applying them to physical activities with schoolchildren of different ages by describing them. “Pick skittles up!” game The goal: development of physical qualities of schoolchildren - speed, movements coordination, differentiated efforts, etc. Equipment: skittles (cones, small balls, etc), two belts (of different color). Game rules: participants stay back by back to each other, regular grip of each others’ belts. In front of each participant a line is drawn, skittles are placed on the lines. Every child has to drag an adversary with one hand and pick up skittles with another hand. Competitors are not allowed to break the grip. Upon the first round is completed and the winner is decided, competitors go on to the second round and change a hand of the grip. Recommendations: a teacher has to always be able to spot for a competitor. Tips for increasing the difficulty: 1. Increase the number of skittles, 2. Decrease the size of a skittle, 3. Increase a distance to the skittles line, 4. Increase the weight category of an adversary, 5. Repeat the game, 6. Concede a weaker adversary. Pic.1 Pick skittles up! “Elevate an adversary of the floor and take out of the circle” game The goal: development of elementary wrestling skills and physical qualities. Equipment: twp belts (of different color). Game rules: competitors enter a circle, stand against one another, cross (right or left) belt handclasp, the objective for a competitor is to rise an adversary of the floor and bring out of the drawn circle. A person can keep on contending if he is being elevated of the floor till he is taken out of the circle. Upon the first round is completed and the winner is decided, competitors go on to the second round and change a handclasp. Recommendations: a teacher has to always be able to spot for a competitor. Pic.2 Elevate an adversary of the floor and take out of the circle! Tips for increasing the difficulty: 1. Increase the circle diameter, 2. Increase the weight category of an adversary, 3. Repeat the game, 4. If competitors are equal a game can be prolonged or shortened. “Drag an adversary behind your line” game The goal: development of elementary wrestling skills and physical qualities. Equipment: twp belts (of different color). Game rules: one participant stands with his/her back to another competitor. The second one grips the first one’ belt with both hands. The objective for a competitor is to drag an adversary behind the a drawn line. Upon the first round is completed and the winner is decided, competitors go on to the second round and may change position or a grip. Recommendations: a teacher has to always be able to spot for a competitor. Tips for increasing the difficulty: 1. Increase the circle diameter, 2. Increase the weight category of an adversary, 3. Repeat the game, 4. If competitors are equal a game can be prolonged or shortened. Pic.3 Drag an adversary behind your line! “Drag an adversary out of the circle by belt reverse grip” game The goal: development of elementary wrestling skills and physical qualities. Equipment: twp belts (of different color). Game rules: competitors enter a circle, stand against one another, holding each other’s belts with reverse grips. The objective for a competitor is to drag an adversary out of the circle. Competitors are not allowed to break the grip. Recommendations: a teacher has to always be able to spot for a competitor. Tips for increasing the difficulty: 1. Increase the circle diameter, 2. Increase the weight category of an adversary, 3. Repeat the game, 4. If competitors are equal a game can be prolonged or shortened. Pic.4 Drag an adversary out of the circle by belt reverse grip! Use of aforementioned games with elements of Kalmyk national wrestling on the regular basis at PE classes before the Martial Arts course let pupils prepare for this course by improving physical qualities needed in this kind of sport, create elementary wrestling skills and decrease injury risk. References 1. Подвижные игры: учебник / Л.В.Былеева, И.М.Коротков, Р.В.Климкова, Е.В.Кузьмичева.М.: Физическая культура, 2006.-288 с. 2. Подвижные игры: Учебное пособие для студентов ВУЗов [текст] – М.: ТВТ Дивизион, 2009.216 с. 3. Цандыков В.Э. Использование игр с элементами калмыцкой национальной борьбы для детей с ослабленным физическим развитием / «Спорт и образование»: Материалы V Региональной науч.-практич. конфер. по физической культуре и спорту.- Москва, 2010.- С.44-48. 4. Цандыков В.Э. Использование игр с элементами калмыцкой национальной борьбы в учебно-тренировочном процессе студентов, занимающихся борьбой / Актуальные проблемы совершенствования физической подготовленности студенческой молодежи в современных условиях: сборник научных трудов / под науч. ред. канд. мед. наук, доц. Т.И.Волковой.Чебоксары: ЧИЭМ СПбГПУ, 2010.- С.180-185. 5. Цандыков В.Э. Усложнение игр с использованием элементов калмыцкой национальной борьбы как фактор дальнейшего повышения уровня развития физических качеств / Психология и педагогика: методика и проблемы практического применения. Сборник материалов XI Международной научно-практической конференции. В 3-х частях. Часть 3 / Под. общ. ред. С.С.Чернова.- Новосибирск: Изд-во «СИБПРИНТ», 2010.- С.162-167. National sports as means of promoting physical training among schoolchildren (case study of Kalmyk national wrestling) V. Tsandykov, State Educational Institution Children Recreation-Educational Center “South-Eastern”, city of Moscow Preservation and promotion of ethnocultural values is the important issue nowadays. As these values contribute to achievement of personhood and its development, civic development what is essential for the younger generation. One example of these values inherited from our ancestors is Kalmyk national wrestling called “Beki barildan”. It is so popular in the Republic of Kalmykia that almost every holiday was and is being held accompanied with competitions on this wrestling. People of all ages are aware of its rules, everybody can wrestle regardless of age. Almost every people living in the vast territory of the Russian Federation has its national wrestling. The Tatars have “Keryash”, the Yakuts – “Hapsagai” and “Kurdatsan-tustuu”, peoples of the Northern Caucasus – “Tutush”, the Tuvan people – “Huresh”, the Buryats – “Buhe barildaan”, the Chuvash people – “Kureshu”, the Russians – “V shvatku” and “Ne v shvatku”, the Bashkirs – “Kuryash”, the Kalmyks – “Beki barildan”, the Chukchis – “Teikev”, etc. Importance and influence of centuries-old folk heritage – Kalmyk national wrestling – for formation of outlook, tolerance and individuality of a youngster is enormous. Though this national sport has not been studied well enough in modern science. So detailed in-depth research on the subject should be conducted. The goal of the article is promotion of Kalmyk national wrestling among schoolchildren by exposure to its traditions thus creating pupils’ wants in systematic physical training and healthy lifestyle. Several ancient traditions of Kalmyk national wrestling are still kept alive, for example, to arrange a date of competition beforehand and inform all the people possible. The second one is that a wrestler should have seconds who guard him to the floor covered in fabric in order not to let spectators and an adversary recognize a competitor. The second tradition is still observed but only as a ritual. Traditional warm-up is held bright before a warsle: wrestlers perform a short foot tapping dance to tune of Kalmyk dombra or harmonica. The best dancer gain additional score thus if wrestlers are equal this feature may assist one’s victory. That’s why some wrestlers dance like professionals. Dancing warm-up pursues several goals: - Mental approach to a wrestle, - Exposure to Kalmyk culture, - Learning dance movements, - Decrease of injury risk, - Motivation to better dance performance. Other traditions are embroidery on sport clothes, welcoming each other and a referee, awards. In ancient times wrestlers were awarded significant expensive prizes, sometimes they were awarded with cows, horses and sheep. Nowadays winners in Kalmyk national wrestling also get prizes. It can be a sheep, but a car or a bicycle as well. Kalmyk national wrestling “Beki barildan” and traditions embodied in it are factors of exposure the younger generation to ethnocultural values hence breeding tolerance to cultures of many peoples of the Russian Federation and provoke interest to systematic physical training. Use of Kalmyk national wrestling and its elements in PE classes in various educational institutions is one of the components contributing to formation of physical, mental, cultural and moral development of a personality. References 1. Джангр: Калмыцкий народный эпос / Пер. с калм. С.И. Липкина.- 5-е изд. Элиста: Калмыцкое книжное издательство, 1989.- 363 с. 2. Калмыцкая национальная борьба. Правила соревнований.- Элиста: Калмиздат., 1997. 3. Лесгафт П.Ф. Руководство по физическому образованию детей школьного возраста.Часть II.- Издание 2-ое пересмотренное и дополненное.- С-Пб., 1909, с. 415. 4. Небольсин П. Очерки быта калмыков Хошеутовского улуса. – С.- Петербург, 1852. – с. 114. 5. Смирнов П. Путевые записки по калмыцким степям Астраханской губернии. / Тексты статей по изданию: Астраханские Епархиальные Ведомости, 1879.- Элиста: Калмыцкое книжное издательство., 1999.- 248 с. 6. Цандыков В.Э. Калмыцкий народный эпос «Джангар» о месте и роли национальной борьбы в системе воспитания и подготовки к жизни / В.Э.Цандыков // Вестник Калмыцкого Университета. Научный журнал.- № 6.- 2008.- С.90 – 93. 7. Цандыков В.Э. Калмыцкая национальная борьба: традиции от прошлого к настоящему // Молодежь и наука: реальность и будущее: Материалы II Международной научно-практической конференции (г. Невинномысск, 3 марта 2009): Т. III.- Невинномысск: НИЭУП, 2009.- С.169-171. 8. Цандыков В.Э. Страницы истории и основы базовой техники калмыцкой национальной борьбы «Бөки барилдан».- Элиста: ЗАОр «НПП «Джангар». 2009.- 190 с., ил. Active and sport games as an instrument of pupils’ social competences development. L. Tsoboleva P.E. teacher, Municipal Educational Institution “Secondary school #10”, city of Severodvinsk Games can be considered as anticipation and training of activities that must take place later. (A. Vallon) The Concept of modernization of Russian education till the year 2010 states that "a developing society needs modernly educated, ethical, active people who can make their own decisions in a situation of choice, who are able to work, who can be characterized by mobility, dynamism and constructability." This task is supposed to be solved in case that during a period of school education a pupil is taught how to live in a society, in other words, if he/she gains necessary social competence. Analyzing the term “competence”, we can point out that with all multifold definitions competence is a personal trait and experience in a given sphere. Competence of a pupil assumes a set of certain personal traits. Among key competences the important position is taken by social one that is a combination of knowledge and skills vital for living in a society. Some school graduates are diffident, extremely shy or some are vice versa very aggressive and too active. Both edges disturb not only surrounding people but teenagers themselves. Undoubtedly, the best results in development of social competence can be reached when a pupil participate actively in the process of his/her formation a personality. Implementation of a «Physical Culture" training program along with other subjects has a positive effect on the development of social competence. As shown by experience, it is heavily contributed by active and sport games, which take a significant share of the program on physical culture and which are widely practiced in extracurricular activities. The game is an activity which represents a conscious, proactive efforts aimed at achieving conventional goals, voluntarily established by players. Features of games are determined by specific competitive activity, which distinguishes it from other sports. Competitive rivalry in a game follows established rules, using unique competitive action - playing techniques. Presence of an opponent is obligatory. In team games a winner or a loser is team as a whole, rather than a single participant. A single player may play very good but if a team loses then he/she loses as well. Conversely, if a student plays badly, but the team wins, he/she wins with the team. It is nice to see how, carried away by the game, students forget about their weaknesses and literally surpass themselves, demonstrating the results which are impossible in conditions of normal activity. Fillings that are inseparably connected with the game, such as exhilaration and insatiable desire to win legitimately cause the participants’ display of courage, wits, strength, and develop such valuable personal qualities as determination, focus, operational thinking, a sense of responsibility, a partnership that will help achieve success in various situations in future. Victory in the game increases self-confidence and stimulates further activity of students, encourages explicitly or covertly, consciously or subconsciously strives for excellence in other important activities, as well as develops interest to overcome the difficulties and obstacles to target. Specifically incorporated properties of games such as fair, equitable competition and public encouragement of pursuit of superiority, excellence, which are important in modern society are extremely useful for realization of educational purposes. Specificity of team games defines a number of requirements to participants, their views, attitudes, personal traits and the nature of action in the match. Consequently, the game promotes collectivism, the ability to sacrifice own interests for the sake of team wins, the desire to see and understand a common interest in every moment of competition. The impact of a team on its member can be very tough, strong, and efficient, that contributes to the development of relevant personal qualities: mutual understanding, respect, honesty, because in the game, students learn how to win honestly and to lose with dignity. In active and sport games there are recreated quite complex and vivid emotive interpersonal relationships such as cooperation, mutual assistance, and mutual aid, as well as competition, confrontation, when oppositely directed desires face each other. Thus, we can say that in the game, scholars get into social