PM_worksheet_C14(Teacher)
advertisement

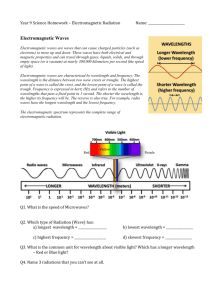
Name:______________________________ ( ) Class:_________ Date:___________ WORKSHEET Chapter 14: Electromagnetic Waves 14.1 1. Electromagnetic Waves (a) An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave and is produced by oscillating electric and magnetic fields. (b) As we go across the electromagnetic spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays, the frequency increases and the wavelength decreases, while the speed in vacuum remains constant. (c) The speed of all electromagnetic waves in vacuum is 3 × 108 m s−1. 2. 3. State whether the following statements are true or false. (a) Electromagnetic waves require a medium for propagation. T/F (b) The speed of light in water is slower than in vacuum. T/F (c) The frequency of light in water is the same as in vacuum. T/F (d) The wavelength of light in water is longer than in vacuum. T/F (e) The speed of red light is faster than that of blue light. T/F (f) The wavelength of red light is longer than that of blue light. T/F (g) The frequency of red light is higher than that of blue light. T/F Explain how sunlight is able to reach the Earth through outer space, which is largely made up of vacuum. Sunlight is comprised of electromagnetic waves. Therefore, it does not require a medium in order to be transferred. 4. Write down the seven colours of white light in order of increasing frequency. Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet 5. Write down the components of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency. Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, gamma rays © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1 6. Design a mnemonic that will help you to remember the order of the waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. Ronald Macdonald I Love Ur X’mas Gift. (Note: Let the students be creative.) 7. Name three components of the electromagnetic spectrum that have lower frequency than visible light. Radio waves, microwaves and infrared radiation 14.2 8. 9. Applications and Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Complete the table below by briefly descibing one application of each of the following types of radiation. Type of EM radiation Microwaves Application Microwave ovens for cooking food Infrared radiation Remote control signals for controlling television sets Ultraviolet radiation Sterilisation of medical equipment X-rays Imaging of bones for diagnosis of fractures Gamma rays Killing cancerous cells State and explain which type of electromagnetic wave can be used in a burglar alarm. Commonly used burglar alarms are passive infrared detectors. A burglar alarm detects changes in the level of infrared radiation in the environment. For example, when a person enters a room, the alarm will detect the increase in the level of infrared radiation. 10. The radio station Class 95 FM transmits radio waves at a frequency of 95 MHz. What is the wavelength of the radio waves transmitted? v = fλ 3 × 108 m s−1 = 95 × 106 Hz × λ Wavelength λ transmitted = 3.16 m © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 2 11. Radio waves are transmitted by a vertical aerial whose length is half a wavelength. Given that electromagnetic waves travel at a speed of 3.0 × 108 m s–1 and the frequency of the signal is 100 MHz, what is the length of the aerial? Using the wave speed formula, speed wavelength = frequency 3 × 108 m s−1 = 100 × 106 Hz = 3.0 m Thus, length of aerial = 0.5 × 3.0 m = 1.5 m 12. The Sun emits both infrared and ultraviolet radiation. What is the effect on an atom after it absorbs (a) infrared radiation? On absorbing infrared radiation, the atom will gain kinetic energy and vibrate more vigorously. (b) ultraviolet radiation? On absorbing ultraviolet radiation, the atom will get ionised by losing one or more electrons. 13. Explain whether cell phones can cause cancer through the ionisation of cells. No. Cell phones make use of microwaves, which can only heat up our cells. They do not damage cells directly though ionisation. Low energy radiation such as visible light, microwaves and radio waves do not cause cancer. 14. Explain why there is a need for the following guideline with regards to exposing patients to X-rays in Singapore: “If the medical condition of a patient who has had an X-ray examination done within the past year does not change or no new injury has been sustained, the patient is advised to refer to the X-ray image taken previously, instead of undergoing an additional X-ray examination.” X-rays have high energy and are able to ionise and damage our cells. Prolonged exposure may cause radiation sickness, cancer or even death. © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 3