STATE FINAL ORAL EXAMINATION
advertisement

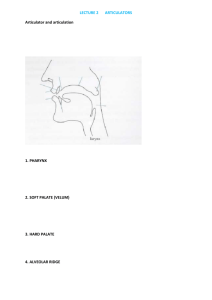
STATE FINAL ORAL EXAMINATION SUBJECT DIVISIONS 2008 LINGUISTICS 1. Phonetics and Phonology [the sound-producing system; consonant articulation; vowels and cardinal vowels; stress and intonation; assimilation; minimal pairs, phonemes and allophones, complementary distribution; features; syllables and syllabic phonology] 2. Morphology [the minimal meaningful units of language; word structure; conversion (creativity); derivational and functional affixes; compounding; acronyms; case] 3. Syntax [categories; structure; phrase structure rules; X’ categories; complements; modifiers; transformations; deep structure vs. surface structure; universal grammar and parametric variation] 4. Semantics [semantic relations involving words and sentences; meaning (denotation and connotation; sense and reference; intention and extension; semantic features); syntactic structure and semantic interpretation (thematic roles); fuzzy concepts; prototypes and basic level terms; metaphor; the lexicalization and grammaticalization of concepts; the SapirWhorf hypothesis] 5. Pragmatics [beliefs, attitudes, and presuppositions; discourse; Austin’s theory of speech acts; conversational strategies (Grice’s maxims of conversation, conversational implicature)] 6. Historical Linguistics [the nature and causes of language change; sound change; phonetic vs. morphological change; morphological change; syntactic change; lexical and semantic change] 7. The Classification of Languages [genetic classification and the Indo-European language family; typological classification: phonology; typological classification: morphology; typological classification: syntax] 8. Psycholinguistics [language and the brain (biological foundations); language areas and (mal-)functioning; issues in child language acquisition; competence vs. performance mentalism and behaviourism; language, thought, and culture; understanding and producing utterances; language production and its relation to comprehension; psychological factors affecting second language acquisition; bilingualism] 9. Language Acquisition [comparing L1 and L2 acquisition; the influence of L1 on L2 acquisition (earlier approaches: the contrastive analysis hypothesis, error analysis); the interlanguage hypothesis (Selinker); the importance of age in CLA and SLA; individual differences in SLA - factors affecting second language acquisition; classroom and naturalistic language acquisition (instructed and uninstructed SLA); communication strategies] 10. Sociolinguistics [language choice in multilingual communities (diglossia, codeswitching, and code-mixing); language maintenance and shift in different communities (language death, loss, shift); linguistic varieties and multilingual nations; sex- and agerelated linguistic behaviour; language change (why, when, and how); cross-cultural communication (similarities and differences); context, style, and class] 11. Computational Linguistics [computational phonetics and phonology, including speech synthesis and speech analysis; computational morphology; computational syntax, including natural language generation; computational lexicology and computational semantics; practical applications of computational linguistics: indexing and concordancing, machine translation; computational lexicography] I. Required Primary Source: O’Grady et al. (1993) Contemporary Linguistics. An Introduction (Second Edition). St. Martin’s Press. New York [All Subject Divisions] II. Required Supplementary Source: Willem, Meijs. Computers and Dictionaries in Ch. Butler (ed.) (1992) Computers and Written Texts, pp. 141-165 [11] III. Recommended Supplementary Sources: András L. & Stephanides, E. An Outline of Present-Day English Structure 1. Budapest: Tankönyvkiadó [1] Arnold, I. V. The English Word. Moscow: High School Publishing House [2] Austin, J. L. (1962) How to Do Things with Words. Oxford: Clarendon Press. Reprinted by OUP, 1975 [5] Bauer, L. English Word-Formation. Cambridge: CUP [2] Brown, H. D. (1987) Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. Prentice Hall [9] Burnard, Lou. Tools and Techniques for