interaction, and therefore, they develop social competence. The main criteria of social competence of pupils being shown in the active and sport games are the following: - Ability to work with adults and peers; - Willingness to follow the rules of the game; -Willingness to systematically acquire new knowledge and skills and share them with others; - The ability to respond properly to the views, positions, attitudes of other team members; - Ability to understand other players as representatives of the interests of the team; - The ability to specifically interact with the team in the game; -Ability to use non-verbal, specific for this game, symbols and signs; - Ability to use originality of the functions assigned to the player. The experience lets us suggest that the vast majority of pupils understand that the relationships in the game and outside it are very different. Accepting my provisions to a game as provisions of more experienced and knowledgeable person, they learn to listen to the elders, not to reject their opinions and advice, which is an important factor of successful socialization. The desire to express themselves in the game better motivates pupils to acquire new skills and abilities, they have a need for additional physical education and sport: many of them attend sports sections for football, volleyball and basketball, annually my graduates continue their studies in universities on "Physical Education" and are involved in coaching. It should be noted that the game is constantly modeling the situation where, with limited time and constantly changing environment it is necessary to assess the situation, choose the desired action. As a result, the students gain psychological resilience: the ability to control their emotions, listen and take criticism by classmates and a teacher properly, which will also affect successful socialization in future. As a part of extracurricular activities I implement independently compiled additional educational programs with currently 63% of pupils involved. I hold activities, many of which have become traditional: school tournaments in basketball, volleyball and etc. Our pupils are the future of the country. In order to prevent child neglect and delinquency, together with form masters I organize work on attraction pupils to a healthy lifestyle and skills of social adaptation. In our school we have a Weekend Club - family sporting events that bring such positive results as following: they allow spending some free time, that a mother or a father dedicate to a child profitably, they also can be considered as a pattern for a pupil of the further family life. The positive changes are noted in the analysis of participation in city Olympics among schools: in the 2005-2006 academic year – 5th place on volleyball among males older age group, in 2006 - 2007 account. PM – 5th place on volleyball among males in older age group, 3rd place in the game "Sniper" among pupils in the younger age group: in 2007 - 2008 academic year – 7th place in volleyball , 2nd place in the city championship in volleyball among males in older age groups: in 2008 - 2009 academic year – 1st place in volleyball among males in older age group. Each year our pupils become members of the city youth team in volleyball, which successfully performes in the regional competitions: 3rd place in 2007 and 4th place in 2008. Within a school methodical week “The role of my subject in social adaptation of schoolchildren” in 2009 we questioned pupils of the 11th grade on “How do you benefit from sport games at P.E. lessons for future adult life?” Typical responses were as follows: developing their skill, coordination, strength and endurance, developing such traits as solidarity, partnership, and improving health. Thus, active and sport games are the strongest means of socialization of students. On the one hand, games improve physical indicators at the expense of life conditions of a human body, and on the other hand- demonstrate and reveal certain traits of character that affect a pupil’s future adult life, learn how to adapt to changing circumstances. Psycho-physiological characteristics of physical training stages V. Umnov, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk In general, education efficiency depends on physical education teachers and coaches’ ability to organize the educational process in accordance with pedagogical, psychological and physiological regularities forming the basis of modern educational theories and conceptions (Zh.K. Holodov, V.S. Kuznetsov, 2009). However, artificial division of studying of physical education and sporting activities among the scientific disciplines leads to duplications and contradictions in interpretation of some statements. Besides, the facts of related disciplines are not taken into account. By the way, a famous Russian psychologist B.F. Lomov (1978) said that, while explaining the behavior as a whole, any psychological theory not including neurophysiological mechanisms, as well as any physiological theory ignoring the psychic, is one-side. So, we think that it is efficient to study the physical actions training (PAT) process from both psychology-pedagogical and phychophysiological points of view. In the modern theory of PAT in accordance with peculiarities of didactic goals and teaching methods, the PAT process can be divided into stages, the number of which differs depending on the author. Physiologists say there are 3 stages, while teachers and psychologists think there are from 3 to 6 ones. We prefer the theory of V.D. Maznichenko (1981) including 5 stages of training and explained psychophysiologically by E.P. Ilyin (1983, 2009). Let’s analyze them. Stage 1. The aim is to teach a pupil the basics of a physical action, as well as to give a pupil a visual form of the action. On this stage a pupil gets information through the optic and auditory canals. Pupils get just a general idea of the physical action and do not train it yet. A pupil understands the aim but does not know how to reach it. This stage is fundamental because the adequate image of a physical action lets then master it successfully. On this stage the physical action basic (PAB) is being formed, which is essential for its performance. This idea was proved by such psychologists as P.J. Galperin, A.V. Zaporozhets, and N.A. Menchinskaya, as well as L.P. Matveev (1991). PAB includes some general logical plan of the action and basic initial points of its performance, so pupils understand what the basic movements are and how to perform them. It is proved that mistakes and failures are often caused not by little number of exercise, but by not giving a proper PAB. When a pupil is not given the full system of instructions about the action to be performed, he has to act by trial and error. But if a proper PAB is given beforehand, there are fewer mistakes and the action is mastered more successfully. Stage 2 (equals to Stage 1 in physiological theories). The aim is to give the basic of a physical action technique and to teach a pupil to perform an action roughly at least. On this stage a pupil tries to perform an action for the first time. This stage is characterized by broad irradiation of excitation to the nerve centers while the internal inhibition is retarded and processes of the central nervous system are random. Irradiation of excitation causes generalization of responses and excessive fixity of motor system, for irrelevant muscle groups are being involved. The physiological situation is added to psychological one. Emotional reaction to novelty, excessive activation of conation, diffidence and sometimes anxiety are intrinsic to this stage. This causes shielding motor responses and constrained movements. The action performance control is realized with the help of visual and acoustic analyzers. But muscular sensations are weakly differentiated. That’s why interoceptive (inner) control on this stage is on the background compared to exteroceptive (external) one. So, the idea about a physical action is formed with the help of external feedback, which means information a person gets while performing an action and analyzing the results. Stage 3 (equals to Stage 2 in physiological theories). The aim is to form a “comprehensive motional skill” (Zh.K. Holodov, V.S. Kuznetsov, 2009). On this stage the excitation is concentrated in the nerves centers which are essential while performing a physical action. Internal inhibition is being developed that helps to more precise differentiate the signals about an action especially from proprioreceptors. This time exteroceptive control (“external” feedback) is equal to proprioceptive (interoceptive) control (“inner” feedback). The proper performance of the physical actions, ensured by the physiological changes stated above, helps to remove diffidence and anxiety. Shielding motor responses interfering with proper physical action performing are gradually being removed as well. Motional dynamic stereotype is starting to be formed. According to E.P. Ilyin (2009), motional dynamic stereotype is a system of movements or behavioral habits which are being performed in a certain sequence and are combined into a chain where the end of a previous action is the beginning of the following one. Dynamic stereotype lets repeat a movement technically correctly within the same conditions and reasonably change it if the conditions vary (running on various kinds of surface, wrestling with various contestants and so on). When the motional dynamic stereotype is formed, a pupil understands ways of performing an action, but his attention is intense and he/she is concentrated mostly on movements. If his/her attention is turned to the surrounding situation or classmates, the performance quality gets worse. Stage 4 (equals to Stage 3 in physiological theories). The aim is to transfer a motional skill to a technique. This stage is characterized by stabilization, high rank coordination and automatic movement performance. The technique of a physical action is stable. The movement control is realized with the help of proprioceptive signals while visual feedback is left behind. On this stage a motional technique, or partially automatic physical action in psychology, is being developed. It means that when developing a motional action, the role of its conscious control is not being reduced: the movement is controlled when attention is moderately concentrated and sometimes distracted, or when attention is concentrated casually (quick movement control without enough understanding). E.P. Ilyin (1983) is concerned that the opinion proving that a technique is realized without conscious participation and that technique managing is transferred from the cortex to subcortex, is not true. Of course, some movements are performed like inborn reflexes (for example, withdrawing a hand when it is hurt) and some simple physical actions are performed at the subconscious level. But A.N. Krestovnikov believes that a compound physical action is an intricate chain conditioned proprioceptive reflex and is controlled by the conscious which has the following functions: a) launching (an adequate action programme is chosen) b) monitoring; c) estimating. So, a footballer estimates the situation and consciously chooses a pass to use: low or high, long or short, cross or diagonal, etc. Depending on conditions and goals of an action that has become a technique, the studied movements being its part can be performed automatically or not, while the action on the whole is conscious because a pupil understands the aim, goals, means and results of the performance. This means that automatic performance in physical education and sports is minor, though very important. What are the features of a motional technique? A.T. Puni, a famous Russian psychologist, tried to answer this question and single some of them out (table 1). Table 1 Features of a motional technique (A.T. Puni, 1978) On the character of an action Physiologically On peculiarities of perception performance Forming of a motional dynamic Conscious directed to conditions Integrity of an action. stereotype with the help of the and quality of performance. Absence of excessive muscle first and second signal systems Conscious control and regulation tension and unnecessary working together. Automatic of an action on the base of movement. Lightness. Efforts performance. muscular feeling, specialized and time economy. Exactness senses of perception, recepts and stability of a movement and speech and thought structure.. processes. Attention concentrated on initial points of movement performance and final efforts. Gradualness and irregularity of a technique developing (curves of exercise) Gradualness of a motional technique development is reflected in its phases: a technique occurs thanks to a range of partial transformations during a relatively long time. Irregularity of its developing is expressed in various quality growth on different stages. There are various curves of exercise, but in psychology they can be divided into two types (pic. 1): 1) curves with negative acceleration (at first a technique is developed quickly but then its developing becomes slower and slower), 2) curves with positive acceleration (at first a technique is developed slowly but then its developing becomes quicker and quicker). Quality growth of a technique Plateau Negative acceleration Positive acceleration Repeated trials of a physical action performance Pic. 1. Phases of technique developing According to professor L. B. Itelson, the first type of curves is intrinsic to the process when a pupil mostly learns by trial and error. The second type of curves is intrinsic to the process when a pupil performs well thanks to good understanding. However, researches in sports psychology prove that people with flexible nerve processes and high excitation master motional techniques the quickest: balancing position (I.V. Kuznetsov, 1970; V.M. Shadrin, 1978), bending and straightening the body while learning simultaneous one-step skiing step (V.P. Merlinkin, M.E. Bubnov, 1974). People with inert nerve processes master motional techniques slower, but then they reach the performance level of people with flexible nerve processes. So, we can say that the stated above curves of exercise depend on the main peculiarities of nervous system. It is proved that people with flexible nerve processes make a lot of corrective movements while mastering a technique, and this may explain why they learn by trial and error. People with inert