Chapter 10. Molecular Shapes, Valence Band, Molecular Orbital
advertisement

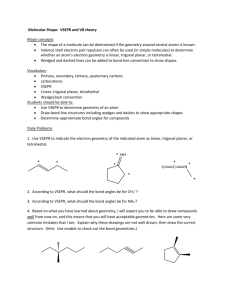
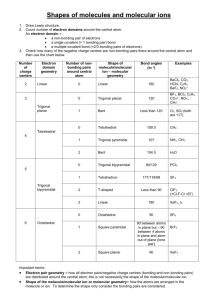
73 Chapter 10. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory & Molecular Orbital Theory I) Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory 1) VSEPR Theory provides a way of predicting molecular structure - three dimensional arrangement of the atoms in a molecule. 2) VSEPR model is useful in predicting the molecular geometry of molecules. 3) Core Concept: Main postulate of VSEPR model is that structure around a given atom in a molecule is determined by minimizing electron-pair repulsions. A) How does VSEPR Work? i) Must have correct Lewis structure drawn. ii) Molecular Geometry is always taken from central atom’s point of view. iii) VSEPR designation used to assign geometry of molecule. ABxEy A = central atom B = # atoms directly attached to central atom. E = # lone pairs directly attached to central atom. x,y = integer values B) Match VSEPR designation with entry in VSEP table. 74 Table 10.1. # Atoms Bonded to Central Atom VSEPR Table Molecular Geometry VSEPR Designation Examples 2 # lone Set Total pairs attached to central atom 0 2 Linear AB2E0 BeCl2 3 2 0 1 3 3 Trigonal planar Angular (V-shaped) AB3E0 AB2E1 BF3 , NO3SnCl2 4 3 0 1 4 4 AB4E0 AB3E1 CCl4 NH3 2 2 4 Tetrahedral Trigonal pyramidal Angular (V-shaped) AB2E2 H2 O 5 0 5 AB5E0 PCl5 4 1 5 AB4E1 TeCl4 3 2 2 3 5 5 Trigonal bipyramidal Irregular tetrahedron T-shaped Linear AB3E2 AB2E3 BrF3 XeF2 6 5 0 1 6 6 AB6E0 AB5E1 SF6 IF5 4 2 6 Octahedral Square pyramidal Square Planar AB4E2 XeF4 75 II) Hybridization 1. Mixing of individual atomic orbitals to form “special orbitals”. 2. The number of “special orbitals” (hybridized orbitals) must always be the same as the number of atomic orbitals. A) Types of Hybridized Orbitals (See Table 10.3 & Know These) Hybridization Molecular Geometry Bond Angle Examples 1. sp linear 180o CO2 N2 2. sp2 trigonal planar 120o BF3 3. sp3 tetrahedral geometry 109.5o CH4 4. dsp3 trigonal bipyramidal 120o (base) 90o (apex) PBr5 5. d2sp3 octahedral 90o SF6 B) Sigma & Pi Bonding C2H4 (ethene) H2C = CH2 has 1 and 1 bond bonds - covalent bond where electron pair shared between two atoms along the bond axis. bonds - overlap of parallel p-orbitals