Ch6StudyGuide
advertisement

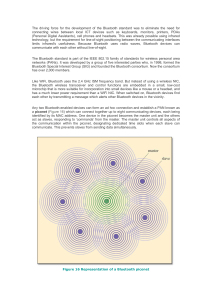
OLATUNDE OLYMPIO ACSG 525 STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 6 Chapter 6 High Rate Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPAN) This chapter focuses on the study of two HR WPAN technologies and standards; WiMedia (IEEE 802.15.3-2003) and Ultra Wide Band (UWB). Use the following questions and remarks as a study guide to read and understand the contents of this chapter: HR WPAN: 1) What is meant by HR WPAN? What are the applications for HR WPAN? The IEEE 802.15.3-2003 is a WPAN technology optimized for the transmission of multimedia voice and video signals. It also defines the specification for HR WPAN supporting speeds of 11, 22, 33, and up to 55 Mbps in the 2.4GHz ISM band. It enables multimedia connectivity between portable and fixed consumer devices within the home and can link more than 200 wireless devices using low cost and low power radio module. 2) What is the name (number) of the HR WPAN project developed by IEEE to ensure interoperability and standards among data networking technologies? IEEE 802.15.3-2003 WiMedia: 3) What is WiMedia ? Since the IEEE standard defines only the MAC and the PHY layers, the WiMedia Alliance was formed to support the development of any necessary higher level protocols and software specifications for 802.15.3 4) What are the two architectures for WiMedia? The WiMedia group defines two different architectures, called application profile, for the upper layers of the protocol stack. One is used for multimedia audio/video applications and the other for data transfer applications. Either or both architectures can be implemented on a device. The lower two layers of the stack(MAC and PHY) defines by the 802.15.3 standard are implemented in hardware. 5) Which part of the spectrum WiMedia operates in? The current IEEE 802.15.3 operates in the 2.4 GHz of the ISM band and support two different channel plans: a coexistence channel plan (three non overlapping channel to enable better coexistence with 802.11b WLANs in homes and businesses) and a high density channel plan (four non overlapping channels to support higher density applications such as hotels and conference centers in which large number of WiMedia devices may be installed and no 802.11b networks are within range). 6) What type of modulation is used in WiMedia? Since HR WPAN supports five different data rate, different modulation scheme are used depending on the data rate. QPSK (quadrature phase shift keying) is used for 11 Mbps, DQPSK for 22 Mbps, 16-QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation) for 33 Mbps, 32-QAM for 44 Mbps, and 64-QAM for 55Mbps. The 22 Mbps data rate is not coded with TCM to allow all devices in the WPAN to detect traffic without having to decode the trellis code first. 7) What is a trellis code modulation and its advantage? The trellis code modulation encodes the digital signal in such manaer that single bit error can be detected and corrected. This encoding is also known as the forward error correction (FEC). Multiple bit errors can be detected but only single bit errors can be corrected. This technique saves time and system resources because it avoids retransmission of the data when a single bit error occurs. 8) What are the enhancements to the PHY layer? To prevent interference with 802.11b a number of enhancements are included in the PHY layer of 802.15.3: passive scanning (each device scans the channels to detect an existing piconet before joining or starting a new one. The first device to be turn on in an area scans the frequencies to find an unused channel.), dynamic channel selection (once the device locates a channel that is not being used, it selects the channel to be used in the area), ability to request channel quality information (802.15.3 devices can request channel quality information from other devices, the PNC can initiate a channel change if there is interference), link quality and signal strength indication (devices can request link quality information between themselves), transmit power control (devices can decrease or increase signal strength to improve the quality of their links). 9) What is a PNC, child piconets, and neighbor piconets? The first device in an area assumes the role of piconet coordinator (PNC). The PNC provides all of the basic communication timing in a piconet. This is done by sending beacon (a frame containing information about the piconet, such as the piconet’s unique identification). The beacon also indicates when the devices are allowed to transmit and for how long. The piconet is peer-to-peer and devices can transmit data directly to each other based on the timing instruction sent in the beacon by the PNC. Child piconets are separate piconets in which the child piconet is a member of the original or parent piconet. The child piconet’s PNC can exchange data with any member of the parent or child piconet. Neighbor piconets are separate piconets that have their PNC but that depend on the original piconet’s PNC to allocate a private block of time when their devices are allowed to transmit. 