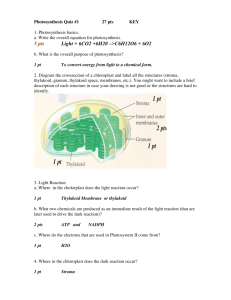
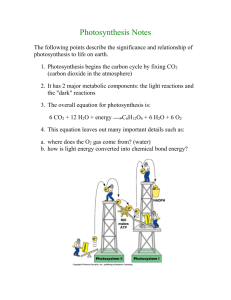
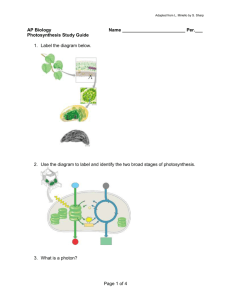
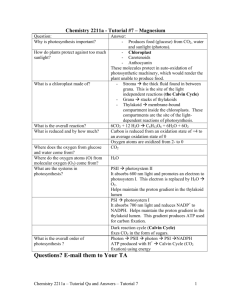
Ch. 10 Photosynthesis
advertisement

DUBLIN HIGH SCHOOL AP BIOLOGY CH. 10 STUDY GUIDE: CELLULAR ENERGY - INTRODUCTION AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS KEY TERMS autotroph noncyclic photophosphorylation heterotroph thylakoid photosynthetic autotroph grana photon stroma ground state chemiosmosis excited state Calvin cycle chlorophyll RuBP(=RuDP) light dependent reaction(=light reaction) Leaf anatomy light-independent reaction(=dark reaction) Cuticle photophosphorylation Epidermis photosynthetic unit Mesophyll reaction-center molecule Spongy absorption spectrum Palisade action spectrum Stomata Photosystem I Guard cells P700 Bundle sheath cyclic photophosphorylation C3 Photosynthesis NADP photorespiration carbon fixation Kranz anatomy Photosystem II C4 Photosynthesis P680 PEP 1 WORD ROOTS auto - = self; - troph = food (autotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules without eating other organisms) chloro - = green; - phyll = leaf (chlorophyll: photosynthetic pigment in chloroplasts) electro - = electricity; magnet - = magnetic (electromagnetic spectrum: the entire spectrum of radiation) hetero - = other (heterotroph: an organism that obtains organic food molecules by eating other organisms or their by-products) meso - = middle (mesophyll: the green tissue in the middle, inside the leaf) photo - = light (photosystem: cluster of pigment molecules) QUESTIONS 1. Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron gain or loss; gain or loss of hydrogen and oxygen. 2. Write a summary equation for the reaction of photosynthesis. 3. Explain why almost all organisms depend upon photosynthesis to satisfy their energy needs. Use the terms autotroph and heterotroph in your explanation. 4. Describe the general organization of a photosynthetic unit. 5. Use diagrams to trace the flow of electrons during cyclic photophosphorylation. 6. Use diagrams to trace the flow of electrons during noncyclic photophosphorylation. 7. Using a diagram trace the flow of electrons from water through the various electron carriers to NADP, indicate how a H+ ion concentration gradient is established within the thylakoid. Indicate the enzyme complex that can use the energy of the gradient to phosphorylate ADP. Diagram chemiosmosis in a chloroplast. 2 8. Explain how the products of the light reaction are used to reduce CO 2 in the Calvin cycle to form PGAL and describe the fate of this PGAL. 9. Draw a chloroplast, label its parts and indicate where the various photosynthetic reactions take place. 10. Compare and contrast the components and structures of photosystem I and photosystem II. 11. How is a proton gradient established across the thylakoid membrane? How does this result in the synthesis of ATP. 12. What features distinguish cyclic from noncyclic photophosphorylation? 13. What features of the chloroplast are especially important in enabling the process of photosynthesis to proceed? 14. How are ATP and NADPH produced and utilized in photosynthesis? 15. Compare and contrast the pathways of carbon fixation in C3 photosynthesis and C4 photosynthesis. 16. Evolution often proceeds by "adding on" to whatever evolved formerly. Use what you know about photosynthesis to support the suggestion that Photosystem I evolved before Photosystem II. 17. Diagram a C3 and a C4 leaf. 18. What kinds of interactions exist between photosynthesis and respiration? 3