Microcontroller & Microprocessor Systems Course Syllabus
advertisement
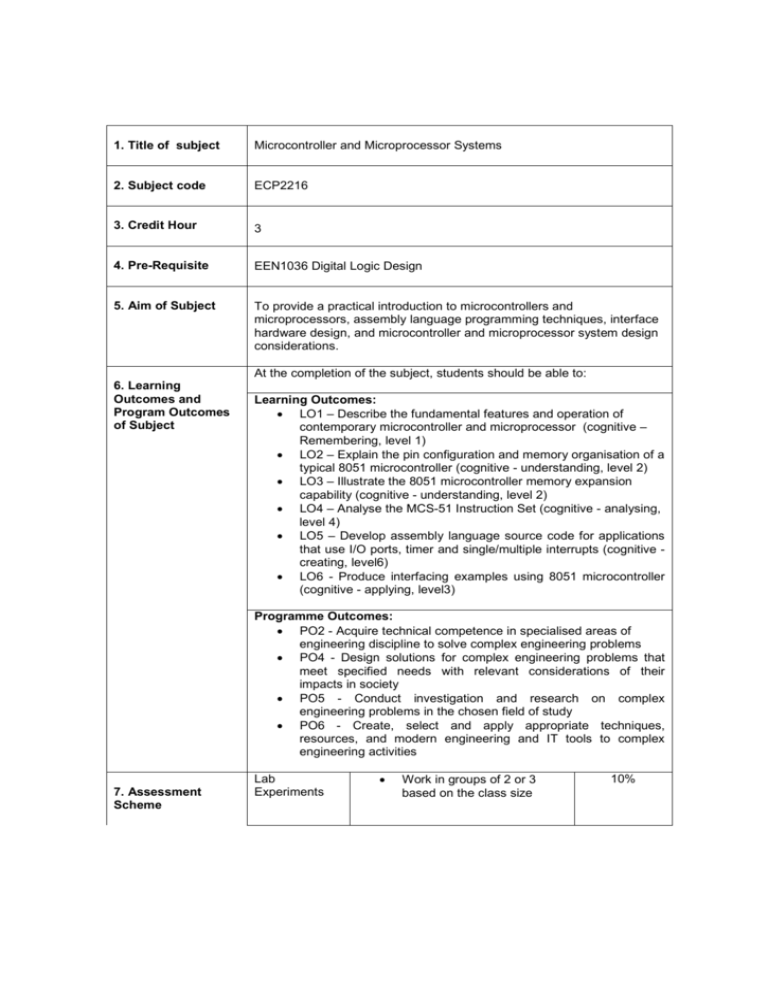
1. Title of subject Microcontroller and Microprocessor Systems 2. Subject code ECP2216 3. Credit Hour 3 4. Pre-Requisite EEN1036 Digital Logic Design 5. Aim of Subject To provide a practical introduction to microcontrollers and microprocessors, assembly language programming techniques, interface hardware design, and microcontroller and microprocessor system design considerations. At the completion of the subject, students should be able to: 6. Learning Outcomes and Program Outcomes of Subject Learning Outcomes: • LO1 – Describe the fundamental features and operation of contemporary microcontroller and microprocessor (cognitive – Remembering, level 1) • LO2 – Explain the pin configuration and memory organisation of a typical 8051 microcontroller (cognitive - understanding, level 2) • LO3 – Illustrate the 8051 microcontroller memory expansion capability (cognitive - understanding, level 2) • LO4 – Analyse the MCS-51 Instruction Set (cognitive - analysing, level 4) • LO5 – Develop assembly language source code for applications that use I/O ports, timer and single/multiple interrupts (cognitive creating, level6) • LO6 - Produce interfacing examples using 8051 microcontroller (cognitive - applying, level3) Programme Outcomes: • PO2 - Acquire technical competence in specialised areas of engineering discipline to solve complex engineering problems • PO4 - Design solutions for complex engineering problems that meet specified needs with relevant considerations of their impacts in society • PO5 - Conduct investigation and research on complex engineering problems in the chosen field of study • PO6 - Create, select and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and modern engineering and IT tools to complex engineering activities 7. Assessment Scheme Lab Experiments • Work in groups of 2 or 3 based on the class size 10% Tutorial / Assignment 8. Details of Subject • • Group mini-project To enhance understanding of basic concepts in lecture 30% Test /Quiz • Written exam 10% Final Exam • Written exam 50% Topics Hours Basics of Microcontroller and Microprocessor A basic microprocessor system: the CPU, memory, I/O, and buses subsystems, basic operation of a microprocessor system: fetch and execute cycle, differences between microcontroller and microprocessor, the architecture of some typical 8-bit micro-controllers, 16-bit microprocessors and their features. 3 The MCS-51 Microcontroller Features of the 8051 – the core of MCS-51 family, block diagram and definitions of the pin of the 8051, I/O port structure, memory organisation: general purpose RAM, bit addressable RAM, register bank, special function registers, external memory, memory space mapping and decoding, bus control signals timing, a typical 8051 microcontroller based system. 8 MCS-51 Instruction Set and Assembly Language Programming Addressing modes, the MCS-51 instruction set and typical examples, assembly language format, assembler directives, operation of assemblers and linkers, programming examples. 8 On-chip Peripheral Devices and Interrupt System I/O ports: operations and uses of I/O ports Timers: their operations, programming, and applications, serial port: operations and programming, typical applications. Organisation of the interrupt system, interrupt vectors, interrupt timings, serial port interrupts, and external interrupts, implementation of single and multiple interrupts. 8 9. Teaching and Learning Activities 10. Laboratory Interfacing Examples Keypad, seven-segment LED display, LCD display, ADC and DAC chips, and input / output port expansion, description and uses of hardware development tools 5 Contemporary Microprocessors Overview of different generations of microprocessor, highlights of architectural and technological advancement of IA-32 processors (80386, 80486 and Pentium), 64-bit processors (e.g. Intel Itanium, AMD AMD64), multi-core processors (e.g. Intel Core2Duo, AMD X2). 4 This subject will be delivered using the following means: • Lecture Hours = 36 hours • Supervised Tutorial Hours = 8 • Laboratory Experiments = 6 Total Contact Hours = 50 1. Familiarization with the trainer & programming fundamentals 2. Timer and dot matrix LED display programming. Textbook 1. Koo Voon Chet et al., “The 8051 Cookbook: A Complete Guide to Architecture, Programming and Interfacing”, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, Malaysia, 2006. Reference Materials • 11. Reading Material • • • • • • • I. Scott MacKenzie and Raphael Phan, "The 8051 Microcontroller, 4th Edition,” Prentice-Hall Inc., U.S.A., 2007. Richard H. Barnett, “The 8051 Family of Microcontrollers”, Prentice-Hall Inc., U.S.A., 1995. Muhammad Ali Mazidi et al., “The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems: Using Assembly and C”, 2nd Edition, Prentice-Hall, U.S.A., 2006. John B. Peatman, "Design with Microcontollers", McGraw-Hill, U.S.A., 1988. Walter A. Triebel and Avtar Singh, “The 8088 and 8086 Microprocessors, The: Programming, Interfacing, Software, Hardware, and Applications”, 4th Edition, Prentice Hall, US, 2003. A K Ray, K M Bhurchandi, “Intel Microprocessors architecture, Programming and Interfacing”, McGraw-Hill , 2001. Barry B. Brey, “INTEL Microprocessors 8086/8088, 80186/80188, 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium, Prentium ProProcessor, Pentium II, III, 4”, 7th Edition, Prentice Hall, US, 2006. Intel’s hardware design resource center http://developer.intel.com/design/index.htm