Name: ______ Period: _____________ Date: _______ SPRING
advertisement

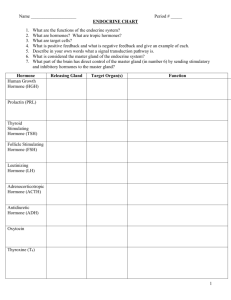
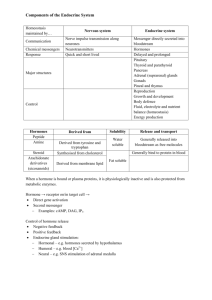
Name: _____________________________________________________________________________ Period: ___________________ Date: _________________________________ SPRING SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW Completion of this review will count as FIVE bonus points added on to your semester exam grade. Your semester exam is 100 multiple-choice questions. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What are some functions of the digestive system? 2. What is peristalsis? 3. List the structures that food would pass through as you ingest it at your mouth and pass it through your body. 4. Give some examples of both mechanical digestion and chemical digestion. 5. Define: absorption. Where in the digestive system does most absorption occur? 6. Identify the location of the following serous membrane (digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular system) a. Visceral Pericardium b. Parietal Pleura c. Parietal Peritonium 7. Label the leader lines on the digestive system picture. 8. What are some functions of the following structures? a. Liver 9. b. Gallbladder c. Pancreas d. Small intestine e. Large intestine f. Stomach What mesentery covers most of the abdominal organs, acting like a cushion to protect the organs? 10. What purpose do all of the folds & villi have in the small intestine? 11. What are the names of the folds of the inner lining of the stomach? RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1. What are some functions of the respiratory system? 2. Label the picture to the right. 3. Briefly describe the following conditions… a. Chronic bronchitis 4. b. Pneumonia c. Emphysema d. Dyspnea e. Asthma Briefly describe the function of the following structures… a. Nasal conchae b. Hard palate c. Tonsils d. Epiglottis e. Pharynx 5. Which of the respiratory structures is a shared passageway with food in the digestive system? 6. What is the difference between internal respiration and external respiration? 7. List the structures that air would pass through as you breathe it in at your nose, and it passes all the way down to your lungs CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 8. What are some functions of the cardiovascular system? 9. List the three layers of the heart wall, from external to internal. 10. Put the following in order of flow from the heart: capillaries, arterioles, venules, arteries, veins 11. What is the difference between the pulmonary and systemic circulation systems? 12. What are the chordae tendinae? 13. Identify whether the blood vessel/chamber is high in oxygen (O) or high in carbon dioxide (CO2). _____1. Aorta _____2. Pulmonary Artery _____3. Pulmonary Vein _____4. Vena Cava _____5. Right Ventricle _____6. Left Ventricle _____7. Left Atrium _____8. Right Atrium 14. What THREE blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood back into the right atrium? (For the third one, think about circulation of the cardiac vein returning to the right atrium.) 15. Gas exchange within the cardiovascular system occurs in the _____________________________ (arteries, veins, capillaries). 16. Fill in the chart comparing arteries and veins… try and do it without looking at the one in your notes! Arteries Blood flow away or to the heart? Blood pressure inside higher or lower? Walls overall thicker or thinner? Lumen smaller or larger? Valves or no valves? Veins 17. Circle the correct choice in the following statements about blood. a. Blood ( thicker / thinner ) than water. b. Blood is slightly ( acidic / basic ) in its pH level. c. Plasma makes up about ( 35 / 55 / 75 )% of blood. d. The 90% of plasma is ( salt / proteins / water ). e. The cells that have a biconcave shape are ( erythrocytes / leukocytes / plasma ). 18. Which node in the heart is also known as the “pacemaker”? 19. Circle the correct choices: Atria are (receiving/discharging) chambers, are (superior/inferior) to the ventricles, and are (smaller/larger) than the ventricles. 20. What is a pulse? 21. Label the leader lines on the heart picture. 22. Complete the following table concerning ABO blood groups. Antigens on Erythrocytes: Antibodies in Plasma: Can donate blood to type: Type A Type B Type AB Type O 23. What blood type is the universal donor? What blood type is the universal recipient? Can receive blood from type: NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. What is the difference between the central nervous system & the peripheral nervous system? What “organs” are involved in each? 2. What is myelination? What color does myelinated nervous tissue have? What color does unmyelinated nervous tissue have? 3. Label the leader lines on the neuron & brain picture 4. What is the synapse? 