Ch 4 Fingerprint Outline Dactyloscopy The Study of Fingerprints
advertisement
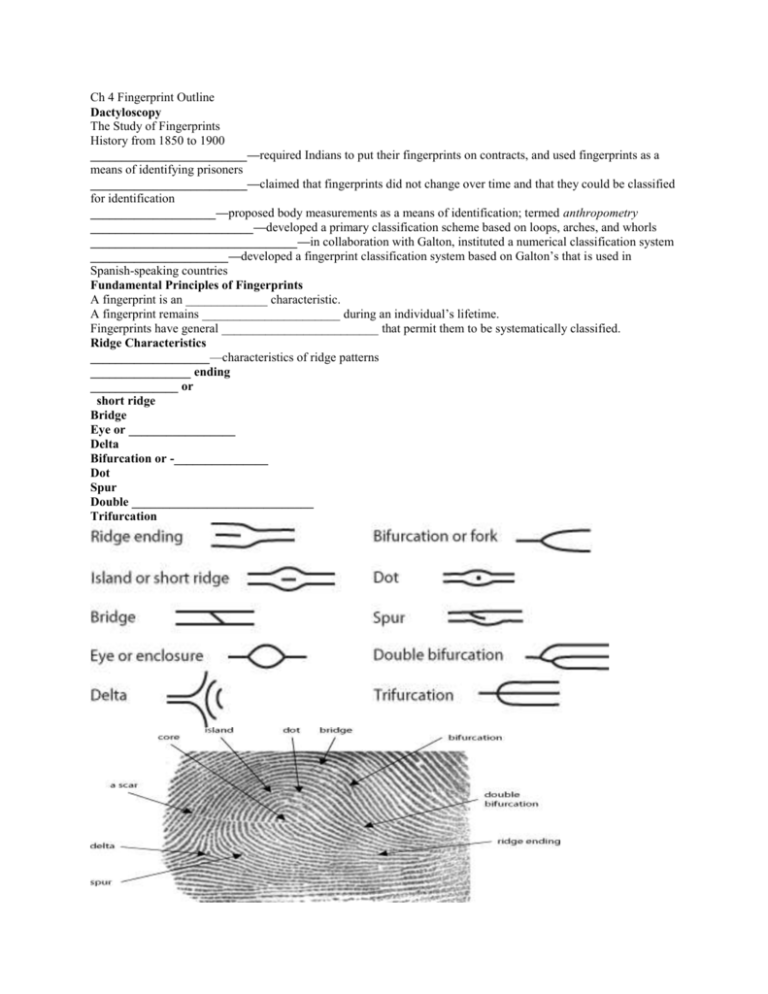
Ch 4 Fingerprint Outline Dactyloscopy The Study of Fingerprints History from 1850 to 1900 _________________________—required Indians to put their fingerprints on contracts, and used fingerprints as a means of identifying prisoners _________________________—claimed that fingerprints did not change over time and that they could be classified for identification ____________________—proposed body measurements as a means of identification; termed anthropometry __________________________—developed a primary classification scheme based on loops, arches, and whorls _________________________________—in collaboration with Galton, instituted a numerical classification system ______________________—developed a fingerprint classification system based on Galton’s that is used in Spanish-speaking countries Fundamental Principles of Fingerprints A fingerprint is an _____________ characteristic. A fingerprint remains ______________________ during an individual’s lifetime. Fingerprints have general _________________________ that permit them to be systematically classified. Ridge Characteristics ___________________—characteristics of ridge patterns ________________ ending ______________ or short ridge Bridge Eye or _________________ Delta Bifurcation or -_______________ Dot Spur Double _____________________________ Trifurcation Arch Simplest form; only ___________% of population has an arch. An arch has __________________ of the finger and cross to the other side while ________________________. They _______________ have type lines, deltas, or cores. Types Plain ________________ Loop _______________% of the population has loops. A loop must have _____________________________ from the same side. Loops must have one ______________________________________. Sometimes fingerprint can contain more than one loop. Types ____________________—opens toward the thumb _____________________—opens toward the “pinky” (little finger) Whorl ______________________% of the population has whorls. A plain or central pocket whorl has at least ______________________________________. A double loop is made of ___________________. An __________________ is a pattern not covered by other categories. Whorls have at least two _______________________ Types Plain Central ________________ Double _________________ __________________ Loop Whorl Arch Primary Classification The Henry-FBI Classification System Each finger is given a ________________________________________________ Assign the number of points for each finger that has a _______________________ into the equation: right right left left left index ring thumb middle little +1 __________________________________________ = ____________ right right right left left thumb middle little index ring +1 That number is your primary classification number. There are no legal requirements in the United States on the number of ______________________ required for a match. Generally, criminal courts will accept ______________________________________________________. Latent Prints Latent fingerprints are those that are not ______________________. These prints consist of the natural secretions of human ____________________________________________________ Most secretions come from three glands: __________________—secretes largely water, with both inorganic (ammonia, chlorides, metal ions, phosphates) and organic (amino acids, lactic acids, urea, sugars) compounds. Most important for fingerprints. ____________________—secretes pheromones and other organic materials. ____________________________—secretes fatty or greasy substances. Developing Latent Prints Developing a print requires substances that interact with secretions, causing the ____________________________________. It may be necessary to attempt more than ______________________________, done in a particular order so as not to destroy the print. _____________________________—adhere to both water and fatty deposits. Choose a color to contrast with the background. __________________________—fumes react with oils and fats to produce a temporary yellow-brown color. ____________________________—reacts with amino acids to produce a purple color. _____________________—reacts with chloride to form silver chloride, a material that turns gray when exposed to light. __________________________—“superglue” fumes react with water and other fingerprint constituents to form a hard, whitish deposit. In modern labs and criminal investigations, lasers and alternative light sources are used to view latent fingerprints. These were first used by the FBI in 1978. Since lasers can damage the retina of the eye, special precautions must be taken. Other Prints _____________—several common patterns ______________—electronic pulses measured on a spectrograph ____________________—size of foot and toes; friction ridges on the foot ______________—can be compared and identified by type of shoe, brand, size, year of purchase, and wear pattern ________________—friction ridges can be identified and may be used against suspects _________________ are taken at birth as a means of identification of infants. _________________—bite marks are unique and can be used to identify suspects. These imprints were placed in gum and could be matched to crime scene evidence. The _______________________________ in the eye may be unique to individuals. They are used today for various security purposes. The ________________________________________________—a computer system for storing and retrieving fingerprints Established in the ______________________, AFIS enables law enforcement officials to: Search large files for a set of ____________________________ Compare a single print, usually a latent print developed from a ___________________________________ By the 1990s, most large jurisdictions had their own system in place. The problem: A person’s fingerprints may be in one AFIS database _________________________________________________ ______________________________—the FBI’s Integrated Automated Fingerprint Identification System, which is a national database of all 10-print cards from _____________________________________________ Use of some type of body metrics for the purpose of identification. (The __________________ system may actually have been the first biometry system.) Used today in ________________________________ Examples include retinal or -_________________________________________________________. Other functions for biometrics: can be used to control entry or access to computers ____________________________________________________________________________________________