Faculty of Agriculture - The University of Jordan
advertisement
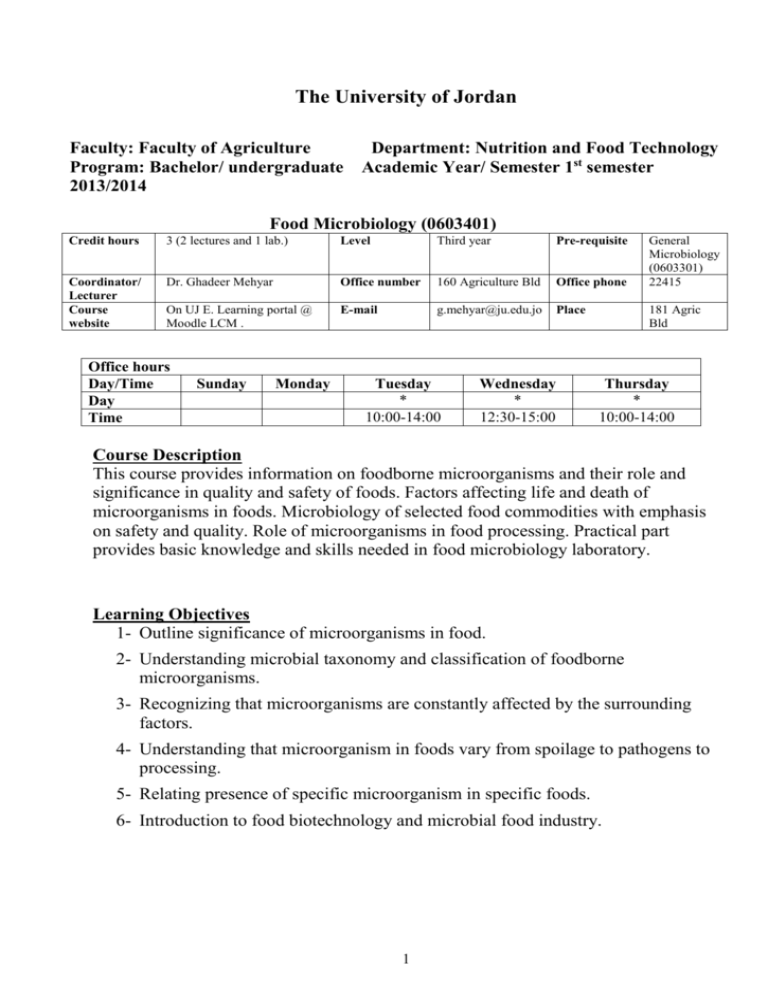
The University of Jordan Faculty: Faculty of Agriculture Department: Nutrition and Food Technology Program: Bachelor/ undergraduate Academic Year/ Semester 1st semester 2013/2014 Food Microbiology (0603401) Credit hours 3 (2 lectures and 1 lab.) Level Third year Pre-requisite Coordinator/ Lecturer Course website Dr. Ghadeer Mehyar Office number 160 Agriculture Bld Office phone On UJ E. Learning portal @ Moodle LCM . E-mail g.mehyar@ju.edu.jo Place Office hours Day/Time Day Time Sunday Monday Tuesday * 10:00-14:00 Wednesday * 12:30-15:00 General Microbiology (0603301) 22415 181 Agric Bld Thursday * 10:00-14:00 Course Description This course provides information on foodborne microorganisms and their role and significance in quality and safety of foods. Factors affecting life and death of microorganisms in foods. Microbiology of selected food commodities with emphasis on safety and quality. Role of microorganisms in food processing. Practical part provides basic knowledge and skills needed in food microbiology laboratory. Learning Objectives 1- Outline significance of microorganisms in food. 2- Understanding microbial taxonomy and classification of foodborne microorganisms. 3- Recognizing that microorganisms are constantly affected by the surrounding factors. 4- Understanding that microorganism in foods vary from spoilage to pathogens to processing. 5- Relating presence of specific microorganism in specific foods. 6- Introduction to food biotechnology and microbial food industry. 1 Intended Learning Outcomes (ILOs): Successful completion of the course should lead to the following outcomes: A. Knowledge and Understanding: Student is expected to A1- Identify foods as microbial ecosystems. A2- Recognize important microorganisms affecting food quality and safety. A3- In case study for each of foodborne bacteria, yeasts and molds A4- Understand factors inside the foods and surrounding the foods that affecting life and death of microorganisms in foods. A5- Understand each food commodity-related microorganisms. A6- Know the best ways of used microorganism in food industry. B. Intellectual Analytical and Cognitive Skills: Student is expected to B1-Learn how to control food spoilage and diseases microorganisms. B2- How to benefit from processing and technological microorganism in food industry. B3- How to deal with different foods infected by different microorganisms. C. Subject-Specific Skills: Student is expected to C1- Identify methods of microorganism control to preserve food and make food consumption safe C2- Identify microbial flora and microorganisms of public health importance to selected food commodities. C3- In case study of different foods and their related microorganisms. C4- Differentiate between good (processing) and bad (spoilage and pathogenic) food related microorganisms. D. Transferable Key Skills: Students is expected to D1- Acquire skills needed in food microbiology laboratory to enumerate, isolate and identify microorganisms relevant to food quality and safety. ILOs: Learning and Evaluation Methods 2 ILO/s Learning Methods Evaluation Methods A. Knowledge and Lectures and Discussions Exam, Quiz Lectures and Discussions Exam, Quiz C. Subject-Specific Skills Lectures and Performing Exam, Quiz and Results of (C1-C4) laboratory experimentations the experiments performed D. Transferable Key Skills Lectures and Performing Exam, Quiz and Results of (D1) laboratory experimentations the experiments performed Understanding (A1-A5) B. Intellectual Analytical and Cognitive Skills (B1-B3) 3 Course Contents Content Reference Number of lectures/ week 2/ 1st ILO/s 1- Role and significance of microorganisms in foods - Primary sources of microorganisms in foods - Food as an ecosystem - Food-borne microorganisms as spoilage flora and as pathogens Chapter 1 Adams and Moss 2- Bacteria important to foods - Taxonomy of bacteria - Bergye’s Manual and the Prokaryotes - Gram negative and gram positive bacteria important to food Chapter 3 Ray and Bhunia 4/ 2-3th A-2, B-1, B-3, C-2 Use of bacteria in food production and preservation - Spoilage bacteria - Bacterial foodborne infections and intoxications Chapter 18 Ray and Bhunia 3/ 4 th A-2, A-3, B-2, B-4C-1, C-2 3- Yeasts important to foods - Taxonomy of yeasts - Use of yeasts in food production Chapter 2 Adams and Moss 4/ 5-6 th A-2, A-3, B-1, B-3, C-1, C-2 4- Molds important to foods - Taxonomy of molds - Use of molds in food production - Molds as spoilage microorganisms - Mycotoxins Chapter 2 Adams and Moss 4/ 7 th A-2, A-3 B-1, B-3, C-1, C-2 Midterm exams Theory Practical 5- Factors affecting life and death of food-borne microorganisms - Intrinsic factors - Water activity - pH and acidity and organic acids - Oxidation-reduction potential - Nutritional content, A-1, B3 Chapter 2 Jay 8th 9/ 9-13 th Chapter 3 Adams and Moss Chapter 3 Jay Chapter 6 Ray 4 13/11/2013 20/11/2013 A-1 to A-4, B1, C-1, C-2 anti microbial constituents - biological structures and Bhunia - Extrinsic factors - Temperature - Relative humidity and gases in the environment - Implicit factors and microbial interactions 2/ 14 th 6- Microbiology of selected commodities - Vegetable and their products - Fruits and their products - Cereals - Spices - Sugars, cocoa, chocolates and confectionery Chapter 5 Adams and Moss A-2, A-3, A-5, B-1, B-3, C-2, C-3 7- Food fermentations and introduction to food biotechnology - Food fermentation - Traditional biotechnology - Role of biotechnology in food. Chapter 10 and 2/ 15 th 14 Ray and Bhunia A-6, B-2, C-4 Practical (laboratory) section Part IV Jay D-1 Part III Jay One 3 hours laboratory/ week Learning Methodology 1. Lecture and discussion (2 hours/week). 2. Quizzes and exams 3. Laboratory experiments (3 hours/ week) Projects and Assignments NA 5 Evaluation Evaluation Point % Date Theory midterm Exam 30 20/11/2013 Lab. midterm Exam 10 13/11/2013 Reports 10 Throughout the course Final theory exam 35 24/12/2013 Final lab exam 15 To be assigned by the registration Main Reference/s: 1- Adams, M. R. and Moss, M. O. 2004. Food Microbiology. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge. 2- Jay J.M., Loessner, M. J. and Golden, D. V. 2005. Modern Food Microbiology. 7th edition Springer, New York. 3- Ray, B and Bhunia, A. 2008. Fundamental Food Microbiology. 4th edition. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group, NW. References: 1- Forsythe, S. J. and Hayes, P. R. (1998). Food Hygiene, Microbiology and HACCP. 3rd edition. Aspen Publishers, Inc. 2- Ray, B. (2001). Fundamental Food Microbiology. CRC Press, Boca Raton. 3- Doyle, M. P., Beuchat, L. R. and Montville, T. J. (1997). Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers. American Society for Microbiology. 4- Center for Food Safety & Applied Nutrition (2001). Bacteriological Analytical Manual Online U.S. Food & Drug Administration, U. S. Department of Health and Human Services. (http://www.cfsan.fda.gov/~ebam/bam-toc.html) 5- Harrigan, W. F. (1998). Laboratory Methods in Food Microbiology. Academic Press, London. 6