10) What are the MAC layers functions? The IEEE 802.15.3 MAC layer is designed to provide a connection time (fast with no complicated setup), a short one octet device ID (fast connection and access time), the ability to obtain other devices capabilities (by request to the PNC or self capability advertisement), peer-to-peer networking (all devices can communicate directly to each other), data transport with QoS (voice, music and video), security, and efficient data transfer (multiple devices can communicate on the same network). 11) What is a wake superframe? The wake superframe is the superframe designated by the PNC in which devices that are in power save mode wake up and listen for the frames addressed to them. 12) What is the general MAC frame format? Efficient data transmission is accomplished using superframes. A beacon is used to set allocated time for the device in the piconet and to communicate management information for the piconet. An optional contention accessperiod (CAP) is used for association, to communicate commands, or for any asynchronous data that may be present in the superframe. The channel time allocation period (CTAP) which include channel time allocations (CTA) and management channel time allocation (MCTA). 13) What is mesh networking (802.15.5)? The IEEE 802.15.5 is a proposed standard for mesh networking, in which each device connects to all devices within range, effectively creating multiple paths for transmission. UWB: 14) What is Ultra Wide Band ? UWB is a communications technology that uses a wide bandwidth (typically defined as greater than 20% of the center frequency or 500MHz). UWB is usually used in short-range wireless applications but can be sent over wires. UltraWideband advantages are that it can carry high data rates with low power and little interference. 15) How does UWB works? What type of modulation is implemented in UWB ? UWB uses short analog pulses for signaling and does not rely on traditional modulation methods. UWB uses impulse modulation (amplitude, polarity, or position of an analog pulse represents either 1 or 0). UWB signals can be transmitted using simple technique by very simple transmitters. Several techniques can be used by UWB but the most commonly used is the biphase modulation (half –cycle positive analog pulse to represent a 1 and half cycle negative analog pulse to represent a 0). Another method is the multiband orthogonal frequency division (MB-OFDM). Each frequency band is 528 MHz wide which is further divided into 128 frequency channels. These channels are orthogonal and they do not interfere with each other. 16) What does DS-UWB take advantage of? Direct-sequence UWB takes advantage of the fact that one of the effects of transmitting pulses are a nanosecond long, or shorter and that the signal naturally spreads over a very wide frequency band, without using any spreading codes. The entire pulse falls below the level of the background noise. 17) What is the project P802.15.3a? The project IEEE P802.15.3a is a proposed enhancement to 802.15.3 that uses UWB technology to support even higher data rate for multimedia and imaging applications. 18) Why are 802.15.3 and .3a positioned to compete with Bluetooth for market share? 802.15.3 and .3a positioned to compete with Bluetooth for market share because these standards are capable of much higher data rates than Bluetooth. 19) How is IEEE.15.3 HR WPAN security compared to Bluetooth security? Bluetooth security is becoming an issue because of hackers using Bluetooth to attack mobile devices (Bluejacking). Bluetooth is also subject to Denial-of- Service attack, Trojans, viruses and worms attacks. HR WPAN security is based on the Advance Encryption Standard (AES) which is a symmetric key encryption mechanism introduces by the NIST in the United States. 801.15.3 also support message integrity verification at the MAC layer. 20) What is the principal challenge facing 802.15.3 manufacturers? The principal challenge facing 802.15.3 manufacturers is to ensure that the technology is incorporated into their product without significantly increasing the cost for consumers and businesses. 21) What is the protocol functionality limitation of Bluetooth compared to WiMedia? The major limitation of the Bluetooth protocol is its lack of hand-off ( the ability of a device to move from one master or PNC to another without getting disconnected from the network in a network that extend beyond the communications range of each device that controls the communications) capability between piconets. 22) What is the potential effect of 2.4 GHz residential cordless phones, Bluetooth, or IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g on HR WPAN transmission? Using all these technology in close proximity to each other may cause interference because they all use the 2.4 GHz ISM band. One solution is to move the Bluetooth device away from 802.11b/g. Devices manufacturers can also implement the new recommendation of the IEEE15.1 standard that ask the devices to listen to the channel first before transmissions.