nerve processes first try to understand the basic of the action and only then master it. Stage 5. The aim is to master high proficiency skills. A mastered motional technique must be variable and consistent with conditions in which a physical motion is to be performed. Variability is reached thanks to multiple repeats of a movement in various situations changing its kinematic, dynamic and rhythmic characteristics. Variability of situations can be expressed by the following: a) making conditions more difficult (room restriction, contrary weather, etc.) b) changes in a pupil’s physical and psychic state (tiredness, attention distraction, nervousness, other emotions) c) combination with other actions d) increasing of physical efforts and nervous tension This lets a sportsman learn to change details of a physical action in order to reach the result in various situations. Variability of a technique shows a sportsman’s professionalism. Therefore, the stated above characteristics of motional skills and techniques express both their peculiarities and correlation. According to L.P. Matveev (1991), correlation of motional skills and techniques is limited because a skill is the main condition of a technique mastering. A technique here is an automated skill. A technique may become a precondition for mastering a new, more difficult skill. Here is a scheme of a process of teaching physical actions to pupils on physical education lessons and teaching sportsmen: Motional skill Motional technique High proficiency motional skill Correction of psychological state of students majoring in “Sport Management” within the study process B. Usoltsev, G. Gorbunov, G. Ponomarev, M. Shanskov, Baltic State Technical University “Voenmekh” named after D. Ustinov, Russian State Pedagogical University named after A. Herzen, City of Saint-Petersburg Professional reliability of a future specialist is largely determined by personal psychological characteristics and mental abilities, developed with the use of targeted corrective influence. The effectiveness of students training can be assessed by the psychological results, i.e. mental changes that form during study-professional activity. Higher professional school estimates psychological results mostly by formation of professionally and socially significant qualities of a trained specialist which determine his/her professional competence and professional skills (A. Karavanov, 2004). Sport Management is a relatively new field ofstudy in our country. That’s why some its aspects as an educational and professional discipline in universities are not sufficiently developed (B. Usoltsev, M. Shan, 2009). University study is characterized by significant emotional and intellectual stress, hypokinesia and stressful situations that negatively affect students psychological and physiological state. Course has been worked out focused on uncovering the resource capabilities and creative potential of students for the aims of correction of students study-professional activities. For these aims control group (CG) and experimental (EG) group were formed, consisting of BSTU sport management students. Work with the EG used special methods of self-evaluation, psychological trainings and self-adjustment sessions. The course includes not only acquisition of knowledge and formation of useful life and career skills, but also relevant development, self-improvement of listeners within the training process. The course includes 10 classes, which were conducted by the author of this program G. Gorbunov. Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences, Professor. The most important topics of the course are: 1. From self-cognition to self-improvement. 2. Emotional-volitional regulation of behavior. 3. Psychology of success. 4. Mental overstrain - how to combat it. 5. How to keep calm and confidence in important situations, and others. Correction of psychological state of students majoring in “Sport Management” "by the developed course of psychological regulation, showed an established trend towards the improvement of students’ psychological condition. Introduction of such designs contributes to students; overcoming stressful situations in the university study process and help in solving crucial problems related to professional training and development of information resources needed for elaboration of the state standard on "Sport Management". Peculiarities of physical development of 4-6 year old children in the High North Svetlana Vadyuhina, FSI SPE “Northern College of Physical Culture and Sport”, city of Monchegorsk Body of a healthy human always functions in response to outward conditions. That’s why many body indicators of some northern dweller good adapted to extreme northern conditions distinguish from those living in moderate climate. In other words mid-latitude standard is not suitable for well adapted northern dwellers. They have their own standard reached after long adaptation to extreme northern conditions. Kolar polar area is one of the most challenging for living regions where physiological mechanisms tension may lead to disorders in growth processes and development of a child. Negative environmental factors are known t o have greater impact on children than adults (V. Bunak, 1941, Z. Rappoport, 1978, A. Purundzhan, 1990, V, Khrushchev, 1994). Moreover children adapted to cold climate more often have disassociation of indexes of growth and development – increase of several development indicators in particular related to tissues oxygen supply – cardio-vascular and respiratory systems, blood oxygen content – and decrease of growth pace – decline of anthropometric indicators, retention of pubescence. Already 3rd-4th generation of first newcomers from various Russian regions lives in the Kolar polar area. In our opinion there are certain factors contributing to rather quick adaptation and capable to pertly compensate for negative impact of the environment. One of these positive factors for children and adolescents is reasonable motor activity organization (A. Sukharev, 1968, 1972, Z. Rappoport, 1976, V. Khrushchev, 1994). In Murmansk Region schoolchildren physical development studies were carried out in 1937, 1947, 1952, 1957, 1964, 1970, 1974, 1982-84, 1990-92, 1997. Data on study of preschoolers is too various. A comprehensive study has not been conducted. That’s why there are no specific methods of preschoolers physical development. Having analyzed curriculum of preschool educational institutions (PEI) of the city of Monchegorsk of the Murmansk Region we have deduced that the majority of PEI’s have been using the typical program “Education in a kindergarten program” (1985) for carrying out physical education. Anyway it does not provide an opportunity to consider differences in level of children physical development and physical condition affected by negative outward conditions. The goal of our study is to determine the level of physical development and the most commonly encountered somatic types of preschoolers (4-6 years old) permanently living in the High North. The study has been conducted in PEI since 2006 till now covering 90 girls and 90 boys of 4-6 year old. The objectives of the study are: 1. To determine the level of physical development of 4-6 year old children living in a polar area, 2. To determine the most commonly encountered somatic types of preschoolers living in the High North. For addressing the first objective we have carried out anthropometric measurements of – height, weight, shoulder width, width of pelvis, circumferences of – thorax, shoulder, brachium, thigh and surae, distal epiphyses of shoulder, brachium, thigh and surae, rolls of fat of 4-6 year olds and compared them with indicators of children living in mid-latitude of Russia (T. Panasyuk, 2008). Significant differences are obvious in 5 year old girls by all indicator and in 4 and 6 years – by circumference. Insignificant differences in 4 and 6 years girls are noticed in height and weight. Boys have no insignificant differences only in weight. Physical development indexes have been calculated: Age Indexes Pinye 4 year old (n=30) girl boy 33.18889±0.538 33.633±0.958 5 year old (n=30) girl boy 36.305±0.881 38.75714±0.713 6 year old (n=30) girl boy 39.545±1.257 38.294±1.34 Ketle 1 0.165169±0.005 0.15936±0.004 0.164583±0.004 0.164775±0.0037 0.178817±0.0056 0.1811±0.007 Erisman 2686.986±66.77 2723.604±64.11 2862.975±54.199 2956.851±62.62 3168.488±93.95 3227.47±73.84 Somatotype have been defined in line with Heath-Carter scheme. 4 year old children have prevailingly endomesomorphic constitutional type; 5 year old girls – endomesomorphic, boys – ektomesomorphic, 6 year old – ektomesomorphic type. The study results let us conclude that: High North climate conditions influence growth and development of preschoolers. 4 year old girls in 16.6% (3 persons) have very weal development, in other cases – weak. Boys – 27.8% (5 persons) – very weak, other cases – weak. 5 year old: girls 66.67% and boys 85% - very weak, the rest – weak. 6 year old boys: 5.55% - good, 5.55% - weak, the rest – very weak; girls: 11% - weak, the rest – very weak. the most commonly encountered somatic types among the children studied are mesomorphic, endomesomorphic, ekzomesomorphic. References: 1. Лях В.И., Лапицкая Е.М. Мониторинг физического и моторного развития детей, подростков и молодежи Кольского Заполярья: Учеб. пособие. – М.:ИВФ РАО, 2008. – 47 с. 2. Панасюк Т.В. Антропологический мониторинг дошкольников: учебное пособие / Т.В.Панасюк, С.И. Изаак, Е.Н.Комиссарова/ под общ. ред. С.И. Изаак. – М.: Физическая культура, 2005. – 110 с. 3. Панасюк Т.В. Конституциональная принадлежность как основа прогноза роста и развития детей от 3 до 17 лет: диссертация на соискание ученой степени доктора биологических наук защищена 17 сентября, 2008г. 4. Хрущев В.Л. Здоровье человека на Севере: ( медицинская энциклопедия северянина)/ В.Л. Хрущев. – Новый Уренгой, 1994.-508с. Pilates in vocational schools as means of construction employees professional diseases prevention T. Verina, M. Shkurpit Southern Federal University, Pedagogical Institute, city of Rostov-on-Don Promotion of healthy life style among youth is an important component of healthy well-being nationwide. Health and education are interconnected and interdependent. Efficiency of educational process depends on health status of a pupil. A teacher should create conditions for students adaptation to educational environment, preservation and promotion of their health. Upon completing a PE course a young specialist is to reveal his/her own motivation to physical training, regular physical exercising for the aims of career longevity and professional diseases prevention. Our vocational school #7 of the city of Rostov-on-Don trains specialists for construction sphere. Construction-related occupation claims high demands to personal peculiarities and physical qualities of a specialist. These are physical endurance, quick motor response, good motion coordination, proper lower and upper limbs functioning, etc. Training of a construction specialist takes one year in our school. Scarce quantity of hours devoted to physical training within a curriculum is certainly not sufficient for ensuring comprehensive preparedness of a graduate for professional work. At the same time his/her individual physical training skills are not formed. The majority of students finish physical exercising upon receiving diplomas. Anyway this is just a starting point in person’s individual health saving activity. Skilled workmen poll results indicated that 10.1% of respondents do physical exercises in their free time and 2% in work time. What is more 67.1% of the polled are ready to get engaged in physical training, but cannot chose a kind of physical exercises for professional diseases prevention. Most typical diseases are: - Spinal diseases (degenerative disk diseases – 62.7%); - Those of visual analyzer (49.3%); - Varicosity (27.9%); - Nasal diseases (26.8%). They occur due to negative work positions, monotonous labor. Many hour work and hygienic norms neglecting lead to professional diseases. Having analyzed labor activity and professional diseases of construction workers we have made up a conclusion that one of preventive measures can be J. Pilates exercises complex. It is to assist prospective specialists not only in needed physical qualities development and professional diseases prevention but also in turning students to individual utilization of acquired skills in the future. That’s why we have undertaken to use this method in our vocational school as extracurricular and individual exercising. Pilates is an unique and diverse exercise complex involving physical and breathing exercises, which ay once tone up various muscle groups and relieve spinal load. At present it is considered a unique system exerting no negative impact on deformed spine. Repetitions of exercises are minimize, movements are smooth, weak muscles affected and trained. Pilates focuses on joint work of main body muscles. Training methods Pilates exerts the following positive impact: - Training deep muscles needed for body walk balance and healthy and flexible spine, - Affecting emotional state positively, calming nervous system, - Eliminating backache, other pains, correcting posture, easing muscle tension, - Improving oxygen metabolism, supporting immune system, preventing osteoporosis, - Not requiring expensive equipment. The principles of Pilates: 1. Relaxation. Exercising in relaxed manner, almost leisurely. Finishing exercises are used for muscle recovery. 2. Concentration. Concentrating on every movement. 3. Alignment. Watch correct body and limbs alignment. 4. Breathing. When breathing in Pilates muscles should always be in tension – “lateral breathing” – breath in into the lower part of breast. All exercises consider that correct breathing assists mobilizing specific muscles, strengthening. 5. Centering. Particular attention is given to strong abdominals. Transverse muscle of abdomen plays the key role. It lays deeper in abdomen and often neglected by other exercises. Before starting exercising and in order to mobilize transverse muscle of abdomen one should activate pelvic floor and underbelly at same time. 6. Fluidity. Movements are performed slowly in direction from the “strong center”. 7. Endurance. Toning up body deeper stabilizing muscles enables increase of endurance. Endurance is improved gradually. 8. Coordination. Coordinating movements and breathing. 