Programme Outcomes
advertisement
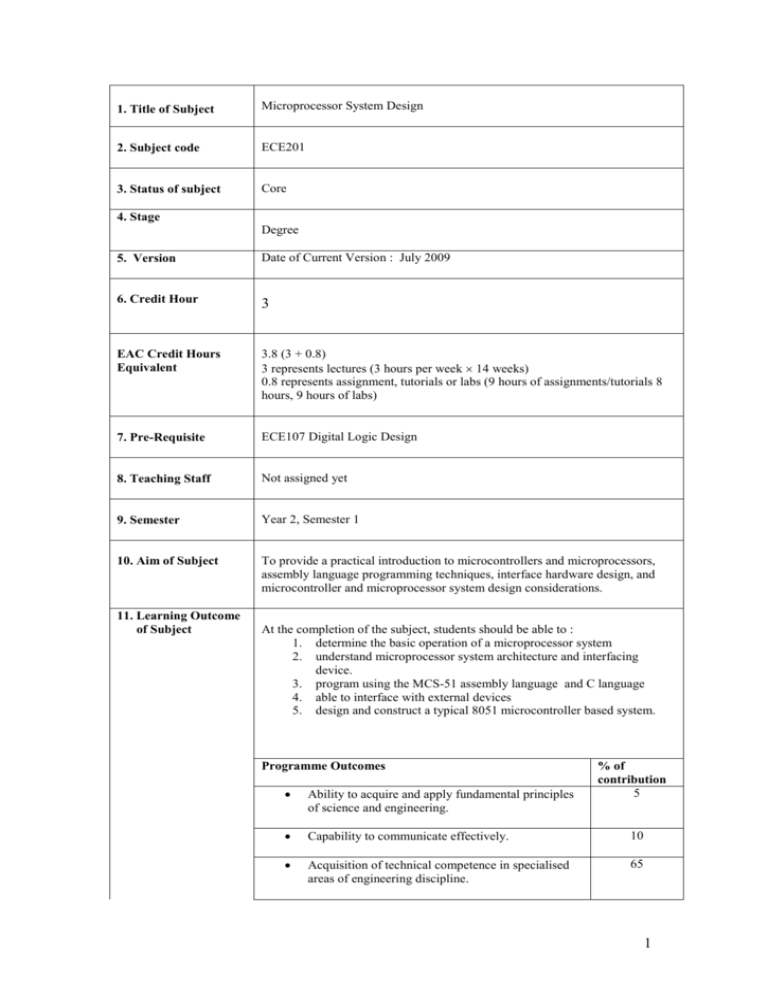
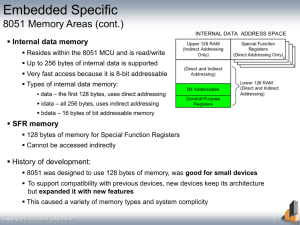
1. Title of Subject Microprocessor System Design 2. Subject code ECE201 3. Status of subject Core 4. Stage Degree 5. Version Date of Current Version : July 2009 6. Credit Hour 3 EAC Credit Hours Equivalent 3.8 (3 + 0.8) 3 represents lectures (3 hours per week 14 weeks) 0.8 represents assignment, tutorials or labs (9 hours of assignments/tutorials 8 hours, 9 hours of labs) 7. Pre-Requisite ECE107 Digital Logic Design 8. Teaching Staff Not assigned yet 9. Semester Year 2, Semester 1 10. Aim of Subject To provide a practical introduction to microcontrollers and microprocessors, assembly language programming techniques, interface hardware design, and microcontroller and microprocessor system design considerations. 11. Learning Outcome of Subject At the completion of the subject, students should be able to : 1. determine the basic operation of a microprocessor system 2. understand microprocessor system architecture and interfacing device. 3. program using the MCS-51 assembly language and C language 4. able to interface with external devices 5. design and construct a typical 8051 microcontroller based system. Programme Outcomes % of contribution 5 Ability to acquire and apply fundamental principles of science and engineering. Capability to communicate effectively. 10 Acquisition of technical competence in specialised areas of engineering discipline. 65 1 12. Assessment Scheme 13. Details of Subject Ability to identify, formulate and model problems and find engineering solutions based on a systems approach. 5 Ability to conduct investigation and research on engineering problems in a chosen field of study. 5 Understanding of the importance of sustainability and cost-effectiveness in design and development of engineering solutions. 5 Ability to work effectively as an individual and a member/leader in a team. 5 Lab Experiments Work in groups of 2 or 3 based on the class size 10% Tutorial / Assignment Group mini-project To enhance understanding of basic concepts in lecture 30% Test /Quiz Written exam 10% Final Exam Written exam 50% Topics Basics of Microcontroller and Microprocessor Hours 5 A basic microprocessor system: the CPU, memory, I/O, and buses subsystems, basic operation of a microprocessor system: fetch and execute cycle, differences between microcontroller and microprocessor, the architecture of some typical 8-bit micro-controllers, 16-bit microprocessors and their features. The MCS-51 Microcontroller 8 Features of the 8051 – the core of MCS-51 family, block diagram and definitions of the pin of the 8051, I/O port structure, memory organisation: general purpose RAM, bit addressable RAM, register bank, special function registers, external memory, memory space mapping and decoding, bus control signals timing, a typical 8051 microcontroller based system. MCS-51 Instruction Set and Assembly Language Programming 8 Addressing modes, the MCS-51 instruction set and typical examples, assembly language format, assembler directives, operation of assemblers and linkers, programming examples. 