5. What are the three major parts of the brain stem? 6. Match the following parts of the brain with it’s function. _____1. Hypothalamus _____2. _____3. _____4. Pineal body Midbrain a. Auditory Cortex b. Vison c. Primary Sensory Area d. Primary Motor Area e. Broca’s Area & Language Comprehension Area f. assists in biological clock (daily/seasonal/life Pons cycles) by releasing melatonin g. _____5. Medulla oblongata and helps to regulate breathing h. _____6. Conveys ascending and descending impulses Frontal Lobe Regulates autonomic activities such as heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, vomiting, defecation, sneezing, coughing _____7. Occipital Lobe i. Helps regulate body temp, water balance, and metabolism (homeostasis) and plays a role in _____8. Temporal Lobe emotions; thirst, appetite, sex, pain, fear, rage, affection, and pleasure centers _____9. Parietal Lobe j. Provides timing for skeletal muscle activity and controls balance and equilibrium _____10. Cerebellum 8. What are the three meninges of the brain, listed from outermost to innermost? 9. What is the sequence of spinal nerves from superior to inferior? 10. Afferent nerves are also called ____________________ nerves, while efferent nerves are also called __________________ nerves. 11. What is another term for a stroke? 12. What is multiple sclerosis? URINARY SYSTEM 13. What are some functions of the urinary system? 14. Define the following terms in relationship to the nephron and glomerular/peritubular capillaries a. Filtration b. Reabsorption c. Secretion 15. What processes happen at the following structures of the nephron? a. Glomerulus b. Proximal Convoluted Tubule c. Distal Convoluted Tubule d. Loop of Henle e. Collecting Duct 16. In the space provided, draw a picture of a kidney, include the following structures: cortex, medulla, pelvis, pyramids, columns, hilus. 17. Label the following pictures of the urinary system and of the nephron. LYMPHATIC SYSTEM 1. What are some functions of the lymphatic system? 2. What is lymph? In what direction does it flow? 3. Briefly describe the job of the following lymphatic organs. a. Spleen b. Thymus gland c. Tonsils d. Peyer’s Patches 4. What is the difference between specific defense and non-specific defense? 5. Identify 6 first/second line of NON-SPECIFIC defense i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. 6. What are the 4 signs of inflammatory response? How does this help stop invading pathogens? 7. What is another name for the specific defense system? 8. Briefly describe the job of the following cells: e. Cytotoxic T Cells f. Helper T Cells g. Suppressor T cells h. Memory B Cells i. Plasma Cells ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 1. Identify which organs release the following hormones. Answer choices may be used more than once. Be sure to know what each hormone does too! j. Hypothalamus o. Thymus k. Pituitary Gland p. Adrenal Glands l. Pineal Gland q. Pancreas m. Thyroid Gland r. Gonads n. Parathyroid Gland _____1. Oxytocin _____2. Androgen _____11. Insulin _____3. Melatonin _____12. Aldosterone _____4. ADH (AntiDiuretic Hormone) _____13. Progesterone _____5. Thyroid Hormone _____14. Lutenizing hormone _____6. Estrogen _____15. Glutocorticoids _____7. Prolactin _____16. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone _____8. Parathyroid Hormone _____17. Growth Hormone _____9. Epinephrine/Norepinephrine _____18. Thymosin _____10. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone MALE REPRODUCTIVE TEST 1. Place the following structures in the order that a sperm must travel. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Urethra Seminal Vesticles Seminiferous Tubules Bulbourethral Gland Prostate Ductus (Vas) Deferens Epididymis Ejaculatory Duct 1. Name 3 structures in the male reproductive system which contribute fluid to semen other than sperm. 2. Which hormone stimulates the production of sperm? 3. What is the purpose of the scrotum? FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 1. Label the picture to the right. 2. Immature cells, oocytes, are surrounded by layers of follicle cells and become mature because of the release of ___________________ hormone. 3. When follicle is mature, the developed egg (ova) will be released (ovulation) by the _____________________ hormone. 4. In the ovarian cycle, the period of follicle growth is called the ________________ phase and lasts ______________ days. 5. After ovulation, the ruptured follicle is now called a _______________ ____________________. 6. Growing follicles releases (estrogen/progesterone), while the corpus luteum releases (estrogen/progesterone). 7. What are the 2 phases of the ovarian cycle? 8. What are the 3 phases of the uterine cycle? 9. About how many eggs are woman usually born? How many eggs are released in a woman’s life span? 10. Where does fertilization usually take place?