9. Regular basis. At least three times a week. 10 reasons to use Pilates for preventing professional diseases: 1. Decrease of diseases risk. Various researches prove that physical activity significantly decreases risk of many illnesses, including diabetes, cardio-vascular diseases, cholesterol related diseases, heart attack, osteoporosis, arthritis, backache, breast cancer, etc. 2. Dignity. Sense of accomplishment appearing after active physical load is one of the most pleasant feelings of a human body. Physical exercising improve not only constitution but also self-esteem. 3. Fast weight reduction. Physical training regulate appetite within a day. 4. Improvement of immune protection. 5. Achieving peace of mind and emotional balance. Stress provokes a reaction in a body releasing hormone of cortisone, which increased concentration may affect health negatively. Physical exercising contribute to decreasing of cortisone and release hormones of “well-being” – serotonin, adrenalin, dopamine, endorphins, which produce feelings of joy, pleasure. 6. Abolition of insomnia. 7. Reenergizing. 8. Significant improvement of brain activity upon doing exercises aimed at stimulating cardiovascular system, according to 3-month Japanese survey. Canadian researches claim that regular exercising decreases risk of Alzheimer disease. 9. Great well-being. Regular exercising alternately compress and ease spinal disks thus keeping them flexible and elastic, spinal bones – healthy. 10. Incentive to communication and active life. Apart from exercising itself pilates is to give people going in for it additional impetus to communication in a gym. As the conclusion we recommend to use pilates at PE classes in vocational construction schools as well as to conduct extra-curricular pilates classes for prevention of professional diseases. Innovation activity in a municipal sports school Olga Vesnina, Headmaster, Municipal Educational Institution «Specialized Children and Adolescent Sports School of the Olympic Reserve №1» Yuri Shlykov, Docent, Department of Theory and Methods of Physical Culture and Gymnastics, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, Candidate of Biological Sciences Protecting the health of the younger generation is of high importance for both the state and the society, because childhood is a critical period for forming the person’s physical and mental health and laying the foundations of his/her morality. One of the main principles of the state educational policy is declared to be “the humanistic character of education and top priority of human values, human life and health…” (Russian Federation Education Law, Art. 2). However, from year to year the statistics points to the gradual decline of the children’s average health level, which is caused to a considerable degree by economic and ecological deterioration. Poor health among children living in the Far North and regions with similar climate is also caused by the lack of iodine in the organism and ultraviolet starvation, which result in children’s lower physical development (height in particular) compared to other regions. A further reason for children’s health impairment is hypodynamia (which is organism’s dysfunction caused by the lack of motion activity). Indeed, researches demonstrate the fact that the majority of modern children suffer from what can be called “motion shortage”, i.e. during the day they move less than they should at their age, which has a negative influence on the skeleton and muscles, their respiratory, digestive and vascular systems. In this paper we would like to describe how we organize the innovation programs of a sports school concerning the introduction of additional physical training activities (such as gymnastics and aerobics) in the curriculum of pre-school educational institutions of our city. This will also enable us to follow the influence of physical exercises on the pre-school children’s health and the improvement of their level of physical development. One of the main tasks set to school teachers is to involve in sports all the children aged between 4 and 6 who attend pre-school educational institutions without splitting them into promising and not promising ones. The aim of the research is to justify the possibility of organizing activities focused on the improvement of the pre-school children’s health within the framework of children and youth sports schools. The represented research was conducted within the framework of the CYSS-1 (Children and Youth Sports School) of Petrozavodsk, which specializes on the three following sports: artistic gymnastics (men and women), rhythmic gymnastics and aerobics. The experimental work in the school is aimed at involving all the children of the city aged between four and six in regular exercising (three times a week) without splitting them into promising and not promising ones. It has become possible to conduct this research thanks to the fact that the CYSS # 1 possesses highly qualified staff (which includes 70 coaches and teachers) and a network of pre-school educational institutions where the officials are concerned with the children’s health and are able to provide with the necessary equipment. Gymnastics and aerobics coaches introduce the children to regular sports activities and stimulate the young generation’s need for the healthy lifestyle. The children involved in this program which lasts three years are stronger, healthier and familiar with the basics of physical education, gymnastics and aerobics when they come to school. Their carriage, the culture of movement and familiarity with elementary sports vocabulary distinguishes them from those who for some reasons were not able to attend pre-school educational institutions that cooperate with the CYSS’s specialists. Those children who demonstrated particular aptitude for gymnastics continued attending training sessions in the CYSS # 1. In order to organize such experimental research we envisaged the following stages: 4. To choose the trend of experimental research according to the city’s health-improving program and corresponding with the social demand. 5. To outline the schedule of the experiment. 6. To create the necessary conditions for carrying out the experiment. Terms and stages of the experiment. After three years of attending sports classes at the pre-school educational institution a group of children with evident physical abilities continue advanced training in artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastics and aerobics in the CYSS # 1. The rest of the children are given recommendations on further physical development. The experiment is planned for the period of 12 years (which is the complete period of studying in the CYSS) and is divided into three phases four ears each. After each year of studies a deep analysis is done at each stage and if necessary appropriate adjustments are made to the further work. After each stage the results of the work are assessed. Stages of the experiment Academic years Yrs 1994Yrs 1995Yrs 19961995 1996 1997 Stage I Yrs 19931994 The minimum number of pre-school educational institutions included into the experiment 20 24 28 32 Stage II Yrs 19981999 Yrs 19992000 Yrs 20002001 Yrs 20012002 The minimum number of pre-school educational institutions included into the experiment 40 44 48 52 III этап Yrs 20022003 Yrs 20032004 Yrs 20042005 Yrs 20052006 The minimum number of pre-school educational institutions included into the experiment 54 58 62 66 Yrs 19971998 36 The experimental program is realized by teachers and coaches who share the main ideas of the experiment and who possess high professional qualifications. Other professionals are also welcome to take part in the experiment. In order to transform pedagogical activity into research one we have outlined the following plan: № 1 Activities Preparation of a list of bibliography to work over within the experiment. Yrs of development 1 2 3 + 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Introduction of innovative and advanced technologies into the discussion practice during pedagogical councils on the topic. Working out a range of topics for individual research based on the individual resource of the teachers. Selecting the topics for the research (on the individual and group basics). Organizing individual work with teachers in order to provide help in the development of innovation process in the department. Bringing the professional skills of the teachers to the level of research work founded on experiment. During visits to trainings defining a group of creative teachers in order to involve them in experimental activities. Developing and putting into practice science-based consulting. Working out the system of diagnostics in order to support experimental and methodological work. Organizing a workshop “The Basics of Pedagogic Technologies”. + + + + + + + + + Doing gymnastics in all its forms (such as basic, rhythmic, artistic and applied ones) including the elements of artistic gymnastics and acrobatics was considered top priority. Forms and methods of work with children. Classes in kindergartens are held to music accompaniment. They select pieces of music which determine the training pace. Music shouldn’t be monotonous and therefore tiresome for the children’s nervous system, it should fit their age and the level of aesthetic development. Positive emotions arising during the practice intensify their physiological effect. Playing active games is given special attention during these practices. Each year we plan to organize group competitions: “New Year’s Cup”, “The 8 th of March”, “The Sunlight Spot”. At the end of each academic year we hold the traditional Gymnastics Festival called “The Spring Swallows” among the city’s kindergartens. The festival program (worked out by Olga Vesnina) includes elements of gymnastics, choreography and acrobatics. Each kindergarten brings forward a combined team which shows group gymnastics exercises to music accompaniment. This year 400 children from 50 kindergartens took part in the 9th Festival. In the course of the experimental work, during the past nine years, each year changes and adjustments were introduced into the program. The decisions on the improvements of the program were made collectively during methodological and coaches’ councils. The research work conducted by the experimental section of the school showed the following: the morbidity level concerning respiratory diseases dropped sharply (by 30-40%), and the level of the children’s physical development increased by 50-60% compared to the beginning of the academic year. This research has been conducted during nine years with experimental groups of 600 – 800 children each year. Conclusion: 1. Organizing similar innovative activity is possible and expedient. We can see that as the result of such activity the increase of the level of physical development led to the decrease in the rate of respiratory diseases. 2. We recommend other sports schools in the city and the republic to make use of our organizational experience in involving large groups of pre-school children in additional physical activities. 3. We consider it possible to extend this experience and introduce three additional lessons of physical education in the secondary school curriculum as well as in kindergartens. This will be the responsibility of sports schools. This will be a contribution of sports schools to improving the health of all the children, not just promising ones. The experimental work proved its usefulness, and since 2007 it has been transformed into a permanent scheme of teaching children the basics of gymnastics. Today the sports school has been granted the status of the School of Olympic reserve (SCYSSOR № 1). Working with pre-school children enables the sports school to carry out quality selection of children, a large part of who continue training in the sports school and reach the established standards of Master of Sports of Russia (35 members). Alexey and Alexander Balandins can serve as a vivid example. Alexander is the member of the national Russian sports team and the candidate to the Olympic national team. The results of such innovative activity confirm that the line of working with pre-school children was properly chosen by the CYSS’s # 1 specialists. Health Education A.Voronov, O.Teselkina, Faculty of Physical Culture, Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, city of Petrozavodsk At present deterioration of nation health status is a critical problem in Russia, it demands drastic cooperative efforts of medics, psychologists, teachers and all citizens of the country. The greatest concern is the health of the younger generation who will determine the quality of labor and social resources of the country in the future. The President of Russia D. Medvedev emphasized this issue in his Address to the Federal Assembly saying that “Children spend the greater part of a day at school, so teachers have to deal with the questions of pupils health as well. I believe that if priority of healthy lifestyle is fulfilled at school, this is to contribute to successful modernization of the health care system in general”. In this regard constituting a value of healthy lifestyle shared by the younger generation is put in the center of the dispute. This goal can be achieved by utilization of new efficient methods, technologies and techniques within educational process. Anyway these novelties require alteration of a curriculum. Health Education as a separate subject should cover all schoolchildren of all ages. For example, in Finland Health Education is taught in 1-6 grades as a part of other disciplines, in 7-9 grades – as a separate subject once a week, and also in senior school. Introduction of this new discipline in 2001 resulted in improvement of health status of children and adolescents of Finland. In this article we want to illustrate the experience of promotion of healthy lifestyle in school of Karelia based on Finnish expertise. Health Education is divided into 3 parts: 1. General health improvement and knowledge about health, 2. Development of social and everyday skills, 3. Learning life safety skills. A pattern scheme of Health Education is presented below: Primary school Secondary school Senior school I stage II stage III stage 1-4 grades 5-6 grades 7-9 grades 10-11 grades Health as a central As a part of Biology, As a separate subject As a separate subject element of Nature Geography, Chemistry, Study Physics The goal of the project “Promotion of healthy lifestyle in schools of the Republic of Karelia” which started in 2006 has been elaboration and introduction of valid methods for Karelian schoolchildren health improvement jointly by Karelian and Finnish specialists on the basis of Finnish experience which has shown good results. The first phase of the program “Promotion of healthy lifestyle in schools of the Republic of Karelia” is creation of a school health team involving project participants, PE, biology, geography teachers, psychologists, parents and pupils and a representative of a school administration. Participation of a school principal in a health team adds more authority to its decisions. A health group may also attract experts from the outside – employees of medical and youth organizations, etc. A perfect health group has to know all ways of promotion healthy lifestyle, i.e. guidance, planning, information transfer, education, marketing and publishing, networking, influencing activity principles and behavior models. Forms of promotion of the program is very diverse: in 1-4 grades health education is integrated into Nature Studies, in 5-6 grades – Biology, Geography, Physics, Chemistry. Central topic of Health Education are growth and development, everyday well-being, society and culture. A memo for schoolchildren has been prepared titled “having learnt how to take care of oneself you will create your own prosperous, promising and joyful future and make your dreams a reality”. Students of 7-9 grades need a comprehensive package of knowledge on leading healthy lifestyle. So for reaching this category of schoolchildren we have utilized Finnish study books “Health Education” for 7-9 grades. We have begun to prepare these books with the support of the Ministry of Education of the Republic of Karelia. Finnish study books “Health Education” have been translated to Russian and adapted by Karleian experts S. Goranskaya, N. Predtechenskaya, M. Burkin, Y. Shlykov, N. Dmitryakova, N. Listkov, O. Gavrilova, N. Skibina. A book for teacher has been also prepared. Three study books and a teacher book constitute a uniform package of knowledge on leading healthy lifestyle for students of 7-9 grades. The book series tracks physical, mental and social development of a teenager. While choosing material for the books we were taking into consideration the level of development, skills and interests of a pupil, as well as rich pedagogical expertise of Karelian and Finnish specialists. 7th grade study book can be called “Basics of Healthy Life”. It consists of 6 chapters and describes changes a teenager notices in him/herself and others. The book speculates on the points of nutrition, physical culture and leisure, as well as personal hygiene. It give introduction to most wide-spread illnesses and infectious diseases. The issues of smoking and drugs are argued. The book provides relevant information on factors influencing a teenager’s personal choice. 8th grade study book “Basics of Growth and Development” teaches to understand problems arising in the awkward age. The book consists of 5 chapters. The starting figure is a teenager him/herself: changes of the awkward age, development of self-comprehension and emotional storm. Disappointment and problems are a part of life but having overcome them a person gets strength reserves for the whole life. Discussion of interpersonal relations begins within a family, then proceeds to friendship and sympathy. Development of sexuality is an important part of a teenager’s life. So provision of relevant knowledge on prevention of unwanted pregnancies and sexually transmitted diseases is essential. 9th grade study book “Basics of Survival” provides some vital advice. Chapter on proper nutrition tells about choice of a diet, weight control, and useful products. Healthy balanced diets help prevent many diseases. Smoking cessation can be relevant already for teenagers. Discussion of drugs and alcohol issues, psychotropic substances illustrates consequences of their use. First aid skills are also described. A teenager is inspired to consider not only his/her health but well-being of the whole society, role of mass media in influencing healthy behavior and health-related ethical problems. In conclusion of the book its authors speculate on the issue of strategic health reserve and its impact on the whole future life. Teacher book provides a comprehensive and ample material for everyday practice. Teaching should become an example of interconnection of a teacher and a pupil focused on challenges of study and life. 7th grade study book and teacher book have already been finalized and issued on CDs. In prospects we plan introduction of the subject in pilot schools (Schools #39, #42, #46, #48, Lyceums #1 and #40) which to begin teaching Health Education in 7th grade in annual amount of 35 hours (allocated from the school component) in 2010 study year. All teachers to be engaged in this activity have completed advanced training in the field at the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy in amount of 36 hours. In Finland Health Education is considered to be a school subject of the utmost importance. The result of its introduction is improvement of health of children and teenagers. The subject is demanding, but a patient understanding pupils teacher is to be acknowledged. We believe that healthy lifestyle science and series of these books will be successful in Karelia. Thus our reward will be health of our children. In conclusion it should be pointed out that we have taken only first steps in implementation of the project on creation of all the needed materials and facilities for conduct of schoolchildren health improvement program. Adapted physical culture for schoolchildren N. Zaitseva The Center of phychologic-medical-social support, Frunzensky district of Saint-Petersburg, city of Saint-Petersurg The “Adapted physical culture for schoolchildren” program includes practical, extra-curricular activities focused on schoolchildren who fall into special medical group due to their health status. Relevance of the program. Motor activity is one of the basic factors of health of a human being. Any types of movements corresponding to the physiological capabilities of a child always bear therapeutic impact. The process of study at school applies extra load on a child body. Pupils are less physically active, spend more time in sitting position. Hence a child experiences the deficit of muscular activity and increase of static tension. Moreover a pupil should also acquire and process different information what leads to eye strain (reading, writing, drawing, etc). These factors predetermine development of health deviations: fault of posture, visual disorders, elevation of arterial pressure, overweight, what in its turn predispose to different illnesses of cardio-vascular and respiratory systems, metabolic disorders, etc. In accordance with the Regulations on medical control of physical education all pupils are devided into several medical groups by their health status. Schoolchildren with major continuing or temporary health disabilities, whose load of physical activity should be significantly reduced, fall into special medical group. The rotation of physical exercises and brain work ensure quick recovery of labor capacity. This is particular important for schoolchildren of special medical group as they experience undue fatigability. Nowadays when not so many pupils belong to the first group of health, and 40% of pupils suffer from scoliosis and 90% - from fault in posture, the “Adapted physical culture for schoolchildren” program is highly relevant. The program is an extra-curricular form of adapted physical activity, and carried out in form of sectional training. The recommendation is to divide children of special medical group into two sub-groups depending on severity and type of illness for the aims of approaching more differentially to assigning modes of motor activities to these pupils. The first sub-group consists of pupils with reversible heath deviations impaired by different diseases. Basic diseases of schoolchildren are fault if posture, weak foot, 1 and 2 degree obesity, decrement in visual acuity, initial and noncomplicated forms of chronic bronchitis. The classes should be conducted by specialists with higher and secondary vocational education on adapted physical culture or teachers who completed advanced training in this field. The second sub-group consists of schoolchildren with organic irreversible changes of organs and systems (cardio-vascular, urinary and liver involvements, superstandard refraction with changes of fundus of eye, etc). Such pupils are registered in a medical institution and only a person with higher medical education can be a PE teacher for such a child. Sectional training of adapted physical culture are conducted twice a week for 45 minutes each class during the whole study year. The groups are formed according to the health status and age of pupils. The groups: #1 (7-10 years old schoolchildren), #2 (11-14 years old schoolchildren), #3 (15-17 years old schoolchildren). The number of pupils per group is 10-15 children. The goal of the program is to teach and train children and teenagers health-improving and prophylactic exercises as well as to elevate a person’s commitment to regular individual physical training. The program objectives: 1. To establish pupils’ health, improve functional and adaptive capabilities of basal systems of organs, 2. To develop and improve basic physical qualities forming basic physical condition of a person, 3. To introduce pupils to basics of healthy lifestyle, principles of labor and leisure division system, sensible nutrition, and organizing individual health-improving physical training. Indications to physical exercises are diseases of musculoskeletal system, respiratory and water-salt metabolic disorders. The structure and content of the program. A pupil is admitted to adapted physical culture classes upon a medical certificate on absence of contradictions for adapted physical training. Functional measurements of the following figures determine the progress of the program: - Measurement of lumbar-spine mobility, - Measurement of body muscle power endurance. The measurements are carried out three times a year for watching the dynamic changes. The components of the program. Physical exercises are basic and specific means of physical development, particular type of motor activity through which targeted impact on a pupil is exerted. 1. combined developing exercises (with accessories, with accessories, in motion, with a ball), 2. breathing exercises 3. eye exercises (by Y. Mendel, T. Avetisov), 4. exercise therapy: a. exercises for correct posture b. exercises for prophylactic and treatment of flat foot c. exercises on scoliosis of 1,2 degree d. exercises on obesity of 1, 2 degree e. exercises on chronic bronchitis. 5. “Health path” special exercises in a fitness gym (individual approach, limitations of load, special exercise equipment). 6. Active games for sub-group #1. Active games are introduced into the program for the aims of diversification of classes and helping pupils in overcoming their diffidence and constrain in motor activity. The achieved results. The “Adapted physical culture for schoolchildren” program has received approval in The Center of phychologic-medical-social support of Frunzensky district of Saint-Petersburg. In 2007/2008 study year 63 schoolchildren from 7 to 17 years old (6 groups) participated in the program. By the end of the study year the majority of pupils would have experienced improvement in posture, by measurements of muscle power endurance, decrease in morbidity rate. In 2008/2009 study year already 130 pupils participated in the program (10 groups). According to the acquired results 70% of them improved their measurement indicators, and on 50% (by normative data) they improved lumbar-spine mobility and muscle power endurance. In 2009/2010 study year already 140 pupils participated in the program (12 groups). According to functional study out of 127 persons, 45 pupils improved their indicators in lumbar-spine mobility (35%), 75 pupils – in muscle power endurance (60%). The acquired data shows the dynamic of progress and significant improvement in musculoskeletal system status. Summarizing, the “Adapted physical culture for schoolchildren” program is successfully implemented in the Center of phychologic-medical-social support of Frunzensky district of Saint-Petersburg for schoolchildren of special medical group for 3 years (more than 100 pupils annually). Improvement of posture is achieved as a result of physical exercises; muscle power endurance is 70% higher. All these features assist to rehabilitation of a child and speed up his/her transfer to preparatory and main groups. Concept of the center of innovative sports and health-improving technologies as means of Kuzbass mass sports movement promotion R. Zhukov, A. Sapego, E. Budanova Kemerovo State University, city of Kemerovo Nowadays innovations are necessary to be a success in a competition. Innovations are a great driving force, making progressive transformations in all spheres of society including education, physical training and sports. The problem of the workforce’s health protection and promotion is actual for Kuzbas, as restoration and development of industrial productions cause inevitable growth in number of workrelated diseases. Corporate physical health-improving programs influence each employee of the company positively because a person participating in the program feels that the company cares for his/her health and lifestyle. It is significant to develop and strengthen motivation for self-education and self-improvement through physical training and sports. Innovative processes get special value in elite sport as the retrospective analysis of preparation and participation of top world athletes in Olympic, world, European and other large competitions show that modern record achievements in sports are an end result of cumulative intellectual and physical energy of a wide range of experts, materialized in the training process. Intellectualization of sports training is the central and dominating factor of sport achievement in modern system of sportsmen preparation. Sport became sphere of high technologies application. It has its own secrets and methods of information analysis, specific scientific and technical potential, its own methodological role of such integrated