Computer-Assisted Text Processing in Ch. Butler (ed.) (1992) Computers and Written Texts, pp. 1-28 [11] Ellis, R. (1985) Understanding Second Language Acquisition. Oxford: OUP [9] Ellis, R. (1989) Are Classroom and Naturalistic Acquisition the Same? in Studies in Second Language Acquisition 11: pp. 305-328 [9] Garnham, A. (1992) Psycholinguistics. Central Topics. Routledge [8] 2 Grice, H. P. (1975) Logic and Conversation in Cole, P. and Morgan, J. L. (eds.), Syntax and Semantics 3. New York: Academic Press. Reprinted in Gleanings [5] [Handout on] Stress and Intonation [1] Holmes, J. (1992) An Introduction to Sociolinguistics. Longman [10] Langacker, R. An Introduction to Cognitive Grammar (Gleanings) [4] Larsen-Freeman, D. & Spada, N. (1993) How Languages Are Learned. Oxford: OUP [9] Lipka, L. (1990) An Outline of English Lexicology. Tübingen: Max Niemeyer [1] Littlewood, W. (1991) Foreign and Second Language Learning. Cambridge: CUP [9] Owes, R. E. (1988) Language Development. Second edition. Merrill Publishing Company (Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 12, 13) [8] Patten, Terry. Computers and Natural Language Parsing in Ch. Butler (ed.) (1992), Computers and Written Texts, pp. 29-52 [11] Pelyvás, P. (ed.) A Reader in Cognitive Grammar for Students of English [4] Radden, G. The Cognitive Approach to Natural Language (Gleanings) [4] Radford, A. (1988) Transformational Grammar. A First Course. Cambridge: CUP [3] Selinker, L. (1972) Interlanguage in Kontra and Thomas (eds.), Readings in AL [9] Steinberg, D. D. (1993) An Introduction to Psycholinguistics. Longman [8] Thomas, J. (1983) Cross-Cultural Pragmatic Failure in Applied Linguistics 4, pp 91-112 [5] N.B. The numbers in angle brackets after each source entry refer to the relevant subject division. 3 BRITISH CULTURE AND CIVILIZATION 1. The Peoples of the United Kingdom The history of conquest, settlement and immigration in Britain. Contemporary race relations. 2. Economy and Society Britain’s economic decline. The structure of the economy. The British class system. The status of women in British society. 3. The British Political System The parties. The electoral system. Parliamentary procedure. Legislative proceedings. The government. The position of the monarch in the British constitution. 4. The Educational System English school history. The current state school system. The independent school sector. The universities. Changes since 1986. 5. The Legal System Sources of contemporary English law. Criminal courts. Criminal procedure. Civil courts. The legal profession. 6. The Welfare State Welfare history. The system of national insurance. The National Health Service. The social services. 7. Britain’s Changing Role in the World The history of the British Empire. The Commonwealth. Britain in the European Community. 8. Post-1945 Political History up to 1964 The Attlee governments. Coservative rule, 1951-64. 9. Political History from 1964 to 1979 The Wilson governments. The Heath government. Labour in power, 1974-79. 10. Thatcherism Ideology and values. The break with post-war consensus. Budgetary policies. Economic changes. Foreign policy. The general elections of 1979, 1983, 1987 and 1992. The Major Governments. Changes since 1990. 4 Required reading: Bromhead, P. Life in Modern Britain. London: Longman, 1991. Oakland, J. British Civilization. London: Routledge, 1992. Sked, A. - Cook, C. Post-War Britain. London: Penguin, 1990. Recommended reading: Irwin, J. Modern Britain: An Introduction. London: Allen and Unwin, 1994. Jenkins, P. Mrs Thatcher’s Revolution. Cambridge: Harvard UP, 1988. Marwick, A. British Society since 1945. London: Lane, 1982. McDowall, D. An Illustrated History of Britain. London: Longman, 1991. Oakland, J. A Dictionary of British Institutions. London: Routledge, 1993. Useful websites: www.icbh.ac.uk/icbh/conthist.html www.britcoun.org/studies www.royal.gov.uk www.cre.gov.uk 5 AMERICAN CULTURE AND CIVILIZATION 1. The geography of the United States. Geographical regions and natural landscapes. American regionalism. Cultural regions in America. 