Chpater 7, Section 3, Objectives
advertisement

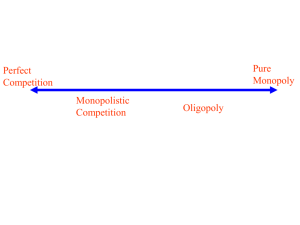
Chapter 7 –Market Structures Section 3 -Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Objectives: Describe characteristics and give examples of monopolistic competition. Explain how firms compete without lowering prices. Understand how firms in a monopolistically competitive market set output. Describe characteristics and give examples of oligopoly. PA Standard: PA6.2.12.B PA6.2.12.F Evaluate the operation of non competitive markets Identify & Analyze forces that change prices Monopolistic Competition: a market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but not identical. Four Conditions of Monopolistic competition: 1. 2. 3. 4. Number of Firms: Many Variety of Goods: Some, Differentiated products Barriers to Entry: Low, Few artificial barriers Control Over Prices: Little, Slight control over price Non Price Competition: 1. 2. 3. 4. Physical characteristics: Location: Service Level: Advertising, image or status: Prices: Under monopolistic competition prices will be higher than in perfect competition, because firms have some power to raise prices. Monopolistically competitive firms face more elastic demand curves than true monopolies do. Output: Profit: Monopolistically competitive firms will earn enough to cover all costs and still make a profit. If they make profits that are well above its costs, two market trends would work to take profits away. Competition would encourage rivals to think of new ways to differentiate their products and lure customers back. New firms will enter the market with slightly different products that cost a lot less than the market leaders. Oligopoly: A market structure dominated by a few large firms Characteristics: 1. Number of Firms: Two to Four firms dominate 2. Variety of Goods: Some variety in goods 3. Barriers to entry: High barriers to entry 4. Control over prices: Some control over the prices Problems with Oligopolies: 1. Price wars: Price cuts that lower the market price to below the cost of production. 2. Collusion: Agreement among firms to divide the market, set prices, or limit production. 3. Price fixing: An agreement among firms to charge one price for the same good. 4. Cartels: A formal organization of producers that agree to coordinate prices and production.