sciences, as cybernetics, theory of systems and theory of information. In these conditions the problem of innovative technologies introduction in Russian physical training and sports becomes extremely important as its solution will allow to more effectively use various sources of financing, including state and commercial, and also will promote quality improvement of the services in physical training and sports. Nowadays the Moscow Center of innovative sports technologies of Moscow Department of physical training and sports is solving problems of elite sports, but innovative physical health-improving directions for people of different age needs further studying as well. We think that the Center of innovative sports and health-improving technologies should solve the following problems: 1. Introducing of innovative technologies to the physical sports branch of the region, strengthening of its innovative infrastructure, increasing of scientifically-innovative activity financing at the expense of economic contracts performance and participation in federal and regional scientific programs; 2. Modernisation and updating of educational and scientific laboratory base of the Faculty of physical training and sports at the Kemerovo State University at the expense of opening of Laboratory of medical and biologic problems of physical training and sports and realisation of research activity using available instruments and laboratory equipment; 3. Working out of the most effective methods and programs for training of sportsmen specialising in various kinds of sports; 4. Functional testing in elite sports, scientific support of leading sport teams and sportsmen of individual kinds of sports; 5. Monitoring of health of pupils, students and teachers of educational institutions, examination of employees’, as well as fitness clubs and other health-improving institutions visitors’, body functional capabilities; 6. Performance of applied researches in physical training and sports sphere, providing employees, students and post-graduate students of the Faculty of physical training and sports with work on scientific and computer equipment available in the laboratory. It is supposed that on the basis of the Centre modern innovative technologies will be developed. Principal kinds of the Center’s activity are as follows: - participation in developing and realisation of the long- and medium-term city, regional and federal target programs directed on development of physical training and sports; - development and realisation of methodology of training process organisation, as well as realisation of methodical management of the processes of organisation and carrying out of competitions at various levels; - methodical supplying of sports-oriented additional education institutions; - studying and analysing of sportsmen’s professional skills growth dynamics, and development of methodical recommendations on improvement of forms and methods of training process organisation; - organisation and coordination of work of complex scientific groups in various kinds of sports, and support of complex scientific groups activity; - organisation of scientific-methods and biomedical supply of sportsmen and sport teams training; - consulting, research, and scientific-methods support of organisation of city sports-entertainment events, inspections, competitions, etc.; - development and realisation of complex target, investment, charitable and other programs directed on solving of social problems in physical training and sports, and carrying out of a complex of practical measures on analysis and their support; - developing of complex regulatory framework to insure qualitative functioning of the region's sports organisations; - participation in accreditation of athletic sports organisations; - control of implementation of the current physical training and sports legislation requirements while rendering of athletic health-improving and sports services; - organisation and carrying out of scientific-methods seminars, conferences, exhibitions and lectures on sports and athletic health-improving subjects; - assistance in establishment and development of direct communication between sport organisations, federations and sport clubs of the region with the similar federal and international organisations; - experts of the Centre can consult on preparation of course and graduation papers, scientific works and theses, as well as select information materials on various physical training and sports subjects. Stages of the project realisation should include a system of interconnected actions. So, at the first stage it is supposed to do the following: 1. Analysis of the problem under study status; 2. Analitycal review of the problem under study; 3. Setting up of the laboratory of biomedical physical training and sports problems, realisation of research activity on available equipment; 4. Functional testing in elite sports, scientific support of top sport teams and athletes in individual kinds of sports; 5. Consulting, research, and scientific-methods support of organisation of sports-entertainment events, inspections, competitions, etc.; 6. Analysis of training methodic and educational work status in additional education sport institutions and athletic sports organisations, working out of actions to increase its efficiency. The second stage implies: 1. Monitoring of health of pupils, students and teachers of educational institutions, examination of employees’, as well as fitness clubs and other health-improving institutions visitors’, body functional capabilities; 2. Performance of applied researches in physical training and sports sphere; 3. Participation in accreditation of athletic sports organisations; 4. Studying and analysing of sportsmen’s professional skills growth dynamics, and development of methodical recommendations on improvement of forms and methods of training process organisation; 5. Working out of methodic and information materials, reviewing of training methodic documentation, and other didactic materials; 6. Generalisation and analysis of the results of experimental work of additional education sport institutions, generalisation and distribution of the most productive experience of heads and experts of athletic sports institutions; 7. Organisation and working out of the necessary documentation on carrying out of sports competitions, exhibitions, etc.; 8. Updating of scientific-methodics support of training process. 9. Working out of long-term plans on manuals edition and methodic materials, selection of their authors, giving assistance to them; 10. Reception and distribution of the information on high technologies of training and education; 11. Control over training methodic work planning and training of physical culture and sports experts. Suggesting opening, changing and evaluating of sports organisations and their divisions' work; The third stage implies: 1. Organisation and coordination of complex scientific groups' work in various kinds of sports, as well as support of their activity; 2. Organisation of scientific-methods and biomedical supply of sportsmen and sport teams training; 3. Participation in working out and realisation of the complex target, investment, charitable and other programs directed on the decision of social problems in sphere of physical training and sports, and also carrying out of a complex of practical measures under the analysis and their support; 4. Participating in development of complex regulatory framework to insure qualitative functioning of the city's sports organisations; 5. Control of implementation of the current physical training and sports legislation requirements while rendering of athletic health-improving and sports services; 6. Organisation and carrying out of scientific sports seminars, sports conferences, exhibitions, lectures etc.; 7. Assistance in establishment and development of direct communication between sport organisations, federations and sport clubs of the city with the similar federal and international organisations; 8. Insuring participating of pupils, students and employees of educational institutions of professional training and members of their families in regular athletic health-improving classes; 9. Formation of scientific knowledge about health, increase of motivation for a healthy lifestyle, promotion of athletic health-improving technologies among pupils of educational institutions of professional training and students of high schools; 10. Stimulation of innovative technologies developing, means and methods of health-improving physical training and sports in solving of problems of social and economic development of society. Promotion of progressive ideas in health improving field, development of a person's culture. We believe that the practical importance of creation of the Center of innovative sports and healthimproving technologies will be expressed in reduction of budget expenses thanks to active promotion of a healthy lifestyle, creation of health-improving activity conditions; insuring of people's participation in regular health-improving classes; promotion of athletic health-improving technologies; creation of objective conditions promoting activization of athletic health-improving work in Kuzbass, etc. The project of development of the Center of innovative sports and health-improving technologies is honored by the letter of appreciation of Kemerovo Administration for participation in the competition "Best city innovative project". Role of the “Physical culture at school” journal in schoolchildren physical education E. Zhukunov Chief editor,“Physical culture at school” journal, Honored worker of culture of the Russian Federation, Member of the Journalists Union of the Russian Federation, Master of sports of the USSR First of all, I’m happy to be in Petrozavodsk again. Close cooperation between the journal and educators of Karelia started a long time ago, since the first All-Russia contest “Master of pedagogical work” in Karelian Kostomuksha, when Gekken was a Minister of education and his deputy was Sinitsina who played an important role in development of school physical culture. Secondly, the present congress takes together representatives of the majority of Russian regions and our communication, business and friendly meetings will by far make benefit to work of our journal and in its turn it will help l Russian pedagogues. Now I’d like to talk about some critical issues of the current system of Russian education, of course, mostly about school physical education and its coverage in our journal. During the last decades there have been a lot of education system reforms that are actually now called “modernization”. And our journal always tries to respond to all these novelties that both have already been accomplished, shaped or abandoned (as, for example, transition to 12-year education, however now it seems to be helpful in decrease of academic load within curricula and in saving pedagogical staff in schools) and have recently appeared by problematic, round-up, theoretical and practical articles. Successful solving of the tasks of school physical education (I remind that our journal is entitled as “Physical culture at school”)is possible only with complex application of P.E. lessons, health and fitness activities during a school day and extracurricular and out-of-school forms of physical education, certainly with necessary facilities and adequate wage for school teachers. During the period of life of the journal, that is 52 years, we have boon discussing possible solutions of these problems. Task work usually starts with syllabus. First, as you know, there was a common syllabus, the there appeared a lot of them, and now there are only two – by V. Lyaha and by A. Matveev. Previously we used to publish in the journal all new syllabi. Now we can’t do it, however the authors agree. But offices publishing these syllabi make copyright claims for reprinting these materials and we have no funds for that purpose. Federal Expert Service doesn’t provide us with the syllabi. But meeting the wishes of school teachers head of physical culture office of Teachers Advanced Training Institution of Kurgan region, candidate of biological science E. Abramov told the journal how to use approved and recommended syllabi, how to adopt them to local opportunities, how to create allowed author syllabi based on them meeting requirements of the State standard. The journal regularly writes about physical culture lessons and its types – theoretical, instructional and methodological, practical and of different purposes – teaching and training, health improving, educational, as well as about all parts of syllabi. In this work are oriented not to the experience og several privileged schools of Moscow, Saint-Petersburg or Surgut, but to the experience of ordinary city and rural schools. In general our writing team usually represents all regions of the country. For example, issue 6 that will be published in September, 2010, is made by 21 authors, only 2 of them are from Moscow, 18 people are from other regions of Russia and 1 person is from Belarus. The articles are devoted to motor education and improvement of physical qualities, development of interests and needs in physical culture, and building-up a system of knowledge about physical culture. We put our attention as on learning results of a pupils as on his-her socialization progress. We regularly write about theoretical issues (for example, articles of V.Lyaha, a doctor of pedagogical science about different theories of physical advancement, article of candidate of pedagogical science V. Karpushin from Saint-Petersburg “Problems of training” in issues 1-3 of 2010 and his counterpart V. Shaposhnikova from former Institution of physical culture n.a. Lesgaft (her latest article was published in issue 2 in 2010). Of course, there are a lot of other theoretical and truly scientific articles. Each issue of the journal includes a lot of articles on all major parts of syllabi: track-and-field, gymnastics and acrobatics, skiing, sport games and on improvement of physical qualities. Obviously, we should emphasize ones on track-and-field - cycle of articles by winner of the All-Russia contest “Master of pedagogical science”, well-known pedagogue from city of Kimra G. Fokin “Lessons of track-and-field” (by grades) and articles ”Zolushka” or “Koroleva” by recent school teacher V. Kucaev (on teaching different field-and-track exercises). Both series proceed, but we are