2. The American system of government. Federal and state institutions. The U.S. Constitution. The courts and the law. Political parties and the election system. Lobbyism. 3. The ethnic composition of the American population. Major ethnic groups and minorities. Civil rights movements in America. From “melting pot” through “cultural pluralism” to multiculturalism. 4. A comparative survey of the American and Hungarian systems of education. 5. Factors contributing to cultural stability: belief systems and myth structures. Ideologies of American destiny and identity. American ethnocentrism. 6. Women in American society. 7. Entertainment and the mass media in the U.S.A. Major television networks. The printed media: major American newspapers (choose 10 for your survey) and magazines (choose 15). Popular culture. Advertising. 8. The survey of a historical period of your choice. Choose one of the following six historical periods for your presentation: the American Revolution, the Civil War decade, the “Gilded Age,” the “Progressive Era,” America between the two world wars, or the U.S.A. since 1945. 9. Hungarian-American links and contacts. The Hungarian contribution to the making of America. 10. Regionalism and multiculturalism in Canada. 6 Required Reading (relevant chapters and parts from the following books): Fawcet, Edmund and Tony Thomas, America and the Americans. Glasgow: Fontana/Collins, 1983. N.B.: Owing to the fact that this source for study is unavailable in a sufficient number of copies, students will have access to xeroxed texts of the following chapters: Chapter 1: Chapter 4: Chapter 5: Chapter 9: Chapter 10: Chapter 11: Chapter 12: “Rich and Varied Sameness”: Regions and People (pp. 11-47) “Democracy and Its Discontents”: Politics and Government (pp. 129-164) “Limping Donkeys and Lumbering Elephants”: Democrats and Republicans (pp. 165-183) “Tomorrow’s Americans”: Schools (pp. 274-307) “The Knowledge-Industrial Complex”: Universities and the Arts (pp. 308-332) “Rule of Lawyers”: The Legal System (pp. 333-365) “Soft Soap and Hard News”: Television and the Press (pp. 366-383) Luedtke, Luther S., ed., Making America: The Society and Culture of the United States. Washington, D.C.: USIA, 1987. Magyarics, Tamás and Tibor Frank, Handouts for U.S. History: A Study Guide and Workbook. Budapest: Panem-McGraw-Hill, 1995. Mittleman, Earl N., An Outline of American Geography. Washington, D.C.: USIA, 1986. Schroeder, Richard, An Outline of American Government. Washington, D.C.: USIA, 1986. Tindall, George B. and David E. Shi, America. New York: Norton, 1989. Walberg, Herbert J., American Education: Diversity and Research. Washington, D.C.: USICA, 1978. Suggested study sources: Boyer, Paul S. et al., The Enduring Vision: A History of the American People. Lexington, Mass., 1994. Brinkley, Alan, The Unfinished Nation: A Concise History of the American People. New York, 1993. Evans, Sara M., Born for Liberty: A History of Women in America. New York, 1989. Fiedler, Eckhard et al., America in Close-Up. London, 1990. 7 Freeman, Joshua et al., American Social History Project: Who Built America? Working People and the Nation’s Economy, Politics, Culture and Society. 2 vols. New York, 1992. Jones, Maldwyn Allen, The Limits of Liberty: American History, 1607-1980. Oxford: OUP, 1983. Kearney, Edward N. et al., The American Way: An Introduction to American Culture. Englewood Cliffs, N. J.: Prentice-Hall, 1984. Lipsitz, Lewis and David M. Speak, American Democracy. New York, 1993. Norton, Mary Beth et al., A People and a Nation: A History of the United States. Boston, 1994. Nye, David, Contemporary American Society. Copenhagen: Academic Press, 1990. Sellers, Charles, May Henry and Neil R. McMillen, A Synopsis of American History. Chicago, 1992. (also available in Hungarian) Stevenson, D. K., American Life and Institutions. Stuttgart: Evans Klett Schulbuchverlage, 1987. Szántó, Miklós: Magyarok Amerikában. Budapest, Gondolat, 1984. Vardy, Steven Bela, The Hungarian-Americans. Boston: Twayne, 1985. Wolfe, Alan, ed., America at Century’s End. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1991. Zinn, Howard, A People’s History of the United States, 1492-Present. Rev. Ed. New York: Harper Perennial, 1995. 8