2 8051 Programming in C 8 Data types and time delay in 8051 C I/O programming in 8051 C Logic operations in 8051 C Data conversion programs in 8051 C Accessing code ROM space in 8051 C Data serialization using 8051 C . On-chip Peripheral Devices and Interrupt System 8 On-chip Peripheral Devices I/O ports: operations and uses of port 0, port 1, port 2, port 3, Timers: their operations, programming, and applications, serial port: operations and programming, typical applications. Organisation of the interrupt system, interrupt vectors, interrupt timings, serial port interrupts, and external interrupts, implementation of single and multiple interrupts 14. Teaching and Learning Activities Interfacing Examples Keypad, seven-segment LED display, LCD display, ADC and DAC chips, and input / output port expansion, description and uses of hardware development tools This subject will be delivered using the following means: Lecture Hours = 42 hours Supervised Tutorial Hours = 8 Laboratory Experiments = 9 Total Contact Hours = 59 5 15. Laboratory 1. 2. Familiarization with the 8051 trainer & programming fundamentals Timer and dot matrix LED display programming. 16. Details of Assignment Title: Design and Implementation of A Microcontroller System Objective: This assignment allows the students to impart the knowledge learned from lectures, tutorial and laboratory experiments, as well as training them to work effectively as an individual as well as a team player. In addition, students could also learn to communicate professionally through technical report writing and presentation. Type: Microcontroller system design and construction Description: In the assignment, the students are required to design, simulate and construct a prototype of a microcontroller system. At the end of the assignment, students will be required to present their works and demonstrate the constructed prototype. Moreover, a technical report on the assignment must also be submitted. Textbook 1. Muhammad Ali Mazidi et al., “The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and C, 2nd Edition” Prentice-Hall, U.S.A., 2006. Reference Materials 1. I. Scott MacKenzie and Raphael Phan, "The 8051 Microcontroller, 4th Edition,” Prentice-Hall Inc., U.S.A., 2007. Richard H. Barnett, “The 8051 Family of Microcontrollers”, Prentice-Hall Inc., U.S.A., 1995. 17. Reading Materials 2. 3 18. Program Outcomes No Program Outcomes Supported by Learning Outcomes (LO) and Activities LO1-5 Exam, test, tutorial, assignment, lab LO1-5 Exam, test, tutorial, assignment, lab LO1-5 Exam, test, tutorial, assignment, lab LO5, Assignment, lab P1 Ability to acquire and apply knowledge of science and engineering fundamentals. P2 Acquired in‐depth technical competence in electronic engineering discipline. P3 Ability to undertake problem identification, formulation and solution P4 Ability to utilise systems approach to design and evaluate operational performance. P5 Understanding of the principles of design for sustainable development P6 Understanding of professional and ethical responsibilities and commitment to them. P7 Ability to communicate effectively, not only with engineers but also with the community at large. Tutorial, assignment, lab P8 Ability to function effectively as an individual and in a group with the capacity to be a leader or manager. Tutorial, assignment, lab P9 Understanding of the social, cultural, global and environmental responsibilities of a professional engineer Assignment, lab P10 Recognising the need to undertake life‐long learning, and possessing/acquiring the capacity to do so Assignment LO4,5 Exam, test, tutorial, assignment, lab Exam, test, tutorial, assignment, lab 4