waiting for some new articles: on gymnastic – articles by spouses Povalyaeves, pedagogues from Samara “About lessons of gymnastic”, multidirectional materials by candidate of pedagogical science M. Gorbachev from Yaroslavl and by R. Kuchkildin and E. Kuchkildin; on sport games – articles “Teaching basketball” and “Basketball secrets” by V. Dihtyarev and B. Torkunov, “Volleyball lessons ” by N. Trutneva, “Preparing of volleyball players via action games” by I. Karceva. And a lot of articles are in stock. But we experience lack of attention to handball and football, so we are waiting for your articles on the issues. One of the contemporary innovations is profile training. In our journal we published articles of V. Lukyanenko and I. Latypova that explained the meaning of military-sporting profile and showed how it could be enlarged and improved. But for now this profile has not stricken roots yet. Many reasons of that are figured out in the article “About profile orientation of high school children” by S. Sokolova. Unified state examination on P.E. is not likely to be introduced. But testing is being applied widely, for example, testing of theoretical knowledge at the All-Russia Olympiad on our subject. The latest article on that topic was published in issue 3 for the year 2010 (the authors are V. Balashov and N. Chesnokov). A responsible part of the work on physical education at school is examination of physical fitness of schoolchildren. Previously we considered this topic. Now we turned our attention back to this issue. We will publish articles “Basis of monitoring of physical fitness of schoolchildren” and “Information support of physical education at school” by doctor of pedagogical science L. Semenov. One of the modern requirements is to attract schoolchildren to P.E. lessons, to interest them with new content as well by including of elements of aerobics, martial arts, Indian yoga, dance exercises, table tennis, etc. All it was covered in the journal. For example, we had a very interesting series of the articles devoted to using of elements of tourism at lessons in primary school authored by T. Klimanova, a pedagogue from Kolomensk state pedagogical university. We also regularly publish articles on content, different fulfillment of the third lesson of P.E. They were devoted to health improving third lessons (2007 – J. Kopylov and co-authors, Moscow), judo lessons (2008 – V. Kuznecov, Moscow), lessons with prior use of action games (M. Ishmuhametov). In issue 3 of the current year we started publishing articles of M. Ishmuhametov “Breathing exercises and selfmassage at the third lesson”. The most important requirement of the contemporary world is improvement of schoolchildren’s health. We have articles on that topic almost in every issue of the journal. Some articles are theoretical (for example “Medical and pedagogical control in an educational institution” and “Health and fitness activity at lessons” by O. Vodyanickaya, “Management of children vacation in a school camp - hygienic requirements” by M. Stepanova and M. Voronova), the others are based on work experience. They are published in columns devoted to educational work, school-day activity, out-of-school activity. Herewith we never call a P.E. teacher as a teacher of health, as against the officials and journalists do, because it doesn’t fit the truth, his/her official status and opportunities. And this opinion of our editorial staff gets in line with the documents of the World Organization of Health declaring that among factors that influence children’s health motor physical activity accounts only for 15%, other factors are heredity, family living standards, common welfare, nutrition, level of health services, ecology, environment, all-school regime and of course genuine health care by a state. And a P.E. teacher cannot be responsible for all these elements. That’s why we pay great attention to the articles that tell about positive physical training activities of all school pedagogical staff or even the whole territories but not about some separate teachers, however, we also publish articles like that. The issue of schoolchildren health is closely linked with work with children of special medical group. This type of work is not being done satisfactory. And again the key problem is poor funding. P.E. teachers cannot undertake everything including work that has to be provided by medical establishments as it can lead to negative consequences for both pupils and teachers. This topic is coveren by articles of O. Kamishanova “Conduct of lessons for special medical group pupils”, E. Sazhneva “About adapted physical education”. The journal also reflects the questions of safety at P.E. lessons because it is another crucial factor of healthsaving of children. The latest articles on the issue are “Trauma prevention at the lessons” by V. Snigerev and “Accident prevention at P.E. lessons” by G. Bezmenov. Many different reforms affected rural schools and educational institutions for orphaned children and for children left without parental care. We always cover problems of physical education at rural schools but the issue of orphanages and boarding schools has been considered only for the last four years. Many authors touch upon this question – V. Chikishev “At a rural school”, V. Malinin “Physical activity of rural schoolchildren: results of the research”, etc. The major challenge set in the sphere of physical education of schoolchildren is to teach them to understand themselves, recognize and estimate state and real abilities of their bodies and to do physical exercises on their own and to have a healthy lifestyle. These all are promoted by physical condition monitoring, project activities, new forms of self-control, improvement of academic training, homework assignments for P.E. These topics are regularly covered in the journal. It’s very important to elevate pupils’ mind constantly, to develop, analyze, synthesize knowledge they get at school. Here in particular articles on intersubject communications and integrated lessons can be helpful. One of them will be published in issue #5 2010. Its authors are A. Voronov, A. Fedorov, E. Fedorova and G. Yanushkina. The key challenge of the modern world is necessity to improve special methodical and common teacher training. This question is considered in special theoretical materials (e.g. in a column “Science to practice”). We also cover omnifarious competitions for pupils and teachers, All-Russia and international conferences, business meetings, foreign experience. Everything that happens at school must follow State standard of secondary education. Its principles, content and some other points were covered in two big interviews with vice-president of the Russian academy of education A. Kuznecov and academic secretary of the Academy M. Ryzhakov (#4, 2009) and with the president of the Academy N. Nikandrov. Doctor of pedagogical science V. Balasevich, recent head of the Federal agency for physical culture and sports V. Fetisov and other respected people express offerings to exclude P.E. lessons from school calendar scale hours. However the journal has not a single article on this question. There is a simple explanation for that. For all 52 years of the journal life, its activity was aimed at creation, but realization of such proposals is a direct way to eliminate such a school discipline as P.E. It becomes more critical in the situation of commercialization of educational activity, because according to all legislations everything that happens not during a school day is not obligatory for pupils. It is they who can choose what they prefer to do, but not a school. Some can argue that this is exactly the point when children choose P.E. lessons because they want to. This system works in the USA… But Russia is not the USA. Here we don’t have their facilities, coaches on different sports and even teachers. There are a lot of proposals about changing of a system of estimating of pupils at lessons, about transition to 10-point system, etc. We cover this question in details (I. Abramovsky “Use of fractional marks”, E. Abramov “About alternative monitoring and evaluation system”). New proposals on health and fitness activity are a return to ideas promoted and implemented 30 years ago (e.g. hygienic gymnastics, prolonged active recreations, physical training breaks, etc). This initiative is positive and the journal responds to the proposals with a number of articles. The third component of successful settlement of the existing tasks in the sphere of physical education is out-of-school physical activity. The journal covers it in several aspects: common physical activity arrangement, sport sections, sport events and their connection with all school departments. The tasks are the same – popularization and quality improvement of the work itself. The journal covers all forms of this work. It is hard to solve all school problems, including ones about physical education, without cooperation with parents of pupils. And this is also what we talk about in our journal. Another demanding challenge is educational work at school, including patriotic and military-patriotic one. Schools face a lot of problems in this sphere and we try to help pedagogues about it. In order to understand what a P.E. teacher, pupils and their parents need, we should now their concerns and demands. This information can be found in the series of articles by S. Schetinina. In the editorial portfolio there are a lot of other interesting articles, however with each issue of the journal it is getting reduced thus needing continuing replenishment. That is why we call our colleagues from all regions of the country for both reading our journal and writing articles of current interest for it. The journal is made not by us but by you – scientists, pedagogues, coaches and school teachers. Our task is to help you to increase the quality of your articles in order for other pedagogues to have an opportunity to use your recommendations. And one more thing to mention. The journal is in the list of the Higher Attestation Commission publications. So published articles in the journal are considered academic works, what is important at a defense of a Candidate or Doctor theses. Draft Concept of Special Olympics Movement in the Republic of Karelia and prospects of its development Sergey Zuev, Chairman of Karelian Regional Organization “Special Olympics of Russia”, city of Petrozavodsk Special Olympics Movement is originated in the USA; its central goal is provision of regular physical exercising and competitions participating for persona with intellectual disorders. The initiator of the Movement was the well-known Kennedy family which that time had mentally disabled child. Contrary to traditional point of view on learning disability of children with intellectual disorders, impossibility to adapt them to real life, obligatory constant supervision, etc, American psychologists and pedagogues proposed to use PE and sport methods and techniques and relevantly organized motor activity for adaptation and social integration of these people. Central idea was that mentally disabled get more out of not traditional education means but of those based on physical exercises, natural need of a human body in motor activity. This need is predetermined genetically and does not depend on any pathology, but certainly limiting opportunities of its actualization. Practical application of Special Olympics programs has proved this suggestion. Use of adapted models of Olympic sports events has contributed to inclusion of this people into society life, acquisition of social practices and behavioral norms, i.e. socialization. Properly organized physical activity assists to a person’s physical and ethical development. The essence of the Special Olympic Movement is not merely inclusion of mentally disabled into socially recognized form of activity, provision of their business, leisure, entertainment, but also giving them a real opportunity for adaptation for life, finding own place in it. Adapted physical activity is not a end in itself, bare spending time of the fated, on the contrary it provides benefits for these people, developing their bodies and minds, easing entry into the society, aiding in learning the world, feeling oneself a part of public life through, for example, World Special Olympic. To these ends it is extremely important to actively develop Special Olympics programs, aspire to increase the number of athletes with mental disorders background. Joint workouts of special and ordinary athletes (United Sports program) positively affect the Movement and its outcomes in general. This concerns not only sport results but this practice arises personal feelings of mercy, benevolence, compassion, wish to help a weaker, etc. this important aspect can not be neglected especially in modern cruel times. For making up an own model of Special Olympics in the Republic of Karelia we have aggregated practices of special education, physical education, administrators, medics, other experts. Analysis of the situation has led to the following conclusions and draw a strategy of Special Olympics development in Karelia: - in 2011 to open a new major in “Adapted physical culture” at the Faculty of Physical Education of the Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, due to absence of human resources, facilities and academic potential for development of adapted physical culture and sports in the Republic of Karelia at present; - to promote joint activities of PE teachers and trainers of Child-Adolescent Sport Schools; - to integrate efforts of state and public organizations for overcoming the problem of “interagency barriers”; - to establish new official infrastructure for adapted physical culture and sports in the Republic of Karelia, including opening of Child-Adolescent Adapted Sports Schools and Adapted Sports Clubs, etc; - study the possibility of creation of an international club for adapted physical culture and sports in cooperation with Finnish colleagues; - to complement Special Olympics program with Special Arts program ensuring their coordination for better social integration of the mentally disabled; - to establish a system of Special Olympics and Special Arts for the disabled children studying at home by individual programs. These conclusions are a roadmap guiding activities of the Karelian republican non-governmental organization for assisting the mentally disabled “Special Olympics of Russia”. The strategic goals of the Karelian branch of Special Olympics of Russia are: - engagement of maximum number of people with intellectual disorders (regardless of their departmental affiliation) to regular physical exercising and sports (persons above 8 years recognized mentally retarded or “disabled due to cognitive disorders and experiencing significant difficulties in learning and undergoing professional training” can participate in Special Olympic competitions); - creative development; - engagement of maximum number of people with intellectual disorders to Special Olympic competitions, creativity festivals, contests for their adaptation and social integration. Competitions in individual events are held in age groups of 12-15 years old, 16-21 years old, 22-29 years old, 30 years and above; in team event – 12-15, 16-21, 22 and above. The priority is integration of efforts, mobilization of operating and newly created resources, coordination of activities of all official and public agencies dealing with the disabled regardless of their departmental affiliation and founders statuses. Algorithm of addressing the issue: 1. working out and concluding of a collective agreement amid the Karelian regional organization “Special Olympics of Russia”, State Committee of the Republic of Karelia on Physical Culture and Sports, Departments on Physical Culture and Sports, Education, Social Welfare of the Petrozavodsk City Administration, special (correctional) educational institutions, boarding schools, extended education institutions of sports, etc. 2. Institutions and organizations where the disabled and/or persons with mental disorders study and/or live take responsibility to organize regular physical exercising on Special Olympics programs for their pupils and their participation in relevant competitions, as well as elaboration of various creativity projects and representing them at festivals, contests. For achieving these objectives all physical training related work has to revised, including payroll schedule for introducing new employees (trainers), auditing and, in some cases, overhaul and modernization of facilities, arrange leasing of such facilities if these are absent. 3. The Karelian regional organization “Special Olympics of Russia” provides all members to the agreement with didactic materials on adapted physical activity classes arrangement, conducts advanced training (on cooperation with the Faculty of Physical Culture) of trainers-teachers and PE teachers attracting experts in the field from the Academy named after P. Lesgaft and International University of Family and Child named after R. Vallenberg. The Organization works out and implements Regulations on holding of sports events by the Special Olympics program. It establishes and considers an unified annual events plan with state agencies, manages institutions and organizations members to the joint agreement, cooperates with sponsors in fundraising for awarding competitions winners, etc. 4. The Karelian State Pedagogical Academy, the Faculty of Physical Culture, opens new major in adapted physical culture (including trainer-teacher and instructor-supervisor of adapted physical culture). "International School League" extended education innovative project in the sphere of physical culture S. Zykov "International School League", city of Moscow Developing the draft “International School League” (ISL), we assumed that formation of physical training habits and publicity of sports among school children can be promoted by regular weekend sports events that include sports competitions and creative contests. For venues for sports events there have been selected school stadiums, built with the participation of "SportStroySiti" enterprise in the Southern and South-Western districts of Moscow. This choice was determined by the fact that these stadiums belong to modern facilities of a new generation appropriate for school competitions. The purpose of the project. The purpose of this phase of the "ISL" project is: popularization of physical culture and sport, promotion of aesthetics of healthy lifestyle, increase of the proportion of people actively engaged in physical culture and sport. Project tasks. 1. To develop ideological principles, conceptual solutions that create the basis for the design of technologies and forms of pilot innovative projects on permanent recreational activities for all groups of population and, above all, for teenagers keen on physical culture; 1.1. Organize the work of research and inculcation group, whose mission is: - to invent and adopt new formats that are aimed at cultivating an ideology of a new society, working out forms that are consistent with the modern challenges and that can set out the directions of development of the society (for example, the cultivation of team spirit, skills of cooperation, the ability to integrate into society, to adapt to different cultural environments, cultivate tolerance, to accept social values, "to work on the team" to develop a sense of patriotism, encourage regular participation, ...); - to develop organizational forms of elaboration and management of events that allow the participants to participate in activities on their own, to develop a format based not on "for the people", but on "by the people” principle, to create participatory mechanisms for the project to become popular and self-organizing; - to develop various types of "areas of nonprofessional sport" - communication grounds, focused on the aesthetics of a healthy lifestyle, and creative projects aimed at co-creation and personal enhancement; - to develop various leisure projects on promotion of places, where sports and entertainment events are not regularly cultivated today (culture and recreation parks, beaches, etc.); - to elaborate popular events entitled "Family Weekend" that give an opportunity for collective pastime for all age categories; - to develop different formats of fun races for younger pupils aimed at holding competitions in the form of a game, so that trainers from various sports could detect a predisposition of a child to a particular sport; - to develop technical, technological and organizational background for implementing the project activities in different conditions; - to design creative contests, technology of training and participation in events, aimed at developing of individual skills and abilities and confirming the desire for self-fulfillment that promotes enlargement of the audience; - to develop forms of organization and conduct activities that consider cooperation of generations; - to develop activities on placemaking, the results of which can be recorded and reflected in various ways (for example, in the Internet) - to create forms of events within the “ISL" in accordance with contemporary aesthetics of public events, to develop original concepts of the events associated with art, to initiate "ISL" events in the modern aestheticized space; - to create an innovative system of accountability to sponsors, investors and partners; - to design a web-site aimed at joint creativity of the project participants. 2. Testing and implementation 2.1. To carry out work on the study of places, suitable for the activity of the League. 2.2. To develop a program of technical re-equipment of the territories and premises necessary for successful organization of pilot events of the League. 2.3. To establish a working group tasked with: - making arrangements for the activities of the League; - recruitment of stuff and volunteers for activities of the League; - organization of the events of the League; - financial support for project demonstrational activities, including the establishment of sponsorship package. 2.4. To carry out promotional activities of the League in/at: - the territory of school stadiums; - Recreational Complexes; - territory of culture and recreation parks; - suburban areas, suitable for competitions in skiing, nonprofessional biathlon, mountain biking; - territories, suitable in competitions on roller sports; - Sports Palaces, where it is possible to organize the work of the project "Palace of nonprofessional sport”; 2.5. To write reports on activities and to prepare presentation materials; 2.6. To conduct presentations of the project at exhibitions, forums, business events; 2.7. To design web-site of the project in the Internet. 3. Development of the project. - to draw public attention to the arrangement of school stadiums according to the projects of new generation; - to draw public attention to the arrangement of recreation parks and sports fields and to holding regular sports and recreational events; - To draw public attention to necessity of providing urban environment with "Palaces of non professional sport" - areas of fashion to an active lifestyle, that are appropriate for weekly sports and leisure holiday weekends, regular creative contests, leisure festival programs. 4. Strategic Development and Partnerships. - to create a supposition for increase of participants audiences in the competitions of the League and its transition from "school" format to "school-student" format; - to create presentations of the League activities in the student format, together with Russian universities interested in a joint realization of the project; - to work out the concept of sports weekend in the "student format" - "Sports and Youth Creativity"; -to design new formats of regular sport festivals and to develop existing ones, that are oriented at a family audience and create a precedent of design and holding of events by the means of cooperation between different generations; - to create formats that allow to include samples of higher sporting skills into a program "Palace of nonprofessional sport"; - to develop and carry out the program "Summer Sports and Creativity Camp ", which is a logical extension of the regular season of the League. - to create patterns of the competitions and other activities of the "ISL” aimed at promotion of sports tourism (including the organization of summer sports recreation camps); - to create patterns of the competitions and other activities of the "ISL” aimed at promotion of cultural exchange between regions and states; - to design a web-site that promotes remote cooperation between regions in implementation of the various projects of the League; - to create a system of training and retraining of specialists in the sphere of management of sports events through educational seminars and workshops; - to create our own mass media and communication media. To date, the tasks assigned for the season 2009/2010 are implemented in full. The last event of the “International School League” in the season 2009/2010 was the festival "Sporting Day of Victory". Presentation of the annual project took place in May, 15, 2010 under the auspices of celebration of the 65th anniversary of the Victory in the Great Patriotic War. The festival was held in the athletics and football complexes of CSKA. The focus of the festival activities was military-patriotic aesthetics. Given the need of Russian society in the availability of effective tools of education of youth and lack of modern projects on the issue we are interested in cooperation with organizations and individuals willing to work with us to solve these problems. For an exemplary content of the regular sports festival we present the program of the festival "Sporting Victory Day". 1. "Palace of non sport" Programs of School League, student leagues, family holiday. 2. "International School League" All events in the athletics complex CSKA were held by International School of the League. The events included honoring of the winners of the season, gives start to the summer season. 3. Festival “Sporting Victory Day" Presentation of the modern leisure format that includes competitiveness, sports and militarypatriotic bases. The festival is timed to the 65-th anniversary of Victory. The competitions involve teams of clubs of the Association of Knights and other associations affiliated to the Council of children's associations of Moscow and other Russian cities. 4. Moscow City Superiority on Taekwondo among schoolchildren. Organizers: Moscow Sports committee, Moscow Federation of Taekwondo 5. Football Cup of the Brotherhood. Tournament on futsal among children and youth national teams of Moscow local communities. 6. 1-st corporate tournament on futsal “PR- brotherhood of Russian State University of Physical Education, Sport and Tourism (RSUPES&T)”. Tournament on mini-football with the involvement of other teams from the number of partners of the university. The teams were made up of students and lecturers, sports journalists, university graduates. 7. Gallery of Modern Art "Sport-Art” Photo projects "Poetry of a yard sport," Sport and Advertising "," P.E. teacher of the 21-st century”. 8. The resulting photo exhibition of 2-nd Moscow contest for the 65-th anniversary of Victory "The Winners". The contest was organized under the patronage of the Moscow Government, with support of the Department of Consumer Market and Services of Moscow. 9. Photo Races “NEO-winners”, “Moment of Victory”, “Sport report” All events were provided with nonprofessional photographing by students of RSUPES&T according to the topics declared. 10. Presentation of the Central Historical museum of sports and physical. The presentation is held in the form of information stands and slide-show with archival materials on the topic “Sportsmen – combatants of the Great Patriotic War”. 11. Field-type Cinema. Non-stop demonstration of a documentary film “Death match” about the game between a Kiev team “Dinamo” and a fascist team, slide-show on the materials of photo exhibitions organized within the Festival. Organizers: “International School League”, Moscow State Department of Education, Centre of nonprofessional sport, RSUPES&T, PR-laboratory of RSUPES&T “PRules of Sports”, magazine “Photo travel”, construction company “Sportstroycity”, department of culture study, sociocultural anthropology and social communications of RSUPES&T. Successful implementation of the project can be possible only in condition of cooperation between designers, sponsors, educational institutions, construction companies that create modern school buildings and stadiums, and sports agencies. We are interested in the development of the International School League, and ready to share the methodological plans, technologies and experience. We are confident that the fashion for sports starts with passion to culture at school.